Neurones and glia
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What are the 4 main types of glia?
oligodendrocytes
astrocytes
microglia
ependymal cells
What are the key differences of glia from neurones?
newly generated in adult brain
don’t have excitable membrane so no APs
don’t form synapses
What is the role of oligodendrocytes?
provide insulation to myelinated axons
How many axons do oligodendrocytes typically myelinate?
3-50

What is the role of microglia?
principal component of immune system of CNS and have similar role to macrophages
What is the main role of ependymal cells?
make CSF in choroid plexus and keep it circulating through ventricular system with cilia beating
What are the roles of astrocytes?
maintain integrity of BBB
CNS homeostasis
take up & processing of neurotransmitters that spill over synapses
regulating energy supply to neurons
release gliotransmitters (e.g. ATP & adenosine)
radial glia migration & axonal pathfinding during development
Where are astrocytes found?
extend processes to “fence in” neurones and oligodendrocytes, dendrites, synapses and nodes of Ranvier
What are dendrites generally specialised for?
input
What is convergence?
information input at synapses on dendrites
What are axons generally specialised for?
output
What is divergence?
information output at presynaptic terminals
What is the main, general role of neurones?
integrate and distribute information
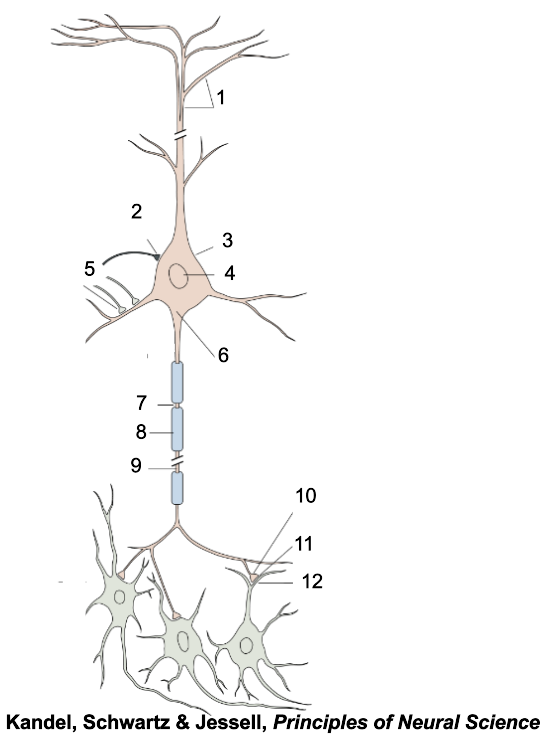
1
apical dendrites
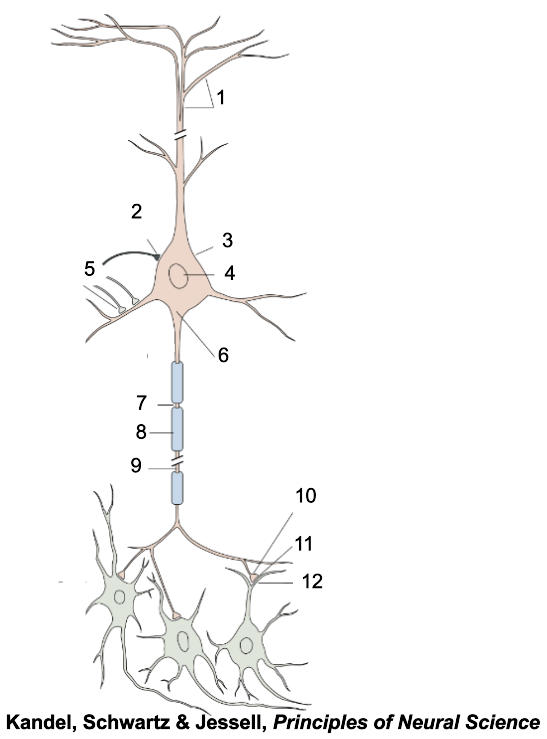
2
inhibitory terminal
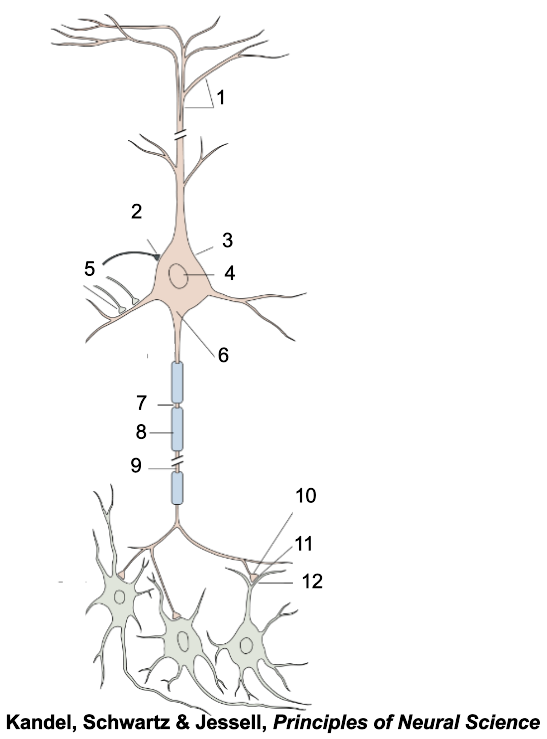
3
cell body
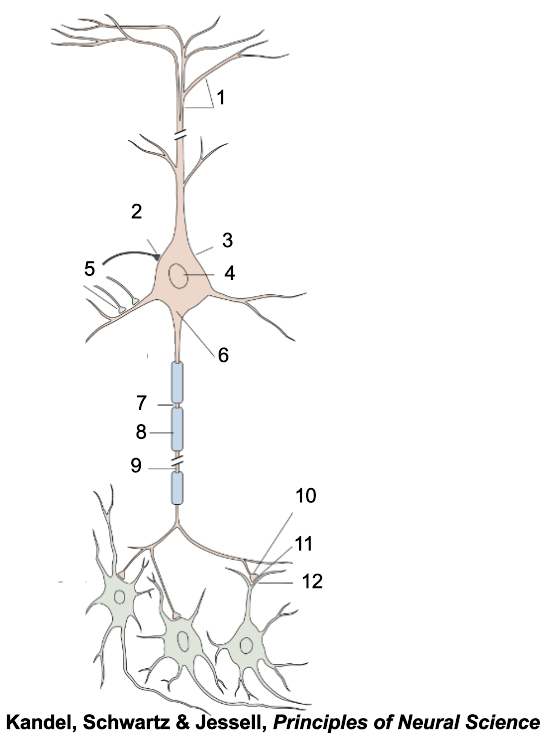
4
nucleus
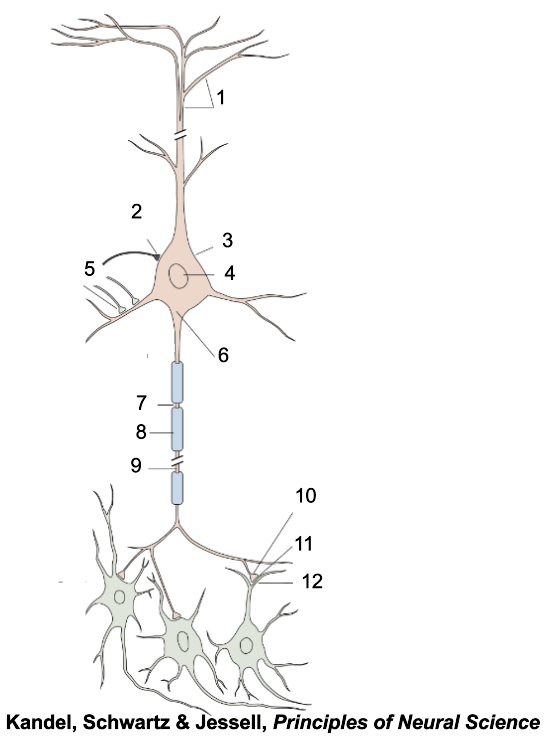
5
excitatory terminal
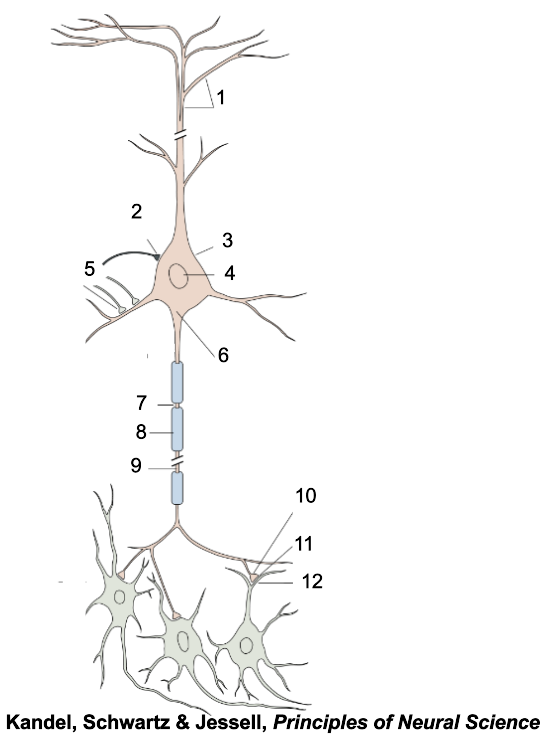
6
axon hillock
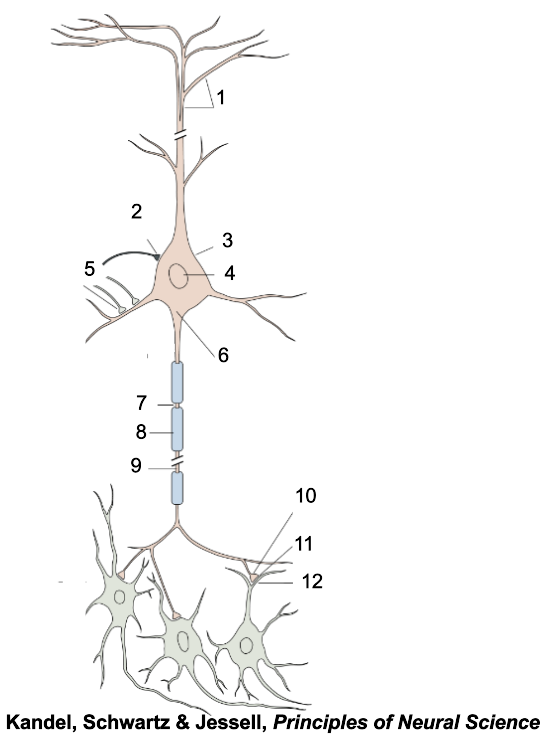
7
node of Ranvier
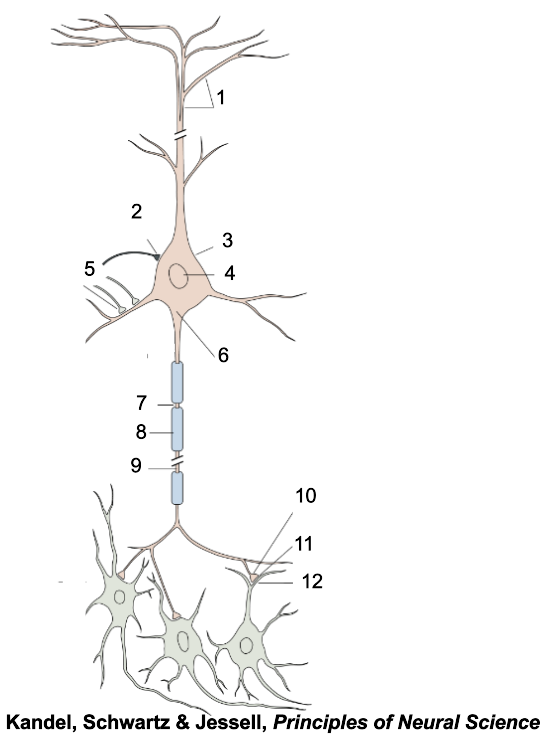
8
myelin sheath
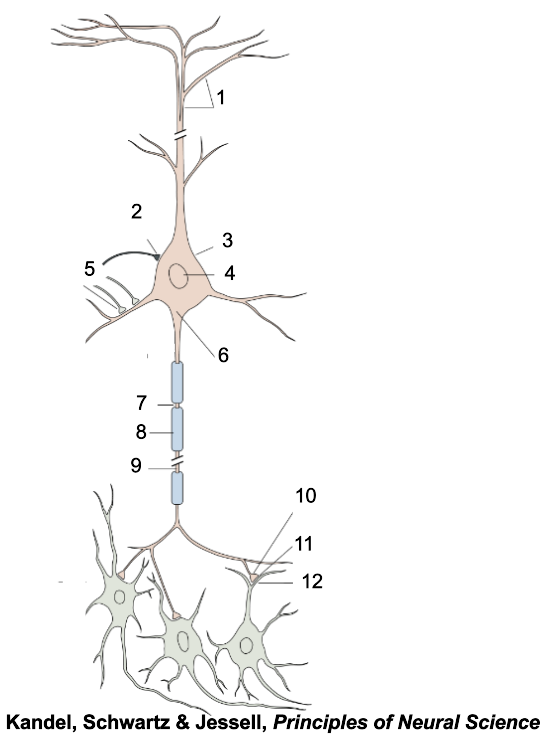
9
axon
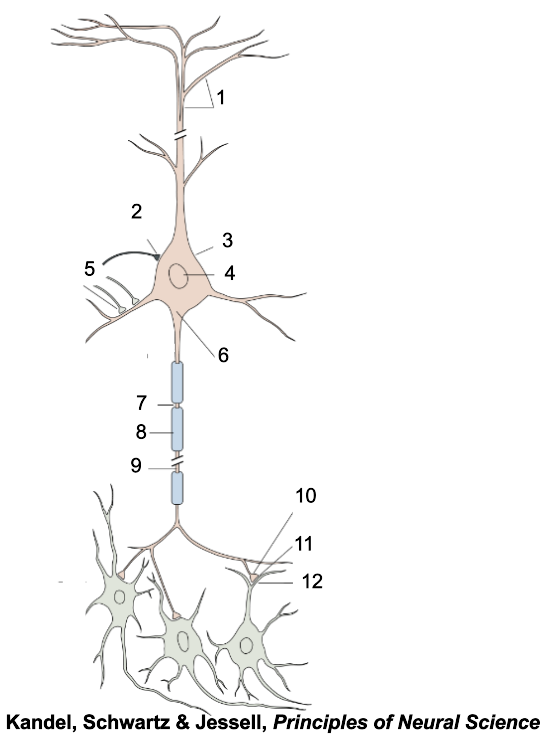
10
presynaptic terminal
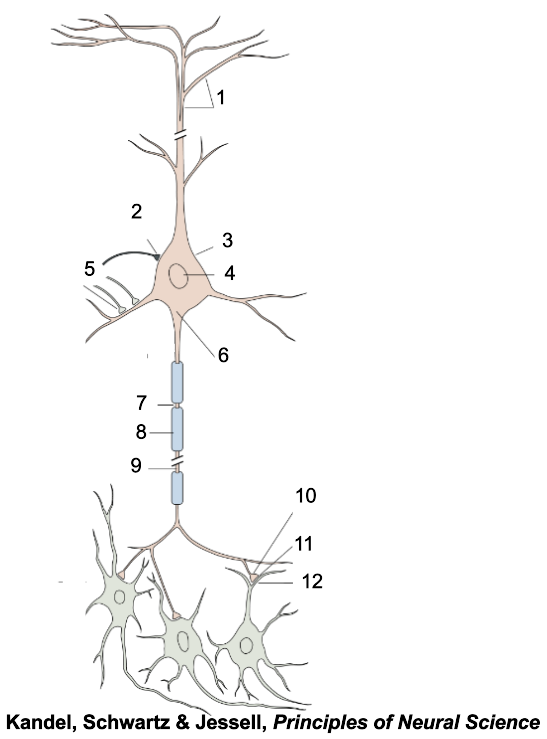
11
synaptic cleft
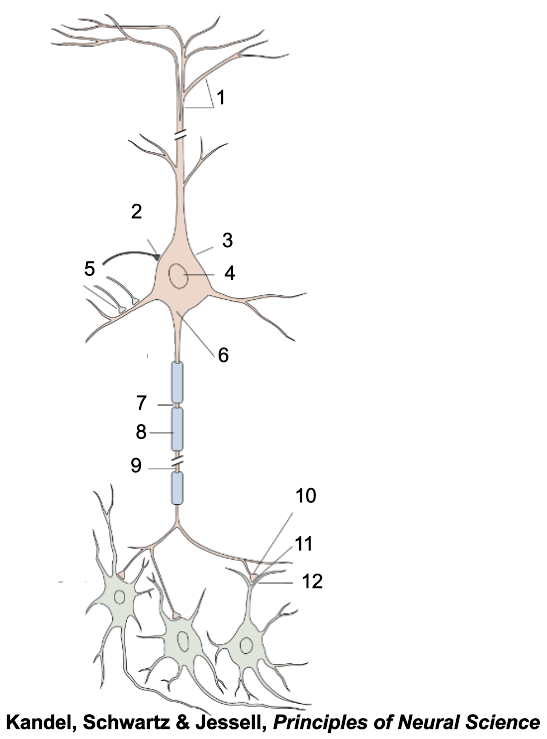
12
postsynaptic dendrite
What is the membrane potential maintained by?
Na+/K+ pump
What does opening an ion channel do?
shift membrane potential towards equilibrium potential for that ion/ions
What are the 4 types of ion channel?
ligand-gated
phosphorylation-gated
voltage-gated
stretch or pressure-gated
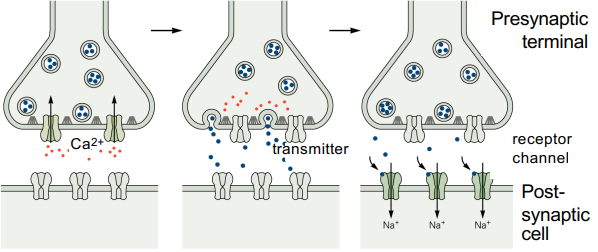
What are key characteristics of chemical synapses?
slow transmission (synaptic delay)
essentially uni-directional
amplification
flexibility
plasticity
What are the 2 types of neurotransmitter receptors?
ionotropic
metabotropic
What are the key characteristics of ionotropic receptors?
faster
directly influence membrane potential
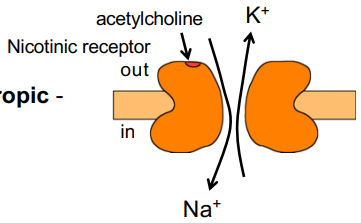
What type of receptor does this image show?
ionotropic
What are the key features of metabotropic receptors?
slower
may indirectly influence membrane potential
Do ionotropic receptors have a depolarising or hyperpolarising effect?
depolarising
Do metabotropic receptors have a depolarising or hyperpolarising effect?
hyperpolarising
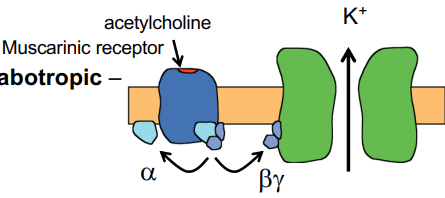
What type of receptor does this image show?
metabotropic
Assuming that membrane potential is -70mV, then what effect will ACh have on membrane potential via nicotinic (ionotropic) versus muscarinic (metabotropic) receptors?
Nicotinic - depolarise
Muscarinic - hyperpolarise
What does EPSP stand for?
excitatory postsynaptic potential
What does IPSP stand for?
inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Are nicotinic receptors EPSP or IPSP?
EPSP
Are muscarinic receptors EPSP or IPSP?
IPSP
What does the direction of change in membrane potential depend on?
ion permeability and starting membrane potential
What is the major fast excitatory neurotransmitter?
glutamate
What is the major fast inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain?
GABA
What is the major fast inhibitory neurotransmitter in the spinal cord?
glycine
What are the major transmitters of the PNS?
noradrenaline and acetylcholine
In the CNS, what act as neuromodulators?
noradrenaline
acetylcholine
dopamine
serotonin
In the CNS, what do noradrenaline, acetylcholine, dopamine and serotonin act as?
neuromodulators
What determines how information is processed to produce an appropriate response?
anatomical specificity of synaptic connections between neurons
neurotransmitter specificity
receptor subtypes
What do neuromodulators lack?
anatomical specificity
What do neuromodulators modulate?
activity of whole neural circuits
Why are neurones connected into circuits?
process information
reduce appropriate responses
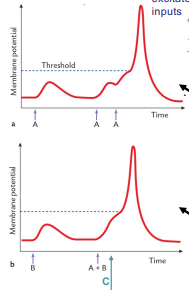
Does A (top) show temporal or spatial summation?
temporal
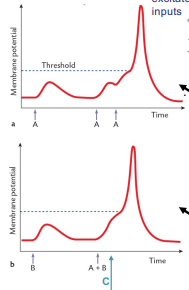
Does B (bottom) show temporal or spatial summation?
spatial
temporal summation
repetitive stimulation of same input at sufficient frequency, epsps summate to produce larger depolarisation
Spatial summation
sub-threshold epsps and ipsps from synapses at different inputs propagate passively to axon hillock where they summate
Inputs from distal regions of the dendritic tree will have ______ effects than inputs on the cell soma.
weaker
What is the likely effect on membrane potential if C is stimulated shortly after A + B?
reduced depolarisation
What is the membrane potential at the axon hillock influenced by? (spatial summation)
the sum of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs to the neuron
What can release of neurotransmitters (e.g. noradrenaline) be inhibited by?
autoreceptor-mediated inhibitory feedback
What does presynaptic (axo-axonic) inhibition do?
reduces transmitter release from a presynaptic terminal & can selectively inhibit certain inputs to a neuron without affecting the synaptic integration of other inputs
What can regulate synaptic transmitter release?
pre-synaptic neurotransmitter receptors
What does high frequency presynaptic stimulation of certain glutamatergic synapses result in?
long-lasting enhancement of transmission - greater magnitude and slope of epsp
What does synaptic plasticity enable?
experience to change behavioural responses
What type of receptor is the NMDA receptor?
ligand- and voltage-gated
What can NMDA receptors detect?
coincident pre- and post-synaptic activity
What happens at normal resting potentials in the NMDA receptor?
Mg2+ ions bind to open channel, blocking ion flow
What happens when the NMDA receptor is partially depolarised?
Mg2+ is repelled
What is the open NMDA channel permeable to?
Na+
K+
Ca2+
In the NMDA receptor, what does increased post-synaptic Ca2+ trigger?
series of changes resulting in LTP
What is Ca2+ influx via the NMDA receptor thought to be important in?
excitotoxic neuronal death during stroke
What can overactivity of NMDA receptors lead to?
neuronal death in stroke