BI111 WEEK 1 - 3
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
DNA
Cytosine
Thymine
Adenine
Guanine
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
mathematical model that predicts genotype frequencies: used as a null/control against which observed data can be compared
Calculate p & q by summing the number of alleles held by all members of the population are b or B. Then, divide through by total alleles in population (population size x 2, as diploid)
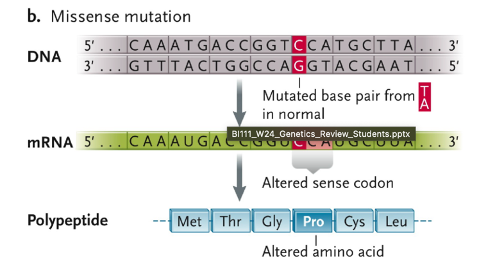
Missense mutation
mutated base pair TA in normal
altered sense codon
altered amino acid
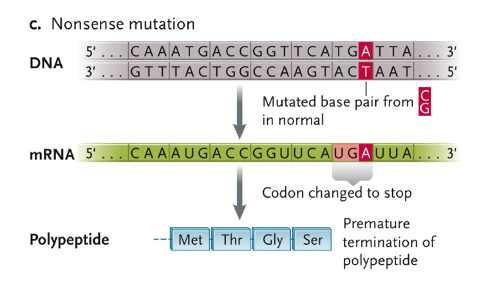
Nonsense mutation
mutated base pair from CG in normal
codon changed to stop
premature termination of polypeptide
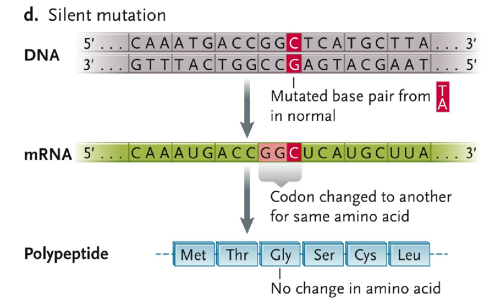
Silent Mutation
mutated base pair from TA in normal
codon changed to another for same amino acid
no change in amino acid
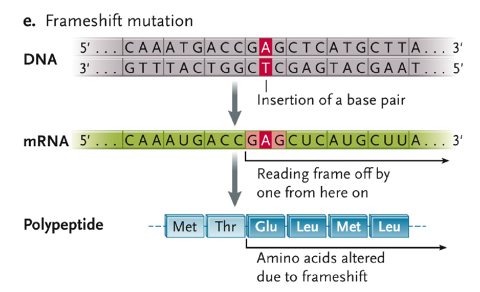
Frameshift mutation
insertion of a base pair
reading frame off by one from here on
amino acids altered due to frameshift
Homozygous
Two identical alleles (AA)
Heterozygous
Two different alleles (Aa)
Species
a group of organisms that is biologically “distinct” from others and evolving along a lineage
Species Concept
a set of conditions that are necessary and sufficient to identify a group of individual species
species concept do not only define what a species is, but in doing so, they also define what a speciation is
Morphospecies Concept
organisms are classified in the same species if they appear identical by morphological (anatomical) criteria
Essentially, if two organisms look similar, they're considered part of the same species. This concept assumes that individuals belonging to the same species will share common physical characteristics. So, if they look alike, they're treated as the same species, regardless of genetic differences or ability to interbreed.
Biological species concept
defines a species as a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring in nature.
According to this concept, members of the same species are capable of mating and producing viable offspring, while individuals from different species cannot produce fertile offspring. This concept emphasizes reproductive isolation as the defining factor for species distinction, highlighting the importance of reproductive compatibility in defining species boundaries.
Ecological species concept
defines a species based on its ecological niche, which includes its role in the environment, its interactions with other species, and its habitat preferences.
a species is defined not just by its physical traits or ability to interbreed, but by its unique ecological role and adaptations. Organisms that occupy different ecological niches, even if they are morphologically similar or capable of interbreeding, may be considered distinct species under this concept. Essentially, it emphasizes the ecological relationships and adaptations of organisms as the primary criteria for defining species boundaries.
Phylogenetic species concept
defines a species as the smallest group of organisms that share a common evolutionary history, as evidenced by their genetic and evolutionary relationships.
This concept emphasizes the evolutionary relationships among organisms, focusing on genetic similarity and shared ancestry to delineate species boundaries. Under this concept, species are identified based on genetic differences and patterns of evolutionary divergence, rather than solely on physical characteristics or ecological roles. It acknowledges that species evolve over time and aims to reflect the evolutionary history and diversification of organisms when defining species.
Practical species concept
is an approach to defining species that considers a combination of factors, including morphology, ecology, behavior, genetics, and evolutionary history.
This concept recognizes that different species concepts may be more applicable or useful in different contexts and aims to integrate various aspects of biology to provide a comprehensive understanding of species diversity. In essence, the practical species concept seeks to balance scientific rigor with pragmatic considerations to effectively identify and classify species in a way that is useful for research, conservation, and management purposes.
Differential Fitness Species Concepts
is a theoretical framework that defines species based on differences in fitness between populations or groups of organisms
This concept emphasizes the role of natural selection and adaptation in driving the divergence of populations into separate species. It suggests that when populations diverge to the extent that they have different levels of fitness in their respective environments, they may be considered separate species.
Retrospective reproductive community concept
is a theoretical framework used in evolutionary biology to define species based on their past reproductive interactions.
According to this concept, organisms are grouped into the same species if they have a shared history of interbreeding, even if they no longer do so.
Allopatric Speciation
refers to the formation of new species due to geographic isolation
In this process, populations of a species become geographically separated, often by physical barriers such as mountains, rivers, or bodies of water. The isolated populations then undergo independent evolutionary changes, which can lead to genetic divergence and the eventual formation of new species. Over time, reproductive isolation may arise between these populations, preventing them from interbreeding even if they were to come into contact again.
Parapatric speciation
is a process of speciation where new species arise from a single ancestral species while inhabiting adjacent or partially overlapping geographic ranges.
In parapatric speciation, there is usually a gradient of environmental conditions or resources across the range of the ancestral species. This gradient can lead to divergent selection pressures acting on different parts of the population, causing genetic differentiation and the evolution of reproductive barriers.
Sympatric Speciation
is a process of speciation where new species evolve from a single ancestral species while inhabiting the same geographic area, without any physical barriers to gene flow.
In sympatric speciation, reproductive isolation evolves within the same population, often as a result of non-geographic factors such as ecological specialization, disruptive selection, or assortative mating.
Deletion
broken segment lost from chromosome
Duplication
broken segment inserted into homologous chromosome
Translocation
broken segment attached to a non homologous chromosome
Inversion
broken segment reattached in reversed orientation
Nondisjunction
failure of homologous pair separate during meiosis 1
failure of chromatid separation during meiosis 2
Euploids
normal number of chromosomes
Aneuploids
extra or missing chromosomes
Polyploids
extra set of chromosomes (triploids, tetraploids)
spindle fails during mitosis