APznzabnsRD3mVEjqBhW5NR3CFUMhzbSAx-ill0iR57FggLT7wmQIOD0omtx7bi9YllFyqNLn8jNMEPmAVw-8FRulyIgOezCzBj6GBMA9IrXxd8JvxpZXKhXpB4Kj1ECsDlHfEh3XSiwjtGBiOAysFu1ZcNA2WwnRLbCDuUkBcaR915Nnhy9_ZyDklJB98XvUPAvHKSfiMkkpAJsXL-bnP
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
cycads
are vascular, seed plants that are palm - like and are called Sago Palms . The leaves are found in a cluster at the tops of the trunks .
more than 300 million years now
the great importance of this taxon lies heavily on its contribution in understanding the evolution of seeds presence of nitrogen fixing bacteria in its roots
Manoxylic woods
large pith, wide cortex, spongy wood with lots of parenchyma, fewer tracheid’s
CYCADS
fern-like leaves-pinnate (use fern terminology) - petiole, rachis, pinnae
Thick stems with armor of bracts & leaf bases
Coralloid roots
what is the family of cycas?
what is the family of strangeria?
what is the familt of zamia?
cycadaceae
strangeriaceae
zamiaceae
what is the 3 extant families of cycads
strangeriaceae
zamiaceae
cycadaceae
is the smallest family of cycads
strageriaceae
strangeriaceae contain the genus of
strangeria
bowenia
Fernlike leaves bearing pinnae with a prominent midrib and numerous dichotomously branching lateral veins; simple cones; female cones with biovulate megasporophylls; includes only Stangeria paradoxa, a southern African
strageriaceae
zamiaceae
a family of cycads that are superficially palm or fern-like.
Singly pinnate compound leaves, bearing leaflets with parallel, dichotomously branching veins ;simple cones; female cones with biovulate
Zamiaceae
is the type genus and the only genus recognised in the family Cycadaceae. About 113 species are accepted
cycadaceae
The best-known Cycas species is
cycas revoluta
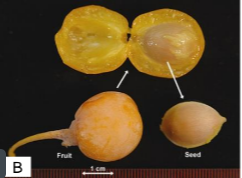
what is this part?

THE LIVING FOSSIL
GINKGO
DETERMINE EACH PHOTOS

DETERMINE WHICH IS FEMALE AND MALE SHOOT?


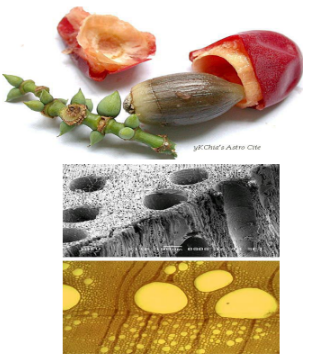
Appearance of G. biloba ripened fleshy seed coat;
Fleshy outer layer of ripened seed of Ginkgo tre
enumerate the division of coniferophyta
pinus
araucaria
podocarpus
phyllocladus
agathis
most common at the higher latitudes, towards the poles.
About 50 genera and 550 species
conifers
Monoecious
Spirally arranged, needle-like leaves (1-2 vascular bundles enclosed within a common sheet
Winged pollen grains •Female cone (spirally arranged ovuliferous scales)
Coniferophyta

Pinus lambertiana cones and needle fascicles
present in the main trunk
develop in axils of scaly leave
shorten to the tip giving pyramidal appearance
apical branch grow indefinitely
LONG SHOOT

do not have apical buds
also known as brachy blast
develop in axils of scaly leaves and foliage leaves
shed every two or three years leaving scars on stems
DWARF SHOOT

2 kinds of branches of leaves of pinus
scale leaves
foliage leaves

short lateral branches on which the leaves arise
grow in the axils of scale leaves of the long shoots
spur shoot

phyllocladus

agathis
is an evergreen shrub or small tree growing to 8–30 ft (2.4–9 m) high. The green leaves are deeply lobed, up to 1 in (2.5 cm) long, although they can be longer. Red male strobili (cones) in bundles, summer.
Phyllocladus aspleniifolius var alpinus is found in subalpine forests in North and South Islands, New Zealand. The leaves are cladodes, flattened stems. Hardy in the UK
is one of the few species of conifers that can grow in the humid tropics. In the Philippines, Almaciga grows in almost all mountainous forests, but most particularly in Quezon, Zambales, Palawan, Cagayan, Abra, Kalinga Apayao, Nueva Vizcaya, Samar, Zamboanga and Davao. Almaciga, which can grow up to sixty meters tall with a trunk of three meters wide, produces valuable resin that can be used as a source of income for the many rural people in the Philippines
agathis philippinensis
is a division of plants grouped in the gymnosperms (i.e. conifers, cycads, and ginkgos) that consists of some 70 species
gnetophyta

welwitsia mirabilis

ephedra fragilis

gnetum gnemum
gnetum gnemum seeds

gentum gnemum male strobilii (up)
gnetum gnemum female strobilus (down)

dicotyledons

monocotyledons

monocot and dicot

basal angiosperm
magnoliids
monocots
eudicots

order: amborellales
family: amborellaceae

ORDER: nymphaeles
FAMILY: nympaeceae

evergreen trees or shrubs having aromatic oil cells
with glabrous, spiral, pellucid- punctate, exstipulate leaves,
the flowers with numerous, spiral tepals
austrobaileyales illiciaceae
perennial herbs or evergreen shrubs.
with jointed stems, opposite, simple leaves,
small, inconspicuous flowers in slender, terminal spikes
chloranthaceae

monoecious species, with hermaphrodite flowers, greenish white
white to yellow are glabrous or downy and pale to yellowish brown.
The perianth is glabrous or puberulent outside and densely pubescent inside.
The purplish-black fruit is an ovate, ellipsoidal or subglobose drupe.
cinnamomum spp.
Leathery evergreen ovate to elliptic leaves (to 10” long) are glossy dark green above and variable pale green to gray-brown beneath.
Fragrant white flowers (to 8-12” diameter) usually have six petals.
Flowers bloom in late spring, with sparse continued flowering throughout the summer.
family of : magnoliaceae
scientific name: magnolia grandiflora
12 families of monocots
araceae
arecaceae
agavaraceae
dioscoreaceae
iridaceae
liliaceae
musaceae
pandanaceae
poaceae
commensalinaceae
orchidacea
zingeberaceae
shrubs, tree-like, or vines, palms have two methods of growth: solitary or clustered
Palms have large, evergreen leaves that are either palmately ('fan-leaved') or pinnately ('feather- leaved') compound and spirally arranged at the top of the stem
arecaceae = palmae

monocotyledonous flowering plants in which flowers are borne on a type of inflorescence called a spadix.
rhizomatous or tuberous
often found to contain calcium oxalate crystals or raphide
araceae


wha family is this?
belanophoraceae
leaves are alternate and adaxially circinate
with at least one leaf surface containing hairs with mucilage-producing glands at the tip
flowers are bisexual, usually with three carpels and five sepals, petals and
stamens
droceraceaae
sn: drosera rotundifolia l.
main part of a bladderwort plant always lies beneath the surface of its substrate.
terrestrial species sometimes produce a few photosynthetic leaf-shoots.
form long, thin, sometimes branching stems or stolons beneath the surface of their substrate
lentibulariaceae

evergreen shrubs or lianas
leaves are opposite or whorled, or alternate in some species
flowers are white, pink, red, or orange, and are produced singly or in large panicles.
melatomataceae
sn: medinillia sp.


mitrastemonaceae

easily distinguished from other plants, as they share some very evident derived characteristics or synapomorphies.
Among these are: bilateral symmetry of the flower (zygomorphism),
nearly always highly modified petal (labellum), fused stamens and carpels, and extremely small seeds.
orchidaceae

trees, shrubs, lianas, vines, epiphytes, and perennial herbs
leaves are very long and narrow, sheathing, simple, undivided, with parallel veins;
the leaf margins and abaxial midribs are often prickly
pandanacaea
The monster flower consists of about 28 species native to Southeast Asia, all of which are parasitic upon the roots of Tetrastigma vines (family Vitaceae).
The genus includes the giant , sometimes known as the corpse flower, which produces the largest known individual flower of any plant species in the world and is found in the forested mountains of Sumatra and Borne
Rafflesia arnoldi
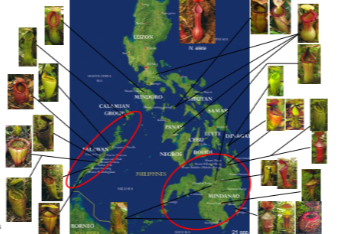
nepentaceae