Section 6 - hemolysis
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
State the length of normal RBC survival in circulation.
~120 days
State the 3 main physiologic functions of the RBC membrane
(Maintain osmotic balance, maintain cell shape and deformability, transport cellular ions and gasses)
1) Maintain osmotic balance between plasma and cell cytoplasm. Compare RBC in isotonic (normal), hypotonic soln (swollen), Hypertonic soln (crenated)
2) Maintain shape and deformability- cells deform to streamline and reduce resistance.
3) Transport cellular ions & gasses: cation pump regulate balance of Na+ & K+
-gasses = O2 & CO2
-Anions = HCO3-, Cl-
-Cations = Na+, K+
State the role of sialic acid in the RBC membrane
(negative charge, cellular repulsion)
provides a negative charge to maintain cellular repulsion. Prevents RBCs from clumping together & protects RBC’s from premature detection by immune system.
is an integral protein- goes across lipid bilayer
State the function of Spectrin in the RBC
(Provides cytoskeleton)
Modulates shape and deformability
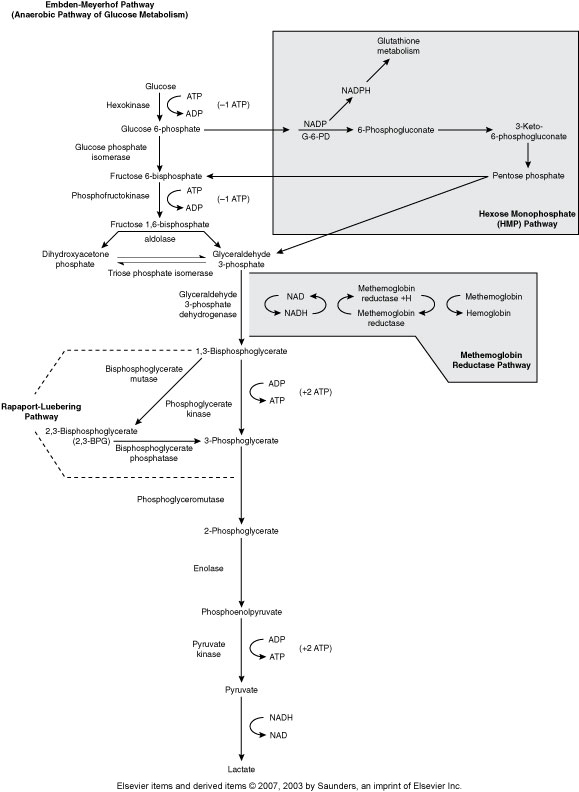
Embden-Meyerhof Pathway (Metabolic pathway)
(Anaerobic Glycolysis)
RBC major source of cellular energy (90-95% or RBC glucose consumption)
Net gain of 2 ATP
Pyruvate Kinase is one of the most common ENZ deficiencies that affects RBC
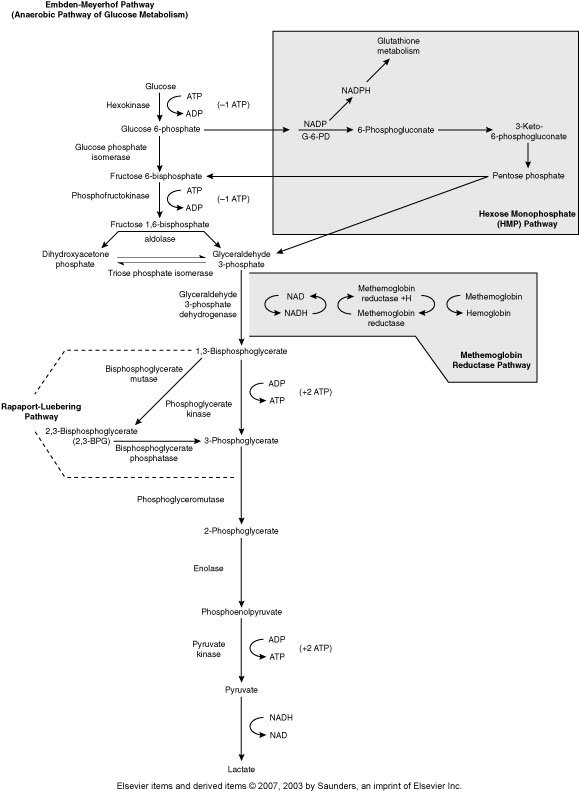
Hexose Monophophate Pathway/Shunt (Metabolic pathway)
(Aerobic glycolysis, Oxidative)
How the body fights oxidative injury to RBCs
The main enzyme is Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)
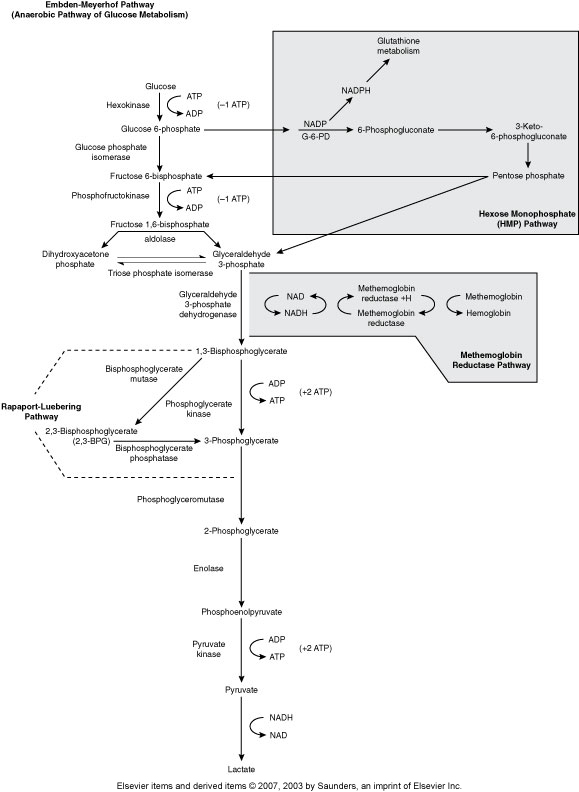
Rapport-Luebering Pathway (Metabolic Pathway)
(Regulates oxygen delivery to the tissues)
2,3,-biphosphglycerate
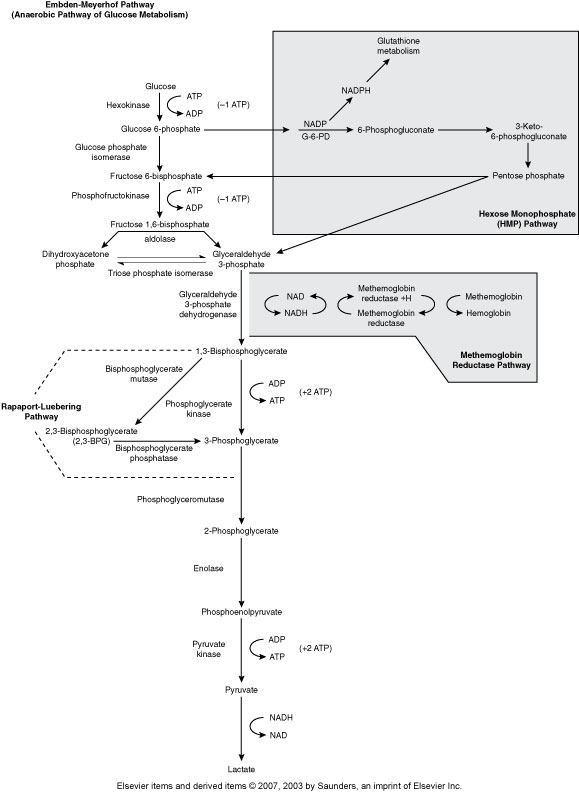
Methemoglobin Reductase Pathway (Metabolic Pathway)
(MHR keeps Fe in Hgb reduced to the 2+ state)
Main enzyme is Methemoglobin reductase
Hgb with Fe3+ is methemoglobin
Without methemoglobin reductase we get methemoglobinemia, resulting in cyanosis .
Methemoglobin can’t carry 02
Hereditary enzyme deficiency, toxic substances that oxidize hgb, Hgb M disease
State the primary function of hemoglobin
(gas transport)
To transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and CO2 from the tissues to the lungs for exhalation
What are the 2 major components of a normal Hgb molecule?
(Heme & Globin)
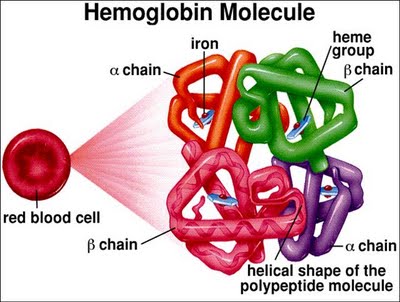
Describe the function and composition of heme
Ring of C, H, & N atoms called propophyrin IX (pyrole ring) with an atom of ferrous (Fe2+) iron inserted
There 4 Hemes in each hgb
Describe Globin
(Amino acid chains of Hgb)
Teach hemoglobin molec has two pairs of poly. p. chains
141-146 aa per chain
Ferritin
(Iron +apoferritin)
Major storage form of Fe
Heme Iron
Iron in the “ferrous” or +2 form
Transferrin
(Plasma transport protein)
Fe3+ iron bound to plasma transport protein
Carries Iron in the Ferric state
Hemosiderin
(Intracellular storage form of Fe)
Breakdown product of ferritin
Found in the kidneys
also acts to store Fe
List the Intrauterine Hemoglobins
(Gower 1, Gower 2, Portland)
1) Gower 1 (ζ2ε2) zeta2 epsilon2
2) Gower 2 (a2ε2) alpha2 epsilon2
3) Portland (ζ2γ2) zeta2 gamma 2
List the Hemoglobin found at birth
(HgB F & Hgb A)
1) Hgb F (α2γ2) alpha2 gamma2 (60-90%)
2) Hgb A (α2β2) alpha2 beta2 - the rest is filled by the deficit left by Hgb F
Normal Adult Hemoglobin Chains
List ~% & Composition of each chain
(Hgb A, Hgb A2, Hga F
1) Hgb A (α2β2) alpha2 beta2 (> 95%)
2) Hgb A2 (a2δ2 ) alpha2 delta2 (~ 2%)
3) Hgb F (a2γ2 ) alpha2 gamma2 (1-2%)
Normal intrauterine Hemoglobin Chains
List ~% & Composition of each chain
Gower 1 (zeta2 epsilon2)
Gower 2 (alpha2 episilon 2)
Portland (zeta2 gamma 2)
Hemoglobin-Oxygen Dissociation curve
(Describes respiratory movement, oxygen loading/unloading)
Normal curve
2,3-BPG
(Control Hgb affinity for oxygen)
2,3-biphosphoglycerate
Increases the affinity for oxygen
P-50
The partial pressure at which hgb is 50% saturated under standard in vitro conditions
Reference Range:
P50 = 26-30 mmHg
As the P50 goes up, oxygen affinity goes down and more oxygen is released to the tissues.
Shift to the left
(Increases Hgb affinity for O2, decreases O2 delivery to tissue)
Cause abnormal Hgbs with increase O2 affinities
undesirable
Decrease BPG
about 12% of oxygen is delivered to tissues
P50 goes down to ~ 23 mmHg
Shift to the right
(Decreases Hgb affinity for O2, increases O2 delivery to tissues)
Mediate by increased 2,3-BPG
In response to hypoxia
desireable
P50 increases to ~40 mmHg
50% opposed to 25% of oxygen delivered to tissues
RBCs have become more efficient
Methemoglobin
(Hgb w Fe in 3+ state)
Can’t carry oxygen
Results in Shift to the left
Causes:
1) presence of nitrites
2) Decreased methemoglobin reductase
3) inherited hgb M disease
Sulfhemoglobin
(sulfur is added to pyrole ring)
Conversion of Fe to the ferric +3 state
HOWEVER, normally only 1-2 hemes affected and actually REDUCES remaining Hgb for oxygen so more oxygen can be delivered to tissues
Results in SHIFT TO THE RIGHT
Carboxyhemoglobin
(Carbon monoxide binds to Heme iron)
Hgb loves CO 200x more than O2
CO Bonds more slowly, but more strongly than O2
Completely eliminates O2 transport
Cherry red blood
MASSIVE SHIFT TO THE LEFFT
Define: cyanosis
Bluish-purple discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes that occurs when there's a decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Methemoglobinemia will lead to this
length of normal rbc survival in circulation
120 days
3 physiologic functions of the rbc membrane
1) maintaining osmotic balance between plasma and cell
2) Maintain cell shape and deformability - flexibility of cell allows for them to squeeze through vasculature and reduce flow resistance
3) Transport cellular ions & gases selective permeability - K+/Na+ pumps, O2, CO2, H2O, anions
Permiability of
1)H2O
2)Anions
3)Cations (K+/Na+)
1) simple diffusion
2) Integral proteins (channels) facilitate diffusion
3) Cation pumps (Cation gradients across the membrane are actively maintained by pumps keeping intracellular sodium low and intracellular potassium high)
Form of iron that is incorporated into the heme molecule
ferrous (Fe2+)
Define: Transferrin
Plasma protein that carries iron in Ferric (Fe3+) form
Define: Ferritin
Apoferritin carrying iron. A major storage form of iron
Found in most tissues as a cytosolic protein - also in plasma
Define: Apoferritin
The protein shell of ferritin, meaning it is the iron-free form of the protein
Define: Hemosiderin
Intracellular storage form of iron; breakdown product of ferritin
Define: cyanosis
Bluish-purple discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes that occurs when there's a decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Methemoglobinemia will lead to this