A level Bio 2.1 Cell Structure and Microscopy
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pls rate it 5 stars if you find it helpful :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
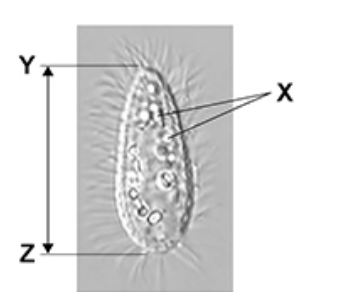
Explain why it is not possible to determine the identity of the structures labelled X using an optical microscope. (2)
Resolution (too) low (1)
Because wavelength of light is (too) long; (1)
Suggest one explanation for the faster rate of plasmid replication in cells growing in a culture with a high amino acid concentration.(2)
(Amino acids used in) protein synthesis (1)
(So) more DNA polymerase (1)
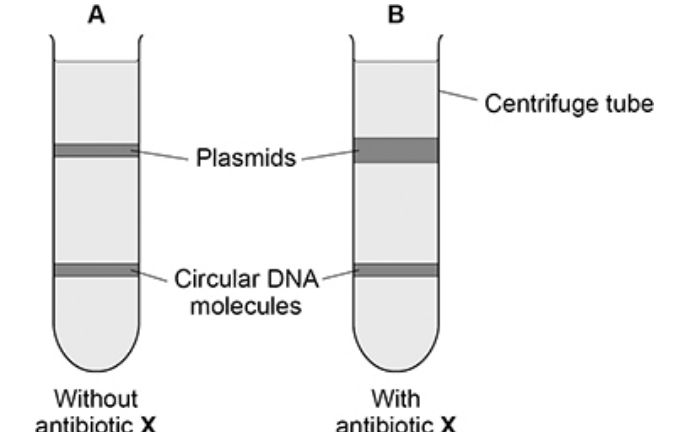
A scientist prepared a culture of a bacterial species.
• She extracted the plasmids and the circular DNA molecules from a sample of cells taken from this culture (A).
• She then added antibiotic X to the culture and let the cells divide for 4 hours.
• She then extracted the plasmids and the circular DNA molecules from a sample of these cells (B).
• The scientist separated the plasmids from the circular DNA molecules in A and in B using ultracentrifugation
What can you conclude from the figure above about a structural difference between the plasmids and the circular DNA? Explain your answer. (2)
Circular DNA is bigger/heavier/denser (1)
(Because band) moved further/is lower (in tube)/closer to bottom (of tube) (1)
Describe how a sample of chloroplasts could be isolated from leaves(4)
Grind the leaves in a cold, isotonic, buffered solution to break open the cells while preventing osmotic damage, and pH changes. (1)
Filter the mixture to remove large pieces of tissue and cell debris. (1)
Centrifuge the filtrate at a low speed to separate out the heavier cell debris. (1)
Collect the supernatant and centrifuge again at a higher speed so the chloroplasts form a pellet at the bottom.(1)
Give one feature of the chloroplast that allows protein to be synthesised inside the chloroplast and describe one difference between this feature in the chloroplast and similar features in the rest of the cell. (2)
Ribosomes (1)
Are smaller than cytoplasmic ribosomes (1)
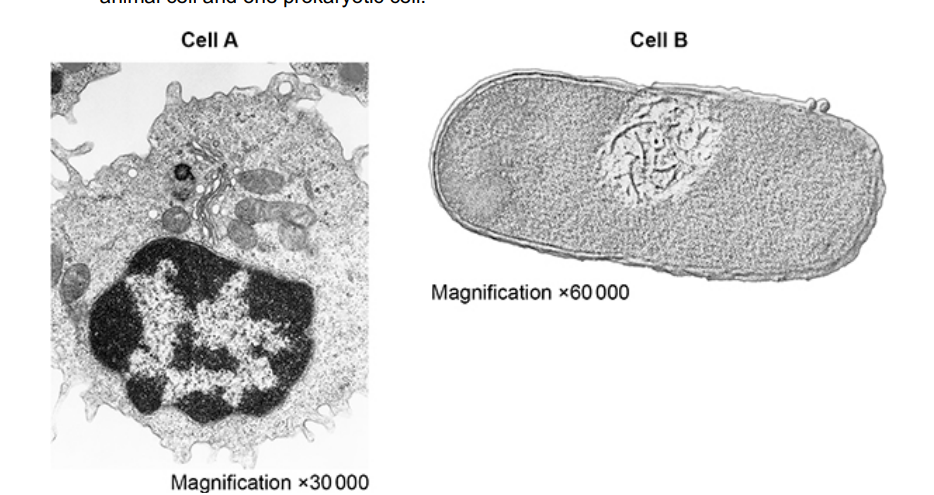
The figure below shows transmission electron micrographs of two cells, one animal cell and one prokaryotic cell.
Contrast the structure of the two cells visible in the electron micrographs shown in the figure above. (5)
A has a nucleus whereas B has free DNA (1)
A has mitochondria whereas B does not (1)
A has Golgi body whereas B does not (1)
A has no cell wall whereas B has a murein cell wall (1)
A has linear DNA whereas B has circular DNA (1)
Eukaryotic cells produce and release proteins.
Outline the role of organelles in the production, transport and release of proteins from eukaryotic cells.
Do not include details of transcription and translation in your answer(4)
DNA in nucleus is code (for protein) (1)
Ribosomes/rough endoplasmic reticulum produce (protein) (1)
Mitochondria produce ATP (for protein synthesis) (1)
Golgi apparatus package/modify (1)
Suggest why a nucleus may not be visible in a microscopic image (1)
the nucleus is not stained(1)
Give one advantage of viewing a biological specimen using a transmission electron microscope compared with using a scanning electron microscope.(1)
Higher resolution (1)
The detail shown in the diagram above would not be seen using an optical microscope. Explain why. (2)
Light has long(er) wavelength (1)
so lower resolution (1)
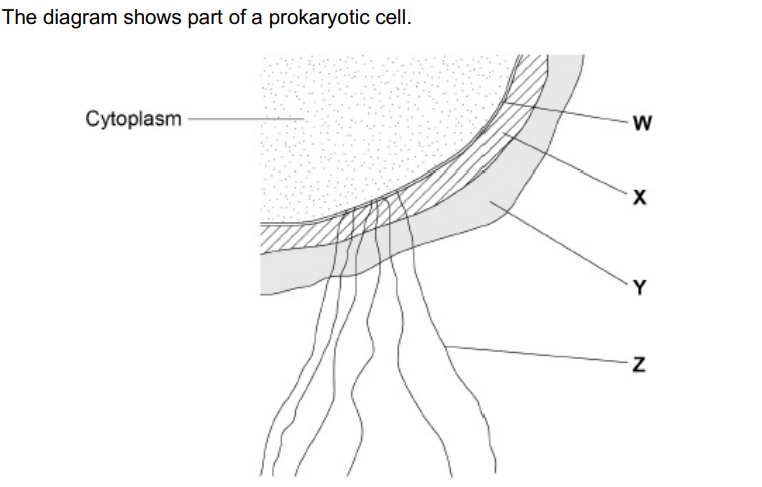
Name the structures labelled W to Z in the diagram.(2)
W – (cell surface) membrane
X – cell wall
Y – capsule
Z – flagellum
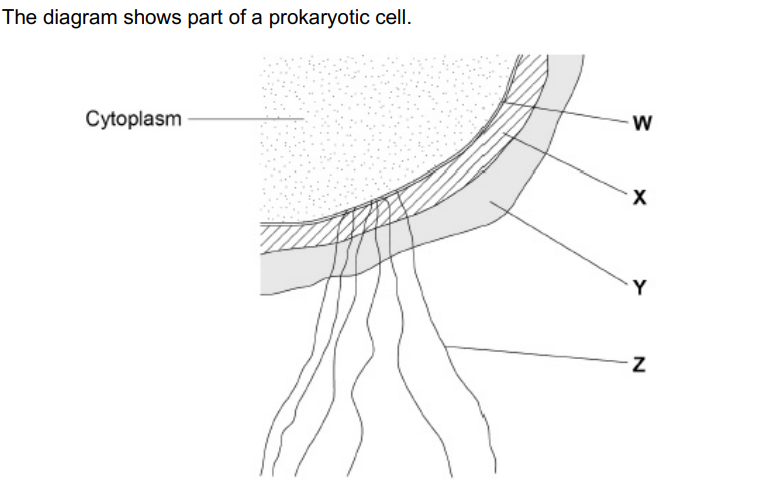
Name the main biological molecule in W and X (2)
W - Phospholipids
X - Murein
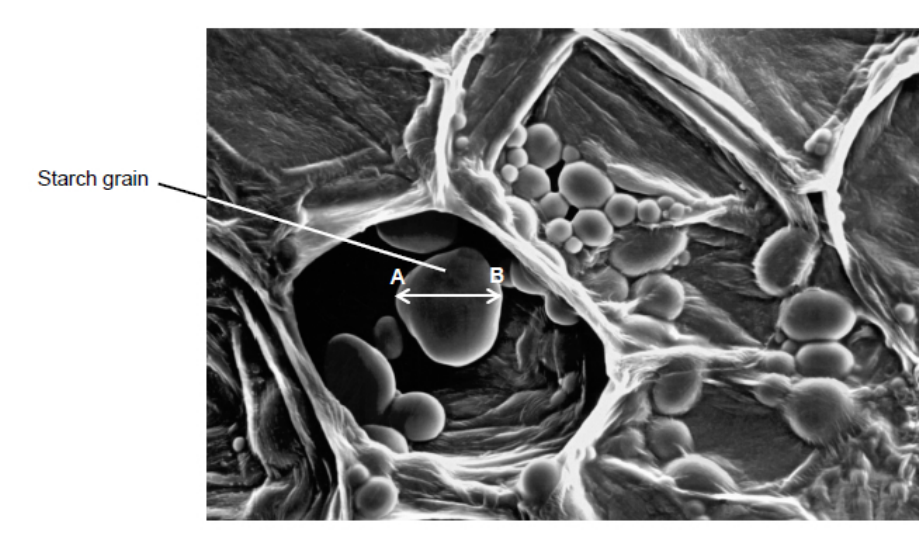
What type of microscope was used to obtain the image shown in the diagram above?
Give one piece of evidence to support your answer.
Scanning electron (microscope) (1)
3D (image) (1)
DNA and RNA can be found in bacteria.
Give two ways in which the nucleotides in DNA are different from the nucleotides in RNA. (2)
DNA contains thymine and RNA contains uracil(1)
DNA contains deoxyribose and RNA contains ribose (1)
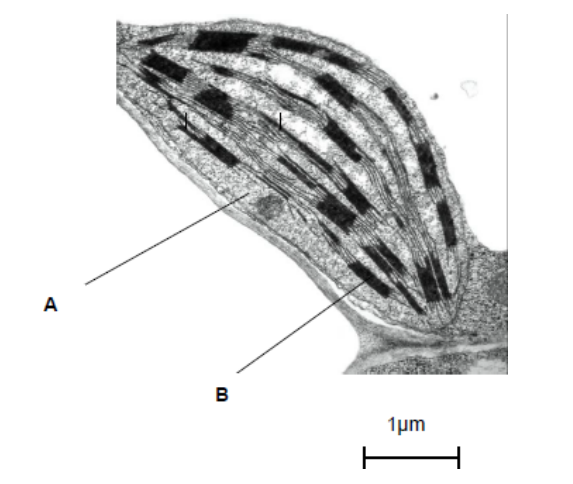
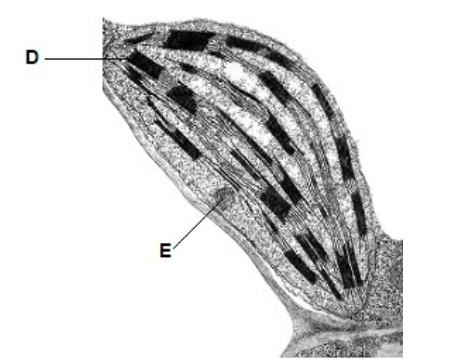
Name the parts of the chloroplast labelled A and B. (2)
A-stroma
B-granum
Name two structures in a eukaryotic cell that cannot be identified using an optical microscope. (2)
Ribosome (1)
Lysosome (1)
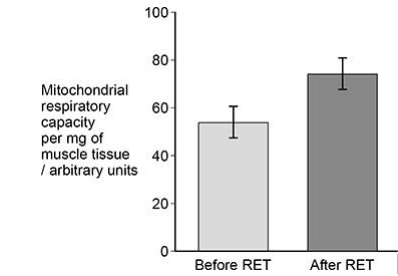
Mitochondrial respiratory capacity is a measure of maximum ATP production in a mitochondrion. Scientists investigated the effect of a resistance exercise training (RET) programme on the respiratory capacity of mitochondria in skeletal muscle tissue. RET develops muscle strength.
The scientists:
• took samples of muscle tissue from 11 young males before and after
a 12-week RET programme
• recorded the respiratory capacity of the mitochondria in the samples of muscle tissue.
The graph below shows some of the scientists’ results.
The error bars represent ± 2 standard deviations from the mean, which
includes over 95% of the data.
Using all the information, evaluate whether 12 weeks of RET wouldimprove athletic performance in the general population(5)
For
1) SDs do not overlap so significant difference/increase (in respiratory capacity)
2) Increase in ATP linked to increase in muscle contraction
Against
1) Only males (in investigation)
2)Only 11 (individuals in investigation) OR Small sample size
3) RET may not strengthen required muscles OR Athletic performance not investigated
4) Results may differ depending on age
(5)
A student used an optical microscope to observe a piece of tissue from the lower surface of an orchid leaf. The piece of leaf tissue observed was very thin. Explain why this was important (2)
Single/few layer(s) of (cells/tissue) (1)
So light can pass through (1)
The student produced a biological drawing of the leaf tissue they viewed through an optical microscope
Give three ways the student could ensure they produce a correct biological drawing of the leaf tissue.
Assume the student uses a sharp pencil.
Use continuous lines (1)
Do not use shading (1)
Show magnification/scale (bar) (1)
Describe and explain how you would use cell fractionation and ultracentrifugation to obtain a sample of nuclei from muscle tissue.(6)
Grind to break open cells (1)
Filter to remove (intact) tissue/cells/debris (1)
cold (solution) to prevent enzyme activity (1)
Isotonic solution to prevent osmosis (1)
Buffered solution to stop enzymes denaturing (1)
Centrifuge at low(er) speed so nuclei in pellet/move to bottom(1)
Describe the role of organelles in the production and release of enzymes by animal cells. Do not include details of transcription in your answer.(5)
DNA in nucleus codes for enzyme/protein(1)
Ribosomes/rough endoplasmic reticulum produce enzyme/protein(1)
Rough endoplasmic reticulum modifies/processes/transport enzymes /protein (1)
Mitochondria produce ATP (1)
Golgi apparatus modify enzymes/protein (1)
Vesicles move (protein) to cell(-surface) membrane(1)
Some strains of Streptococcus bacteria are more likely to cause lung disease than other strains.
Strains that do not cause lung disease are quickly destroyed by phagocytes.
Phagocytes are stimulated when they bind to murein on Streptococcus bacteria.
Each strain of Streptococcus bacteria has a capsule of different thickness from the others.
Suggest how Streptococcus bacteria with a thicker capsule are more likely to survive and so cause lung disease. (2)
Thicker capsule so phagocytes less likely to bind to murein (in cell wall) (1)
Reduced phagocytosis so more binary fission(1)
Explain why viruses are described as acellular and non-living.(2)
(Acellular) not made of cells (1)
(non-living) have no metabolic reactions (1)
Give the three structural features found in all virus particles and describe the function of one of these features (2)
Genetic material, capsid and attachment protein (1)
Capsid protects the genetic material (1)
Give one reason why antibiotics are not effective against viruses (1)
Do not have metabolic processes (1)
Cells that secret enzymes contain a lot of rough endoplasmic reticulum(RER) and a large Golgi apparatus
Describe how RER is involved in the production of enzymes(2)
Contains ribosomes (1)
To make protein (1)
The structure of a cholera bacterium is different from the structure of an epithelial cell from the small intestine. Describe how the structure of a cholera bacterium is different (5)
Cholera is prokaryote(1)
A cholera has circular chromosomes and an epithelial cell has linear chromosomes (1)
A cholera bacterium is much smaller in size (1)
A cholera doesn't have mitochondria (1)
A cholera bacterium has a cell wall(1)
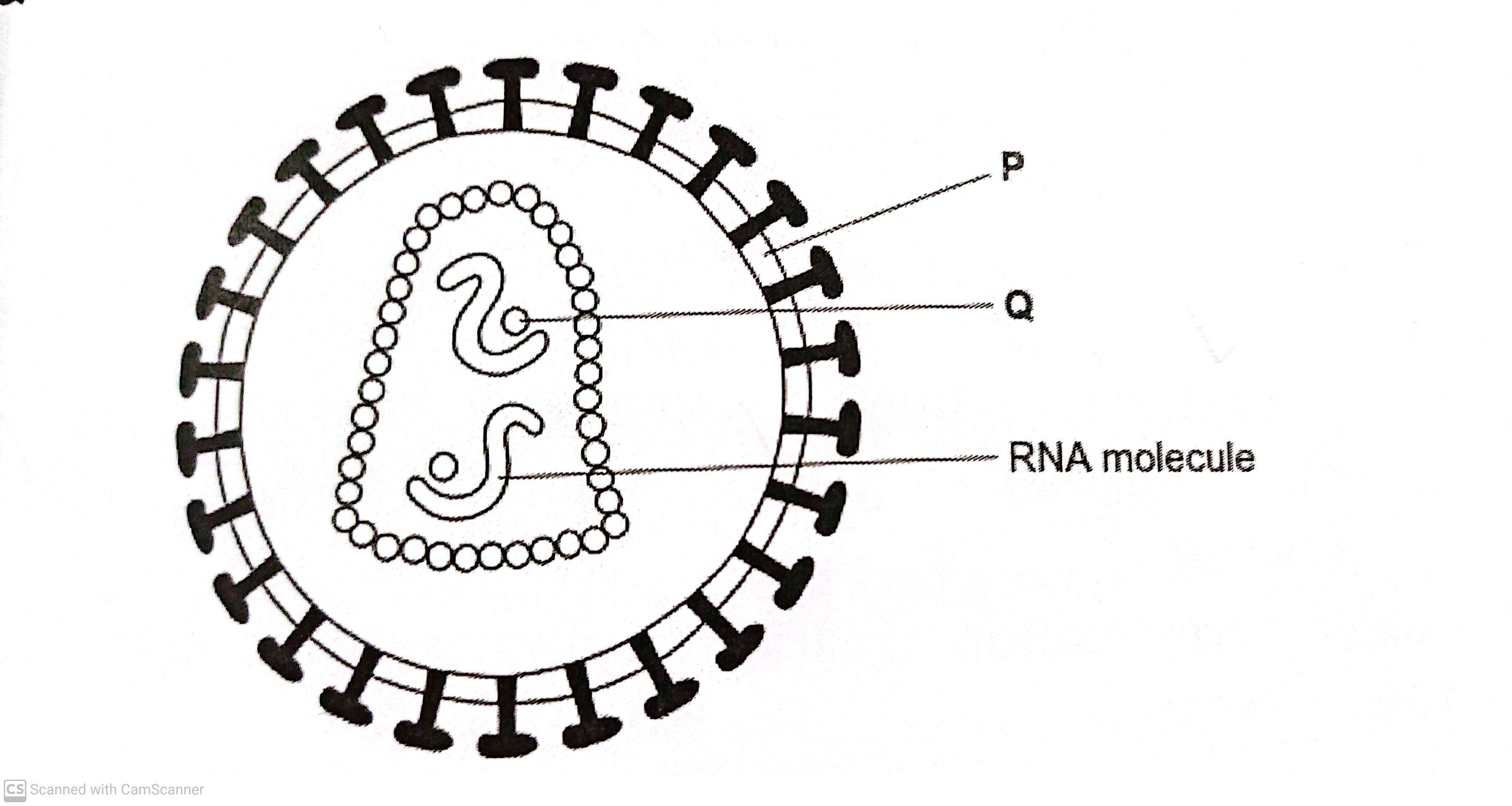
The diagram shows a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Name structure P and enzyme Q (2)
Structure P - cell membrane
Enzyme Q-reverse transcriptase (2)
DNA and RNA can be found in bacteria.
Give two ways in which nucleotides in DNA are different from the nucleotides in RNA (2)
DNA contains thymine and RNA contains uracil(1)
DNA contains deoxyribose and RNA contains ribose (1)
Cholera bacteria can be viewed using a transmission electron microscope or a scanning electron microscope
Give one advantage of using a SEM rather than a TEM (1)
Thin sections don't need to be prepared (1)
Describe the principles and the limitations of using a transmission electron microscope to investigate cell structure (5)
Electrons pass through thin specimen (1)
Denser parts absorb more electrons (1)
Electrons have a short wavelength so gives high resolution (1)
Must be in a vacuum (1)
Specimenrs must be thin (1)
A biologist prepared a sample of organelles labelled C from liver. He used the following method.
1) Added to the liver tissues an ice cold, buffered solution with the same water potential as the liver tissues.
2) Mixed the liver and solution in a blender
3) Filtered the mixture from the blender
4) Spun the filtered liquid in a centrifuge at a low speed. A pellet appeared in the bottom of the centrifuge tube.
5) Poured off the liquid above the pellet into a second centrifuge tube and spun this at a higher speed to obtain the sample of organelles labelled C
Explain why the solution the biologist used was ice cold, buffered and the same water potential (3)
Ice-cold - to slow enzyme activity so enzymes don't digest the organelles(1)
Buffered- maintains the pH so the enzymes don't digest (1)
Same water potential-prevents osmosis so no lysis (1)
A biologist prepared a sample of organelles labelled C from liver. He used the following method.
1) Added to the liver tissues an ice cold, buffered solution with the same water potential as the liver tissues.
2) Mixed the liver and solution in a blender
3) Filtered the mixture from the blender
4) Spun the filtered liquid in a centrifuge at a low speed. A pellet appeared in the bottom of the centrifuge tube.
5) Poured off the liquid above the pellet into a second centrifuge tube and spun this at a higher speed to obtain the sample of organelles labelled C
Explain why the biologist used a blender and then filtered the mixture (2)
Produce homogenate (1)
To remove large cell debris (1)
A biologist prepared a sample of organelles labelled C from liver. He used the following method.
1) Added to the liver tissues an ice cold, buffered solution with the same water potential as the liver tissues.
2) Mixed the liver and solution in a blender
3) Filtered the mixture from the blender
4) Spun the filtered liquid in a centrifuge at a low speed. A pellet appeared in the bottom of the centrifuge tube.
5) Poured off the liquid above the pellet into a second centrifuge tube and spun this at a higher speed to obtain the sample of organelles labelled C
Name the organelles that made up most of the first pellet after centrifugung at a low speed (1)
Nuclei (1)
A biologist prepared a sample of organelles labelled C from liver. He used the following method.
1) Added to the liver tissues an ice cold, buffered solution with the same water potential as the liver tissues.
2) Mixed the liver and solution in a blender
3) Filtered the mixture from the blender
4) Spun the filtered liquid in a centrifuge at a low speed. A pellet appeared in the bottom of the centrifuge tube.
5) Poured off the liquid above the pellet into a second centrifuge tube and spun this at a higher speed to obtain the sample of organelles labelled C
The second centrifuge tube was spun at a higher speed to obtain the sample of organelles labelled C in the diagram (step 5) Suggest why (1)
Mitochondria is less dense than nucleus (1)
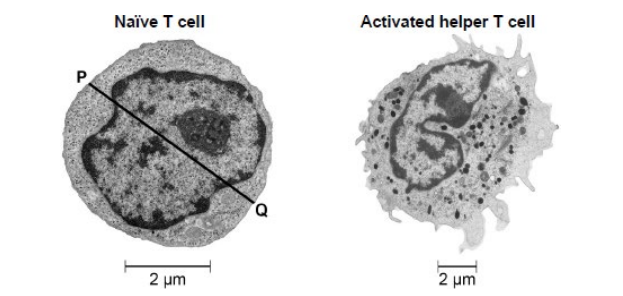
The figure below shows electron microscope images of the two types of cell.
State one feature that shows the images in the figure in part (a) were taken with an electron microscope and not an optical microscope. Explain your answer. (2)
Nucleolus/lysosomes/ribosomes are visible (1)
EM has greater resolution (1)
Scientists investigated the activation of T lymphocytes. The scientists studied two types of cell:
• naïve T cells, which are T cells that have not yet been in contact with a foreign antigen
• activated helper T cells, which are T cells that have been activated by a foreign antigen.
State one role of a helper T cell (1)
Stimulating phagocytes (1)
Name two biological molecules that can be coded for by a gene.
Do not include a polypeptide or protein in your answer. (2)
rRNA (1)
tRNA (1)
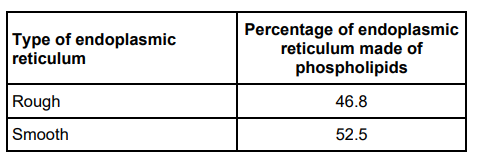
Scientists investigated the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum. The table below shows some of the scientists’ results
Use the data in the table to suggest how the structure of rough endoplasmic reticulum is different from the structure of smooth endoplasmic reticulum and how this is related to their functions. (3)
Less phospholipids in RER (1)
(More protein/glycoprotein/ribosomes) RER – production/transport of proteins (1)
(More phospholipid) SER – production/modification/packaging of lipids (1)
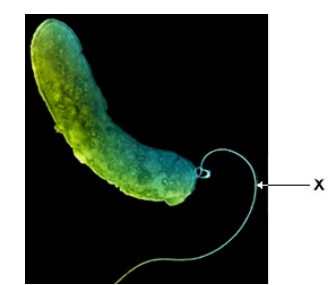
The figure above is different from an image of this bacterium obtained using a transmission electron microscope. Describe and explain one difference between these images. (2)
(Only) surface visible with SEM, but internal structures visible with TEM (1)
(Because) electrons deflected/bounce off (using SEM) (1)
Name two structures found in all bacteria that are not found in plant cells (2)
Circular DNA (1)
Murein cell wall (1)
Name two features of HIV particles that are not found in bacteria. Do not include attachment protein in your answer. (2)
Capsid (1)
RNA genome (1)
Describe the structure and function of the nucleus. (4)
Structure
1) Nuclear envelope
2) Chromosomes/chromatin
Function
3) (Holds/stores) genetic information/material for polypeptides (production)
4) Production of rRNA/ribosomes
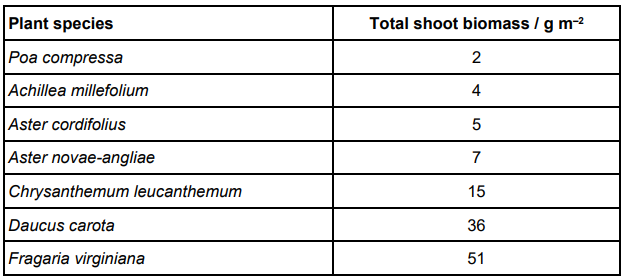
Scientists investigated the effect of the number of fungal species in soil on the diversity of plant species. The table below shows their raw data for soil containing 14 fungal species.
Suggest one reason the scientists used biomass instead of the number of individuals of each plant species when collecting data to measure diversity. (1)
Too small/numerous to count individuals
or
too time consuming