Comparative Anatomy Lecture exam 1
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
Natural selection
environment put selective pressure on an organism
selective pressure
when a advantageous trait is favored in an environment
Alfred R. Wallace
Survival of the fittest
Mendel
Support Darwins natural selection, characteristics are inherited
Punctuated equilibrium
rapid change in species followed by stasis
Three tiers of evolution
Microevolution, macroevolution, mass extinction
homologous
features that share common ancestry regardless of function
Analogous
Features with similar function but different ancestry
Homoplastic
features with similar appearance but not function or ancestry (mimicry)
Vestigial organ
non-functioning structure (tailbone, wisdom teeth) NOT APENDIX
Two types of symmetry
Radial and bilateral
Radial symmetry
invertebrates have central axis
bilateral symmetry
vertebrates have midsagittal plane
Segmentation
repeating sections within an organism (vertebral column, tape worm)
Allometry
unequal growth rate in different body parts
Isometry
equal growth rate of all body parts
Increase size increases
stress on skeletal elements and oxygen/nutritiondemands
more surface area is typically ——-
better
hypertrophy
increase mass of a cell
atrophy
loss of tissue substance
Chordate characteristics
Notochord, pharyngeal slits, endostyle, dorsal nerve cord, postanal tail
Where does notochord develop from?
mesoderm
Pharyngeal slits
facilitate feeding/digestion
When does differentiation happen?
Gastrulation and Neurulation
Endostyle
accumulate food and move to GIT, becomes thyroid
ontogeny
embryonic development
Gastrulation
formation of gut, and germ layers
Neurulation
formation of neural tube
organogenesis
formation of organs
tissue
group of cells that perform a function
organ
a group of tissues that perform a function
order of zygote development
zygote —> morula —> blastula with blastoderm
Three germ cell layers
Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
What is in ectoderm?
Skin, central and peripheral nervous system, adrenal medulla
what is in mesoderm?
Kidneys, repro system, bone/cartilage, muscles,lymph, splean
What is in the endoderm?
GIT, Liver, endocrine system, bladder, respiratory tract
Types of tissue in body
Epithelium, connective tissue (bone), muscle, nervous
Squamous epithelium
flat
cuboidal epithelium
cube
columnar epithelium
tall, specialized
transitional epithelium
between squamous and cuboidal
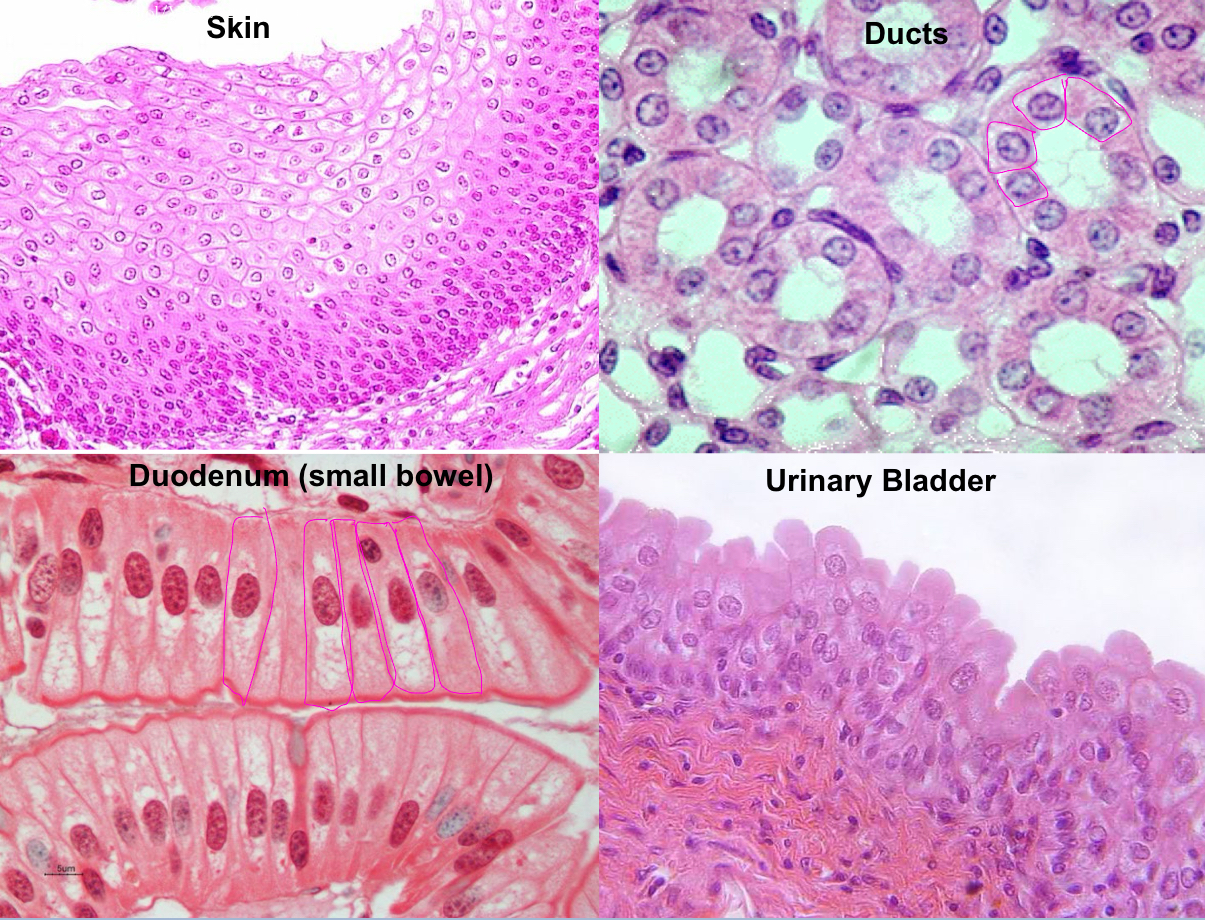
What type of epithelial cells?
Squamous, cuboidal, columnar, transitional
Exocrine gland
product secreted into duct
endocrine gland
products secrete into blood
Three types of cartilage
hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage
Reproductive toxicology research is done on —- bc——
Mice, rabbits, and zebra fish bc clear embryo and rapid reproduction
New in vertebrate after chordates
vertebral column replace notochord, cranium
Agnathans
without jaw (lampray)
Gnathostomes
jaw, make preditor prey relationship/change in diet, everything beyond agnathas
Placoderms
boney armor on external body
placode
embryonic structure that gives rise to other structures (hair follicle, feather, teeth)
Chondrichthyes
cartilagenous skeleton
chondro-
cartilage
Actinopterygii
endoskeleton ossification, otoliths (hearing)
Sarcopterygians
give rise to tetrapods
Amniotes
all terrestrial vertebrates except amphibia
Amnion
innermost embryonic membrane of reptile, bird, mammal
Aves
outnumber all other vertebrate besides fish
Mammalian characteristics
hair, mammary gland
Metatheria
early live birth
Eutheria
placental animals
Skull function
protect brain and sensory organs, support jaw
Chondocranium
Basal plate, ethmoid, optic, otic, occipital, cartilagenous
Splanchnocranium
arise from brachial arches, ancient skill, develop mandibular
Dermatochranium
predominate part of skull
Cranial bones
all bones in skull
Skull phylogeny
trend is to reduce number of bones and adapt to feeding style
Chondrichthyes
chondrocranium dominant
Snake
dislocation of mandible
avian sclerotic bones
hardened around eye
turbinates
filter and warm air in nasal cavity
Notochord/vertebral column function
locomotion, prevents compression, long axis, support head
ribs function
protect viscera, respiration
notochord in vertebrates
only present in embryo
vertebral column regions
cervical, thoracic, lambar, sacrum, caudal
processes
projections for muscle/tendon insertion
zygapophyses
pre and post, prevent twisting
diapophyses and parapophyses
rib articulation only in thoracic
cervical
transverse foramen
acoelous
flat end vertebrae
amphicoelous
limit motion, shark
heterocoelous
saddle joints allow flexibility (birds)
Annulus fibrosus
fibrocartilage ring in intervertebral disk
nucleus pulposus
gel-like notochord remnant center of intervertebral disk
two parts of intervertebral disk
annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus
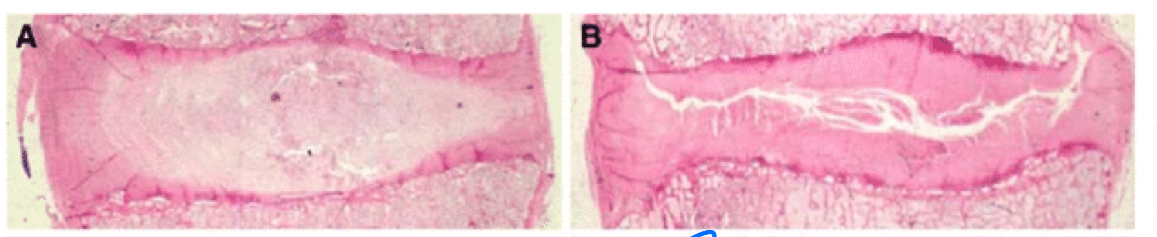
IVDD
B. lack nucleus pulpous
Sternum origin
endochonrium
true ribs
meet at sternum
gastrila vs thoracic
dermal and abdominal ribs vs upper ribs endo
Atlas
nodding
axis
twisting
pectoral girdle evolution
separate skill from limbs
adipose fin
small fin dorsal near caudal fin
pelvic vs anal fin
pelvic more cranial ventral
clavicle in amphibians
may be present
no clavicle in mammals
dog, horse, cattle, sheep
yes clavicle in mammals
primates, cats, mouse, rabbit, bullfrog
furcula
wishbone/clavicle in bird
pectoral girdle in mammals
scapula and clavicle