Epithelium (HAnat/Phys) - 11/07/22
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:50 AM on 11/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
1
New cards
Cells
What makes tissue?
2
New cards
Organs
What else does tissues make?
3
New cards
Systems
Organs make what?
4
New cards
Organisms
Systems make what?
5
New cards
Carry on the same function, make tissues
Cells that ____________ and work together make _______
6
New cards
Tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function
7
New cards
Specific jobs
Cells specialize in ______
8
New cards
Interweave to form the "fabric" of the body
What do Tissues do?
9
New cards
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and nervous tissue
What are the primary tissue types?
10
New cards
Heart and liver cells
What are examples of tissue?
11
New cards
If a small group of cells have a very specific job, then other cells can't easily replace them if something goes wrong in the body
Hazards of cell specialization
12
New cards
Heart cells in the muscles can't be replaced if many or all of the heart cells in the muscles die from cancer (heart failure)
What is an example of the hazards of cell specialization?
13
New cards
Work together make tissue
Cells that _______ make ______
14
New cards
Epithelial tissue or epithelium
Epithelial cells make what?
15
New cards
Lines the body, covers the body, and makes up the glandular tissue
What are the 3 jobs of epithelial tissue?
16
New cards
Epithelial Cells
Skin cells that cover the outside of the body and lines the internal surfaces of the organs
17
New cards
Epithelial tissue/skin
Anything that exits or enters our body must pass through _______
18
New cards
Selectively permeable
Cells are ________
19
New cards
Protection, Absorption, Filtration, and Secretion
What are the 4 epithelial functions?
20
New cards
Osmosis and diffusion
Cells on the skin control _______ and _____
21
New cards
Covering/Epithelial tissue
What is the 1st line of defense for our entire body?
22
New cards
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
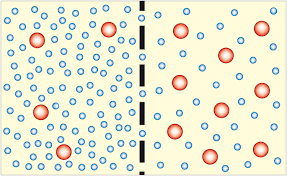
23
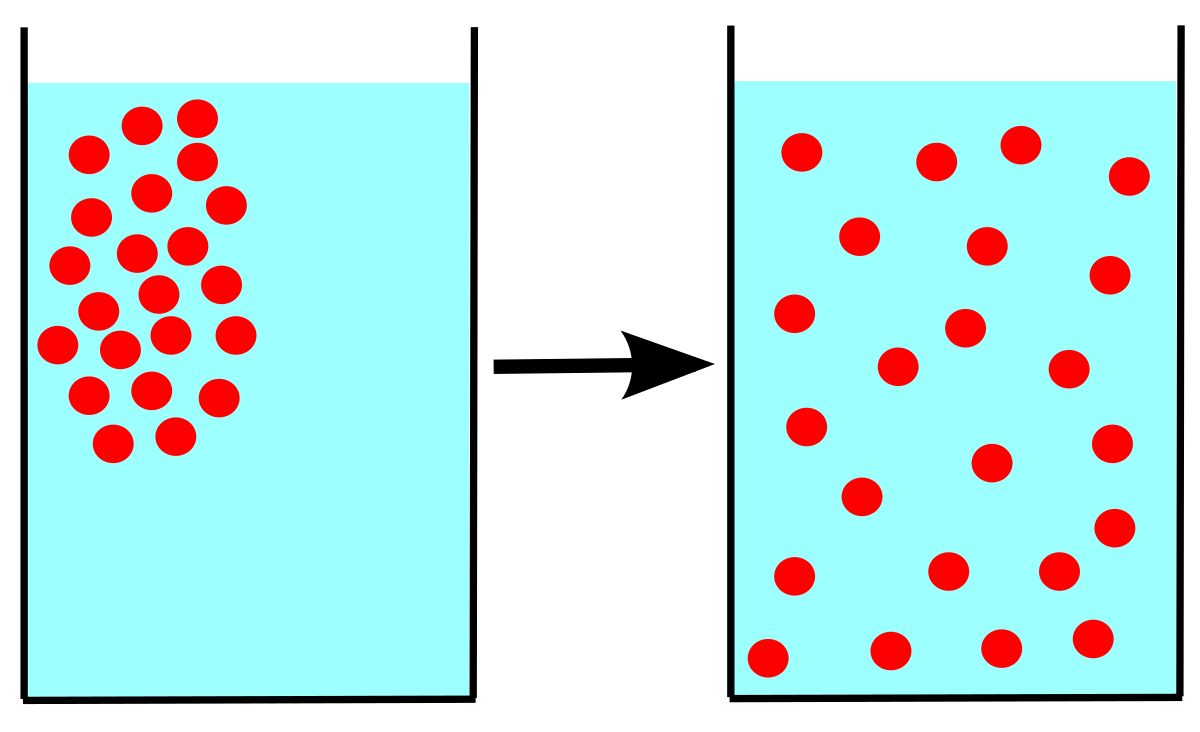
New cards
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
24
New cards
Epithelial does not let harmful things into the body like bacteria
Protection
25
New cards
Absorbs vitamin and nutrients
Absorption
26
New cards
Vitamin D from the sun, UV rays, heat
What are examples of absorption?
27
New cards
Filters what goes in and what goes out; only takes in good things like nutrients and vitamins
Filtration
28
New cards
Sweats; the passage of material formed by a cell to its exterior
Secretion
29
New cards
1. epithelium of the skin protects us against bacterial and chemical damage
2. epithelium lining of the respiratory tract has cillia, which sweeps dust and other debris away from the lungs
3. epithelium specialized to absorb substances lines some digestive system organs such as the stomach
4. epithelium in the lungs absorbs oxygen and exhales the bad stuff
2. epithelium lining of the respiratory tract has cillia, which sweeps dust and other debris away from the lungs
3. epithelium specialized to absorb substances lines some digestive system organs such as the stomach
4. epithelium in the lungs absorbs oxygen and exhales the bad stuff
What are 4 examples of epithelium functions?
30
New cards
Glandular Epithelium
Composed of cells that are specialized to produce and secrete substances
31
New cards
Gland
Is a single cell or group of cells (tissue) that is adapted for secretion
32
New cards
Proteins
Secretion contains ______
33
New cards
Pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, ovaries, testes, and pancreas
What are the 6 examples of glands?
34
New cards
Growth
What is the pituitary gland important for?
35
New cards
Nutrition/metabolism
What is the thyroid gland important for?
36
New cards
Adrenaline
What is the adrenal gland important for?
37
New cards
Eggs
What do ovaries produce?
38
New cards
Sperms
What do testes produce?
39
New cards
Hormones and enzymes
What does the pancreas produce?
40
New cards
Produces and secretes substances such as sweat, oil, digestive enzymes, mucus, and hormones
What do glands do?
41
New cards
Apical surface, basement membrane, avascular
What are the unique characteristics of epithelium?
42
New cards
Apical Surface
The top surface of tissue that is exposed to the surrounding environment
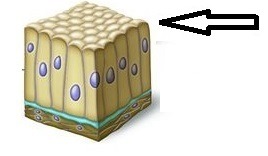
43
New cards
Basement Surface
The lower surface of the tissue
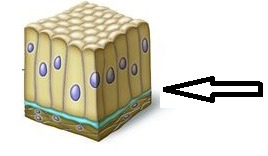
44
New cards
Basement Surface
Contains material secreted by both the epithelial cells and the connective tissue cells that are next to the epithelium
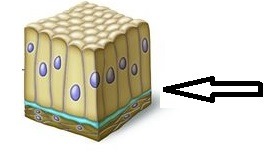
45
New cards
No. They are avascular
Do epithelial tissue have a blood supply of their own?
46
New cards
Relies on diffusion from the capillaries in the underlying connective tissue for food and oxygen
Epithelial tissue relies __________________
47
New cards
A body tissue that provides support for the body and connects all of its parts; grows back through mitosis when disconnected from other tissues
Connective Tissue
48
New cards
Bone (osseous), Cartilage, Dense connective tissue (fibrous), Loose connective tissue, and reticular connective tissue
What are the five types of connective tissue?
49
New cards
Blood supply (vascularized) except in cartilage, ligaments and tendons; Located in the dermis or the lower level of skin; includes an extracellular matrix
What are the 3 characteristics of connective tissue?
50
New cards
Extracellular Tissue
Composed of several different cell types and is made of parts secreted by other cells; allows the tissues to bear weight
51
New cards
Osteocytes
What are bone cells called?
52
New cards
Bone (Osseous) Tissue
Have bone cavities called lucanae, which is surrounded by layers of the matrix
53
New cards
Connection and support
What is bone good for?
54
New cards
Calcium and collagen fibers
What does the matrix, surrounding the bone cavities, contain?
55
New cards
More flexible than bone
Cartilage Tissue
56
New cards
Chondrocytes
What are the cells called for cartilage?
57
New cards
Hyaline, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage
What are the three types of cartilage tissue?
58
New cards
Has a lot of collagen fibers and includes a rubbery matrix
Hyaline
59
New cards
Breastbone, lareax, and nose
Where is hyaline located in?
60
New cards
Forms cushion-like discs in the spine
Fibrocartilage
61
New cards
Contains structures elasticity
Elastic Cartilage
62
New cards
Ear canal
Where can elastic cartilage be found in?
63
New cards
Forms tendons and ligaments
Dense Connective Tissue (fibrous)
64
New cards
Lower layers of the skin
Where is dense connective tissue located in?
65
New cards
Has ropelike, strong tissue that forms into sheets
Describe dense connective tissue.
66
New cards
More stretchy compared to tendons
Ligaments in dense connective tissue are __________
67
New cards
Fibroblasts and fibrocytes
The cells of dense connective tissue are called _________
68
New cards
Immature
Are fibroblasts immature or mature?
69
New cards
Mature
Are fibrocytes immature or mature?
70
New cards
Softer, more cells, few fibers
Loose Connective Tissue
71
New cards
Areolar and adipose tissue
What are the two types of loose connective tissue?
72
New cards
Mature cells
-cyte
73
New cards
Immature cell
-blast
74
New cards
Is called the "glue" of the organs because it "strings" them together
Areolar Tissue
75
New cards
Looks like a cobweb, is soft, pliable
Describe Areolar Tissue.
76
New cards
Most widely distributed tissue in the body
Areolar Tissue is the most __________
77
New cards
Edema
What is the watery solution that surrounds Areolar tissue called?
78
New cards
Phagocytes that are searching for food
What is located in Areolar tissue?
79
New cards
Insulates and protects organs, cushions your eye sockets, fuels body with energy
Adipose Tissue
80
New cards
Areolar tissue and fat cells beneath the skin
What are adipose tissue made up of?
81
New cards
Breast, Arms, Stomach, and Hips
Where is adipose tissue located in?
82
New cards
Network of cells that form a layer called stroma
Reticular Connective Tissue
83
New cards
Supplies blood to cells and organs; supports blood cells or lymphocytes in lymphoid organs
What is the function of reticular connective tissue?
84
New cards
Stroma
Layer in the cells that looks like cob-webs
85
New cards
Dermis
Inner layer of skin
86
New cards
Extracellular Matrix
A collection of molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells
87
New cards
Blood cells surrounded by plasma fluid (nonliving); has white blood cells and red blood cells with plasma inside
Vascular/Blood Tissue
88
New cards
Transports blood and nutrients through the body
What is the function of Vascular Tissue?
89
New cards
Blood vessels and the heart
Where is Vascular Tissue located in?
90
New cards
Consists of a network of interwoven reticular fibers which forms stroma or internal framework of organs
What else does Vascular Tissue consist of?
91
New cards
Is the transport vehicle for the cardiovascular system, carrying nutrients, wastes, respiratory gases, and many other necessary substances throughout the body
Blood
92
New cards
Blood
_______ is not a typical connective tissue
93
New cards
Platelets
What is responsible for clotting?
94
New cards
blood are soluble, visible
Fibers of _____ are _____ protein that becomes ____ during clotting
95
New cards
Is highly specialized to contract or shorten to produce movement
Muscle Tissue
96
New cards
Skeletal, Cardiac, and smooth muscle tissue
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue?
97
New cards
Packaged by connective tissue sheets to form organs called skeletal muscles
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
98
New cards
Voluntary because they are continuously moving
Are skeletal muscle tissue voluntary or involuntary?
99
New cards
They pull on the bones and skin leading to movement
What happens when this muscle tissue contracts?
100
New cards
Long, cylindral, multicellular, have obvious striations
Describe muscle tissue.