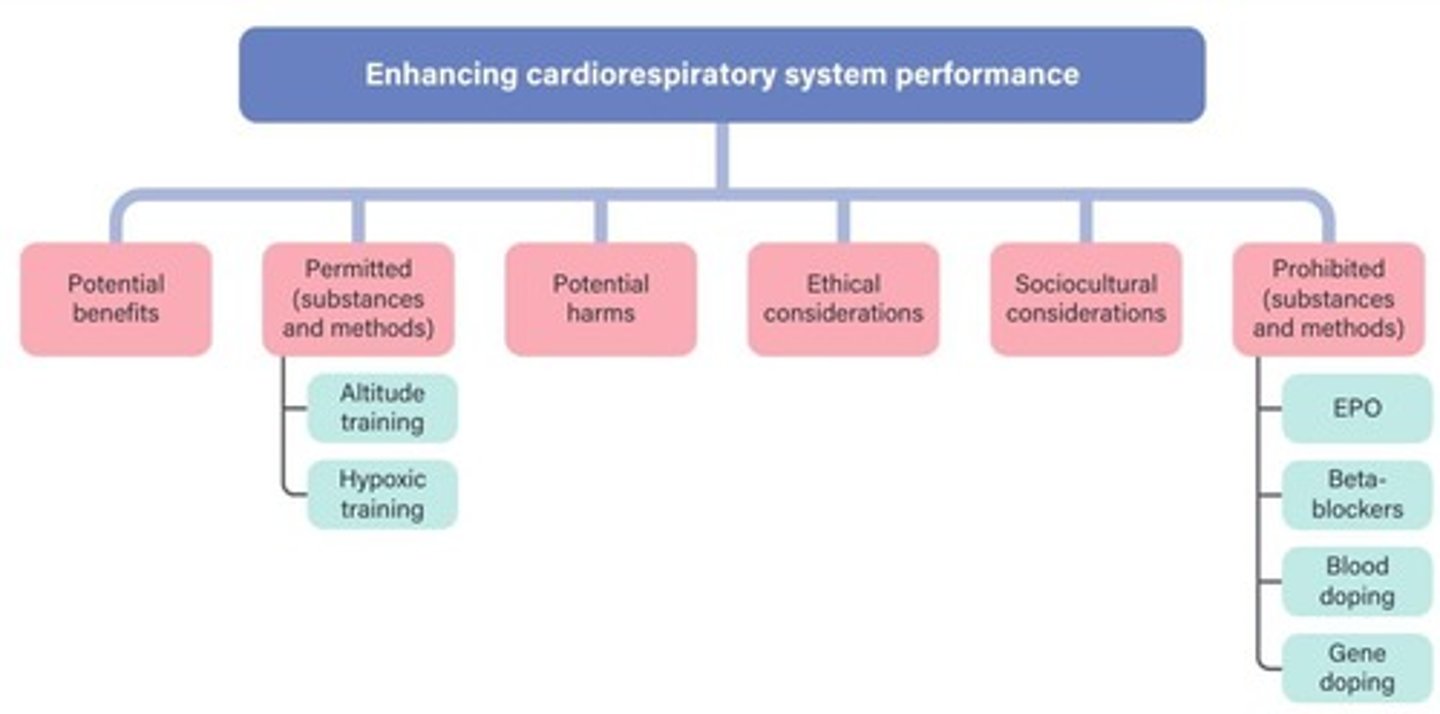
Enhancing Cardiorespiratory Performance in Physical Education
1/250
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
251 Terms
Cardiorespiratory System
System responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients.
Altitude Training
Training at high elevations to improve endurance.
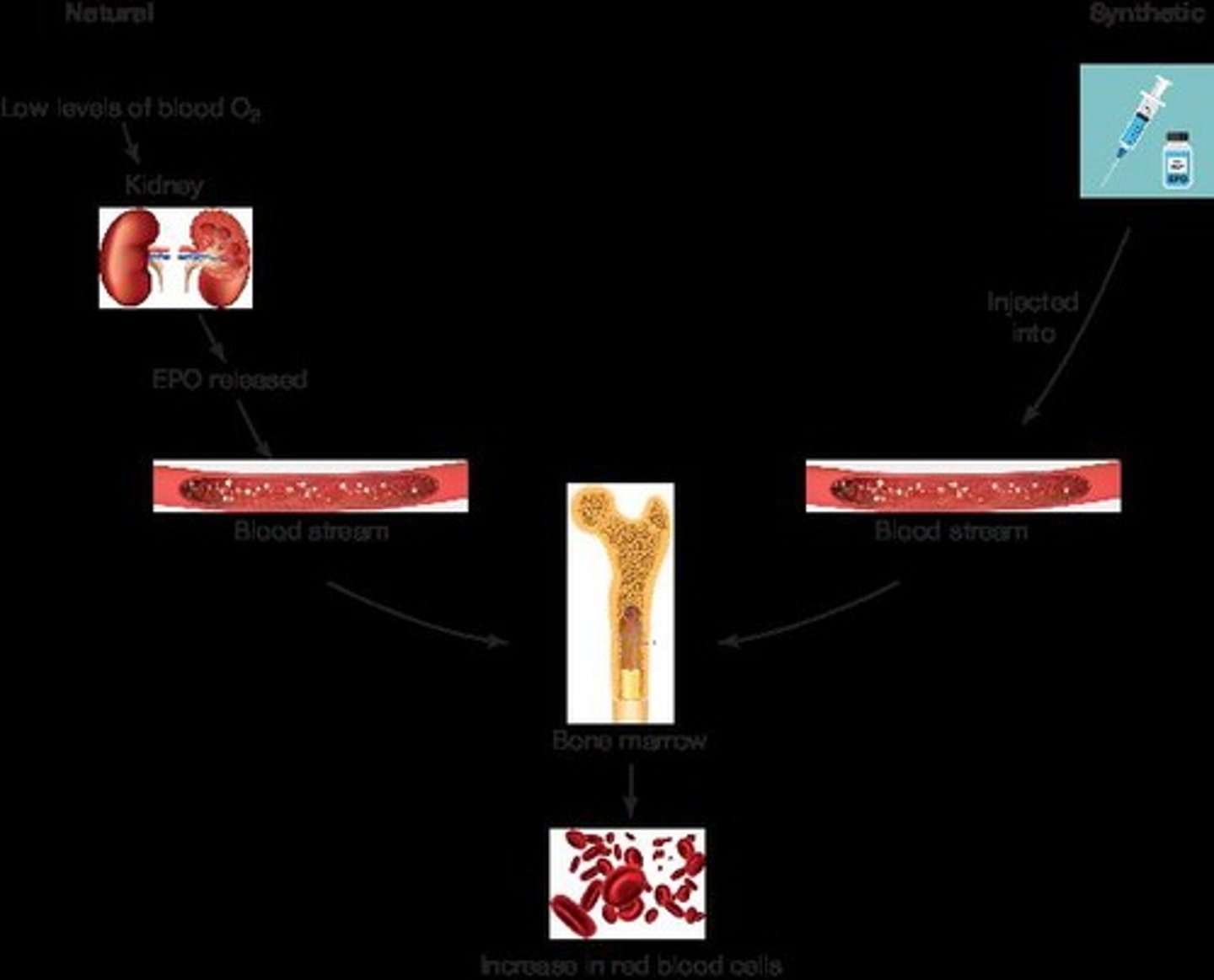
Erythropoietin (EPO)
Hormone that stimulates red blood cell production.
Beta-Blockers
Medications that reduce heart rate and blood pressure.
Gene Doping
Altering genes to enhance athletic performance.
Blood Doping
Transfusing blood to increase oxygen capacity.
World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA)
Organization promoting dope-free sports globally.
Sport Integrity Australia
Australia's agency for anti-doping compliance.
Ergogenic Aids
Substances or methods enhancing physical performance.
Permitted Substances
Enhance performance without health risks or violations.
Prohibited Substances
Enhance performance and pose health risks.
Ethical Considerations
Moral implications of using performance-enhancing methods.
Sociocultural Considerations
Social factors influencing attitudes towards doping.
Health Risks
Potential dangers associated with performance-enhancing substances.
Fairness in Sport
Equitable access to performance-enhancing methods.
Peer Influence
Impact of teammates on doping decisions.
Community Role Models
Athletes influencing societal values and behaviors.
Socioeconomic Status
Economic factors affecting access to training resources.
Transparency in Sports
Openness about performance-enhancing substance use.
Spirit of Sport
Ethical principles guiding fair competition.
Batch Tested Products
Supplements verified for safety and compliance.
Performance Advantage
Significant improvement in athletic ability from doping.
Win at All Costs
Mindset prioritizing victory over fair play.
Role Modeling
Influence of athletes on youth behavior and values.
Performance enhancement
Improving athletic ability beyond natural limits.
Peer pressure
Influence from others to use banned substances.
Hypoxic environments
Simulated low-oxygen settings for performance adaptation.
Deacclimatisation
Decline in endurance after returning to sea level.
Acclimatisation
Physiological adjustments to high altitude training.

Financial incentive
Monetary motivation to use performance enhancers.
Altitude sickness
Health issues from low oxygen at high altitudes.
Red blood cells
Cells transporting oxygen in the bloodstream.
Physiological perspective
Understanding body functions related to performance.
Training facilities access
Availability of locations for altitude training.
Fame and role model status
Influence of public recognition on athletes' choices.
Dissatisfaction with performance
Unhappiness leading to substance use for improvement.
Coach pressure
Influence from coaches to enhance performance illicitly.
Endurance capacity
Ability to sustain prolonged physical activity.
Synthetic EPO
Artificially produced hormone to boost red blood cells.
Autologous doping
Reintroduction of an athlete's own blood.
Homologous doping
Introduction of donor red blood cells.
EPO
Hormone that stimulates red blood cell production.
Potential harms of EPO
Includes hypertension, stroke, heart disease.
Heart rate reduction
Beta-blockers decrease heartbeats per minute.
Widening blood vessels
Beta-blockers help lower blood pressure.
Beta-blockers in sports
Banned in archery, darts, billiards, shooting.
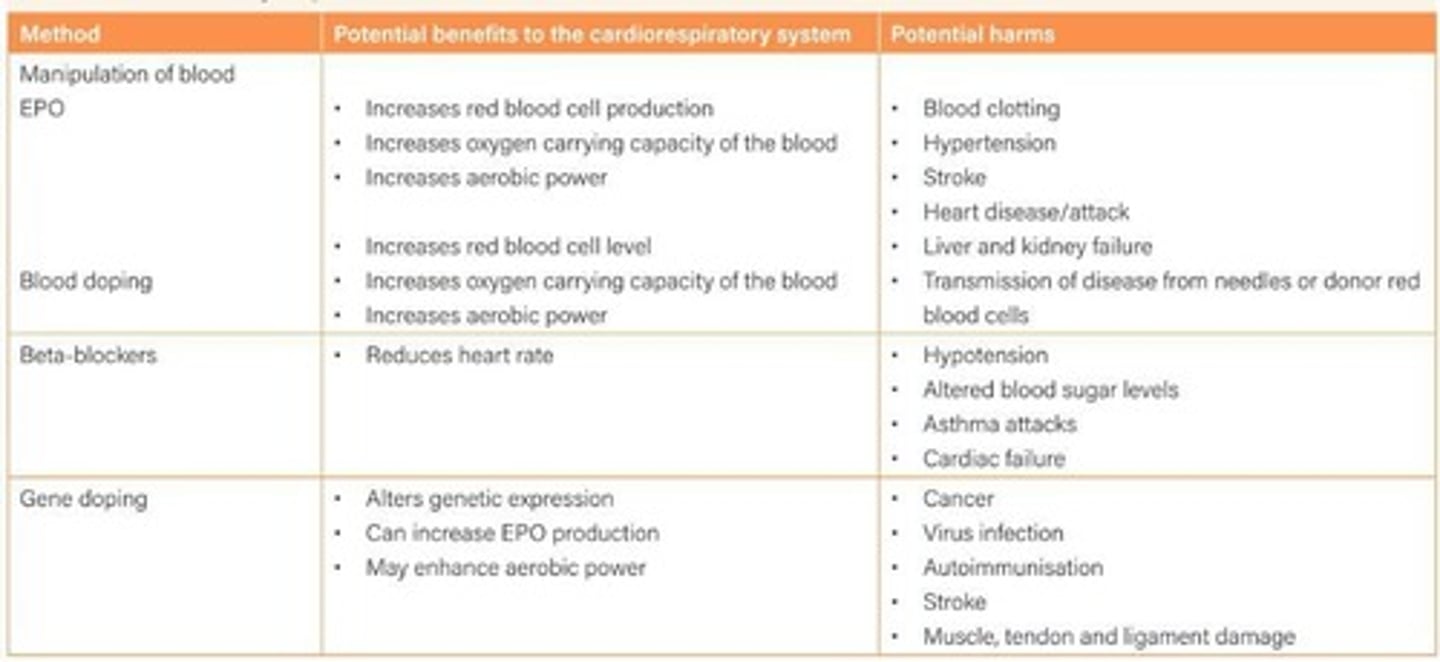
Gene therapy
Used to treat genetic diseases through gene manipulation.
WADA rules
Prohibit non-therapeutic gene doping practices.
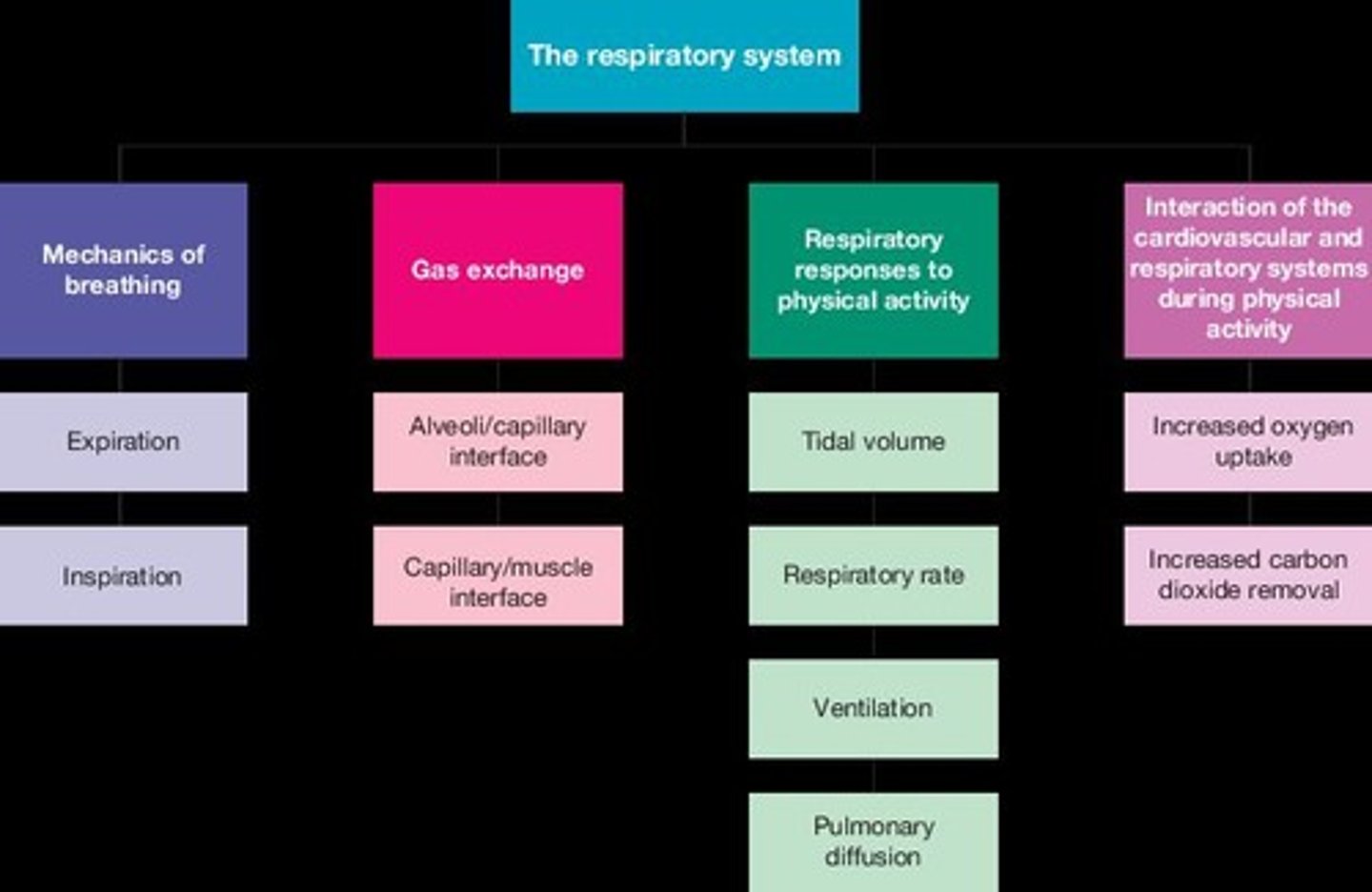
Respiratory system
System responsible for gas exchange in the body.
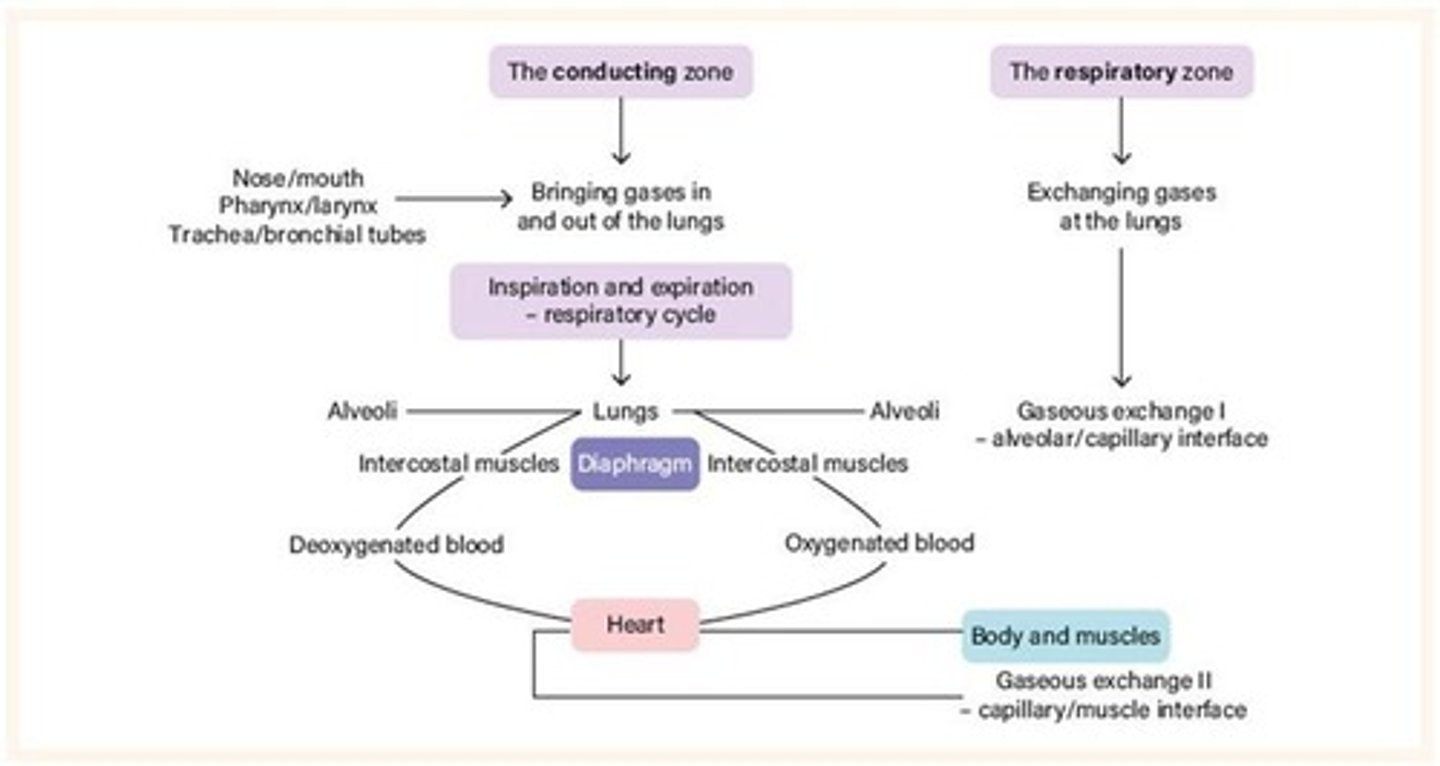
Gaseous exchange
Oxygen and carbon dioxide transfer at alveoli.
Cardiovascular system
Transports oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
Aerobic exercise impact
Enhances cardiovascular and respiratory system functioning.
Conducting zone
Structures bringing air into and out of lungs.
Respiratory zone
Area where gaseous exchange occurs.
Nasal cavity
Initial pathway for air, warms and filters it.
Cilia function
Filters foreign particles from entering respiratory tracts.
Ventilation changes
Alterations in breathing with exercise intensity.
Vocal cords
Create speech as air is expelled.
Heat and water vapor expulsion
Removes excess moisture during exhalation.
Cilia
Hair-like structures that clear airways in lungs.
Pharynx
Throat section connecting mouth and nose.
Larynx
Voice box containing vocal cords.
Trachea
Windpipe providing air passage to lungs.
Bronchi
Two main air passages from trachea to lungs.
Bronchioles
Smaller branches of bronchi delivering air to alveoli.
Alveoli
Microscopic sacs for gas exchange in lungs.
Pleura
Membrane covering lungs, reducing friction during breathing.
Diaphragm
Muscle aiding in breathing by changing chest cavity size.
Inspiration
Active process of drawing air into lungs.
Expiration
Passive process of expelling air from lungs.
Intrapulmonary pressure
Pressure within lungs affecting air movement.
Tidal volume (TV)
Volume of air per breath, measured in L.
Respiratory rate (RR)
Breaths taken per minute, measured in breaths/min.
Ventilation (V)
Volume of air moved per minute, measured in L/min.
Intercostal muscles
Muscles between ribs aiding in breathing.
Gas exchange
Process of oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
Capillaries
Small blood vessels surrounding alveoli for gas exchange.
Adam's apple
Prominent larynx feature more visible in males.
Hyaline cartilage
Type of cartilage providing structure to trachea.
Chest cavity
Space in thorax housing lungs and diaphragm.
Pulmonary ventilation
Total air volume exchanged in one minute.
Ventilation
Volume of air exchanged per minute.
Minute Ventilation
Total air volume per minute; V = RR x TV.
Average Tidal Volume (Men)
600 ml is typical for men.
Average Tidal Volume (Women)
500 ml is typical for women.
Maximum Oxygen Uptake (VO2 max)
Maximal oxygen intake for ATP production.
VO2 max Measurement
Expressed in mL/kg/min for body mass comparison.
External Respiration
Gas exchange at lungs with external environment.
Internal Respiration
Gas exchange within body tissues.
Pulmonary Arteries
Carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Alveolar/Capillary Interface
Site of gas exchange in lungs.
Haemoglobin
Protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells.
Oxygen Movement
Diffuses from capillaries into tissues.
Carbon Dioxide Movement
Diffuses from tissues into blood.
Respiratory Control Centre
Brain stem regulates breathing rates.
Homeostasis in Breathing
Maintaining balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Oxygen Demand Increase
Higher breathing rate meets increased oxygen needs.
Gaseous Diffusion
Movement of gases across membranes.
Pressure Differences
Drive gas exchange at tissues.
Oxygenated Blood
Blood rich in oxygen returning to the heart.