Dictyocaulus viviparus - Cattle lungworm
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What are the relevant species of dictyocaulus and the species they occur in?
Trichostrongyle lungworms
Dictyocaulus viviparus —> cattle, dairy replacement heifer calves
D. filaria —> sheep and goats (highly pathogenic)
D. arnfieldi —> resp dx in horses (non patent) and donkeys (patent infection, no dx, carriers)
What lungworms occur in sheep in the UK?
Dictyocaulus filaria (more in tropics and sub tropics)
Muellerius capillaris
What disease is caused by dictyocaulus viviparus?
Parasitic bronchitis = 'husk', dictyocaulosis
What is the morphology of adult dictyocaulus viviparus worms?
4-8cm long
Slender, white
Male has reduced bursa
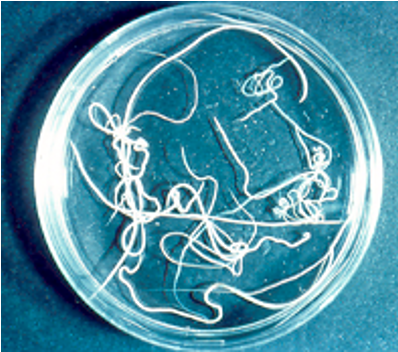
Where in the UK are dictyocaulus vivparus most common?
Wetter west of UK
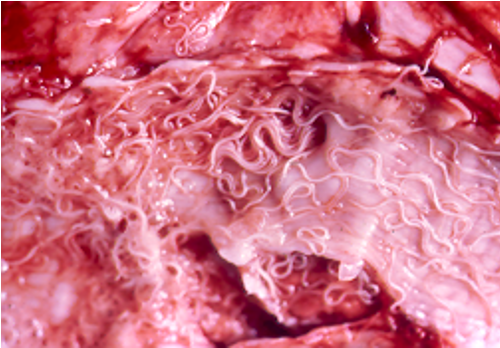
Where in the lungs are dictyocaulus viviparus found?
Trachea and bronchi
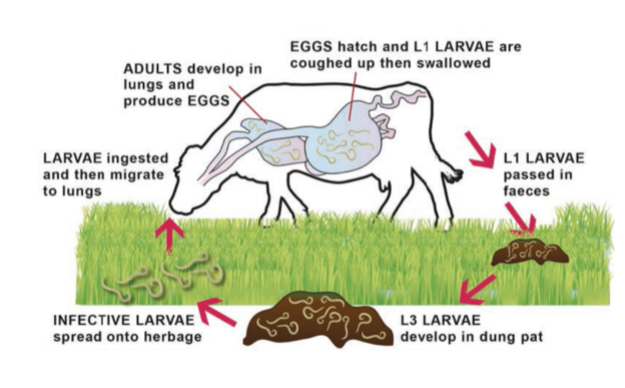
What are the general features of the life cycle of dictyocaulus?
Direct
Female worms ovo-viviparous —> lay larvated eggs which hatch immediately
L1 in lungs coughed up, swallowed, passed out in faeces
What are the features of L1, L2 and L3 of dictyocaulus?
L1 = in faeces
Short and stumpy
Refractile food granules
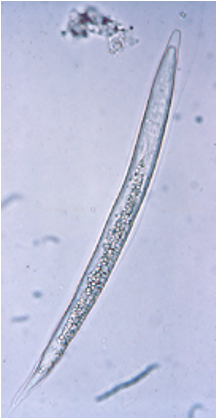
L1-L3 develop in faecal pat on pasture
All ensheathed —> never shed sheath from previous stage
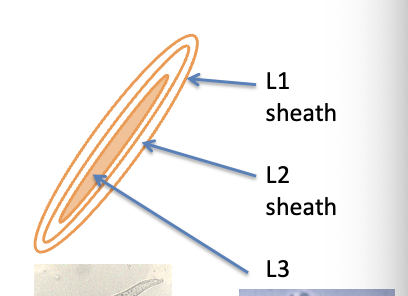
Larvae don't feed
(L3 is infective stage)
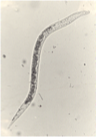
How long does it take for L1-L3 of dictyocaulus?
Can develop to L3 in 5-7 days in optimum conditions
What are the in animal phases of dictyocaulus viviparus life cycle?
Penetration phase
Pre-patent phase
Patent phase
Post patent phase
What happens in the penetration phase of dictyocaulus viviparus life cycle?
0-7 days after infection
L3 ingested, migrates
Lympho-tracheal migration (goes via lymph and blood to reach lungs)
Moults to L4 in LN
L4 reaches lungs (in capillaries of alveoli supplying lungs)
What happens in the pre patent phase of dictyocaulus viviparus life cycle?
8-25 days post ingestion
L4-L5 in lungs (enter alveoli)
L5 migrate up bronchial tree
Adults in bronchi and trachea ~3.5 weeks post ingestion
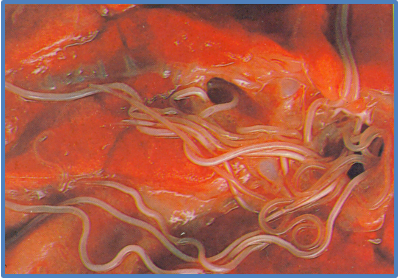
What happens in the patent phase of dictyocaulus viviparus life cycle?
26-55 days after infection
Adult worm in upper respiratory tract reproduce
Eggs and L1s produced
What happens in the post-patent phase of dictyocaulus viviparus life cycle?
55 days +
Immune expulsion of adults
Protective immunity
Which are the most pathogenic phases of the dictyocaulus life cycle?
Prepatent and patent phases
Which calves are most severely affected by dictyocaulus?
Smallest & weakest
Describe the pathology and clinical signs seen in the pre patent phase of dictyocaulus
Intense inflammatory response
Alveolitis, bronchiolitis, bronchitis
Interstitial emphysema
Pulmonary oedema
Coughing, resp distress, tachypnoea, weight loss
Describe the pathology and clinical signs seen in the patent phase of dictyocaulus?
Mature adults in bronchi/trachea
Eggs and L1 swept into alveoli
Intense inflammatory response
Frothy, white mucus
Emphysema, hypoxia
Gasping, coughing, death
Describe the pathology and clinical signs seen in the post patent phase of dictyocaulus?
Resolution of clinical signs
In some animals, epithelialisation of lung tissue, never completely recover
What factors affect the pre parasitic stage of dictyocaulus?
Temperature
Moisture
Dispersal of L3
L3 overwinter on pasture
L1 shed by carrier animals
How are dictyocaulus dispersed form the faecal pat?
Pilobolus fungi in faecal pat bursts and brings L3 with them
Can disperse quite far so hard to evaluate risk
Describe the epidemiology of dictyocaulus in the UK?
(Unpredictable)
Usually in Aug-Sept
Usually in dairy replacement calves
First cycle of infection —> very few L3 picked up, no immunity, no disease
Calves shed L1, these develop to L3, cause outbreaks of disease
Disease can happen from turn out to Nov depending on levels of L3
Immunity short-lived —> needs continual boosting
How many Dictyocaulus worms are needed to cause clinical disease?
800-1000
How is dictyocaulus diagnosed?
Clinical signs
L1 in faeces using a Baermann
Antibody detection ELISA
How does a Baermann funnel work?

Faecal matter suspended in filter at top, larvae are motile and will swim down and will congregate at bottom of funnel
Run off about 10 ml at bottom and can count number of larvae
How is dictyocaulus treated?
Rapid use of anthelmintics
NSAIDs, antibiotics
House most severely affected calves
Why can't you treat prophylactically for dictyocaulus?
If prophylaxis given no immunity builds so adult cattles remain naïve
How does dictyocaulus affect milk yield?
Reduction in milk yield, when overt clinical disease
What vaccine is available for dictyocaulus? What are its features?
Huskvac
Live, attenuated vaccine
1000 irradiated L3 given orally
When do you give Huskvac?
Two doses four weeks apart
Before turnout
Requires natural boosting to maintain immunity
What are the differences between lungworms & gut worms?
