Concept 5.5: Nucleic acids store, transmit, and help express hereditary information
1/10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Gene
A unit of inheritance that consists of DNA to program the amino acid sequences of polypeptides
Dioxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
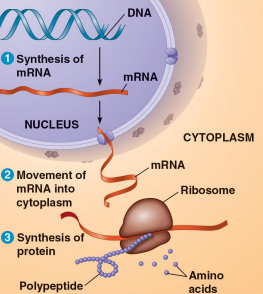
A nucleic acid that comprises genes through monomers called nucleotides and provides directions for its own replication
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
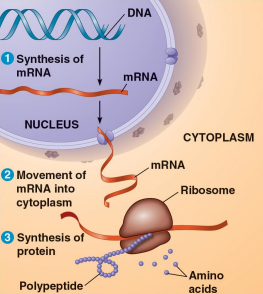
Nucleic acid type that is directed by DNA to control protein synthesis through a process called gene expression
Single-stranded as opposed to double-stranded DNA
Has the thymine (T) base replaced by uracil (U)
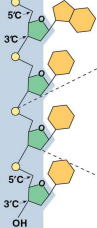
Polynucleotides
The term for nucleic acids as polymers of monomers called nucleotides
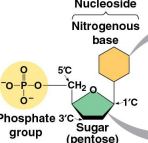
Nucleotides
The monomers of polynucleotides, consisting of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups
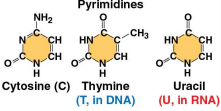
Pyrimidines
One of the two families of nitrogenous bases, comprising cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U)
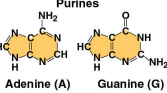
Purines
One of the two families of nitrogenous basis comprising adenine (A) and guanine (G)
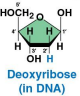
Deoxyribose
The sugar present in DNA
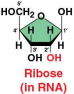
Ribose
The sugar present in RNA
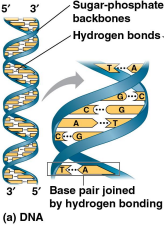
Double helix
The shape of a DNA molecule formed by two polynucleotides in a spiral, running in opposite directions for 5-carbon and 3-carbon sugar strands
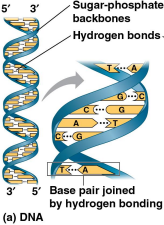
Complementary base pairing
The fact that only certain bases pair with each other in DNA, making it possible to generate two identical copies of each DNA molecule in a cell preparing to divide
Adenine (A) always to thymine (T)
Guanine (G) always to cytosine (C)