module 2 - atoms and elements - exam
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What evidence from J.J. Thomson's experiments with the cathode ray led to the plum pudding model of the atom? (3 points)
The beam was attracted to a positive charge and repelled by a negative charge, showing that atoms contain small, negatively charged particles.
The beam was attracted to a negative charge and repelled by a positive charge, showing that atoms contain small, positively charged particles.
The beam was positively charged and had significant mass, showing that atoms have a positive, dense nucleus.
The beam was neutral and had significant mass, showing that atoms contain neutral particles in the nucleus.
1

Match the scientist to his contribution to the atomic theory. (3 points)
1 - b, 2 - a, 3 - c
Modern atomic theory states that atoms are neutral. How is this neutrality achieved? (3 points)
Equal number of neutrons and protons
Equal number of protons and electrons
More electrons than protons
More neutrons than electrons
2
What is true of electrons? (3 points)
They are positively charged and located inside the nucleus.
They are positively charged and located outside the nucleus.
They are negatively charged and located inside the nucleus.
They are negatively charged and located outside the nucleus.
4
Schrodinger and Heisenberg developed an alternate theory about atomic nature that contradicted some of Bohr's model of the atom. How do changes resulting from new technology and evidence affect the reputation of the atomic theory? (3 points)
Each time a theory is changed because of new evidence, it becomes less popular with the scientific community.
Each time a theory is changed because of new evidence, it becomes weaker and damages the reputations of the scientists involved.
Each time a theory is tested with new evidence, it convinces more people to accept it as truth.
Each time a theory is tested with new evidence, it becomes stronger and more durable.
4
The plum pudding model hypothesized by Thomson shows the scattering of electrons. When was this discovered in relation to other scientist's atomic hypotheses? (3 points)
After Rutherford but before Chadwick
Before Bohr but after Chadwick
Before Bohr and Rutherford
After Rutherford but before Bohr
3
Chadwick worked to isolate the neutral particle Rutherford had proposed. (2 points)
True
False
true
Mendeleev used his arrangement of elements in order of increasing mass and repeated properties to predict the mass and properties of undiscovered elements. (2 points)
True
False
true
Using the periodic table, which of the following elements is most likely to have similar properties as calcium, and why? (3 points)
Potassium (K), because they are both alkali metals
Magnesium (Mg), because they are both alkaline earth metals
Scandium (Sc), because they are both in the fourth period
Argon (Ar), because they both have three energy levels
2

Use the periodic table to match each of the following element symbols to its name, atomic mass, or atomic number. (3 points)
1 - c, 2 - b, 3 - a
A student observes that an element is shiny, bends easily, and can conduct electricity. What type of element is the student most likely observing? (3 points)
Gas
Metal
Metalloid
Nonmetal
2
Zinc has the chemical symbol Zn and the atomic number 30. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons does an atom of zinc-69 have? (3 points)
30 protons, 39 neutrons, 39 electrons
39 protons, 30 neutrons, 30 electrons
39 protons, 30 neutrons, 39 electrons
30 protons, 39 neutrons, 30 electrons
4
An atom has atomic number 5 and mass number 11. How many protons does the atom have? (3 points)
5
6
10
11
5
The image shows the representation of an unknown element in the periodic table.

Based on the representation, which of the following statements about the element is true? (3 points)
The number of neutrons in an atom of the element is 24.
The combined mass of all the protons and electrons is 24.305.
The combined mass of all the neutrons and electrons is 24.305.
The mass number of the most common isotope of the element is 24.
4
Imagine a newly discovered element, Z, with two naturally occurring isotopes. If 87.8 percent of a sample is an isotope with a mass of 267.8 u, and 12.2 percent is an isotope with a mass of 269.9 u, what is the average atomic mass for this element? (3 points)
267.9 u
268.1 u
268.9 u
269.1 u
2
What is the total number of electrons that can occupy the f sublevel? (3 points)
2 electrons
6 electrons
10 electrons
14 electrons
4
What type of orbital is spherical in shape? (3 points)
s orbital
p orbital
d orbital
f orbital
1
Which of the following is not a possible sublevel? (3 points)
1s
2d
3p
4f
2d
Calcium (Ca) has an atomic number of 20. What is calcium's electron configuration? (3 points)
1s²1p61d101f²
1s²1p62s²2p63s²3p²
1s²2s²2p63s²3p64s²
1s²2s²2p63s²3p63d²
3
Which of the following is a reasonable electron configuration? (3 points)
1s²2s²2p63s²
1s²2s²2p63s²3d4
1s²2s²2d102p³
1s²2s²2p³2d6
1
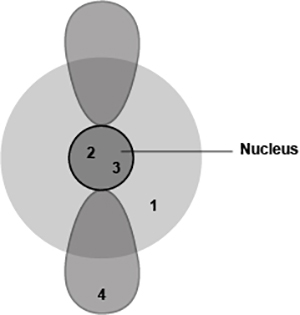
The diagram shows four different locations in an atom.
Which locations are likely to have subatomic particles with the least mass? (3 points)
1 and 2
2 and 3
1 and 4
3 and 4
3; 1 and 4
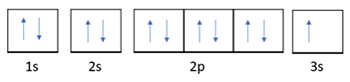
The following orbital notation is for which element? (3 points)
Na
He
F
O
1; Na
The partial electron configuration of an atom with 14 electrons is shown.
1s22s2 2p63s2X
Which of the following does X represent? (3 points)
2d²
3s²
3p²
4s²
3
Energy has both wavelike and particle-like properties, but electrons have only particle-like properties. (4 points)
True
False
false
Which type of electromagnetic radiation has a lower frequency than infrared radiation? (4 points)
Gamma rays
Microwaves
Visible light
X-rays
2

Match each type of electromagnetic radiation to its description. (4 points)
1-d, 2-b, 3-c, 4-a.
Compared to visible light, an electromagnetic wave that has a longer wavelength will also have ________. (4 points)
higher frequency and higher speed
higher frequency and equal speed
lower frequency and equal speed
lower frequency and higher speed
3
What is the wavelength of waves that have a frequency of 2.20 x 10−4 Hz? (4 points)
7.30 x 10-13 m
6.60 x 104 m
5.50 x 108 m
1.36 x 1012 m
4
Electrons further from the nucleus are partially shielded from the pull of the nucleus. (4 points)
True
False
true
As you move from left to right across a period, what happens to the atomic radii? (4 points)
They increase, because of the higher number of occupied energy levels.
They increase, because of the weaker attraction of electrons to the nucleus.
They decrease, because of the stronger effective nuclear charge.
They decrease, because of the increased atomic mass.
3
Which of the following elements would you expect to have the lowest ionization energy value, and why? (4 points)
Fluorine (F), because it is a halogen that naturally forms a negative ion
Lithium (Li), because it has a low effective nuclear charge and large radius
Neon (Ne), because it is a noble gas with a full energy level and small radius
Nitrogen (N), because it is a nonmetal that does not have a full outer energy level
2
Where are the most reactive metals located? (4 points)
Upper left of periodic table
Lower left of periodic table
Upper right of periodic table
Lower right of periodic table
2

230 N
−230 N
120 N
−120 N
2