Chirality
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is a chiral carbon?
A carbon atom attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms
What are optical isomers / enantiomers? Why do they exist?
Two non-superimposable mirror image structures which exist due to the presence of a chiral carbon atom
For each chiral carbon atom there is always one pair of optical isomers

What is optical isomerism a form of?
Stereoisomerism
Optical isomers are ____ ______but will rotate plane-polarised ______ in different directions. One isomer rotates the _____ clockwise and the other anticlockwise.
Optical isomers are chemically identical but will rotate plane-polarised light in different directions. One isomer rotates the light clockwise and the other anticlockwise.
How do you work out the number of optical isomers?
2number of chiral carbons
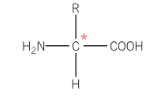
All α-amino acids, RCH(NH2)COOH contain a chiral carbon atom with the exception of what molecule?
Glycine - H2NCH2COOH
Show the general structure of a chiral carbon atom in an amino acid
True or false, chirality only works for carbon atoms?
False - the term applies to any centre that holds attachments that can be arranged as two non-superimposable mirror image forms
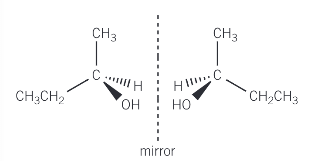
How do we draw optical isomers?
The 3D tetrahedral arrangement of one isomer is reflected into its mirror image to produce the second isomer
Draw the two optical isomers of butan-2-ol

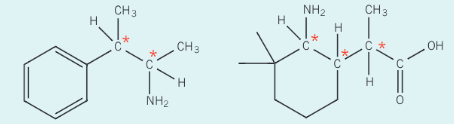
How do you identify chiral carbon atoms from the following?
Identify the chiral carbon atoms which are attached to four different groups or atoms
Remember not to label carbon atoms with two methyl groups
Which molecules cannot be chiral (skeletal formula)?
Benzene ring
Double bonds and triple bonds
Ends of a skeletal chain
Two lines meeting at a point