ciencias
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/172
Earn XP
Description and Tags
matenme
Last updated 6:05 AM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
173 Terms
1
New cards
Water is formed by what type of bond?
covalent bonds
2
New cards
What does the covalent bonds involve
unequal sharing of electrons
3
New cards
What type of bond is the covalent bond in water
polar covalent bond
4
New cards
Which is more electronegative: the oxygen nucleus or the hydrogen nucleus
oxygen nucleus
5
New cards
Intermolecular force of a hydrogen bond, weak or strong?
weak
6
New cards
One pole negative, and the other slightly positive) makes what
dipolarity
7
New cards
A hydrogen bond is not a proper bond but, rather, a **…**
force of attraction
8
New cards
Binding together of two molecules of the same type
cohesion
9
New cards
What is cohesion helpful for?
water transport in plants
10
New cards
Hydrogen bonds can form between water and **other** **polar** molecules, causing water to stick to them.
Adhesion
11
New cards
Hydrogen bonds restrict the movement of water molecules so **a large amount of energy is required in order to** __**increase**__ **the temperature** of water to break these hydrogen bonds.
__**High specific heat capacity**__
12
New cards
To __cool down__, water must lose what
large amounts of energy
13
New cards
When a molecule evaporates it separates from other molecules in a liquid and becomes a vapor molecule. The heat needed to do this is called :
__**High latent heat of vaporization**__
14
New cards
Evaporation has a what effect
cooling
15
New cards
The highest temperature that a substance can reach in a liquid state.
boiling point
16
New cards
Water remains liquid in a temperature range from
0-100 celsius
17
New cards
Water loving?
hydrophilic
18
New cards
Water hating (or insoluble in water)
hydrophobic
19
New cards
When a molecule evaporates it separates from other molecules in a liquid and becomes a vapor molecule. The heat needed to do this is called:
high latent heat of vaporization
20
New cards
Its partially negative oxygen pole is attracted to positive ions and its partially positive hydrogen pole is attracted to negatively charged ions so that both can dissolve
solvent properties
21
New cards
Water adheres to what in cell walls.
cellulose molecules
22
New cards
Carbon is able to form how many bonds?
4
23
New cards
With what elements can carbon bond with?
hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus.
24
New cards
Are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, with a proportion of two hydrogen atoms for every oxygen
carbohydrates
25
New cards
Are molecules that are insoluble in water, including steroids, waxes, fatty acids and triglycerides. In common language, triglycerides are fats if they are solid at room temperature or oils if they are liquid at room temperature.
lipids
26
New cards
Are composed of one or more chains of **amino acids**. All of the amino acids in these chains contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.
Proteins
27
New cards
They are chains of subunits called **nucleotides**, which contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus. There are two types of nucleic acid: ribonucleic acid (**RNA**) and deoxyribonucleic acid (**DNA**).
nucleic acids
28
New cards
The formula for ribose
C5, H10, O5
29
New cards
The formula for glucose
C6, H12, O6
30
New cards
The carbon atoms form an unbranched chain. In saturated fatty acids they are bonded to each other by single bonds.
One end of the chain the carbon atom is part of a **carboxyl group.**
One end of the chain the carbon atom is part of a **carboxyl group.**
lipids
31
New cards
Composed of monomers called **amino-acids**, which join together to form polypeptide chains
proteins
32
New cards
Name the 4 things proteins can bond to.
amine group, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom, R group.
33
New cards
Each nucleotide consists of 3 components
pentose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base
34
New cards
Proteins molecule unit
amino acids
35
New cards
Carbohydrates molecule unit
monosaccharides
36
New cards
Lipids molecule unit
fatty acid + glycerol
37
New cards
Nucleic acids’ molecule unit
nucleotide
38
New cards
Proteins functional group
amino group, -N, -COOH
39
New cards
Carbohydrates functional group
C, H, O, -OH
40
New cards
Lipids functional group
\-COOH
41
New cards
Nucleic acids functional group
pentose, PO4, nitrogenous base
42
New cards
Protein example
elastine, colagene
43
New cards
Carbohydrates example
glucose, galactose
44
New cards
Lipids example
phospholipid, fatty acid, saturated/unsaturated
45
New cards
Nucleic acid example
DNA, RNA
46
New cards
**Sum of all reactions that occur in an organism.**
metabolism
47
New cards
Where does most of the metabolism reactions happen
cytoplasm of cells
48
New cards
2 types of metabolism
catabolism, anabolism
49
New cards
**Is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules**
catabolism
50
New cards
**Is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules**
anabolism
51
New cards
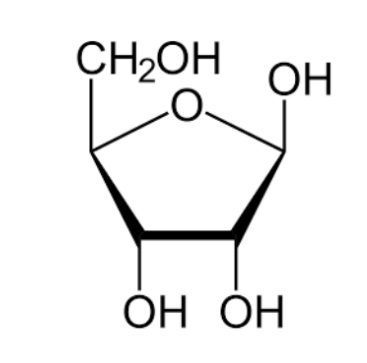
ribose
52
New cards
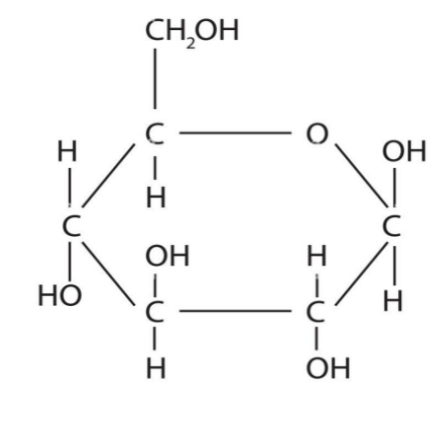
glucose
53
New cards
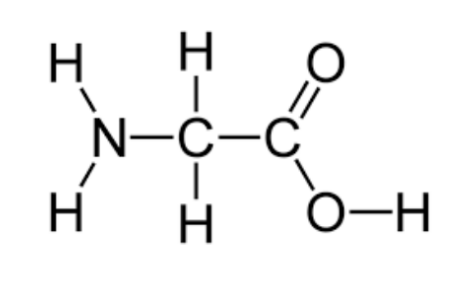
amino acids
54
New cards
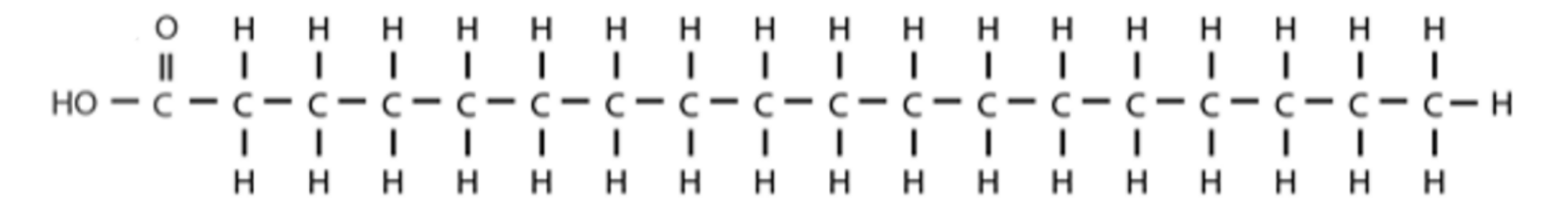
fatty acids
55
New cards
**Building blocks of what biomolecules are made of.**
monomers
56
New cards
The monomer for a carbohydrate is called
monosaccharide
57
New cards
Two or more monomer molecules form
polymer
58
New cards
Monosaccharides: Individual units of sugar.
glucose, fructose, ribose
59
New cards
Disaccharides: Two monosaccharides linked together.
maltose, lactose, sucrose
60
New cards
Polysaccharides: Many monosaccharides linked together.
cellulose, starch, glycogen.
61
New cards
Involves the loss of an –OH from one molecule and an –H from another molecule, which together form H2O
condensation
62
New cards
Linking together monosaccharides to form disaccharides and polysaccharides is a ___ process
anabolic
63
New cards
What is the most abundant organic molecule in nature.
\
\
cellulose
64
New cards
Cellulose is a what of glucose molecules.
polymer
65
New cards
What are the cell walls of plant cells are made of
cellulose
66
New cards
Starch is hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
hydrophilic
67
New cards
Lipids are what in water
insoluble
68
New cards
What is one of the principal groups of lipid.
triglycerides
69
New cards
The building blocks of lipids are
fatty acids
70
New cards
Contain all de hydrogen possible, simple bonds between carbons (fatty acids)
saturated
71
New cards
Contain less hydrogen, have double bonds between carbons and there are two types:
unsaturated: monounsaturated, polyunsaturated
72
New cards
Unsaturated fatty acids can be
cis or trans
73
New cards
Fatty acids: saturated
animals, vegetables
74
New cards
Fatty acids: unsaturated
trans
75
New cards
Fatty acids: polyunsaturated
omega-3, omega-6
76
New cards
Fatty acids: monounsaturated
omega-9
77
New cards
**What is the function of fats in living organisms?**
stored lipids, heat insulators, shock absorbers, double the amount of released energy
78
New cards
**Amino acids have a central carbon atom with four different atoms or groups linked to it**
hydrogen atom, amine group p, carboxyl group and an r group (radical)
79
New cards
Two amino acids joined together
dipeptide
80
New cards
**Consist of many amino acids linked by peptide bonds.**
polypeptide
81
New cards
The number of amino acids in a _________ can be anything from 20 to tens of thousands.
polypeptide
82
New cards
**The main factors that cause denaturation** of proteins are:
pH, high temperature
83
New cards
What is a **proteome**
all of the proteins produced by a cell, a tissue or an organism.
84
New cards
What is a genome
all of the genes of a cell, a tissue or an organism.
85
New cards
ctm Functions of proteins (matenme pls)
catalysis, muscle contraction, cytoskeleton, tensile strengthening, blood clotting, transport of nutrients and gases, cell adhesion, membrane transport, hormone, receptors, packing of DNA, immunity
86
New cards
CELL THEORY
**cell is the single unit of life, all living things are made of cells, all new cells come from preexisting cells**
87
New cards
Name of organisms which are only one cell
unicellular
88
New cards
7 functions of life
metabolism, response, nutrition, growth, excretion, homeostasis, reproduction
89
New cards
Name of a single mass of cells, fused together.
multicellular
90
New cards
DIFFERENT FUNCTIONS IN MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS
bone cells, blood cells, muscle cells, skin cells, nerve cells, endothelial cells
91
New cards
TYPES OF TISSUES
connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, nervous tissue
92
New cards
During early stages of embryonic development cells are capable of dividing many times to produce large amounts of tissue.
stem cells
93
New cards
STEM CELLS NON THERAPEUTIC USES
produce regenerated tissue, treat type 1 diabetes, grow whole replacement organs, produce striated muscle fibers
94
New cards
FUCK ME TYPES OF STEM CELLS
totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent, unipotent
95
New cards
NO SE ACABA LA PUTA PRESENTACION 3.1 As cell volume **increases**:
surface area/volume ratio decreases, substances will not enter the cell as quickly as required and waste products will accumulate, energy cells may overheat
96
New cards
EMERGENT PROPERTY
characteristics of the whole organism, including the fact that it is alive
97
New cards
cell differentiation (bruh i give UPPP)
development of cells in different ways to carry out specific functions.
98
New cards
genetic differentiation
involves the expression of some genes but not others
99
New cards
im sorry pero fuck this ya se la arman con las utimas 3 presentaciones (respuesta: 123)
1234
100
New cards
PREGUNTA 100 organisms that lack nucleus
prokaryotes