Physiology - Endocrine Pt 2 (Thyroid gland)
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
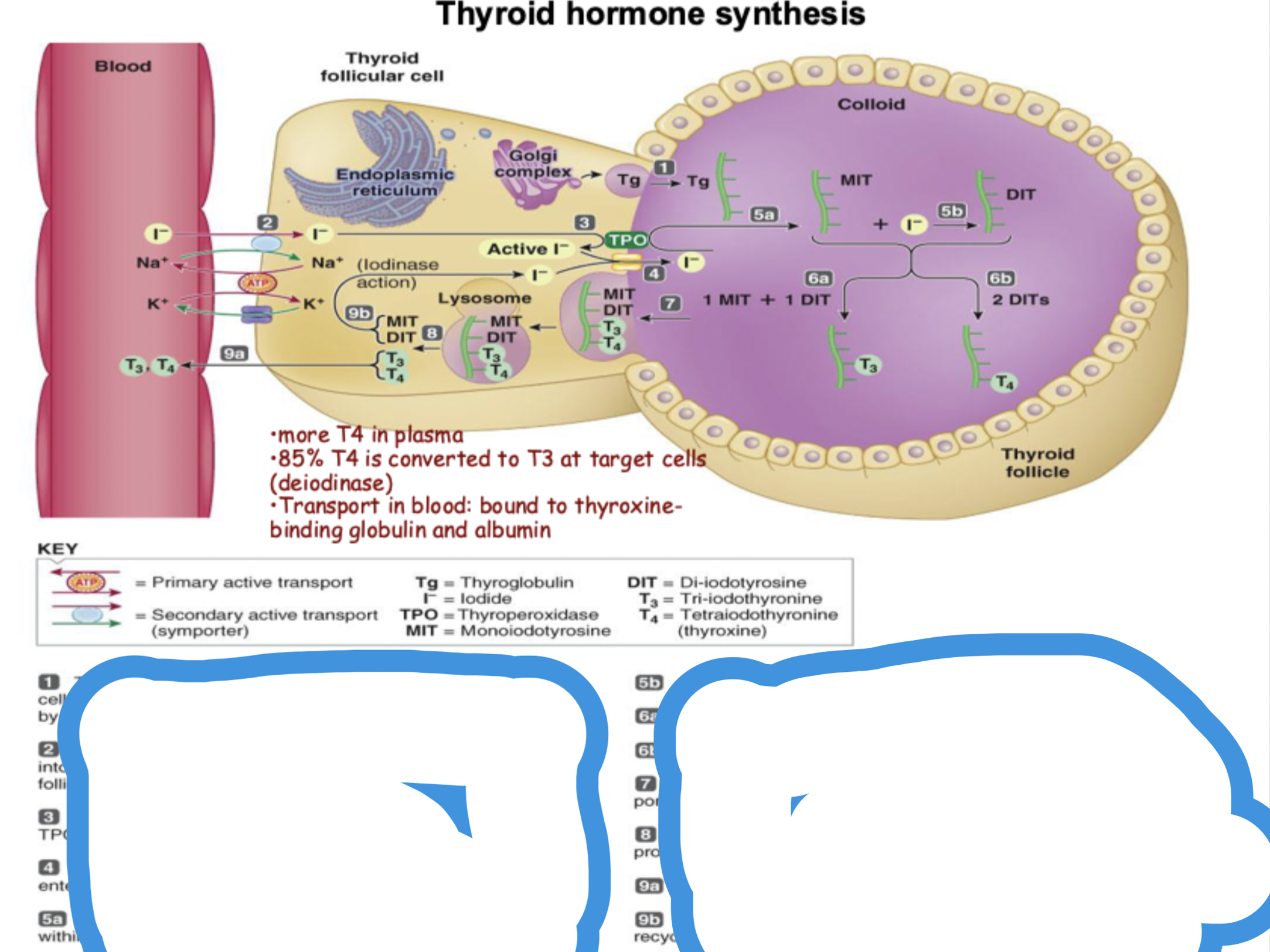
Thyroid hormone synthesis STEPS
tyrosine - containing thyroglobulin produced by the ER/golgi apparatus in the thyroid follicular cells are transported into the colloid via exocytosis
iodide is carried by secondary active transport from the blood into the colloid by symporters in the basolateral membrane of the follicular cells
in the follicular cell, iodide is oxide to active form by thyroperoxidase at the luminal membrane
The active iodide exits the cell through a luminal channel to enter the colloid
Catalysed by thyroperoxidase, attachment of one iodide to tyrosine within the thyroglobulin molecule yield one MIT, attatchment of two iodide to tyrosine yields DIT.
Coupling of one MIT and one DIT yields T3, coupling of two DITS yields T4
On appropriate stimulation, the thyroid follicular cells engulf a portion of tg-containing colloid by phagocytosis
lysozomes attack engulfed vesicles and split iodinated products from thyroglobulin
T3 and T4 diffuse into the blood (secretion)
MIT and DIT are deiodinated, freed iodide is recycled for synthesizing more hormone
Thyroid hormone EFFECTS
Provides substrates for oxidative metabolism
Provides adequate nutrients for ATP synthesis and protein synthesis
increases rate of metabolism
calorigenic affect = increased metabolic activity results in increased heat production
increases heart rate and force of contraction
increases target-cell responsiveness to catecholamines (sympathomimetic)
essential for normal gorwth and development
myeline and synapse formation requires thyroid hormone
regulates microtubule assembly
Name the two catecholamines secreted by the adrenal medulla
and describe how they are stored and released.
epinephrine and norepinephrine, stored in chromaffin graules and released via exocytosis on stimulation of post gangliogonic sympathetic fibers
Discuss the major hormonal changes and the purposes served by each change during the stress response
increased epinephrine reinforces sympathetic nervous system “fight or flight response”, mobilises energy stores (increase blood glucose and blood fatty acids)
increased CRH-ACTH-Cortisol levels, mobilise energy stores and metabolic building blocks (increase blood glucose, fatty acids, amino acids)
increased Glucagon and decreased insulin, to increase blood glucose and fatty acids
increased Renin-angiotensin aldosterone system and vassopressin : conserve salt and water, ATII + ADH, cause arterial vasoconstriction