Intro to Organ Systems
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
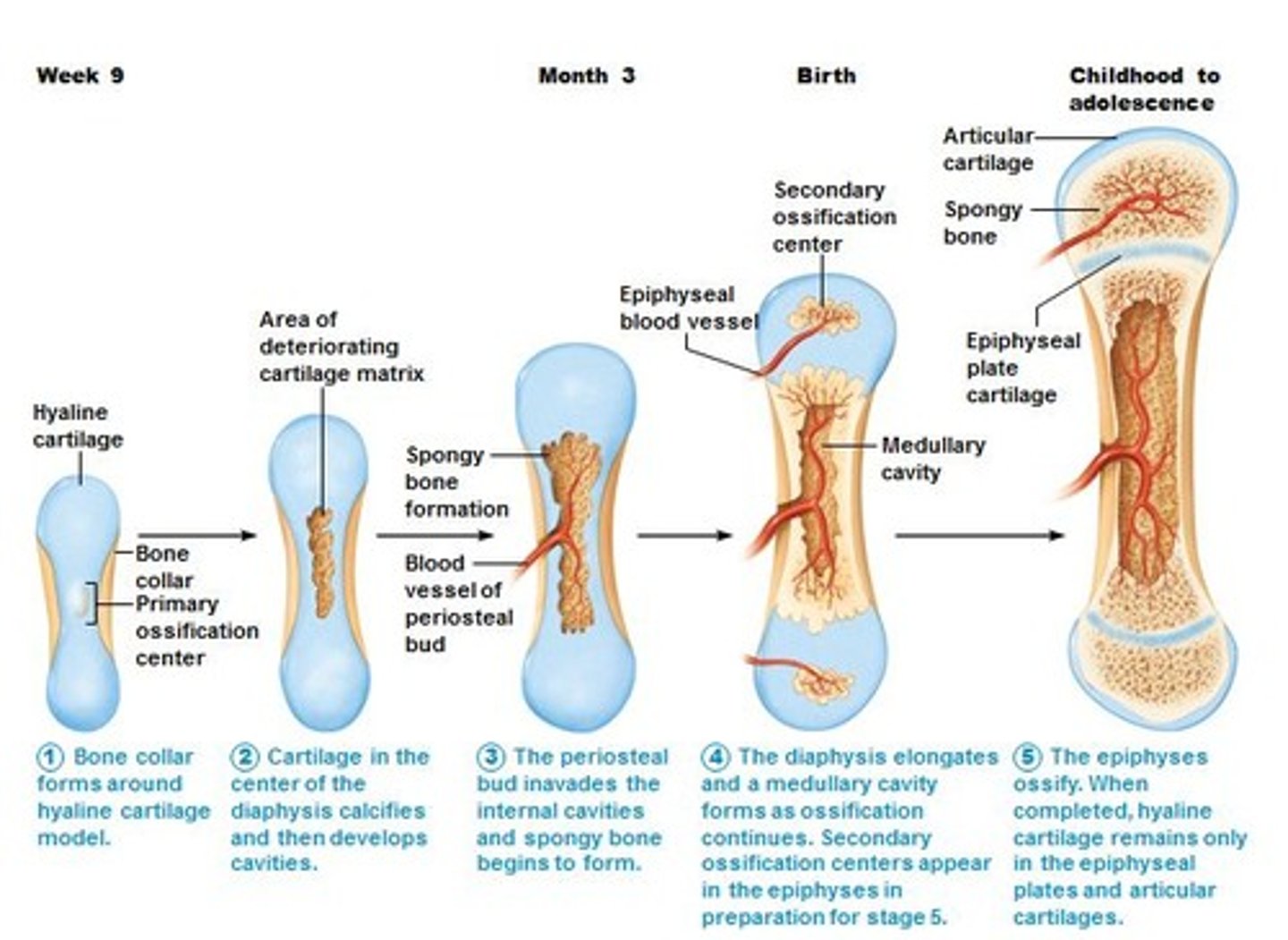
What is endochondral ossification?
the formation of bone from pre-existing hyaline cartilage models. Cartilage is avascular and thus dies by necrosis as bone forms from the middle outward
Why do bone markings exist?
As structures are developing together, bones are soft and are indented by various things pressing into them
What are the 3 kinds of joints (classified functionally)?
1. synarthrosis, immovable
2. amphiarthrosis, slightly moveable
3. diarthroses, synovial (most joints)
What connects synarthroses?
fibrous tissue, varying in length and density
What connects amphiarthroses?
cartilage, hyaline or fibrocartilage, temporary or permanent
What are the 3 features of synovial joints/diarthroses?
1. synovial fluid filled via serous membrane
2. enclosed by joint capsule
3. cartilaginous ends on each bone
What are multiaxial joints?
ball and socket joints, permit movement in more than 2 axis (ex. shoulder)
What are uniaxial joints?
hinge joints and pivot joints, permit movement in 1 axis (ex. elbow)
What are biaxial joints?
condylar and saddle joints, permit movement in 2 axis (ex. the joints between the metacarpals and phalanges or carpal and metacarpal joints)
What is an arthroscope?
a camera instrument used to look into the joints during surgery in order to minimize invasiveness
What is arthroplasty?
Joint replacement
What is the proximal attachment of a muscle? (origin)
location of muscle closest to origin, usually stays relatively stationary during concentric contraction
What is the distal attachment of a muscle? (insertion)
the end of a muscle that moves during concentric contraction
How do muscle injuries show up on imaging?
as bright spots (hyperintense) due to edema
Where do muscle injuries typically occur?
at the myotendinous junction/complex (MTJ) due to a mismatch of tissue at these points making them vulnerable
Why are hamstrings strained so commonly?
they have a very long MTJ
What are aponeuroses?
Long, flat sheets of tendon that attach muscle to bone OR muscle to deep fascia
What part of the nervous system do cranial nerves fall into?
the PNS
Why is there no plexus that is responsible for the face and head?
The cranial nerves govern these areas
Which spinal nerves exit above the vertebra of the same name?
C1-C7
Which spinal nerves exit below the vertebra of the same name?
C8 onward
What happens to spinal nerves as one moves caudally?
the nerves get longer
What does the term "spinal nerve" refer to?
the region of a nerve near the spine that contains both a sensory and motor component and has not branched yet
Which part of nerves near the spine is only sensory?
the dorsal root
Which part of nerves near the spine is only motor?
the ventral root
What is the dorsal ramus?
the shorter portion branching off the spinal nerve that is more axial motor and sensory for skin and muscle
What is the ventral ramus?
larger branch coming off a spinal nerve that innervates sensory and motor more appendicular and has greater implications for injury
What is Hilton's Law?
any nerve serving a muscle that produces movement at a joint also innervates the joint capsule and the skin over the joint and distal to the muscle
How many axons are muscle innervated by?
always multiple
How many nerves are muscles innervated by?
one or multiple
What is paralysis and what causes it?
the total loss of muscle movement as a result of complete motor denervation
What is weakness or paresis and what causes it?
mild or partial loss of muscle movement as a result of partial motor denervation
What is numbness and what causes it?
complete loss of sensation as a result of complete sensory denervation
What is paresthesia and what causes it?
abnormal sensation as a result of partial sensory denervation