Angiosperm Flower Structure, Pollination Methods, and Life Cycle
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are angiosperms?
Flowering plants.
How do bees contribute to angiosperms?
Bees help pollinate plants, allowing them to reproduce.
What happens to angiosperms without bees?
No honey, no reproduction of angiosperms, no crops, and no food.
What percentage of abiotically pollinated species rely on wind for pollination?
98% rely on wind and 2% rely on water.
Why do abiotically pollinated flowers lack colorful or scented features?
There has been no selective pressure favoring colorful or scented flowers since their reproductive success does not depend on attracting pollinators.
Give an example of an abiotically pollinated species.
Hazel carpellate flower or wild celery.

What is biotic pollination?
Most angiosperm species depend on insects, birds, or other animal pollinators to transfer pollen directly from one flower to another.
What is coevolution in the context of plants and pollinators?
The joint evolution of two interacting species, each in response to selection imposed by the other.

What are the main parts of an angiosperm flower?
Petals, sepals, carpels, and stamens.
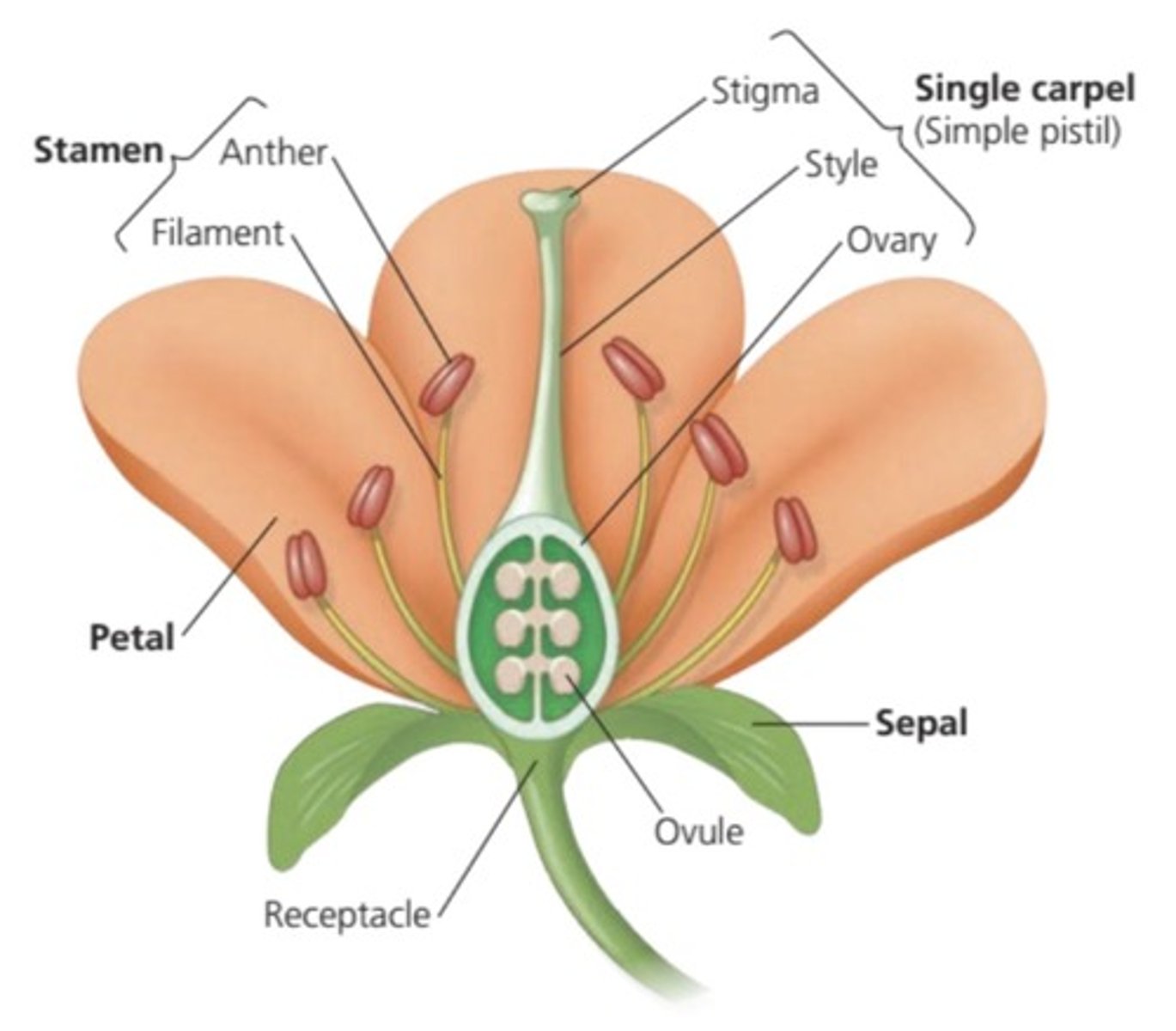
What is the function of petals in angiosperms?
To attract pollinators.
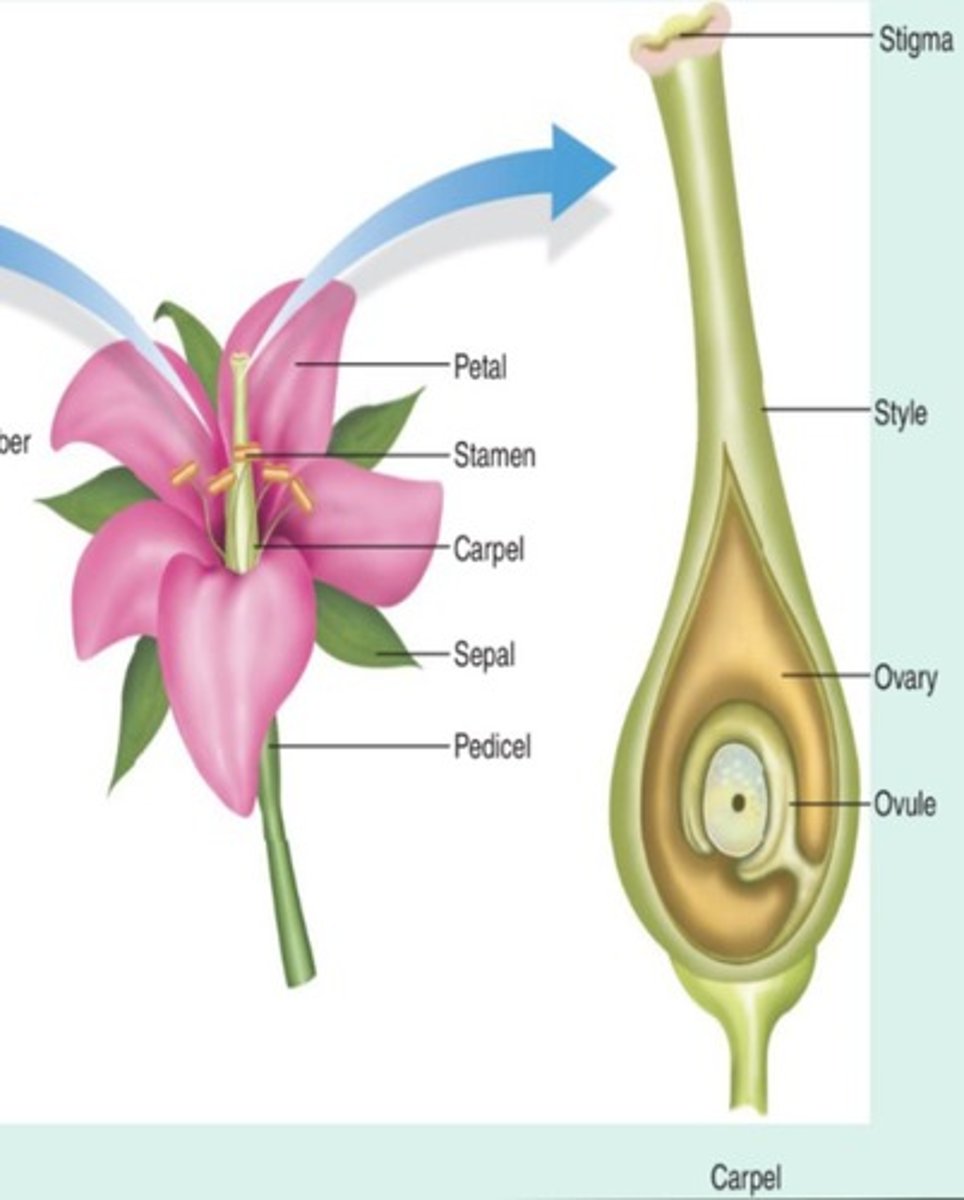
What is the difference between a carpel and a pistil?
A carpel is the fundamental female structural unit, while a pistil is the entire female reproductive organ, which can consist of one or more carpels.
What are the male parts of a flower?
Stamen, which consists of anther and filament.
What does the stigma do in the female part of a flower?
Receives pollen and is sticky.
What is the function of the ovary in a flower?
It becomes the fruit.
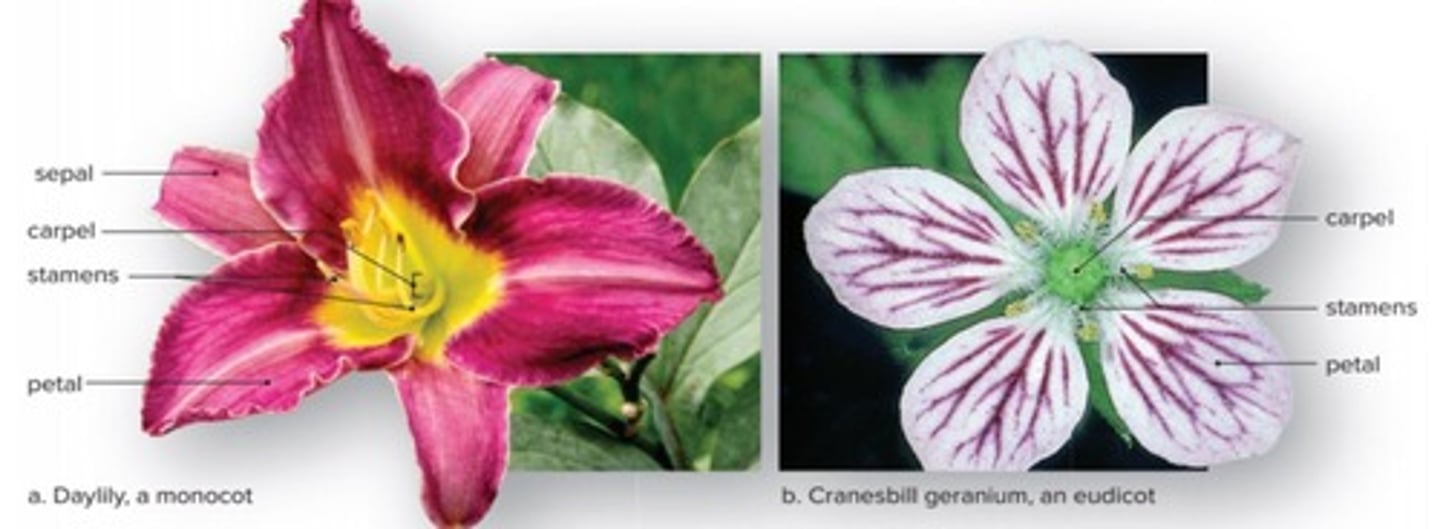
What distinguishes monocot flowers from eudicot flowers?
Monocots have sepals while dicots do not.

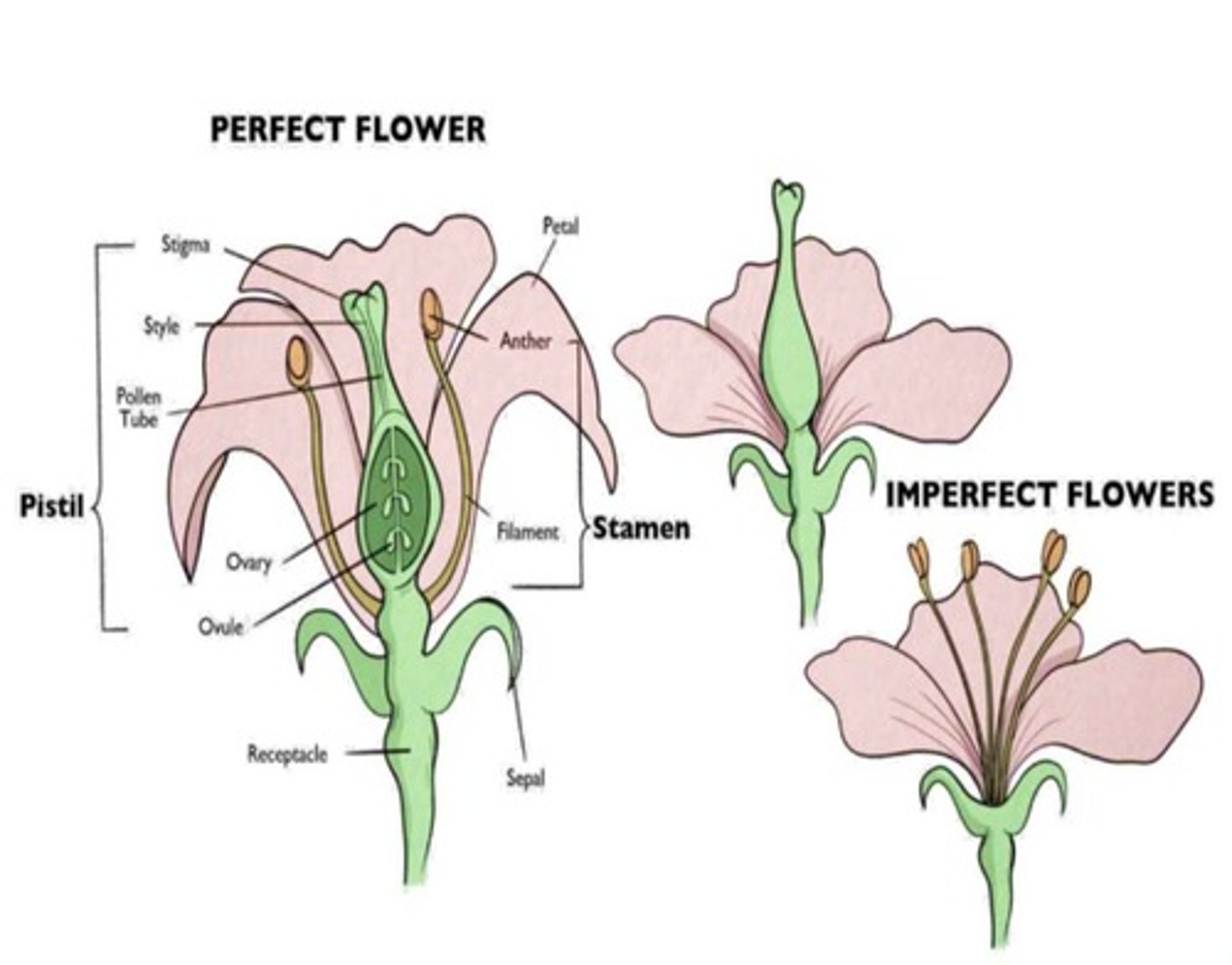
What is a complete flower?
A flower that possesses sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels.
What is an imperfect flower?
A flower that has either just male or just female parts, but not both.
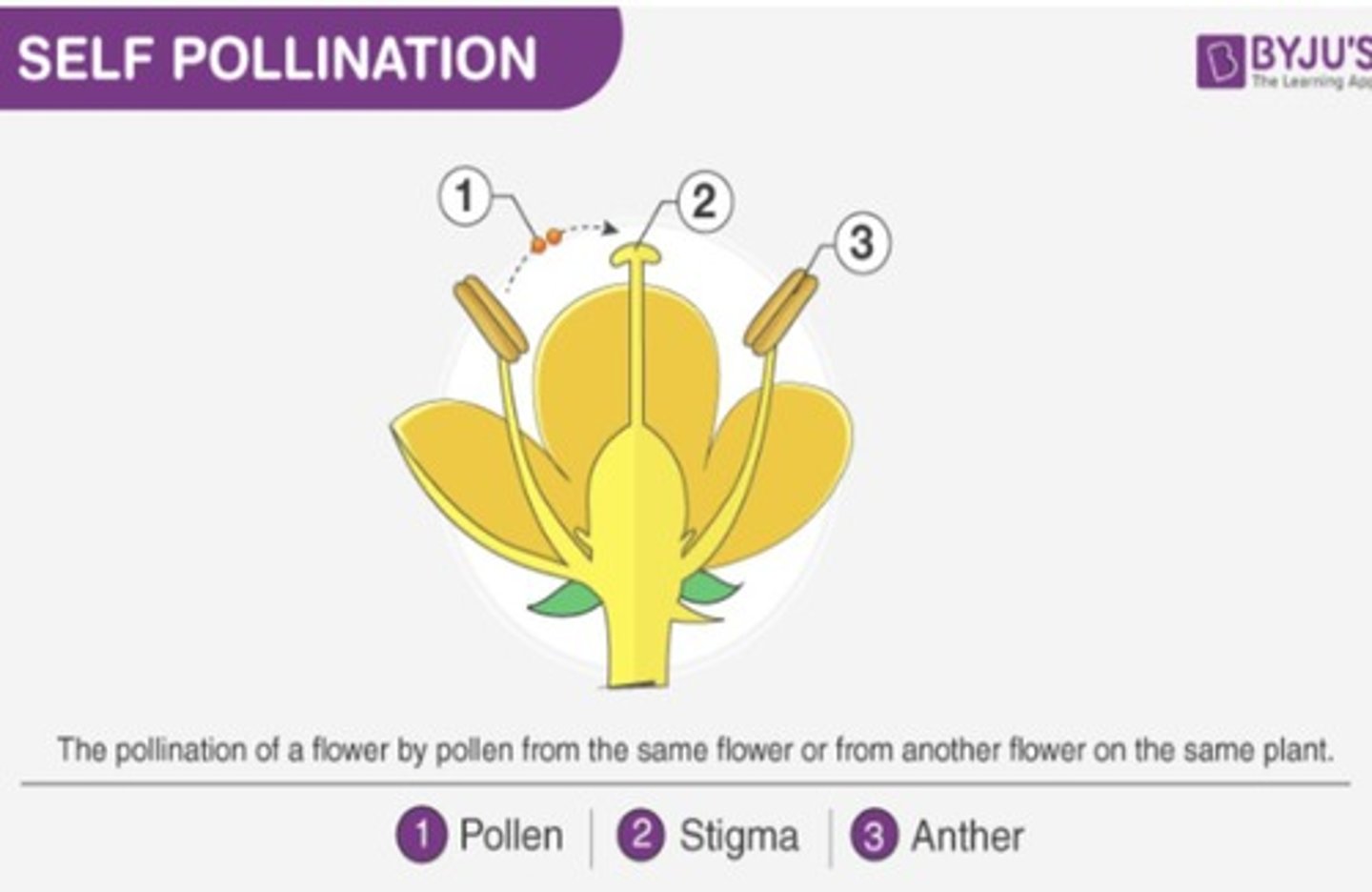
What are the two forms of pollination?
Self-pollination and cross-pollination.
What is alternation of generations in plants?
The life cycle of a plant alternates between a sexual phase and an asexual phase.
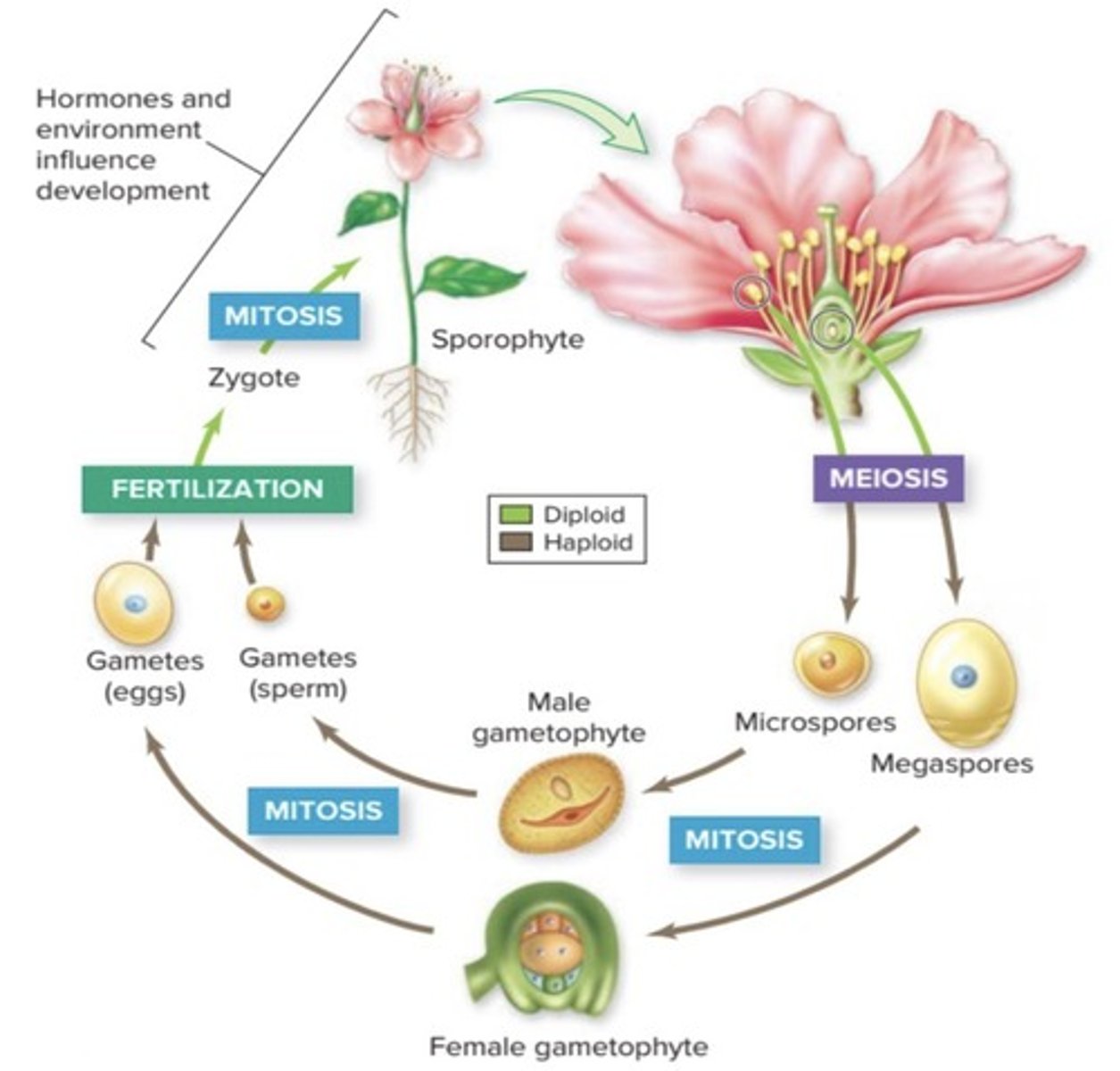
What is the sporophyte generation?
The non-sexual stage in plants where they grow and develop to form flowers.
What is the gametophyte generation?
The sexual stage in plants where sperm and egg cells develop.
What is the process that occurs after pollination in angiosperms?
Pollination leads to fertilization, then the sporophyte generation develops.
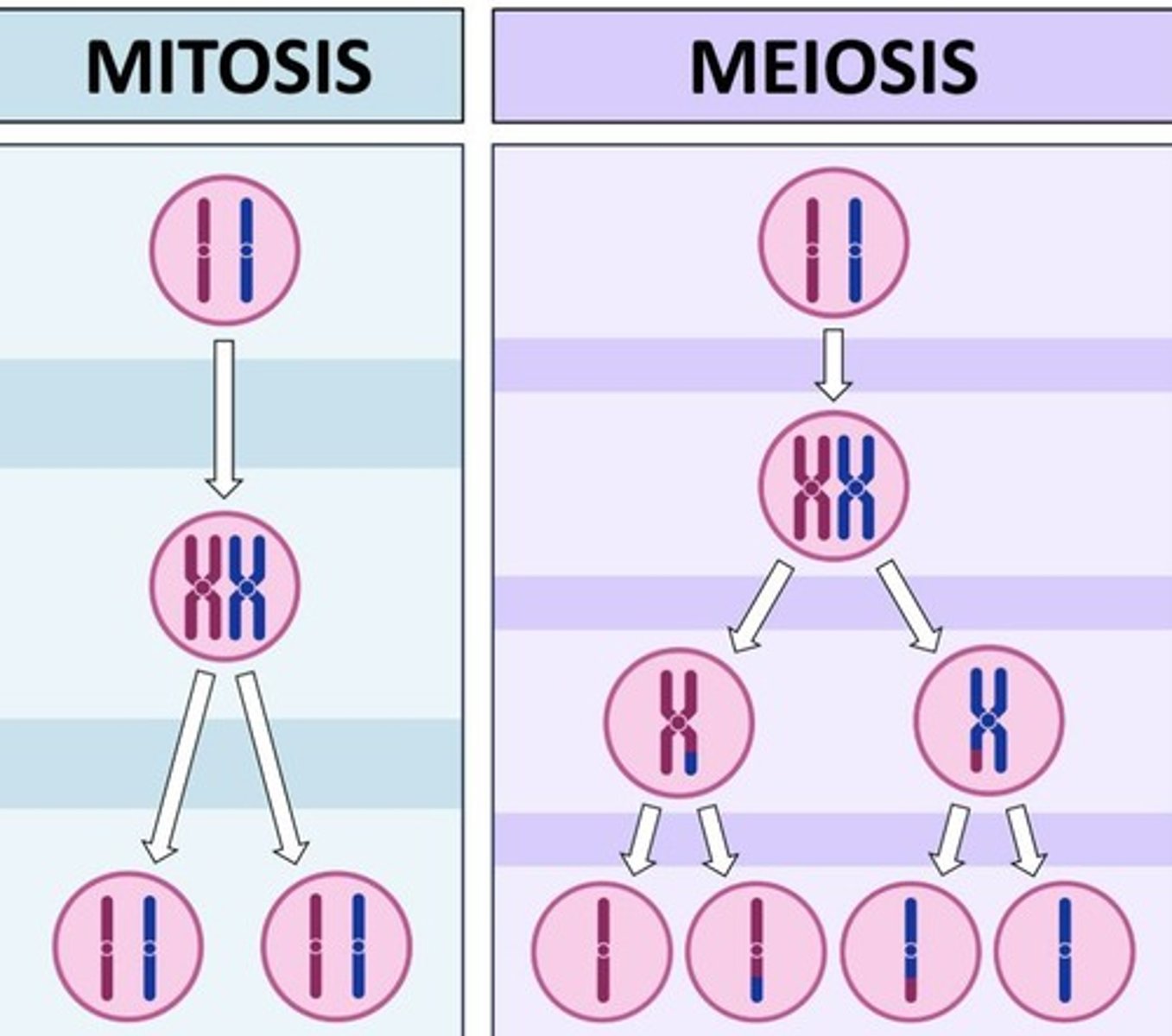
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces 2 daughter cells (body cells), while meiosis produces 4 daughter cells (sex cells).