Respiration, Lipid and Carbohydrate Metabolism in Plants and Humans
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is aerobic respiration?
The controlled oxidation of reduced biological compounds, releasing energy stored as ATP.
What is the balanced equation for the complete oxidation of sucrose?
C12H22O11 + 12 O2 → 12 CO2 + 11 H2O
What are the four main steps of aerobic respiration?
Glycolysis, Oxidative pentose phosphate pathway, Citric acid cycle (TCA cycle), Oxidative phosphorylation.
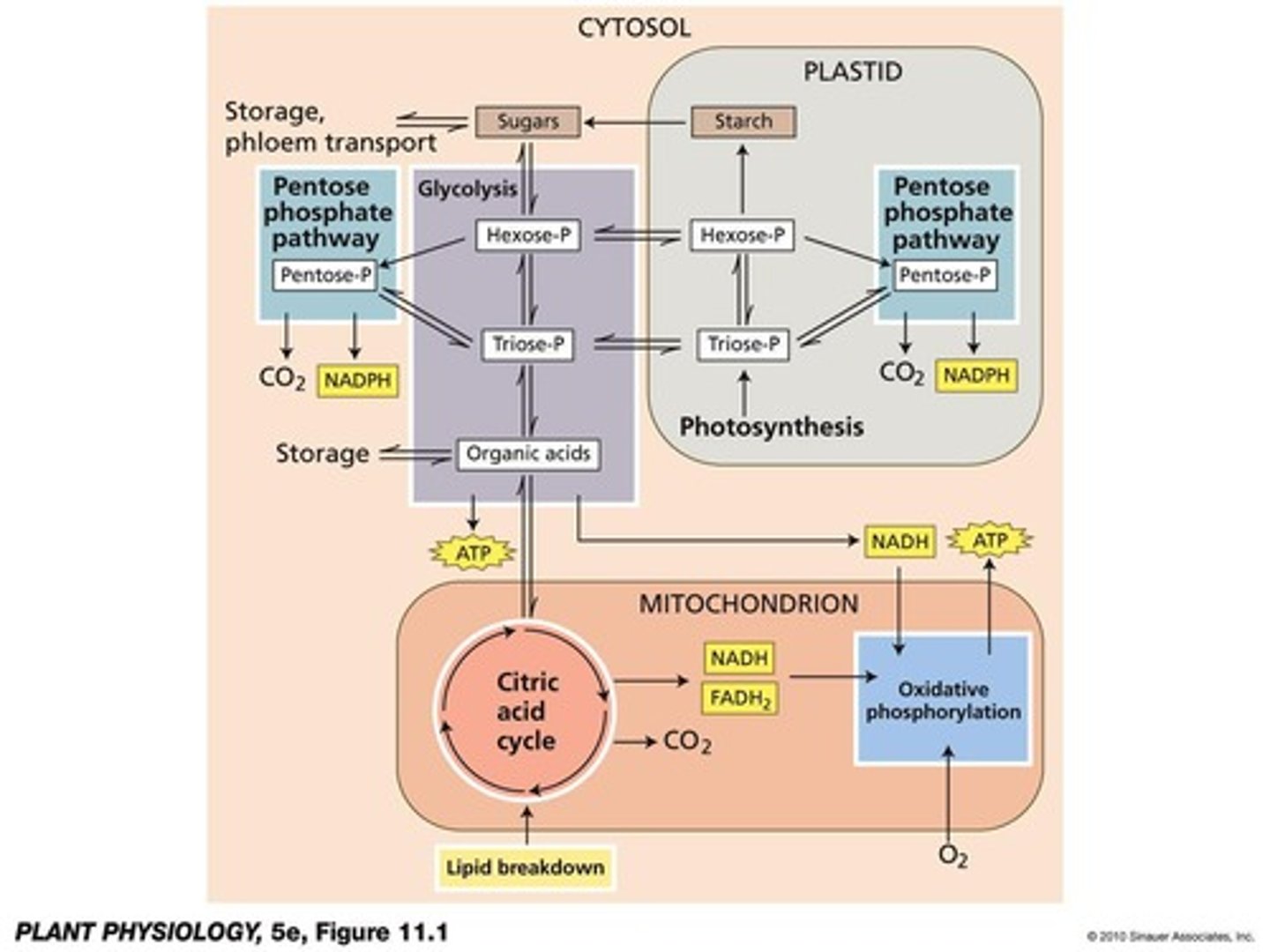
Where does glycolysis occur?
In plastids and cytosol.
What is the main substrate for respiration in plants?
Sucrose.
What are the products of glycolysis?
Small amounts of ATP and NADH.
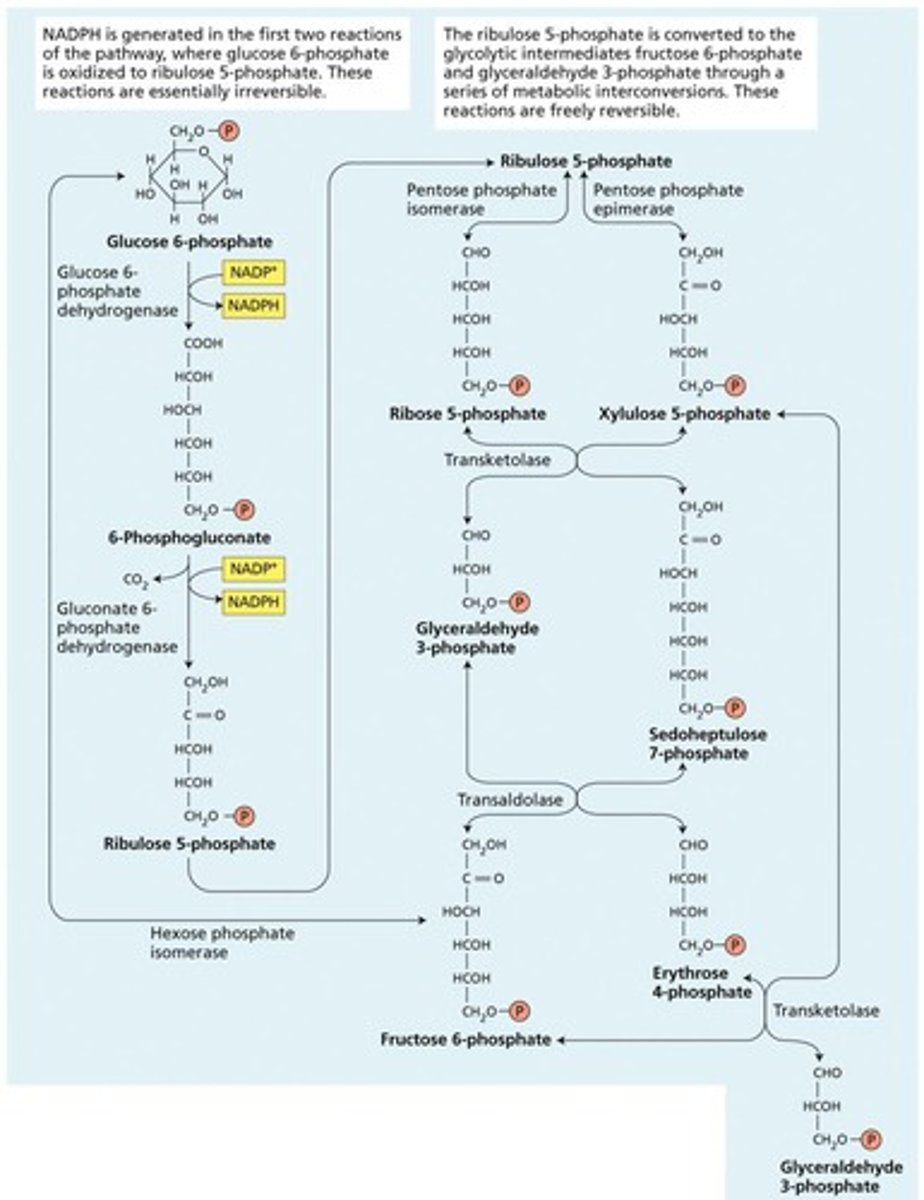
What does the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway produce?
NADPH and ribulose 5-phosphate.
What is the role of NAD+ in respiration?
It undergoes a reversible 2-electron reaction, conserving free energy released in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
What is the significance of the citric acid cycle?
It generates most of the reducing power (16 NADH and 4 FADH2) and occurs in mitochondria.

What are the main products of the citric acid cycle from one pyruvate?
3 CO2, 4 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 ATP.
What is the function of the enzyme invertase?
It cleaves sucrose into glucose and fructose in cell walls.
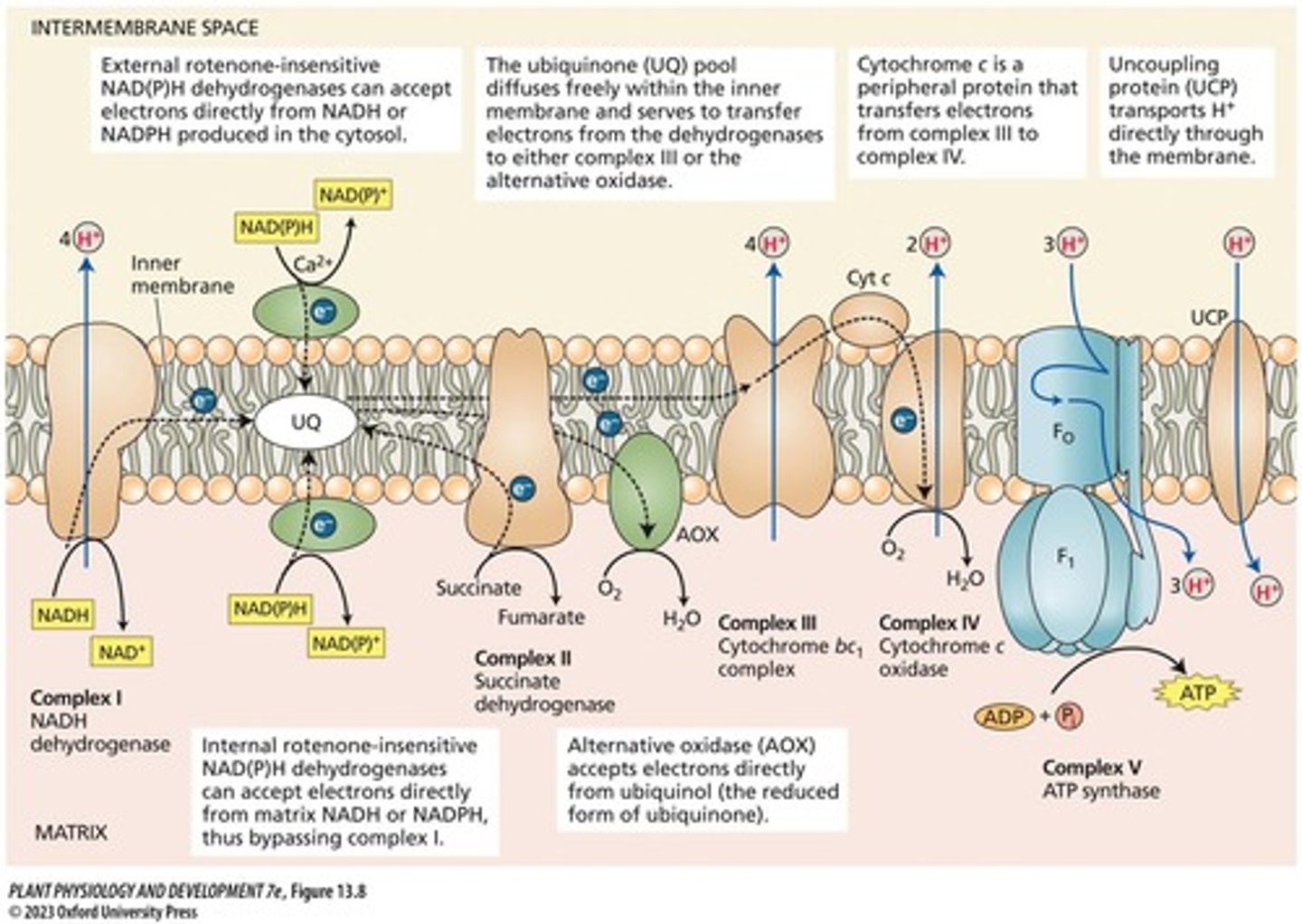
What does oxidative phosphorylation involve?
The electron transport chain on the inner mitochondrial membrane transferring electrons from NADH to O2.
What is the main function of the oxidative pentose phosphate cycle?
To produce NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate for biosynthesis.
What happens during the decarboxylation of pyruvate?
It is oxidized by pyruvate dehydrogenase, producing NADH, CO2, and acetyl-CoA.
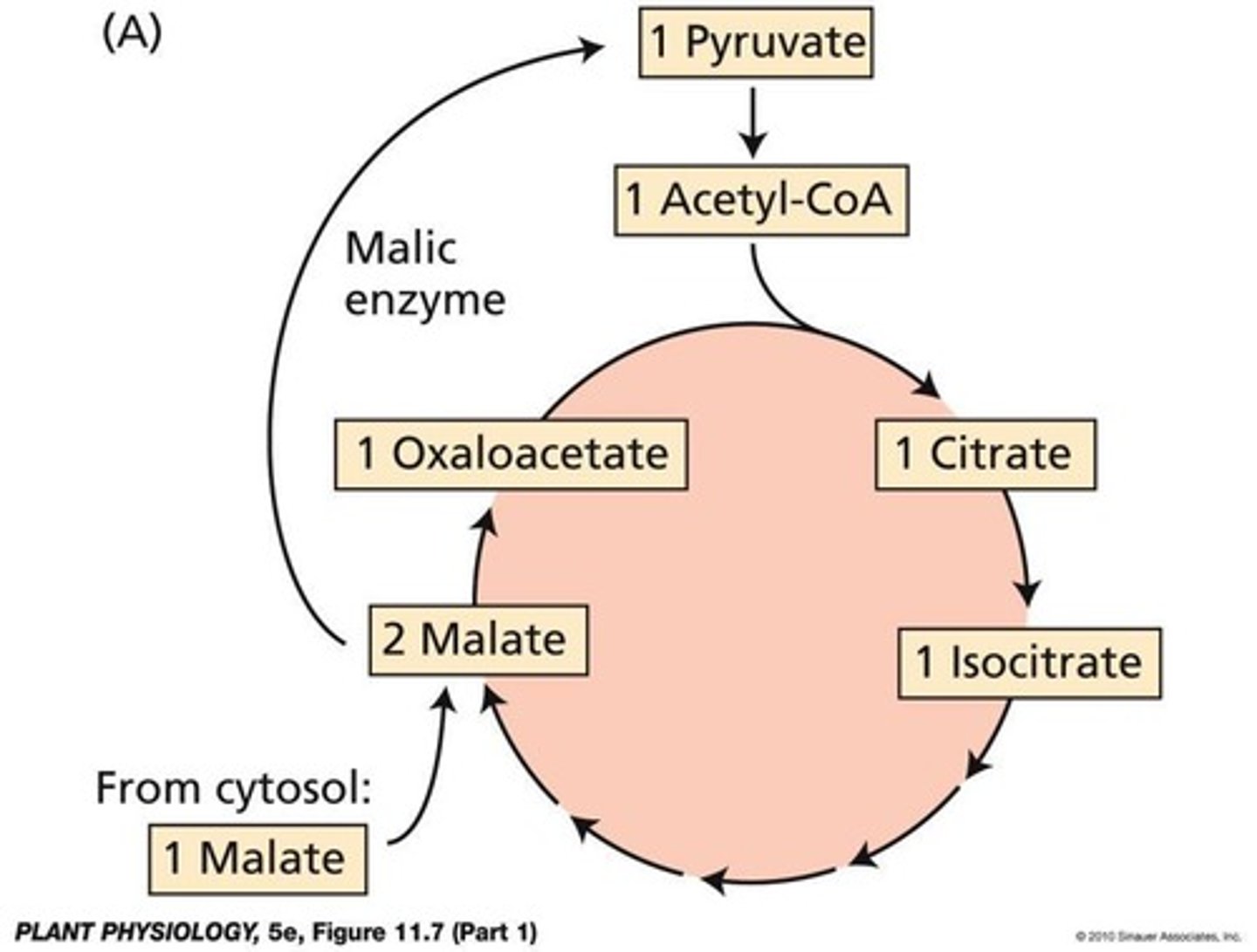
What is the role of malic enzyme in plants?
It converts malate to pyruvate, releasing CO2 and producing NADH or NADPH.
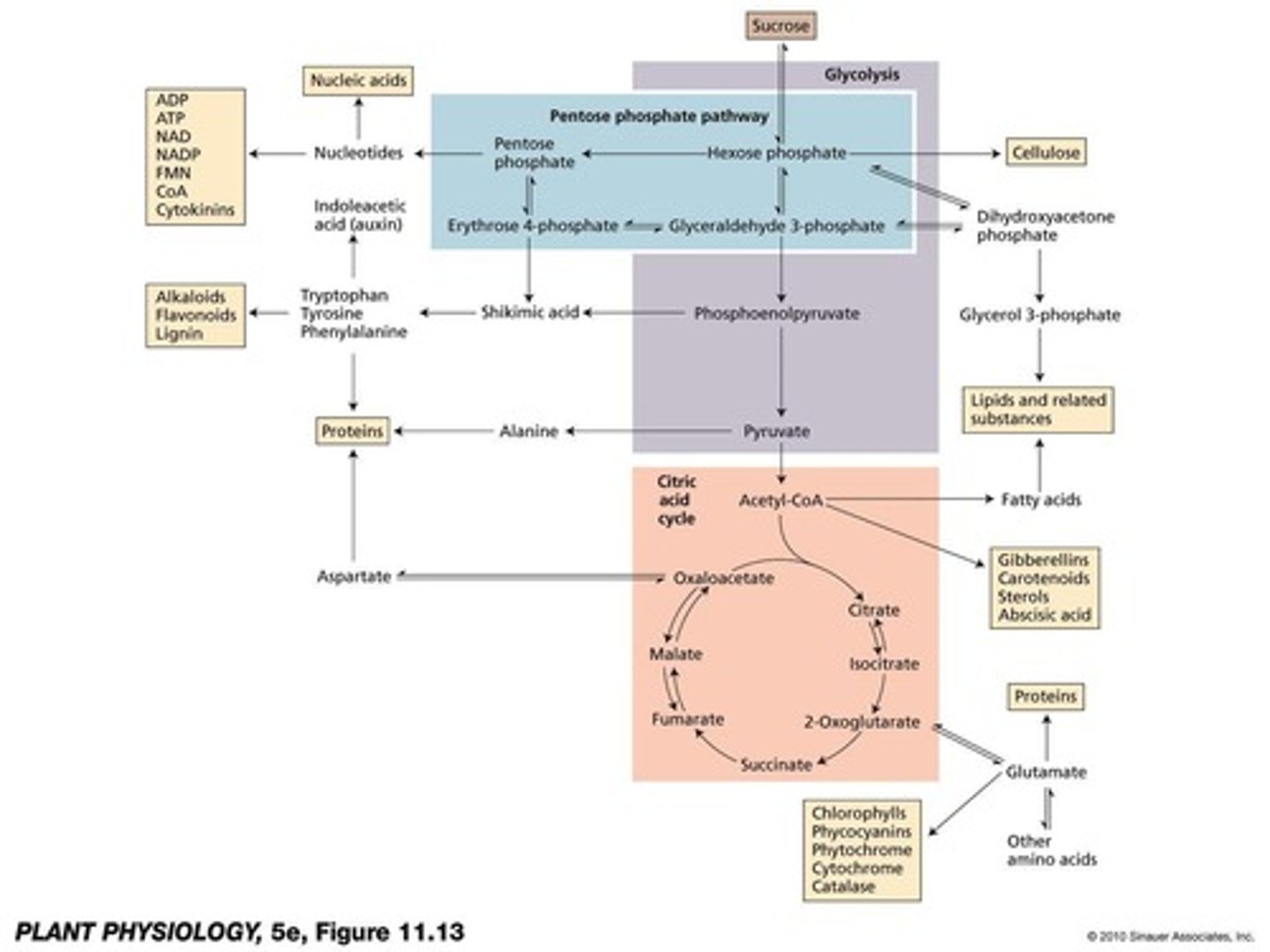
What is the significance of anaplerotic reactions?
They replenish TCA cycle intermediates that are used for biosynthesis.
What is the main product of the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway?
NADPH, which is used in biosynthesis and detoxification.
What is the role of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) in glycolysis?
It is oxidized to generate NADH and is a strong donor of phosphate to produce ATP.
What are the irreversible reactions in the oxidative pentose phosphate cycle?
They convert glucose 6-phosphate to ribulose 5-phosphate with loss of CO2 and generation of NADPH.
What is the final product of the citric acid cycle?
Oxaloacetate, which combines with acetyl-CoA to form citrate.
What is the net ATP gain from glycolysis?
2 ATP (4 produced - 2 consumed).
What is the role of succinyl-CoA in the citric acid cycle?
It is oxidized to oxaloacetate, yielding NADH.
What is produced during the oxidative phosphorylation process?
A large amount of free energy stored as ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
What is the significance of ribose-5-phosphate?
It is needed for nucleotide synthesis (DNA, RNA, ATP) and coenzymes.
What does the term 'anaplerotic reaction' refer to?
Reactions that replenish intermediates of the citric acid cycle.
What is the malic enzyme pathway's role?
It offers flexible pyruvate supply, redox power (NADPH or NADH), generates CO2 for carbon fixation, and has anaplerotic and cataplerotic roles.
Where does oxidative phosphorylation occur?
In the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What must NADH and FADH2 be converted to?
ATP.
What is the final electron acceptor in respiration?
Oxygen (O2).
What is the reaction catalyzed by Complex I in the electron transport chain?
2 NADH + 2 H+ + O2 → NAD+ + H2O.
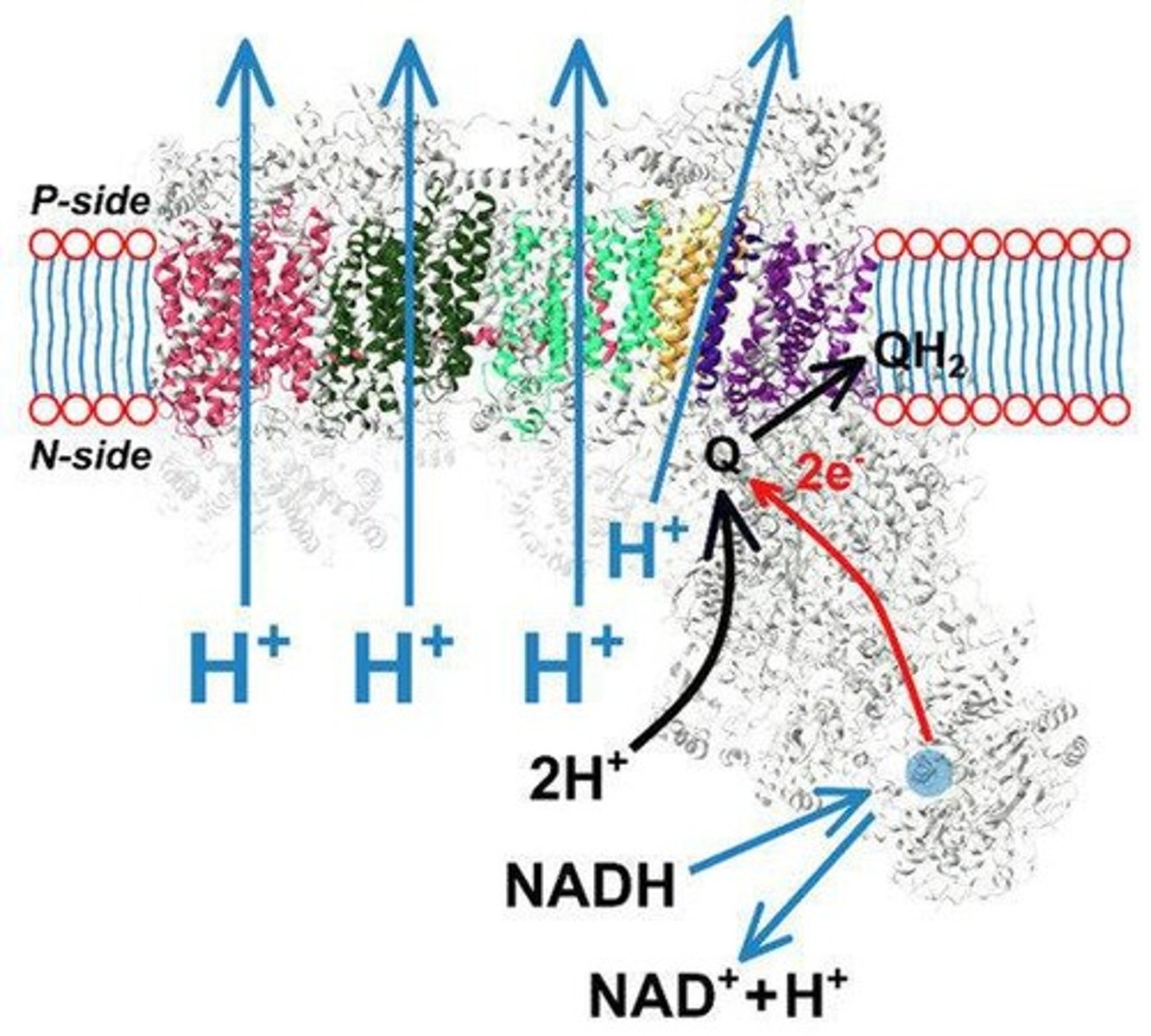
How many NADH are generated from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle for each sucrose oxidized?
4 NADH generated in cytosol and 16 NADH generated in mitochondrial matrix.
What is the mass of an electron?
9.1 × 10⁻³¹ kilograms.
What is the charge of an electron?
-1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ coulombs.
What are the biological roles of electrons?
Chemical bonding, energy transfer, redox reactions, and signaling.
How do living organisms store and transport electrons?
Through NADH, NADPH, and FADH2.
What type of energy does an electron possess when moving?
Kinetic energy.
What is the potential energy of an electron dependent on?
How tightly or loosely a molecule holds it (its redox potential).
What is the function of ATP synthase?
To convert ADP + Pi into ATP.
What is the ADP:O ratio?
The number of ATP synthesized per two electrons transferred to oxygen.
What is the theoretical ADP:O ratio for Complex I?
2.5.
What is the role of alternative oxidase (AOX) in plants?
It provides an alternative respiratory pathway that is insensitive to cyanide and helps prevent over-reduction and ROS formation.
What is the significance of the proton gradient created during mitochondrial electron transport?
It creates an electrochemical potential gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What is the main function of Complex II in the electron transport chain?
To transfer reducing equivalents from FADH2 to ubiquinone.
What is the role of Complex IV?
To catalyze the reduction of O2 to H2O.
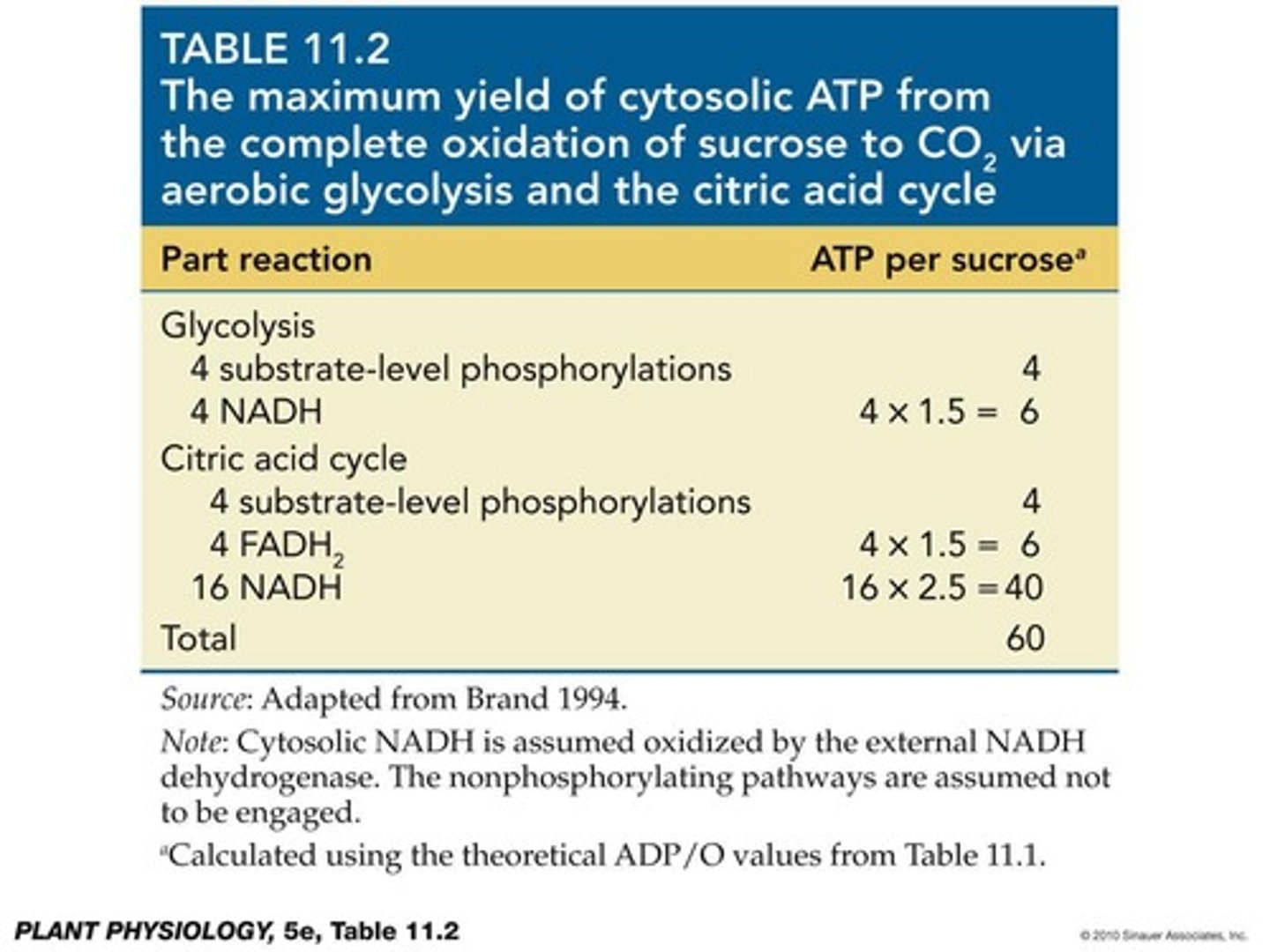
What is the bottom line for ATP production from sucrose?
About 60 ATP per sucrose, including contributions from substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation.
What factors affect the rate of respiration in plants?
Species, growth habit, organ type and age, light, O2 and CO2 concentrations, temperature, and nutrient and water supply.
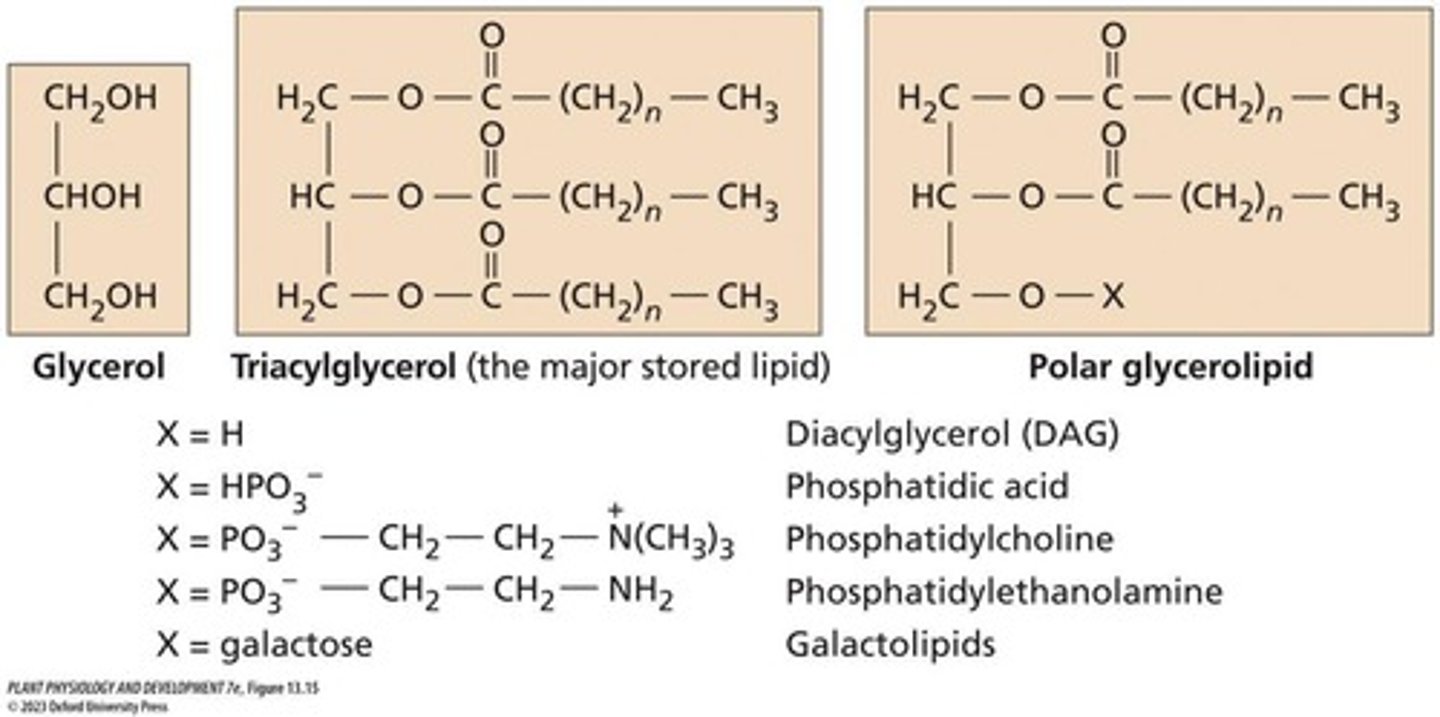
What is the role of triacylglycerols in plants?
They are fats and oils stored in seeds for energy and carbon storage.
What is the function of polar glycerolipids?
They form the lipid bilayers of cell membranes.
How do fatty acids behave in terms of solubility?
They are highly soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in water.
What is the energy content of 1 g of fat?
40 kJ
What is the energy content of 1 g of starch?
15.9 kJ
What are triacylglycerols composed of?
Three fatty acid molecules linked by ester bonds to glycerol.
What type of fatty acids are typically found in plants?
Straight-chain carboxylic acids with an even number of carbons.
What is the primary fatty acid composition of peanut oil?
9% palmitic acid, 59% oleic acid, 21% linoleic acid.
What are oil bodies?
Triacylglycerols stored in seeds, also called spherosomes and oleosomes.
What stabilizes oil bodies?
Oleosin proteins.
What is the structure of lipid bilayers?
Amphipathic with hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
What are glyceroglycolipids?
Lipids where sugars form the head group.
What are glycerophospholipids?
Lipids where the head group contains phosphate.
Where does fatty acid biosynthesis occur in plants?
Exclusively in plastids.
What is the rate-limiting step in fatty acid biosynthesis?
The conversion of acetyl-CoA + CO2 to malonyl-CoA by acetyl-CoA carboxylase.
What is acyl-ACP?
An acyl chain covalently bound to acyl-carrier protein during fatty acid synthesis.
What is the role of isocitrate lyase and malate synthase in plants?
They are unique enzymes that allow glucose regeneration from fatty acids.
What is the glyoxylate pathway?
A modified TCA cycle that bypasses CO₂-releasing steps, resulting in a net gain of two carbons.
How does the human body utilize energy at rest?
Burns ~26 Calories per Kg to maintain vital functions.
What percentage of total calories does the brain consume?
20-25% of total calories used in humans.
What happens to triacylglycerol (TAG) in germinating seeds?
Converted to sugars through hydrolysis and β-oxidation.
What is gluconeogenesis?
The process of converting non-carbohydrate sources into glucose.
What are ketone bodies?
Chemicals generated during fatty acid metabolism, used as energy sources during starvation.
What is the conversion efficiency of fatty acids to glucose?
Less than 10% conversion rate from fatty acid.
What is the primary energy source for the brain during prolonged fasting?
Ketone bodies.
What is the main structural component of membranes in cells?
Phospholipids.
What is the main fatty acid composition of cottonseed oil?
25% palmitic acid, 15% oleic acid, 55% linoleic acid.
What is the significance of desaturase enzymes in fatty acid biosynthesis?
They introduce double bonds into fatty acid chains.
What is the function of phosphatidic acid in polar glycerolipid biosynthesis?
It is formed from the transfer of acyl groups to glycerol-3-phosphate.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in lipid synthesis?
It is one of the sites where different polar glycerolipids are synthesized.