Bio Test
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Protein
Amino Acids
Lipids
Glycerol and fatty acids
Hydrolysis
Breaks the polymers by adding water.
Dehydration Synthesis
Is the removal of water to bind monomers together to form a polymer.
Esophagus
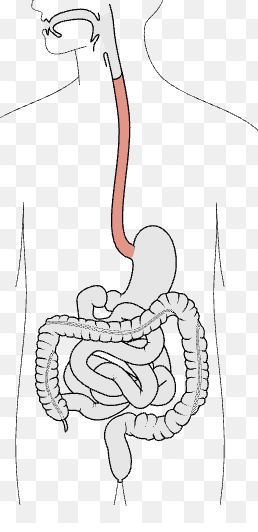
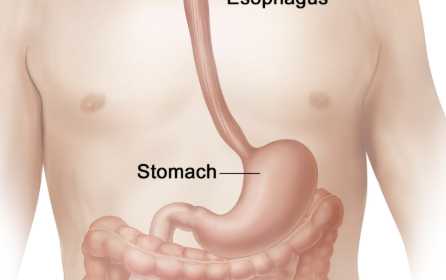
Stomach
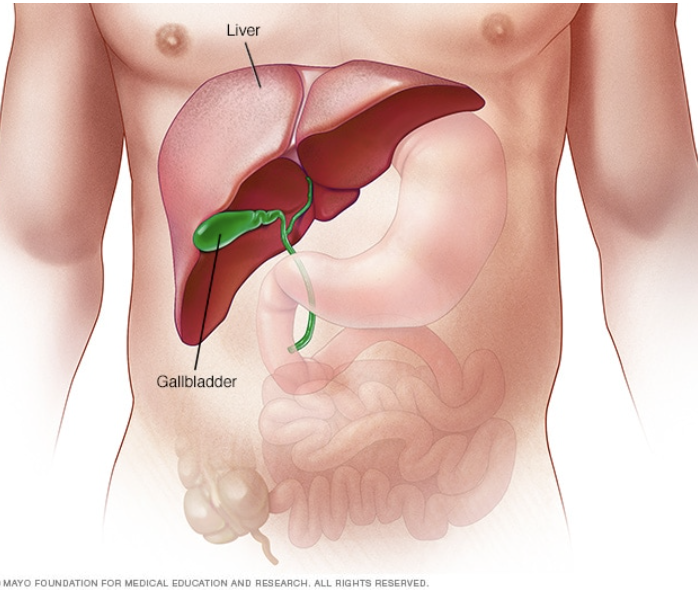
Liver
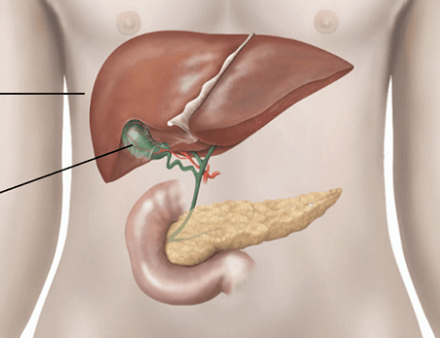
Gallbladder
Pancrease
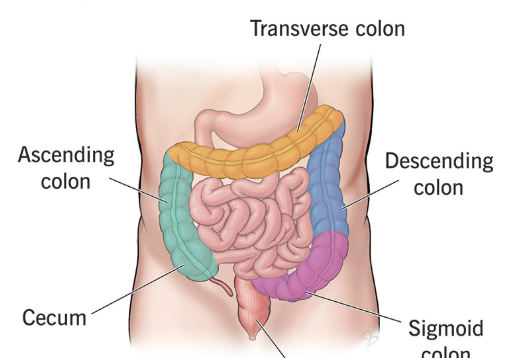
Large Intestine
Small Intestine
Appendix
Role of enzymes
Enzymes are proteins that help speed up metabolism, or the chemical reactions in our bodies.
Key role of the Stomach
Pepsin is produced and proteins are broken down
Key role of the pharynx (throat)
Passageway for food and air
Key role of the small intestine
Building blocks like amino and glucose are absorbed
Key role of the Large intestine
Bulk of the water is absorbed and feces is formed
Key role of the mouth
Site of mechanical digestion and salivary amylase breaks down startch
Substrate
The reactant molecule that an enzyme acts on
Active Site
The specific region of an enzyme where the substrates binds and the reaction occurs.
Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of reaction without being sped up.
Denature
When an enzymee shape changes due to (heat, pH, etc) so the active site no longer works