Freshwater Ecology - Exam 3 Comprehensive
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
anadromous
fish spend lives in saltwater, lay eggs in freshwater
catadromous
fish spend lives in freshwater, lay eggs in saltwater
list features about salmonidae?
includes salmon and trout. predators important in structuring stream ecosystems, fond of cold water. salmon in particular are anadromous.
list features about percidae?
includes perch and darters. largest fish family in NA. they rest on the bottom sediment using their pelvic fins and are major sport fish.
name 2 fish families
salmonidae, percidae
dissolved
smaller ions in the water
colloidal
particles that won’t settle with gravity
particulate
larger, will settle with gravity
total dissolved solids (TDS)
total mass of materials dissolved in the water
salinity
mass of dissolved salts per unit volume
conductivity
proportional to amount of electricity that can be conducted by water
how does an increase in ions affect conductivity of water?
more ions = more conductivity
where does freshwater pH usually range?
6-8
what is pH the measure of?
the concentration of Hydrogen cations in a solution
what is the equation for pH?
-log10[H+]
increase in CO2 increases or decreases pH? why?
decreases the pH, making the water more acidic since CO2 creates carbonic acid when dissolved in the water
alkalinity
the ability of water to buffer changes in pH
karst areas have higher or lower alkalinity?
higher due to limestone content in these areas
hardness
a measure of the amount of dissolved calcium and magnesium ions in the water
what is colorimetric analysis?
a way to measure ion density within water.
reagents are added that bind to the ion of interest to create a color. this water is then put into a spectrophotometer so that the absorbance can be measured because the relationship between absorbance and concentration is linear.
reduction
gain of an electron
oxidation
loss of an electron
% saturation
percent of oxygen that could be dissolved given the saturation concentration
saturation concentration
the maximum amount of substance (solute) that can dissolve in a solvent (water) when water is in the contact with the atmosphere for extended periods of time
what is Gross Primary Production (GPP)?
the total photosynthesis an organism does
what is Net Primary Production (NPP)?
excess energy, GEP - R
EXPERIMENT: 3 clear bottles and 3 dark bottles are suspended in the lake for 1 hour. how do you estimate GPP, NPP, and R?
NPP is the average of the values from the clear bottles. R is the average of the values from the dark bottles. GPP is obtained by adding NPP + R.
Net Ecosystem Production (NEP)
the excess energy of an entire ecosystem
Gross Ecosystem Production (GEP)
all energy made from photosynthesis in an ecosystem
how is total ion mass estimated as? (3 ways)
total dissolved solids (TDS), salinity, conductivity
how do chemicals get in water?
dissolved from land, weathering from land (chemical or mechanical (freeze,thaw,erosion))
ppm
parts per million
ppt
parts per thousand
mg/L
weight of ion per volume of water
activation energy
how much energy a reaction needs to take place
explain how iron works regarding O2 and redox potential.
when reduced, iron exists as Fe2+, ferrous iron. this iron is soluble in water. however, when oxidized (as it occurs with O2), iron exists as Fe3+, precipitating out and settling to the sediment. as oxygen is depleted in the hypolimnion, iron reduces again and dissolves back into the water. thus, the cycle continues if exposed to oxygen again.
what affects saturation concentration?
goes up with lower temperature, higher atmospheric pressure (lower elevation), lower salinity, higher water pressure (depth)
oxic
has some oxygen (aerobic)
anoxic
has no oxygen (anaerobic)
what is the chemical formula for photosynthesis?
CO2 + H2O + light → CH2O + O2
what is the chemical formula for respiration?
CH2O + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy
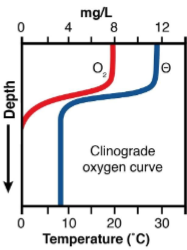
what does the DO of an oligotrophic lake look like in the summer?


what type of lake and in what season is this graph representing?
oligotrophic summer lake
what type of lake and in what season is this graph representing?
oligotrophic summer lake
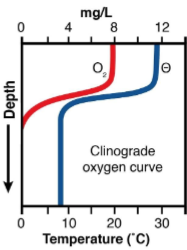
what does the DO graph for an eutrophic summer lake look like?
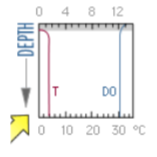
what does the DO graph for an oligotrophic winter lake look like?
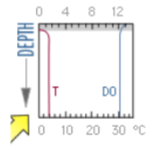
what season and type of lake does this DO graph represent?
winter oligotrophic lake
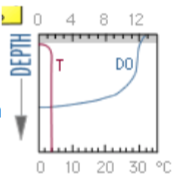
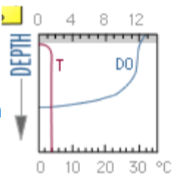
what season and type of lake does this DO graph represent?
winter eutrophic lake
what does the DO graph for a winter eutrophic lake look like?
at what time during a 24h period is the Oxygen highest for a lake or stream?
about 6pm / late afternoon
nutrient
any element required by organisms for growth
uptake
taken into cells
assimilation
incorporated into organic molecules for growth
nutrient limitation
the control of growth or production by a nutrient or nutrients
what controls nutrient limitation?
nutrient availability, nutrient requirements, stoichiometry
nutrient availability
the general availability of a nutrient; is its source common?
what is generally the source of limiting nutrients?
geologic weathering
stoichiometry
relative ratio of nutrients in an organism
what is redfield’s ratio?
a molar ratio of C:N:P required by phytoplankton. the ratio is 106:16:1.
colimitation
more than one nutrient is limiting
nutrient remineralization
release of inorganic nutrients by organisms
ecological subsidies
movement of resources from one ecosystem to another
trophic state
level of ecosystem productivity
heterotrophic state
more heterotrophy than autotrophy
autotrophic state
more autotrophy than heterotrophy
external loading
supply of nutrients from outside the system
point source
a specific location where pollutants enter the water
nonpoint source
a pollutant source that doesn’t come from a single, identifiable location. instead comes from many diffuse sources over a large area
TRUE OR FALSE: it takes more energy to use NO4+ than NO3-
false
how do you test which nutrient is limiting?
use containers floating to the lake and add different nutrients to each. examine the response of algal biomass in each after ~1 week.
TRUE OR FALSE: in highly eutrophic lakes, the nutrient concentrations will be low for dissolved nutrients and high for total nutrients.
true
TRUE OR FALSE: in highly oligotrophic lakes, the nutrient concentrations will be low for dissolved nutrients and high for total nutrients.
false
remineralization is dominated by large or small organisms?
small
what are some examples in which large animals dominate remineralization?
salmon dying after spawning, duck and geese excreting in wetlands, amphibians depositing eggs
how is trophic state characterized?
water clarity, phytoplankton biomass, nutrient concentrations
what are 3 reasons algal blooms matter?
bad for drinking water, kill fish, decrease biodiversity
how do algal blooms kill fish?
hypolimnion anoxia leaves no refuge for cold water fish, anoxic conditions. however, cyanobacterial toxins float at the top.
how does natural eutrophication (ontogeny) occur?
a deep, oligotrophic lake fills with sediment over time and becomes a shallow, eutrophic lake
which occurs faster: cultural or natural eutrophication?
cultural (except volcanoes)
what was one of the first steps to lowering Phosphorus in lakes and streams?
banning phosphates in detergents
TRUE OR FALSE: lake water treatment is more difficult when the hypolimnion is anoxic. explain.
true; when anoxic, phosphorus is locked in sediment. however, when aerated, the phosphorus is released from the sediment into the water.
what are 2 lake treatment methods to lower cyanobacterial algal blooms?
1) adding copper to the water
can contaminate sediments
toxic to crustaceans
should be used as a short term treatment
2) adding barley straw to water
effective at lowering algal biomass, DP, lowering cyanobacteria, decreasing water taste and odor problems
seems to allow substrate to microbes that uptake nutrients
mechanism not well understood
biomass
amount of living tissue
production
the flux of carbon or energy through an ecosystem compartment
autochthonous carbon
carbon obtained from primary production within the system
allochthonous carbon
carbon obtained from external carbon imports
a negative NEP indicates what type of carbon imports?
allochthonous
a positive NEP indicates what type of carbon imports?
autochthonous
secondary production
tissue elaboration by heterotrophs regardless of fate
assimilation efficiency
how good an organism is at extracting nutrients from its food
TRUE OR FALSE: high biomass = high production. explain.
false; an example is that decomposer biomass is often low, but their production is often very high.
assimilation = ? - ?
ingestion - egestion
what causes variation in assimilation efficiency?
food quality, digestive system morphology and physiology, temperature
TRUE OR FALSE: endotherms have a higher assimilation efficiency than ectotherms
true