Steroidal Anti-Inflammatories
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Adrenocorticosteroids can be categorized according to
duration of action
activity
potencies
what are the categorizations of Adrenocorticosteroids based on duration of action?
short-acting
intermediate-acting
long-acting: dexamethasone, betamethasone
what are the short acting adrenocorticosteroids?
hydrocortisone, cortisone
what are the intermediate acting adrenocorticosteroids?
intermediate-acting: prednisone, methylprednisone
what are the long acting adrenocorticosteroids?
dexamethasone, betamethasone
what are the categorizations of Adrenocorticosteroids based on activity?
both gluco- and mineralocorticoid activity:
without mineralocorticoid activity:
what are the adrenocorticosteroids with both gluco- and mineralocorticoid activity?
hydrocortisone and cortisone
what are the adrenocorticosteroids without mineralocorticoid activity?
prednisone and dexamethasone
what are the categorizations of Adrenocorticosteroids based on potencies?
Dexamethasone 25
Methylprednisolone 5
Prednisone 4
Hydrocortisone 1.0
what are some of the many uses of corticosteroids?
• As replacement (Addison’s disease)
• Arthritis
• Asthma
• Inflammatory bowel disease
• Various skin conditions
• Immunosuppression
• Allergy
• Antiemetic
what is the “Fatty” structure located sup. to the kidneys?
adrenal glands
what is the function of adrenal glands?
responsible for the secretion of diff. hormones & mediators
what are the layers of the adrenal glands? (outer to inner)
capsule
zona glomerulosa
zona fasciculata
zona reticularis
medulla
what is the function of the medulla?
responsible for the secretion of catecholamines (adrenaline & noradrenaline)
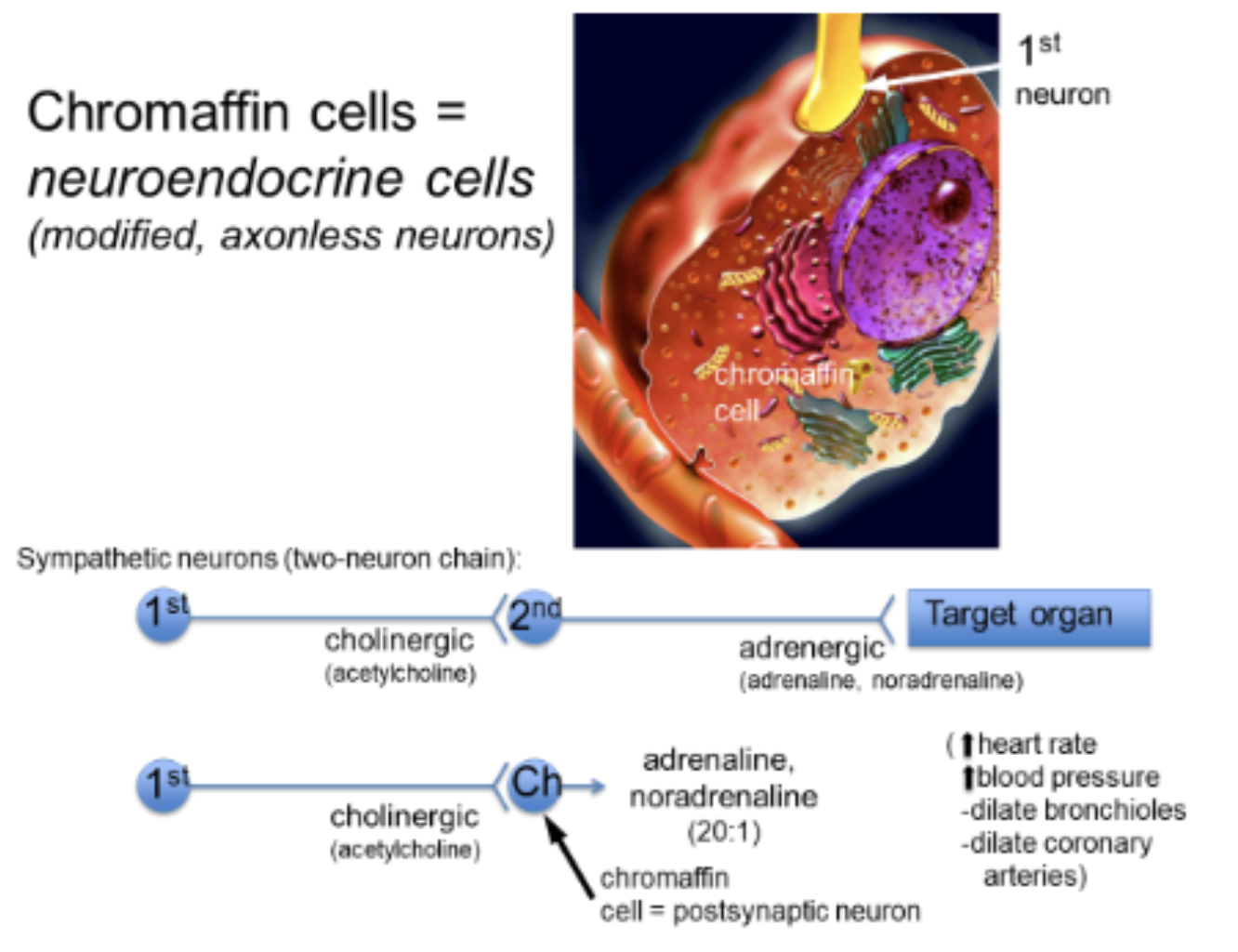
what are the chromaffin cells (neuroendocrine cells)?
cells within the adrenal medulla that mimic the sympathetic system
what does the glomerulosa secrete? fasciculata? reticularis?
glomerulosa → mineralocorticoid
fasciculata → glucocorticoid
reticularis → androgens
when stimulated, chromaffin cells secrete what?
blood
how do chromaffin cells mimic the sympathetic system?
sympathetic neuron is a 2 neuron chain (S + PS)
the 1st axon in CNS synapses on a ganaglion
the 2nd axon is sent to a target organ which stimulates the fight/flight response
medulla neuron in CNS
1st axon synapses on chromaffin cells which releases adrenaline/noradrenaline directly to blood for fight/flight response
what are the endogenous cortisols?
mineralocorticoid & glucocorticoid (secreted from AC)
the adrenal cortex is regulated by what system?
HPA axis (hypothalamus + ant. pituitary + adrenal cortex)
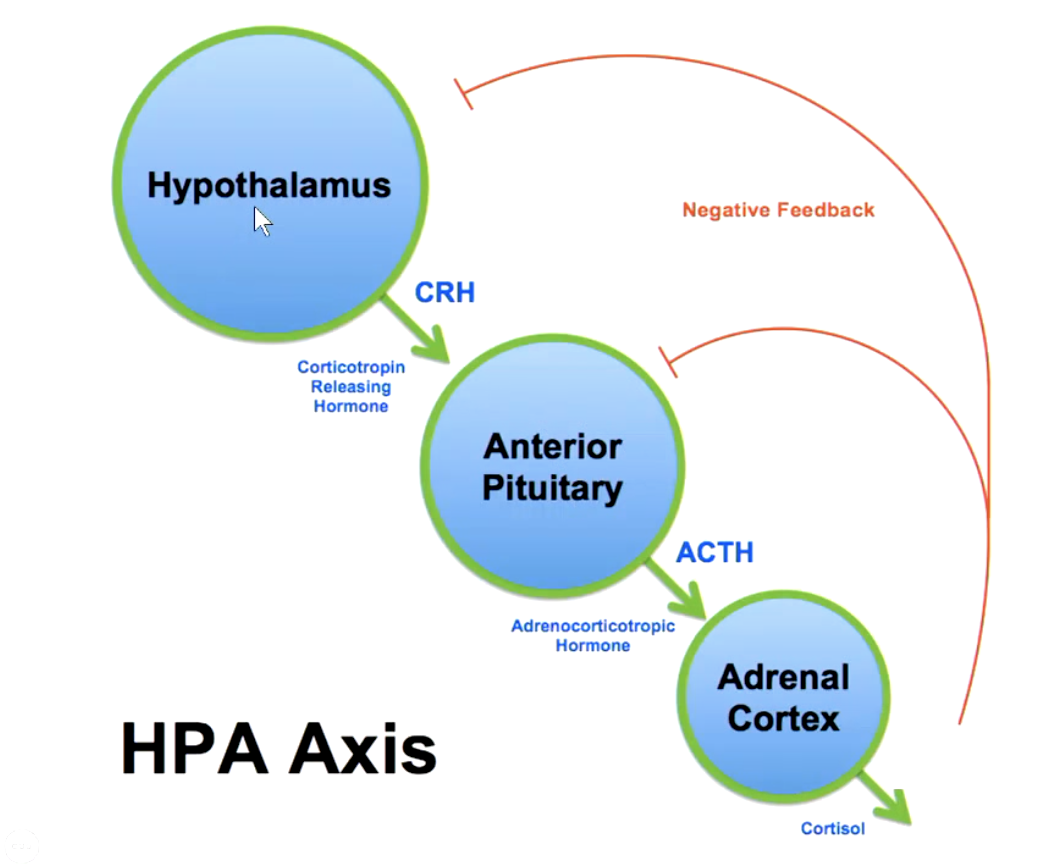
describe the HPA axis cascade when there is low cortisol levels
hypothalamus releases corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)
anterior pituitary releases adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
adrenal cortex releases more cortisol
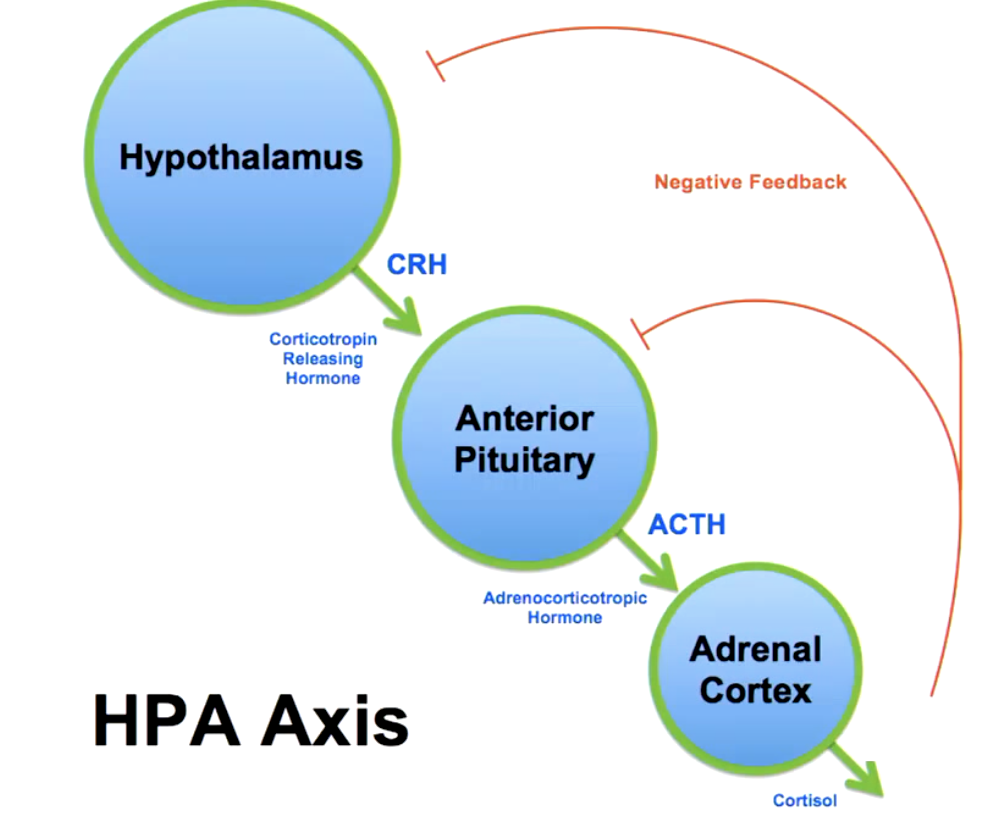
describe the HPA axis cascade when there is high cortisol levels
negative feedback
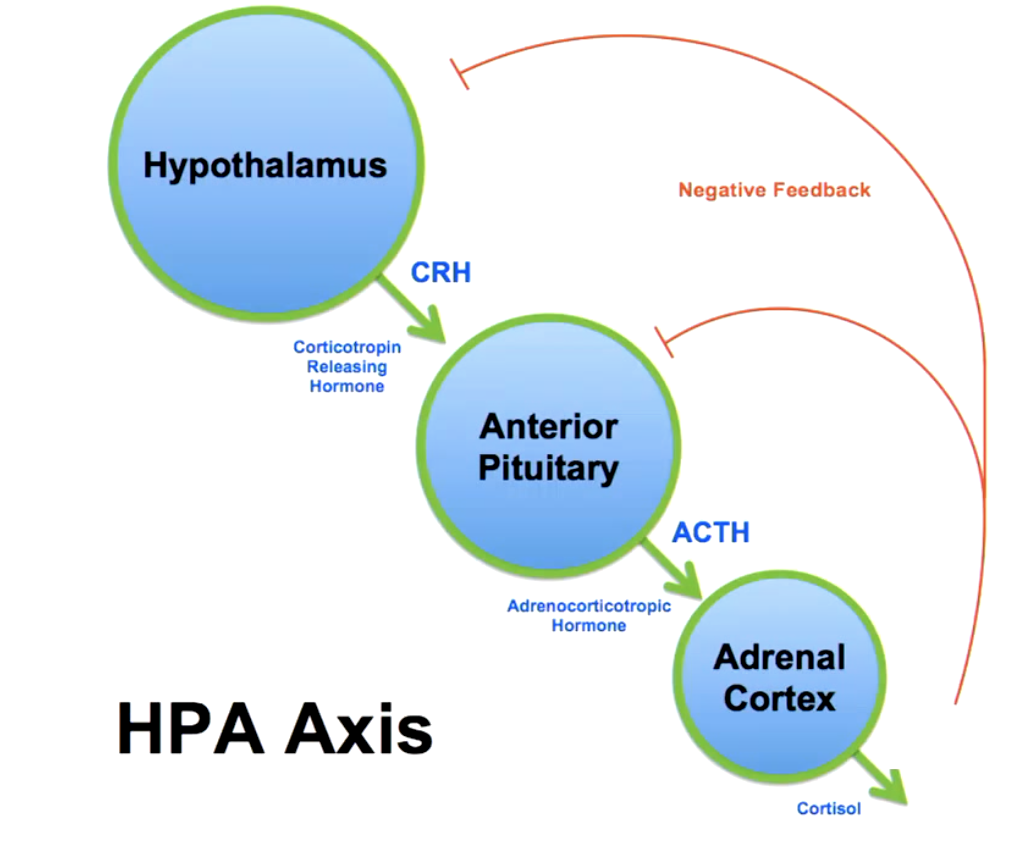
what do mineralocorticoids do?
regulate sodium and potassium
what do glucocorticoids do?
• Changes in carbohydrates & protein metabolism
• Fat redistribution
• Suppression of inflammation, immune function, &
allergy response
• Mood changes
• Calcium absorption and excretion altered
• Reduced growth of new cells (children)
what are the major pathways in which the body responds to (physical stress)?
sympathomedullary pathway & pituitary adrenal system
which pathway is FAST acting with a SHORT duration for how the body responds to physical stress?
Sympathomedullary
which pathway is pathway is SLOW acting with a LONG duration of how the body responds to physical stress?
Pituitary Adrenal System
describe the sympathomedullary pathway
1. HT activates adrenal medulla
2. adrenal medulla releases catecholamines (adr. & noradr.) into the blood
3. body prepares for fight or flight
a. adr. & noradr. reinforce the pattern of sympathetic activation
b. ex: inc. HR & BP, better coronary circulation, bronchodilation
4. body gets more energy to prepare for stress

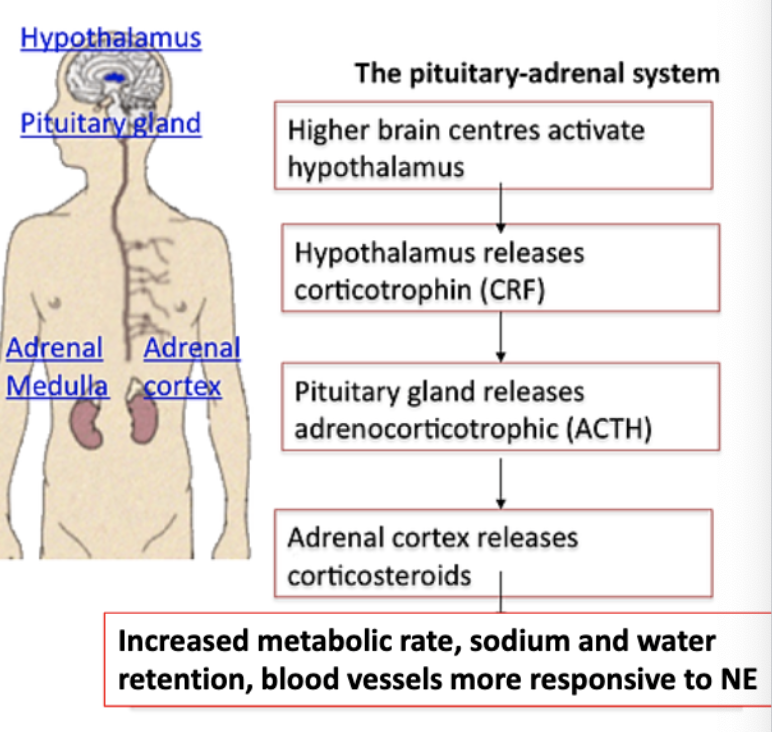
describe the pituitary-adrenal system pathway
1. higher brain center activates HT
2. HT releases corticotropin releasing hormones (CRH)
3. AP gland releases adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
4. adrenal cortex releases corticosteroids
5. inc. metabolic rate, sodium & water retention, blood vesels more respontive to NE a. help body accommodate the stress
what is Addison’s disease?
autoimmune disease that causes the adrenal glands to make too little cortisol & often too little aldosterone
can cause adrenal insufficiency
auto-Abs attack adrenal cortex causing destruction & damage, so not enough cortisol is secreted
adrenal insufficiency can be caused by…?
tumor/metastasis to adrenal cortex
hemorrhage
infections (ex: latent to active TB) that destruct adrenal cortex
not having enough mineralocorticoid (adrenal insufficiency) can lead to…?
not enough sodium-water retention = low fluid volume & low BP ⇒ shock ⇒ possible brain coma & death
what is CUSHING syndrome?
primary disease of corticosteroid excess
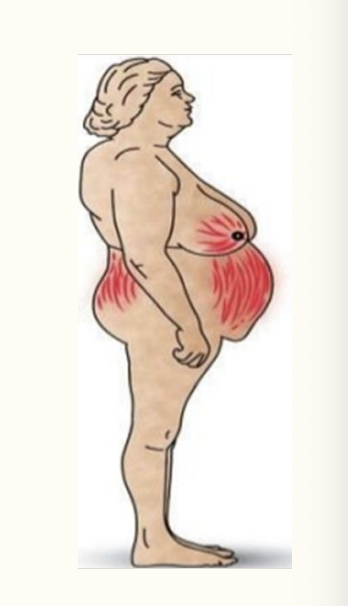
what are the symptoms of CUSHING syndrome?
C: cataracts
U: ulcers
S: dermal thinning, striae
H: hypertension, hyperglycemia
I: infections
N: avascular necrosis
G: glycosuria
O: osteoporosis, obesity (Dorso Cervical fat pad, Buffalo Hump)
I: immunosuppression
D: diabetes
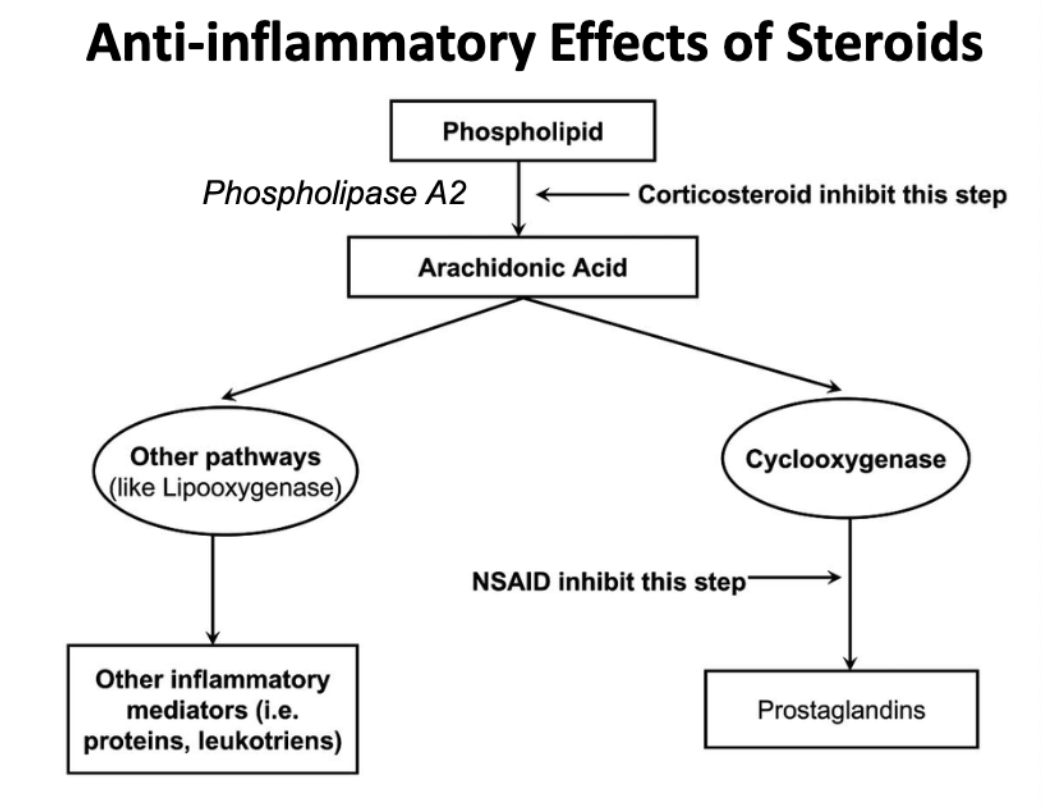
which step of the arachidonic acid pathway do corticosteroids inhibit?
in dentistry, systemic steroids are often effective in the treatment of oral lesions due to…?
noninfectious inflammatory disease
in dentistry, topical corticosteroids can be used for…?
non infections, ulcerative diseases in oral cavity. Inhibit the inflammatory reaction, redness and edem
in dentistry, systemic corticosteroids can be used for…?
third molar extraction, minor and major surgery to reduce edema, pain, trismus, and TMJ disorders
t/f: topical corticosteoirds can be used to treat candidiasis (oral thursh).
false. will make it worse
Because of the wide ranging effects and potency of these drugs, it is virtually impossible to achieve clinical improvement without producing some adverse side effects.
Consequently, it is desirable to limit use, when possible, to:
emergency situations
or to short-term therapy at the smallest effective dose
Many instances of inflammation can be just as effectively treated using
NSAIDS (instead of corticosteroids)
what are the major side effects of corticosteroids that should be of concern to dentists?
Suppression of pituitary adrenal axis
Immunosuppression
Suppression of Beneficial Inflammatory Processes
Recovery of normal adrenal function can take up to _____ following the cessation of therapy, therefore even patients not currently on such Corticosteroids medications present a risk
1 year
suppression of pituitary adrenal axis is a side of effect of Corticosteroids. what does this mean?
Acute adrenal insufficiency
Patients might not be able to respond normally to the stress of dental surgical procedures
In these situations, patients may need extra doses of steroid (usually double or triple the dose) prior to and following dental surgical procedures (dose then tapered down over several days to normal maintenance dose) to properly protect them
immunosuppression is a side of effect of Corticosteroids. what does this mean?
increased susceptibility to infection
may be necessary to provide antibiotic therapy for patients on long-term steroids when oral surgical procedures are planned
Minor/superficial infections may become systemic
Quiescent infections may become active
Normally nonpathogenic organisms may cause systemic disease
corticosteroids are contraindicated in patients with…?
latent tuberculosis
One common use of glucocorticoids is in steroid containing inhalers for the treatment of asthma. Use of corticosteroid containing inhalers has been associated with increased occurrence of
oral Candida related problems
suppression of beneficial inflammatory processes is a side of effect of Corticosteroids. what does this mean?
Inflammatory processes are important for efficient healing of wounds and tissue injury
slow healing of wounds (appropriate management post-op)
mask early symptoms of disease and interfere with proper diagnosis
coritcosteroids are:
anti-inflammatory
anti-pyretic
or analgesic
all of the above