BCHM Exam 3 Before Going on
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Describe how enzymes differ from other catalysts.
enzymes …
are usually proteins, some exceptions (ex. catalytic RNA, ribosomal subunit)
are specific, have an active site where their substrate bonds
moonlighting enzymes: can bind to more than one substrate (have a main reaction and a secondary reaction
can be regulated (turn up/down, on/off)
aren’t always active
work at mild conditions
works at physiological pH and ambient temperature
can’t increase temperature of environment because it risks denaturing proteins
can’t increase concentration of the reactants because there is no space
Explain how enzymes exhibit specificity for their substrates and products.
2 theories
1) lock and key theory
substrate has a shape that matches the active site, the two molecules bind
2) induced fit theory
more accurate model
the active site of the enzyme is flexible and will mold to the shape of the substrate
moonlighting enzymes can mold to the shape of multiple substrates (why they can catalyze different reactions)
- fact- it would take 20 years for a peptide bond to break without an enzyme (chymotrypsin)
Describe how enzymes are classified.
3 types
addition, removal, rearrangement
but translocase is exception, its function is transport
1) oxidoreductase
oxidation-reduction reactions
add/remove electrons
always have an electron carrier (ex. NADH, FAD, FADH2)
oxidation- loss of electrons
reduction- gain of electrons
2) transferases
transfer a functional group from one molecule to another
do NOT use ATP for energy
3) hydrolases
cleave bonds by adding a water molecule, splits into two molecules
ex. phospholipase A2 (PLA2)
4) lyases
remove functional groups via non-hydrolysis reactions
NO WATER
result in the addition/removal of a double bond
5) isomerases
rearrange functional groups within a molecule
mutases: transfer functional groups from one position to another
epimerases: invert functional groups about asymmetric carbons
6) ligases
use ATP to break bonds
ADP and P are released, P is not added to molecule
form C-C, C-S, C-O, and PO3²- ester bonds
7) translocases
move molecules (usually) across the membrane
ex. integral proteins (ATP-ADP translocase)
Relate a reaction’s activation energy to its rate.
activation energy is the energy needed for a reaction to reach its transition state and begin a chemical reaction
lower activation energy increases the rate of the reaction
Describe an enzymes effect on activation energy and the change in energy of a reaction.
enzymes decrease activation energy through the stabilization of the transition state
the transition state is where the enzyme is bound tightest to the substrate
the active site brings the reactants closer together, making product formation quicker
have no effect in the change in energy of a reaction (therefore no effect on exergonic/endergonic)
Describe the roles of the different cofactors in catalysis.
cofactors work with an enzyme to aid in the catalysis
they can be organic/inorganic
metal ions
inorganic cofactors
used for oxidation/reduction
coenzymes
organic cofactors
2 types
cosubstrates: temporarily associate with the enzyme (ex. NAD+, NADH)
prosthetic groups: covalently linked to the enzyme, more permanent
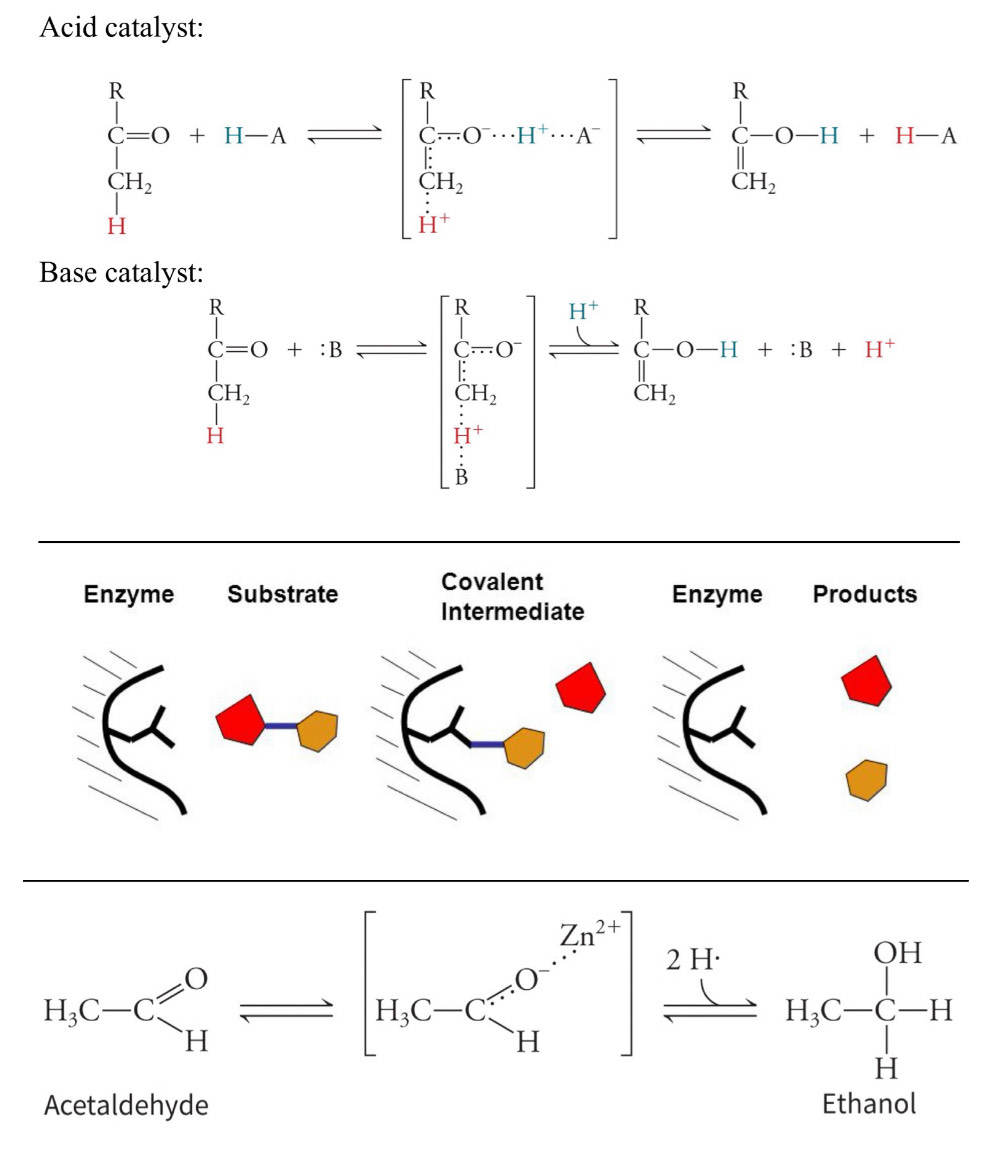
Identify the three types of chemical catalytic mechanisms.
1) acid-base catalysis
proton is transferred (accepted/donated, some have both) between the enzyme and substrate to stabilize the transition state
acid catalyst- proton is donated
base catalyst- proton is accepted
remember that the enzyme must end how it started, know where H goes at end
2) covalent catalysis
covalently bond to a substrate during the transition state
transient/temporary covalent bond
nucleophile (in enzyme active site) forms the bond in search of an electron poor center
two-part reaction process with intermediate between them, first part is covalent bond forming, second part is it breaking (usually higher energy bump)
3) metal ion catalysis
mediate oxidation-reduction reactions to promote reactivity of other groups in enzyme’s active site through electrostatic effects
stabilize the transition state
Assign roles to specific amino acid side chains during catalysis.
1) acid-base catalysis
AAs with ionizable side chains
Asp, Glu, His, Lys, Cys, Tyr
Not Arg
2) covalent catalysis
Ser, Tyr, Cys, Lys, His
deprotonated form because they are great nucleophiles