Commercial Theory Homework Questions
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HW 1, HW 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Ground effect is indicated by a decrease in upwash, downwash, and wingtip vortices.
True or false
True
Describe L/Dmax
airspeed where you can get maximum amount of lift
The left turning tendency of an airplane caused by P-factor is the result of the:
propeller blade descending on the right, producing more thrust than the ascending blade on the left
Name the four forces that cause left-turning tendencies.
engine torque, p-factor, gyroscopic precession, spiraling slipstream
What causes Adverse Yaw?
increase of induced drag on rising wing tip and decrease of induced drag on lowering wing, effect offset by using pro-turn rudder, aircrafts yaws in opposite direction of roll
An airplane said to be inherently stable will:
require less effort to control
What causes an airplane (except a T-tail) to pitch nosedown when power is reduced and controls are not adjusted?
the downwash on the elevators from the propeller slipstream is reduced an elevator effectiveness is reduced
What adjustment needs to be made to the airspeed in order to increase RATE of turn at a constant bank angle?
airspeed needs to be reduced
What adjustment needs to be made to the airspeed in order to reduce RADIUS of turn at a constant bank angle?
airspeed needs to be reduced
The longitudinal stability of an airplane is determined by:
location of the CG with respect to the center of pressure
In theory, if the airspeed of an airplane is doubled while in level flight, parasite drag will become
four times greater
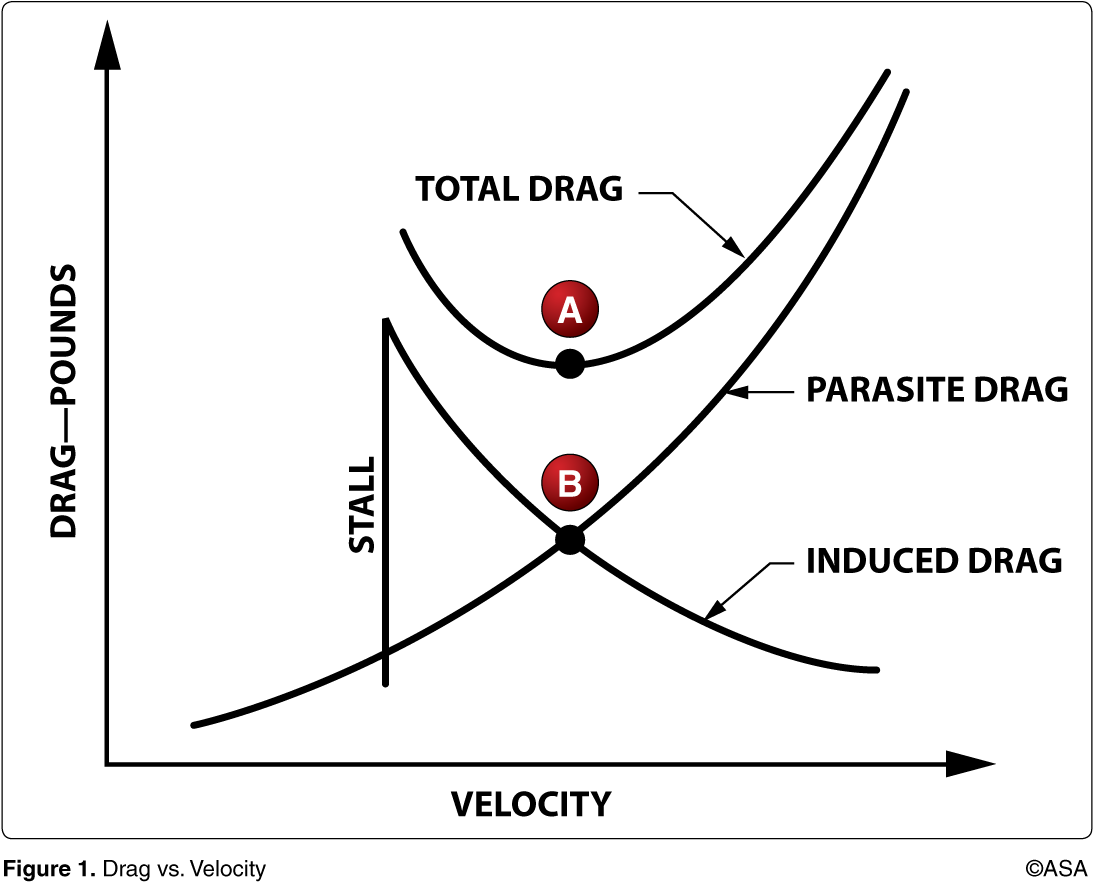
At the airspeed represented by point A, in steady flight, the airplane will
have its maximum L/D ratio
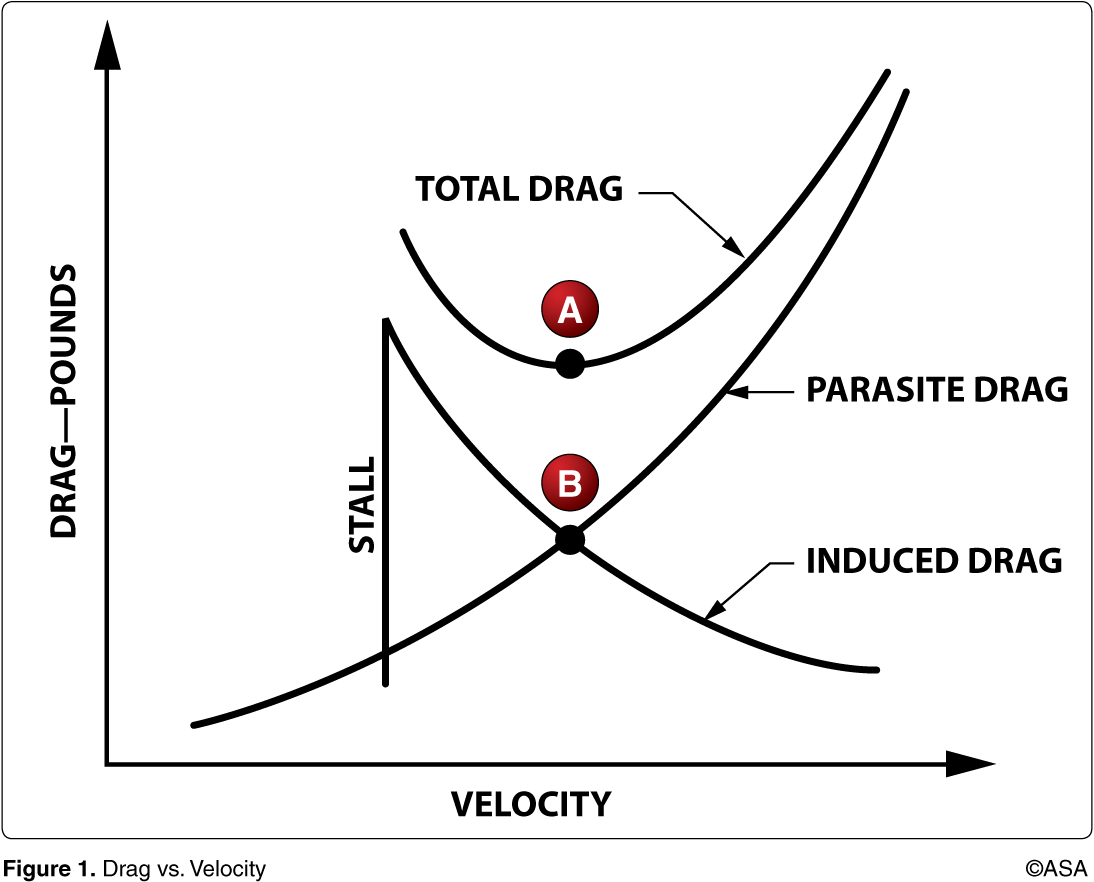
At an airspeed represented by point B, in steady flight, the pilot can expect to obtain the airplane's maximum
glide range
What performance is characteristic of flight at maximum lift/drag ratio in a propeller-driven airplane? Maximum
range and maximum distance glide
As airspeed decreases in level flight below that speed for maximum lift/drag ratio, total drag of an airplane
increases because of increased induced drag
Which statement is true relative to changing angle of attack?
an increase in angel of attack will increase drag
The angle of attack of a wing directly controls the
distribution of pressures acting on the wing
In theory, if the angle of attack and other factors remain constant and the airspeed is doubled, the lift produced at the higher speed will be
four times greater than at the lower speed
An airplane leaving ground effect will
experience an increase in induced drag require more thrust
Longitudinal dynamic instability in an
airplane can by identified by:
A. Bank oscillations becoming
progressively steeper
B. Pitch oscillations becoming
progressively steeper
C. Trilatitudinal roll oscillations
becoming progressively steeper
pitch oscillation becoming progressively steeper
A sweptwing airplane with weak static
directional stability and increased
dihedral causes an increase in:
A. Mach tuck tendency
B. Dutch roll tendency
C. Longitudinal stability
dutch roll tendency
Is internal air pressure higher or lower than external?
lower
When using alternate static source, will your
altitude show an altitude higher or lower than the
actual altitude?
higher
In the Northern Hemisphere, a magnetic
compass may initially indicate a turn towards
the east if:
A. It decelerates while on a southerly heading
B. It accelerates while on a southerly heading
C. It turns left from a northerly heading
turns left from a northerly heading
In the Northern Hemisphere, a magnetic
In the Northern Hemisphere, a magnetic compass will normally indicate a turn toward
north if:
A. A right turn is entered from an east heading
B. A left turn is entered from a west heading
C. The aircraft is accelerated while on an east
or west heading
aircraft is accelerated while on an east or west heading
Does using alternate static air cause airspeed and altitude to indicate higher or lower than actual?
higher
white arc airspeed indication
flap operating range
green arc airspeed indication
normal operating range
yellow arc airspeed indications
caution range
red line airspeed indication
vne
beginning of yellow arc airspeed indication
vno
Which instrument is most likely to indicate incorrectly due to precession errors?
heading indicator
Which statement is true about magnetic deviation of a compass? Deviation
varies for different headings of the same aircraft
What is an operational difference between the turn coordinator and the turn-and-slip indicator? The turn coordinator
indicates roll rate, rate of turn, and coordination; the turn-and-slip indicator indicates rate of turn and coordination
An airplane is located at an airport with an elevation of 5,000 feet MSL and a temperature of 90 degrees F. The altimeter is set to airport elevation. Later that night the temperature plummets to 50 degrees F. Unless the altimeter setting is changed, it will read
5200 feet
Calibrated airspeed is best described as indicated airspeed corrected for
installation and instrument error
True airspeed is best described as calibrated airspeed corrected for
altitude and non-standard temperature
Maximum structural cruising speed is the maximum speed at which an airplane can be operated during
normal operations
Which airspeed would a pilot be unable to identify by the color coding of an airspeed indicator?
maneuvering speed
What is an advantage of an electric turn coordinator if the airplane has a vacuum system for other gyroscopic instruments?
it is a backup in case of vacuum system failure
To determine pressure altitude prior to takeoff, the altimeter should be set to
29.92'“ hg and the altimeter indication noted
Which is the correct symbol for the stalling speed or the minimum steady flight speed at which the airplane is controllable?
V(S)
14 CFR Part 1 defines V(LE) as
maximum landing gear extended speed
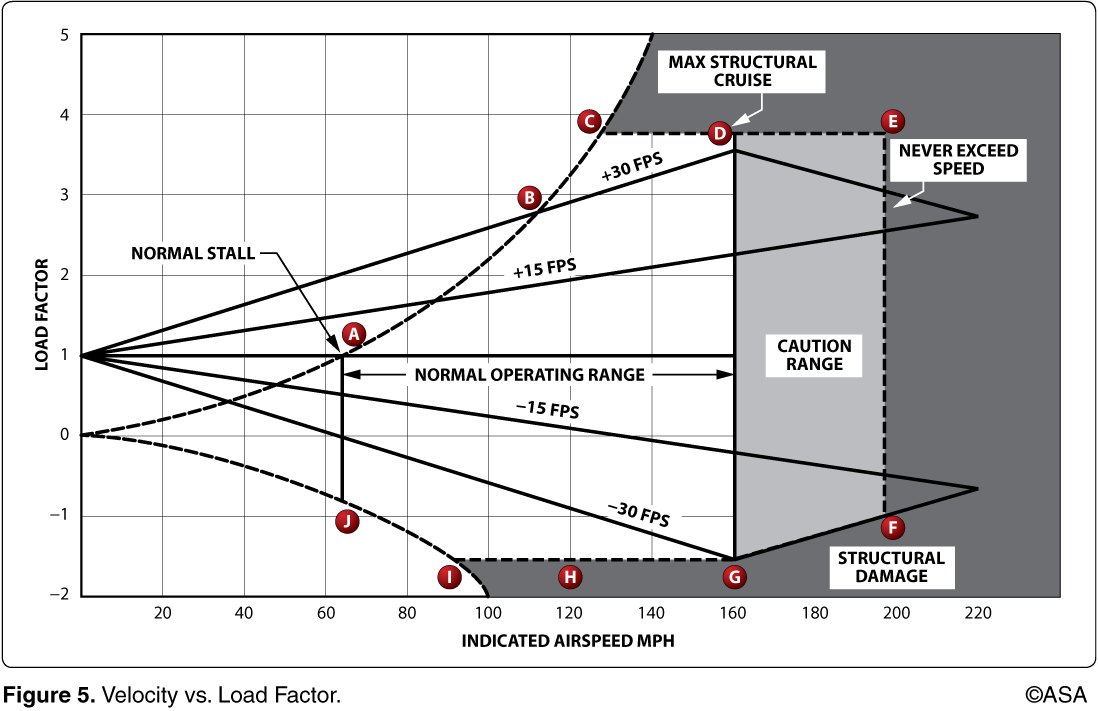
The vertical line from point D to point G is represented on the airspeed indicator by the maximum speed limit of the
green arc
What could be one result of exceeding critical Mach number?
aircrat control difficulties