FNR 225 Exam 2
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
What does it mean to have a mesic forest? What forest type is considered mesic?
not too wet and not too dry; Northern Hardwood
Where are Northern Hardwood forests located?
S.E. and S.C. Canada, N. New England and Lake States, higher elevation Appalachian mountains
What is the climate like in the Northern Hardwood forests?
cold, snowy winters and warm, humid summers
What is the topography of the Northern Hardwood forests?
most has been glaciated, resulting in a variety of soil types
What is the fire risk of the Northern Hardwood forests?
not common, but can occur in droughty locations
What is the land use history of the Northern Hardwood forests?
centuries of commercial timber harvest and clearing for agriculture
During what time period were forests in New England, New York, and Canada cleared for agriculture? What happened in the 1800s?
1600s and 1700s; forests were subsequently abandoned in 1800s when farming interests migrated to Midwest USA and Central Canada
What species dominate the Northern Hardwood forests?
deciduous species (with a few key conifers)
True or false: The Northern Hardwood forests are not a diverse mix of species.
False
As a mesic regions, climax species are _____.
very shade tolerant
What is the key pioneer species of the Northern Hardwood forests?
quaking aspen and red pine
quaking aspen (Populas tremuloides Michx.)
what species is this?
red pine (Pinus resinosa Ait.)
what species is this?
What is unique about quaking aspen?
most widely distributed native tree species of North America (Northern Hardwood and Boreal Mountains; western mountains)
quaking aspen prefers what types of sites?
upland, especially fire prone sites
How does quaking aspen reproduce?
reproduces by seed (Boreal or eastern forests) or root suckers
True or False: quaking aspen is shade tolerant, slow growing, and long-lived.
False. quaking aspen is shade intolerant, fast growing, and short-lived (60 yrs east or 150 yrs west)
Why is quaking aspen easily killed by fire? How do they respond to this?
thin bark; re-sprouts vigorously following cutting or burn
quaking aspen is a ______ in Lake States
pulpwood species
What is the wildlife value of quaking aspen?
favorite browse for deer, moose, elk, and beaver (also preferred species for beaver dams)
What tree species is unique to Northern Hardwood forests?
red pine
What types of soils does the red pine grow in?
Sandy or gravelly soils
True or False: red pine is a shade intolerant, early successional species
True
How often does red pine produce good seed crops?
3-7 years
red pine is ___ lived and can reach ___ in height
short-lived (less than 150yrs); 70 ft
What factor of red pine makes them favorable for telephone poles, log homes, and timber/pulp?
they have excellent tree form
What is the wildlife value of red pine?
seeds eaten by squirrels, chipmunks, and birds
True or false: red pine is the most planted and commercially important species of tree in the Northern Hardwood forests.
True
What serial species is important for the Northern Hardwood Forests?
eastern white pine
What sites does eastern white pine grow best on?
mesic sites
eastern white pine is a ____ species and ____ in shade tolerance.
mid-successional; intermediate
eastern white pine is ____ growing and _____ for eastern species.
moderately fast; great longevity (greater than 500 years)
At the time of European settlement, eastern white pine was _____ in North America
among the largest trees; 200+ ft in height and 10 ft diameter
Which tree was the most important to the early settlement of the NE area. Why?
eastern white pine; crucial for ship masts and lumber (trees marked with an arrow to avoid illegal harvest)
What helps maintain eastern white pine species composition?
natural regeneration
What threatens the eastern white pine?
white pine blister rust from Asia and white pine weevil
eastern white pine (Pinus strobus L.)
what species is this?
What are the most important climax species in the Northern Hardwood forests?
sugar maple, American beech, yellow birch, eastern hemlock, and American basswood
sugar maple are _____ and responds _____ following _____.
very shade tolerant; well to release; long periods of suppression
sugar maples are _____ with good seed in the fall every 2-5 years that require _____ unlike ____
prolific seeders; stratification; red/silver maples
True or false: sugar maples grow extremely fast and can reach only 50 feet in height
False; growth is slow but they reach 100+ ft height and 5ft dbh
Timber for sugar maples is valuable and ____ for what things?
increasing; furniture and bowley alleys
What is the wildlife value for sugar maple?
twigs browsed by deer and seeds and food source for smaller mammals
sugar maple
what species is this?
Which structure is tapped for maple syrup? How many gallons of sap produce 1 gallon of syrup?
xylem; 40 gallons
Which climax species is common throughout all eastern deciduous forests?
American beech
What sites do American beech require?
well-drained mesic sites
American beech are ____ tolerant and keep _____ due to ____.
very shade tolerant; lower limbs; dense shade
During mast years, American beech reproduce by ____ and also ____.
seed; root suckers
American beech is growth is ____ but the species is _____.
slow; long-lived reaching 100ft height and 4 ft dbh
Most large American beech trees have ____. How does this effect its commercial value?
heart rot; not commonly used for lumber
What disease has become a large issue for American beech in the N.E.?
beech bark disease
What is the wildlife value for American beech?
beechnuts favored by wildlife
American beech (Fagus grandifolia Ehrh.)
what species is this?
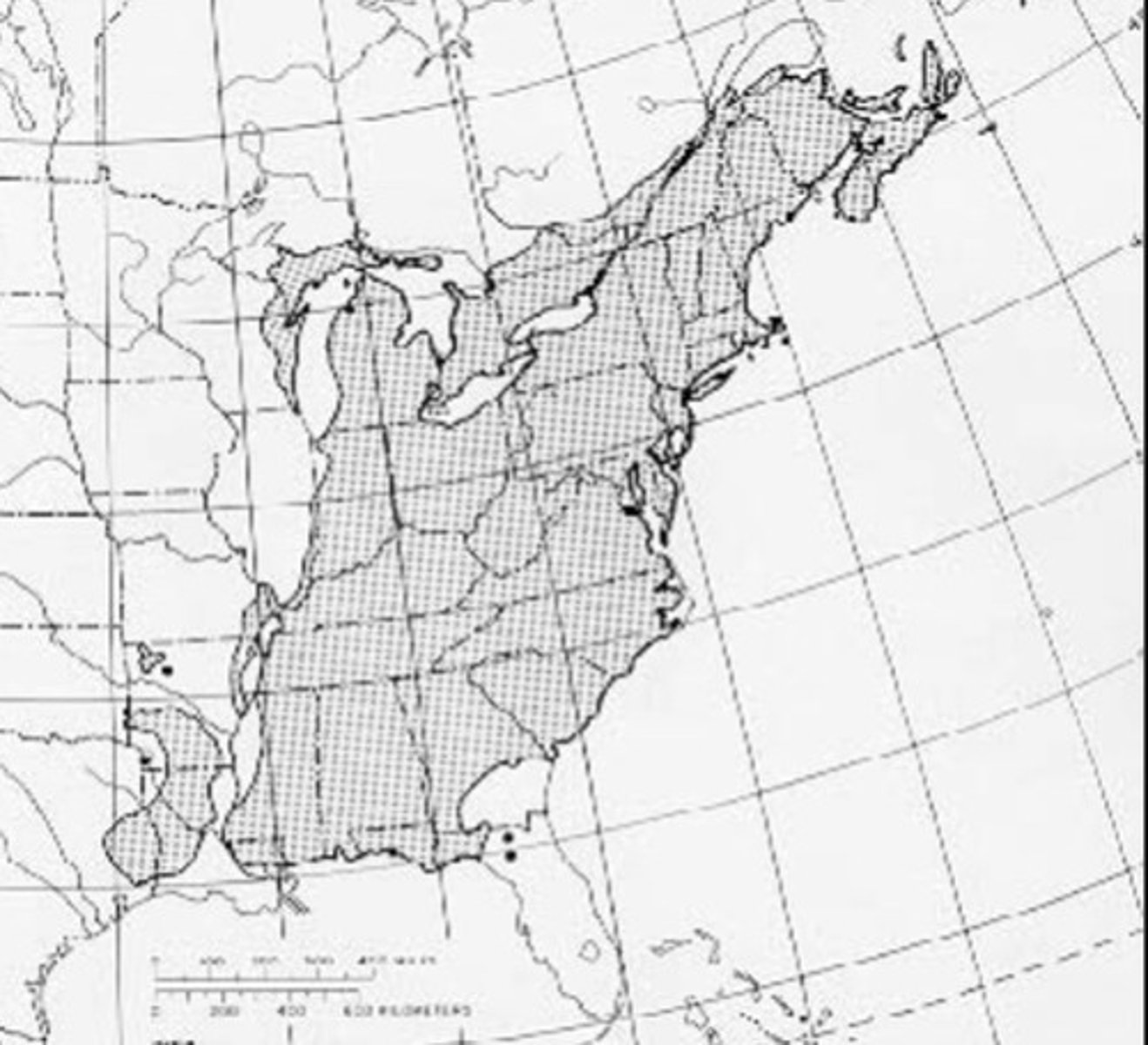
yellow birch is _____ in shade tolerance.
intermediate
Yellow birch are ____ and dispersal occurs via ____.
prolific seeds; wind
What types of soil do yellow birch seeds germinate on?
very sensitive mineral soil and rotting logs/stumps
Growth in yellow birch is ____ and they can reach ___.
slow but faster than maple/beech; 400+ yrs old and 100ft height/6ft dbh
yellow birch is the ______ birch species worldwide.
Largest and longest-lived; produces finest wood
What is the wildlife value for yellow birch?
seed important for overwintering birds
yellow birch (Betula alleghaniensis Britton)
what species is this?
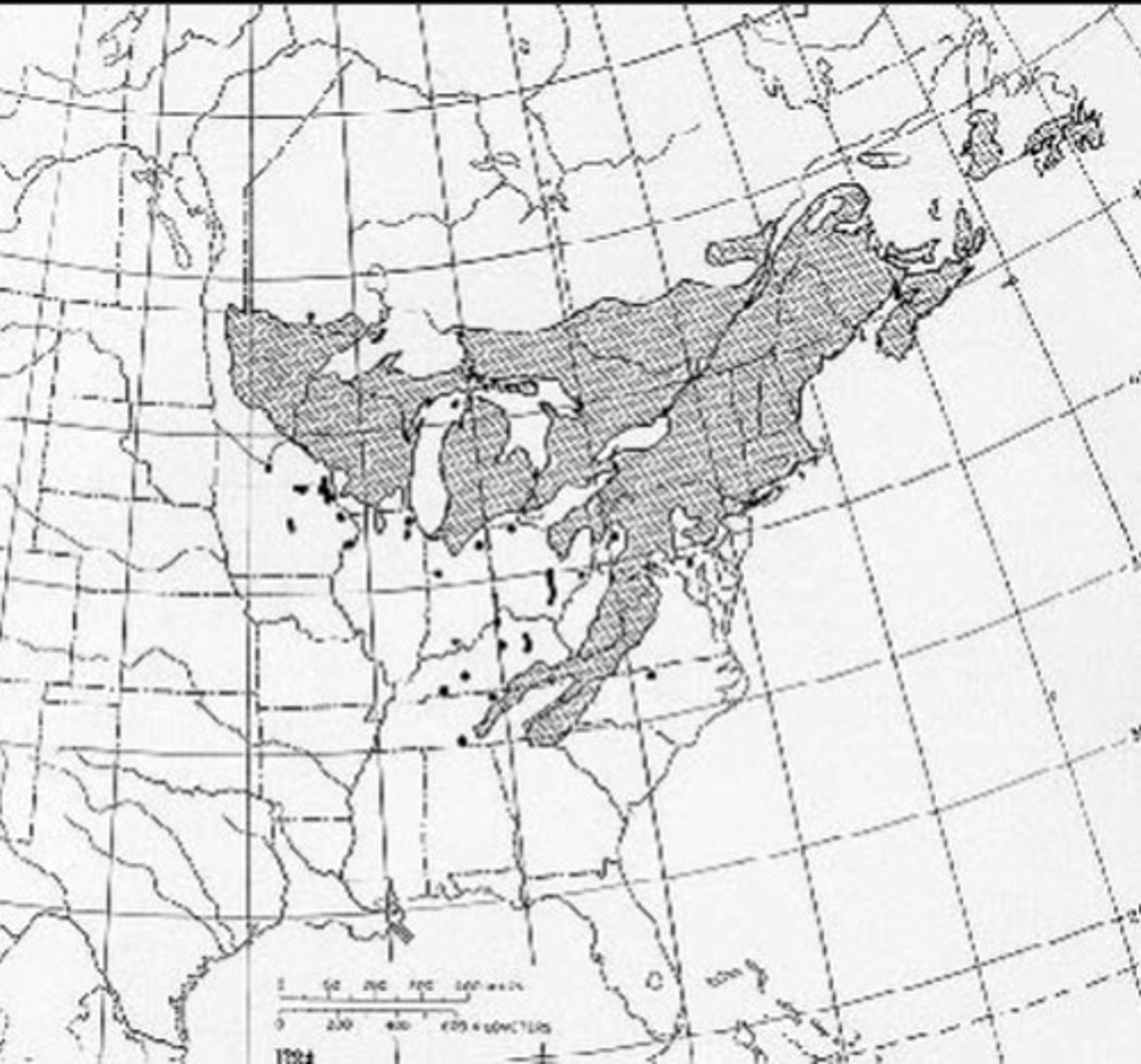
eastern hemlock occurs in the ______ of the Northern hardwood and mixed mesophytic regions
cool, moist valleys, coves, and slopes
Which eastern species is the ultimate climax tree and extremely shade tolerant?
eastern hemlock
eastern hemlock growth is ____ but remarkable ability to ____.
slow; respond to release
How long lived is eastern hemlock? How big do they get?
very long lived (900+ yrs) and 160ft x 7ft
True or false: eastern hemlock wood is extremely valuable.
False
What is the wildlife value of eastern hemlock?
important wildlife cover and winter shelter
What seriously threatens eastern hemlock?
hemlock wooly adelgid
eastern hemlock
what species is this?
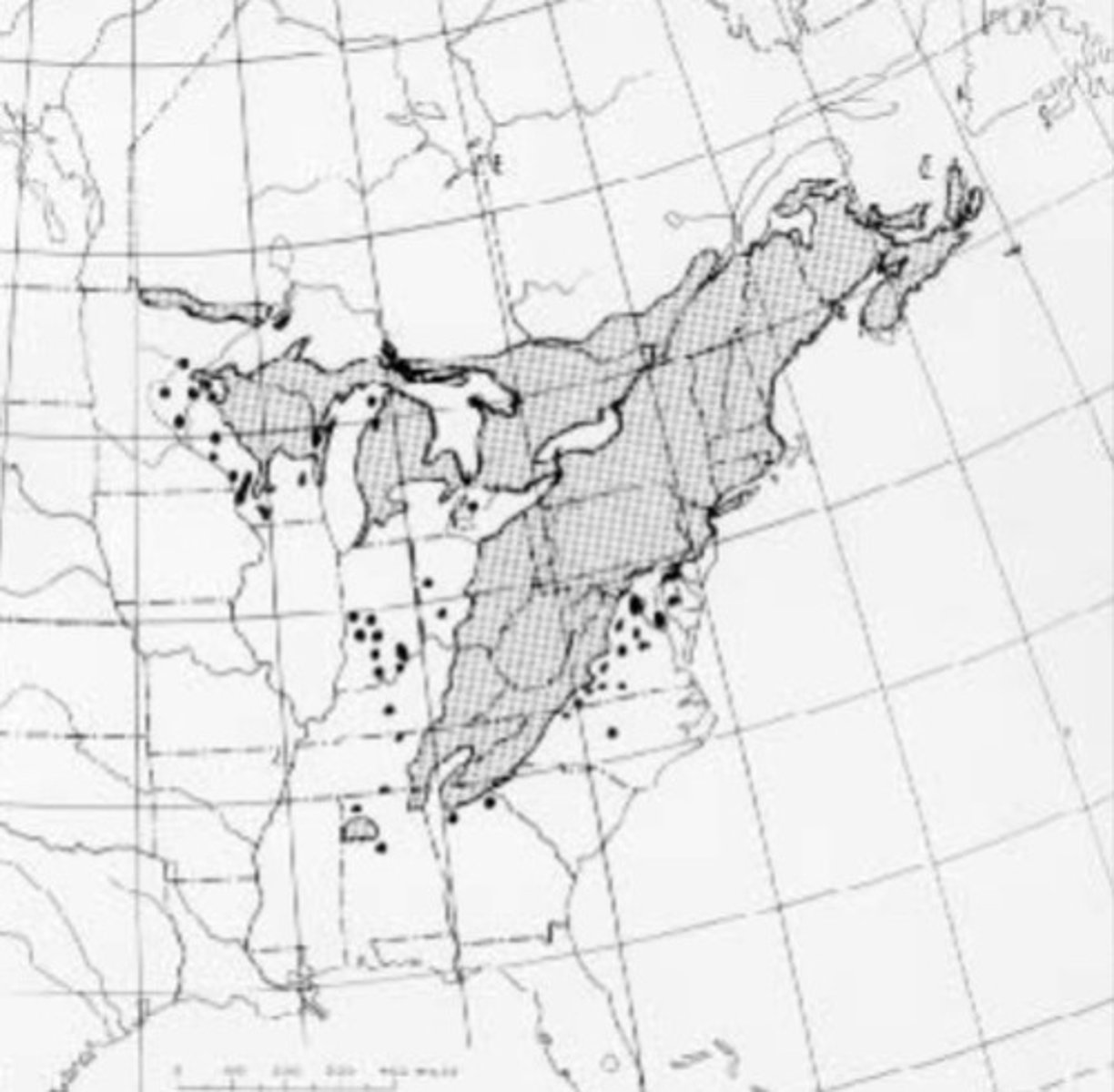
What regions and sites does American basswood prefer?
Northern Hardwood and Mesophytic regions; mesic, deep loamy soils
American basswood reproduces how?
seeds, but prolific stump sprouter (common to have multiple stems)
American basswood is ____ growing and ____ lived for a climax/shade tolerant.
fast and short lived (200 yrs)
American basswood was ____ to be cut commercially. Why?
one of the first; softer of the hardwoods so its more easily worked with
What is the wildlife value of American basswood?
deer browse shoots; birds and small animals eat fruit
American basswood (Tilia americana L.)
what species is this?
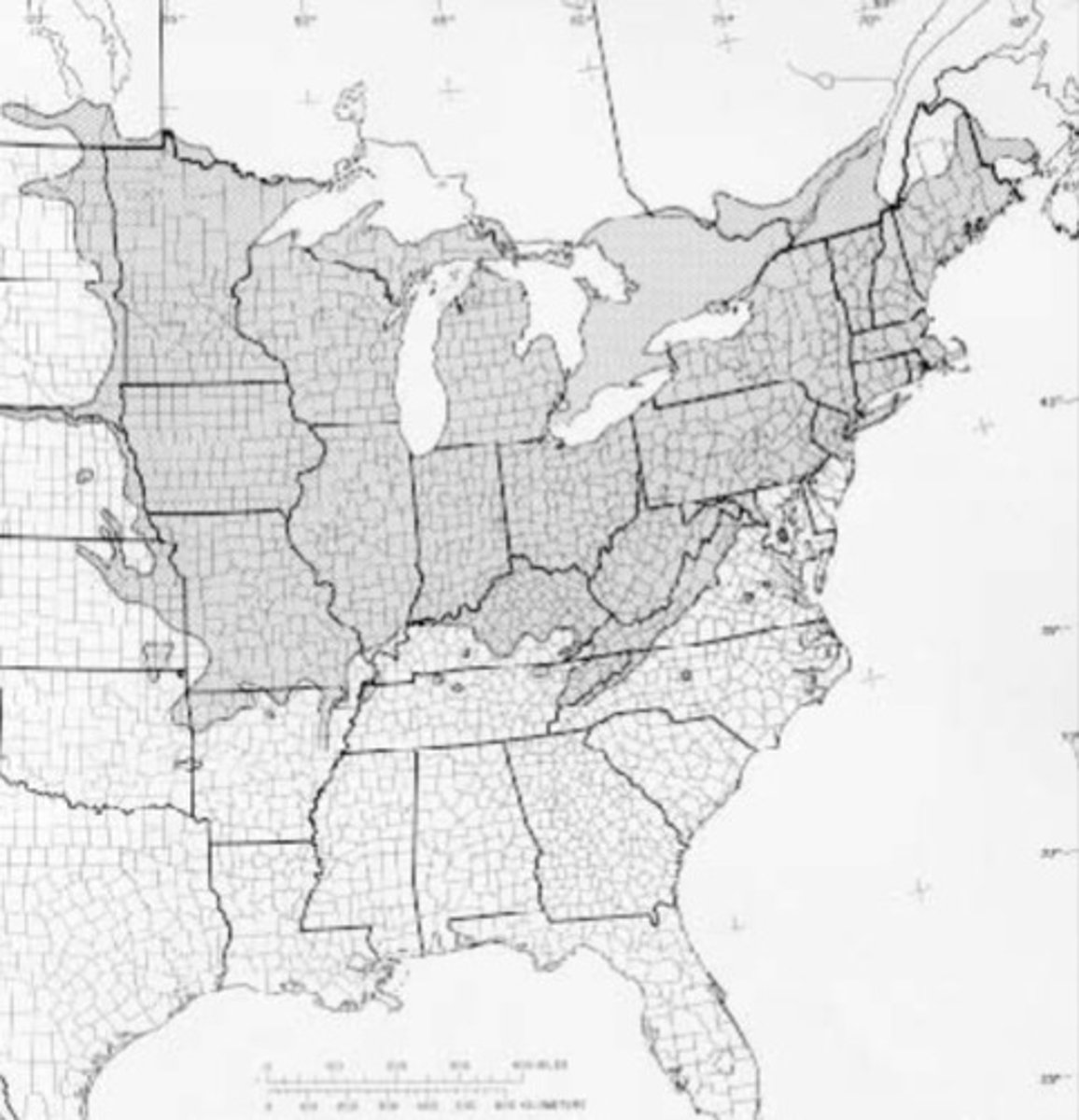
Where are oak-hickory forests located?
large part of eastern deciduous forest; includes much of land south of northern hardwood forest; Indiana
oak-hickory forest climate
- warmer and longer growing seasons than northern hardwood
- greater precipitation
- upland forests drier bcus of warmer temperatures
oak hickory forest topography
gently rolling hills and valleys
fires in oak-hickory forests
occur at low frequency because the region is humid, frequency increased by humans
history of fire management oak-hickory forests
Native Americans did prescribed burns
oaks and hickories are dominant, exact composition varies across sites, large geographic region
oak-hickory forest vegetation
Is Salicaceae mostly monoecious or dioecious?
dioecious
branch rooting
Propagation by cuttings very successful for Salicaceae family because the branches root
Populus traits contributing to increased interest in sequencing of genome/genetic improvement
fast growth, relatively good quality wood
Pulpwood (Populus) rotation age
8 years
Populus small log rotation age
15 years
Populus veneer rotation age
20 years
a 12-year old populus tree height and diameter
>60 feet tall, 1 ft diameter
American sycamore max dimensions
153 ft tall, 11-14 ft in diameter
American sycamore growth rates
pioneer species w/ rapid growth rates, also a climax species (reaches 500+ years)
American sycamore is now primarily used for what?
pulp
American sycamore plantation cycle length
7-10 years
What products are ash trees made into?
furniture, cabinets, tools, baseball bats
emerald ash borer tree kill count in Detroit, MI
over 6 million
How do emerald ash borers kill trees?
eating the vascular tissue that supplies nutrients to the tree
How many ash trees were in Indiana forests prior to the emerald ash borer?
147 million