🚨 | Chapter 15: Anatomy and Physiology of Special Senses
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What are the special senses in humans?
Vision, smell, taste, hearing, and balance.
What percentage of sensory receptors in the body are located in the eyes?
70%.
What percentage of the cerebral cortex is involved in processing visual information?
40%.
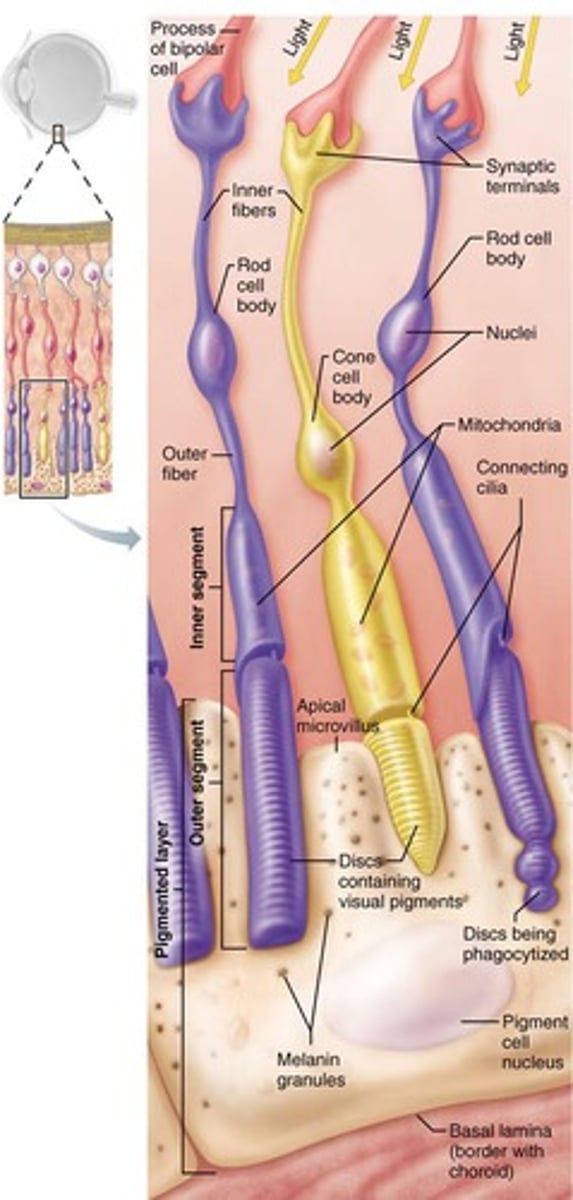
What are the visual receptor cells called?
Photoreceptors.
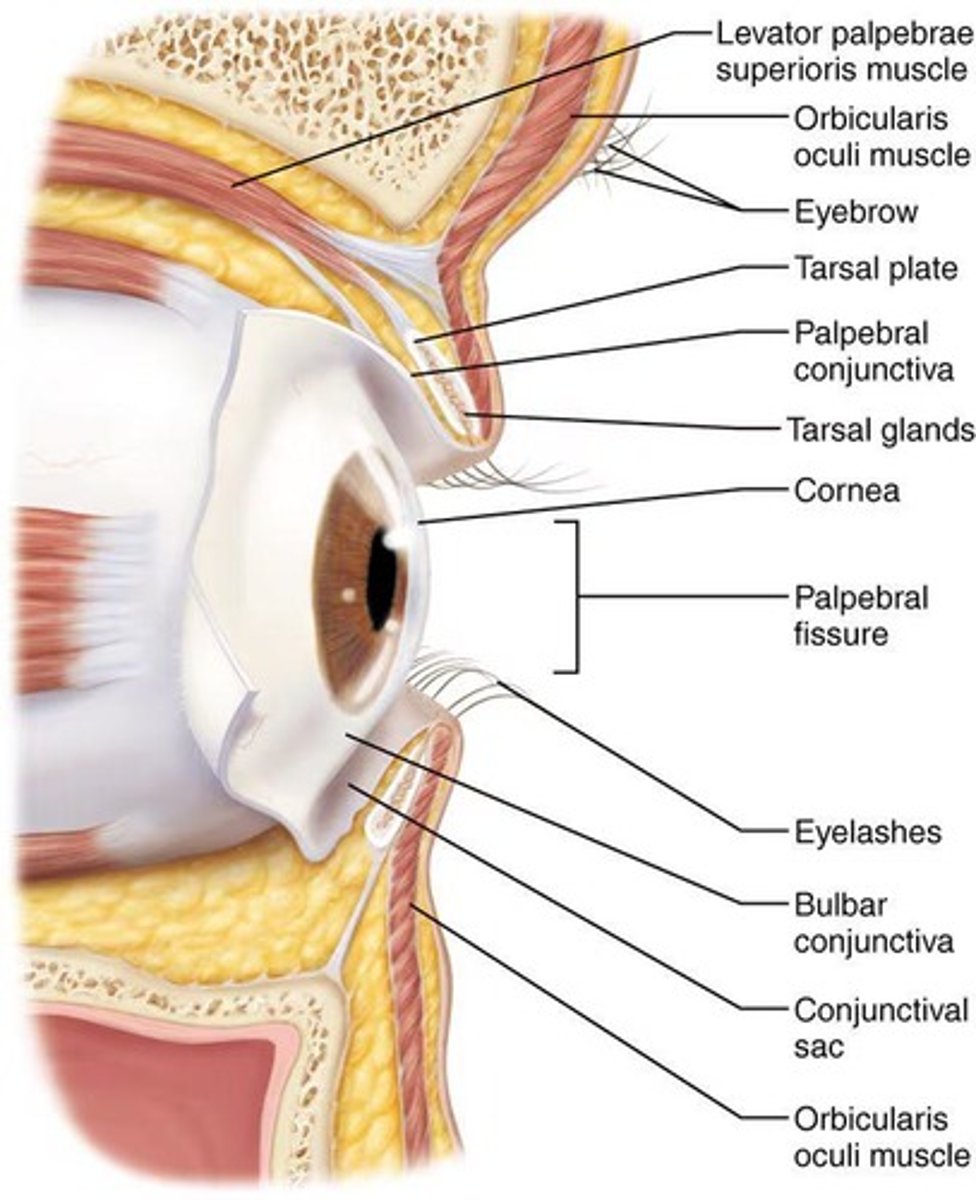
What are the accessory structures of the eye?
Eyebrows, eyelids, conjunctiva, lacrimal apparatus, and extrinsic eye muscles.
What is the function of eyebrows?
Shade the eyes from sunlight and prevent perspiration from running into the eyes.
What is the role of the orbicularis oculi muscle?
It is the eye-closing muscle.
What is the function of the levator palpebrae superioris?
It opens the eye.
What is conjunctivitis?
Inflammation causing redness of the conjunctiva.
What does the lacrimal gland produce?
Lacrimal fluid (tears).
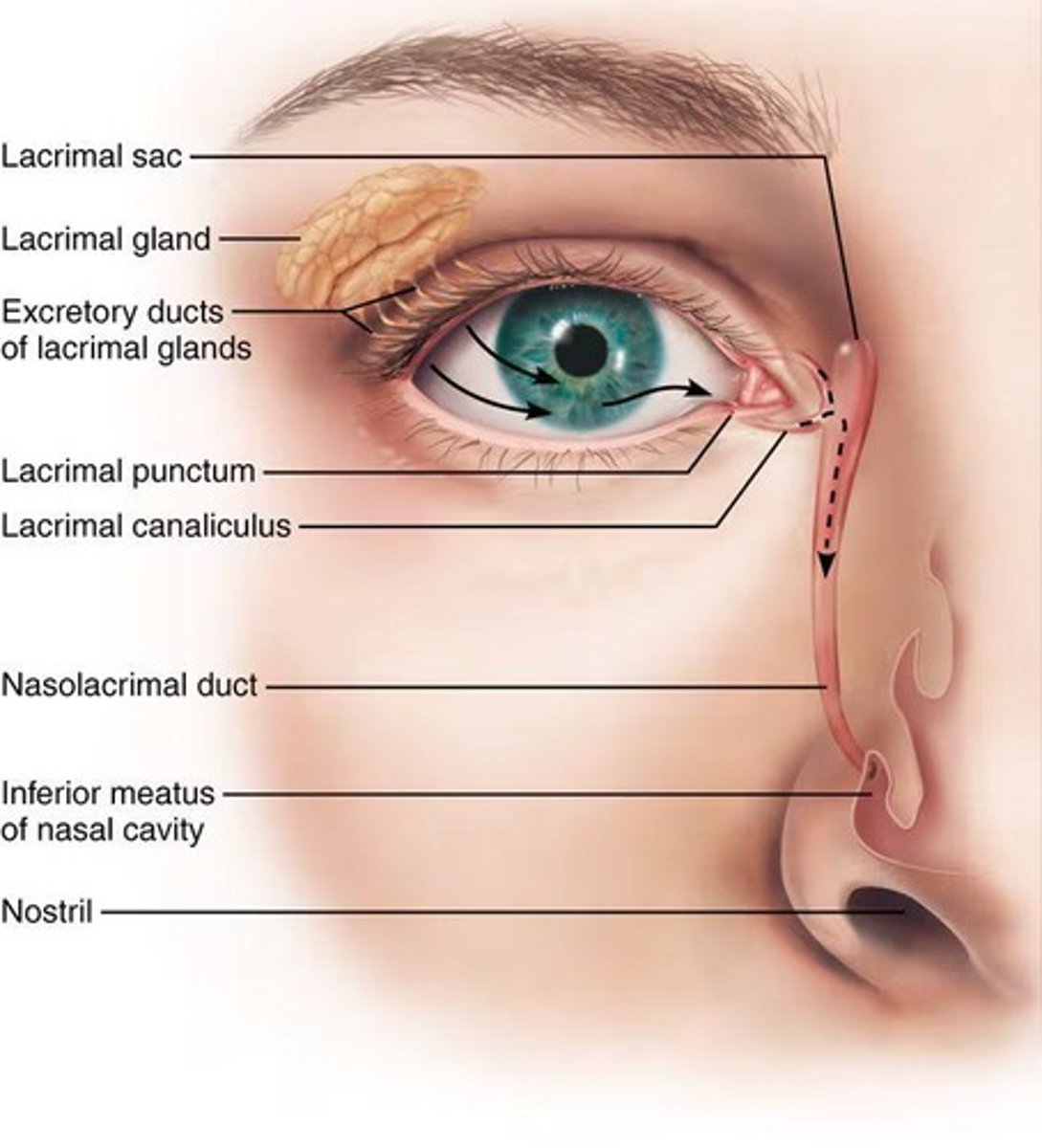
What is the pathway of tears after they are produced?
Tears spread across the eye, drain into the lacrimal sac, and then through the nasolacrimal duct to the nasal cavity.
What is strabismus?
Misalignment of the eyes caused by a lack of coordination in the extrinsic eye muscles.
What are the three layers (tunics) of the eye?
Fibrous layer, vascular layer, and inner layer.
What are the two segments of the eye's internal cavity?
Anterior segment and posterior segment.
What is the sclera?
The white part of the eye that protects the eyeball and serves as an anchoring site for extrinsic eye muscles.
What is the cornea?
The transparent part of the eye through which light enters.
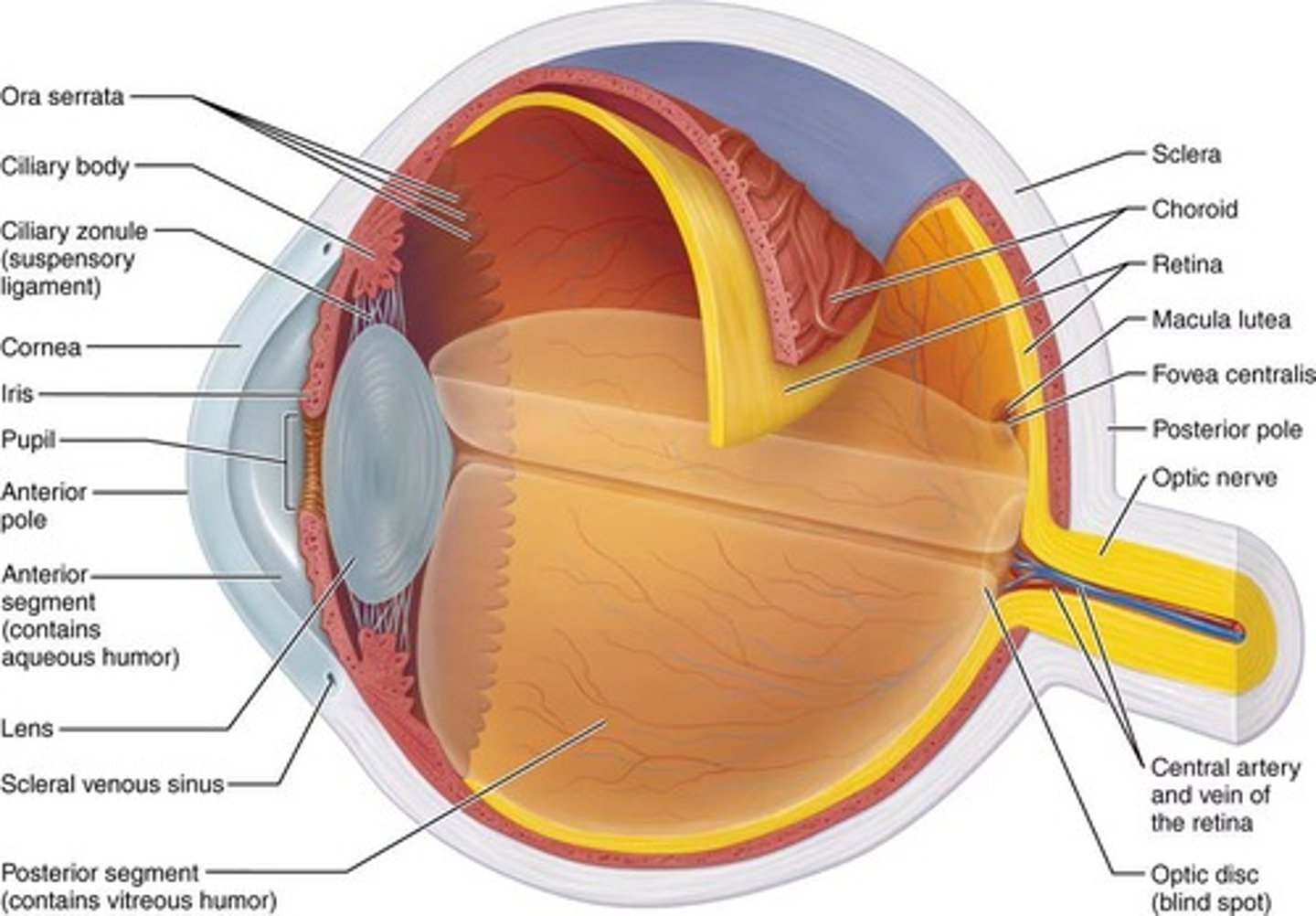
What is the choroid?
The highly vascular and pigmented membrane that nourishes the other layers of the eye.
What is the function of the ciliary body?
It contains smooth muscle responsible for focusing the lens.
What is the iris?
The visible, colored part of the eye that lies between the cornea and lens.
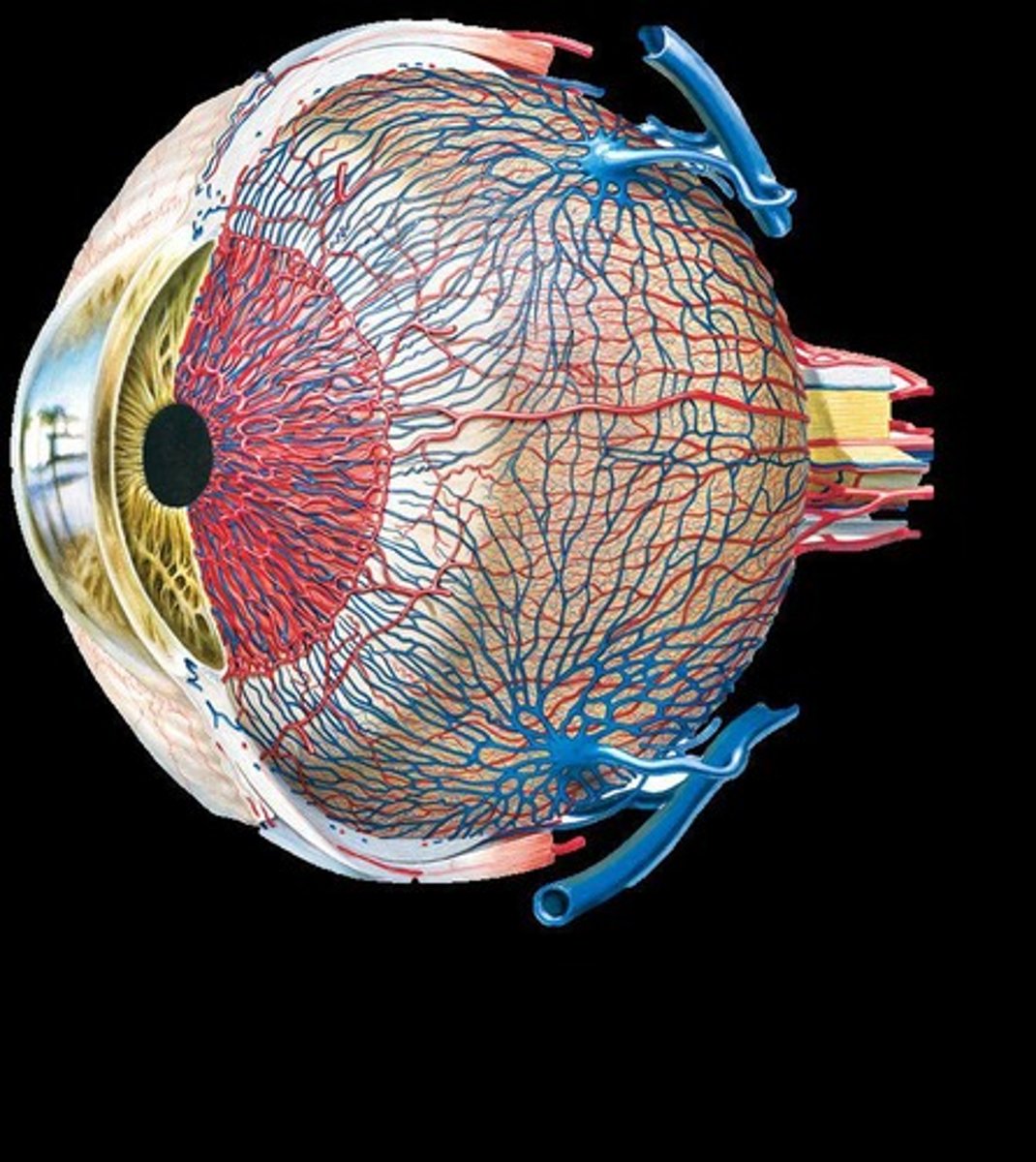
What are the two types of photoreceptor cells in the retina?
Rods (sensitive to low light) and cones (function best in bright light and enable color vision).
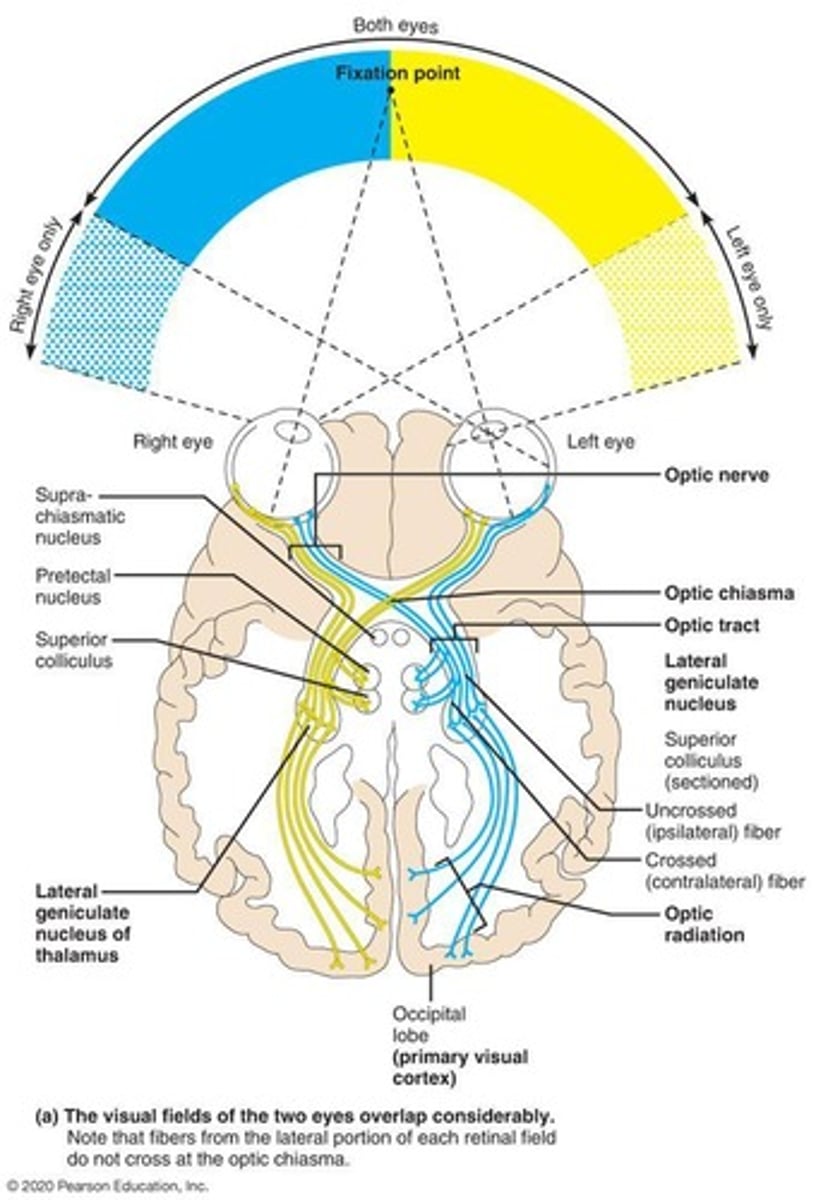
What is the visual pathway to the cerebral cortex?
Optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract, and primary visual cortex.
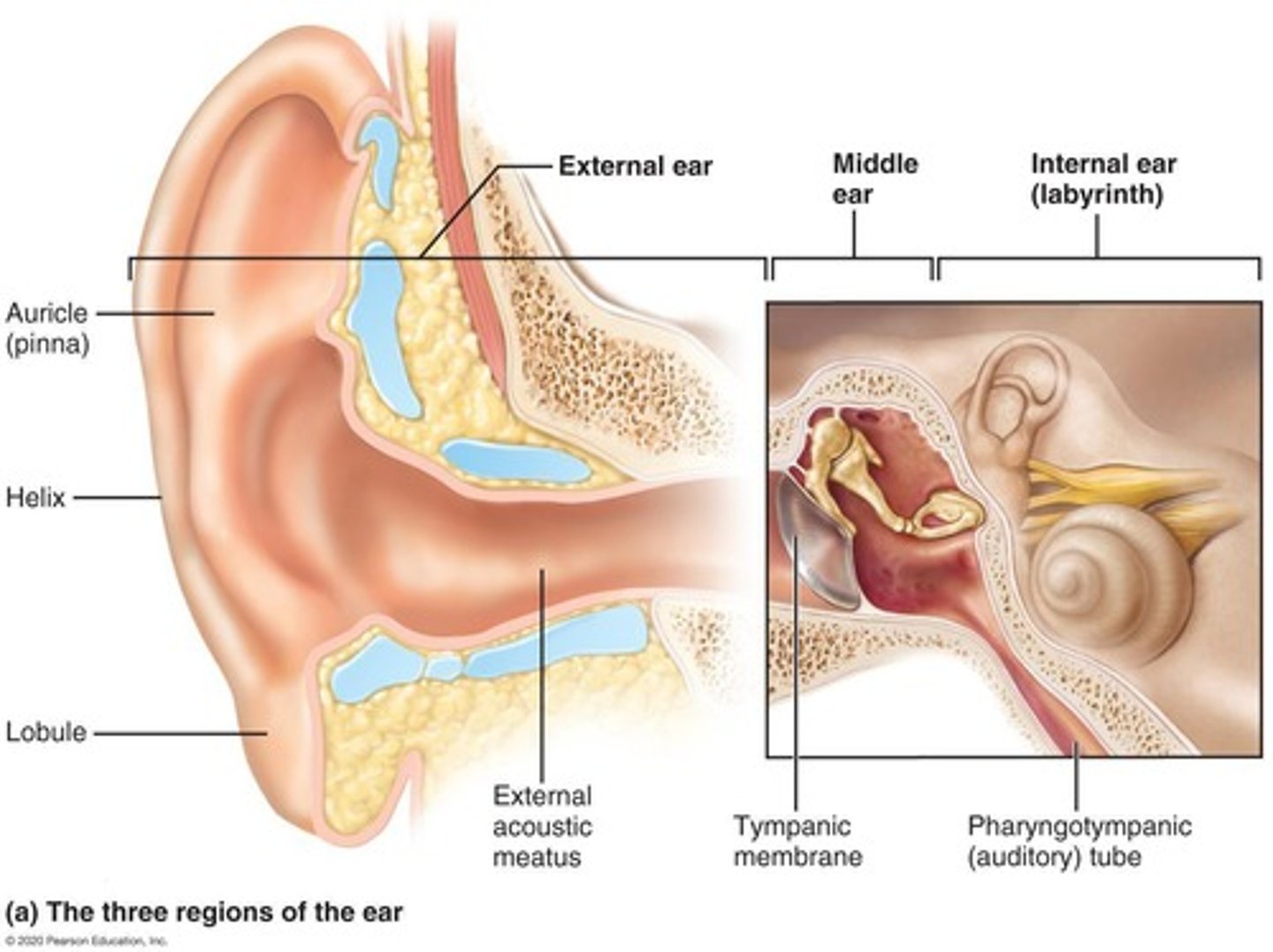
What are the three main parts of the ear?
Outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
What is the tympanic cavity?
A small, air-filled space in the middle ear.
What is the function of the ear ossicles?
Transmit sound from the external ear to the internal ear.
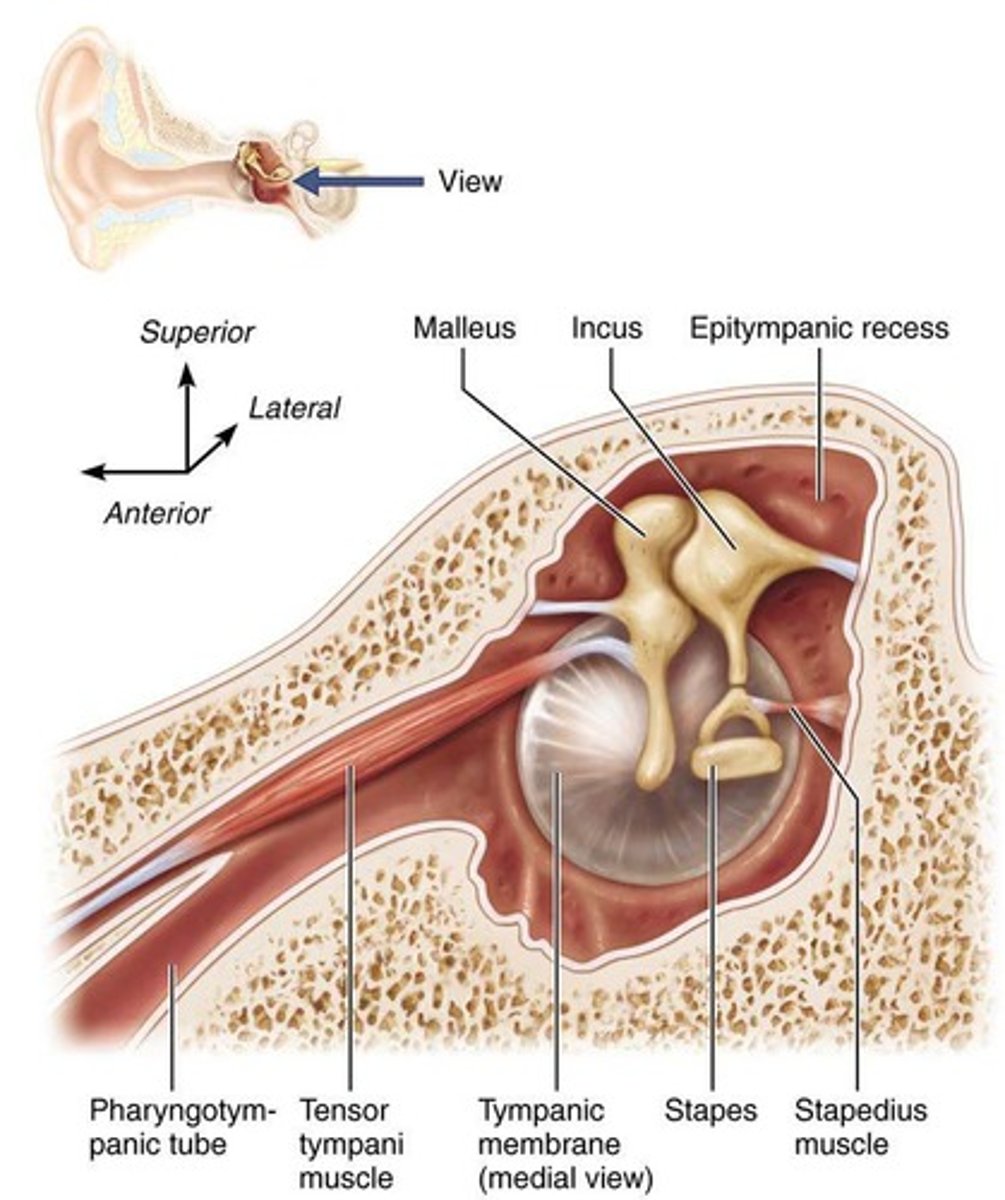
What are the two tiny skeletal muscles in the middle ear?
Tensor tympani and stapedius, which protect the ear from loud sounds.
What are the two main divisions of the inner ear?
Bony labyrinth (filled with perilymph) and membranous labyrinth (filled with endolymph).

What is the cochlea?
A spiral-shaped structure responsible for hearing, divided into three fluid-filled chambers.
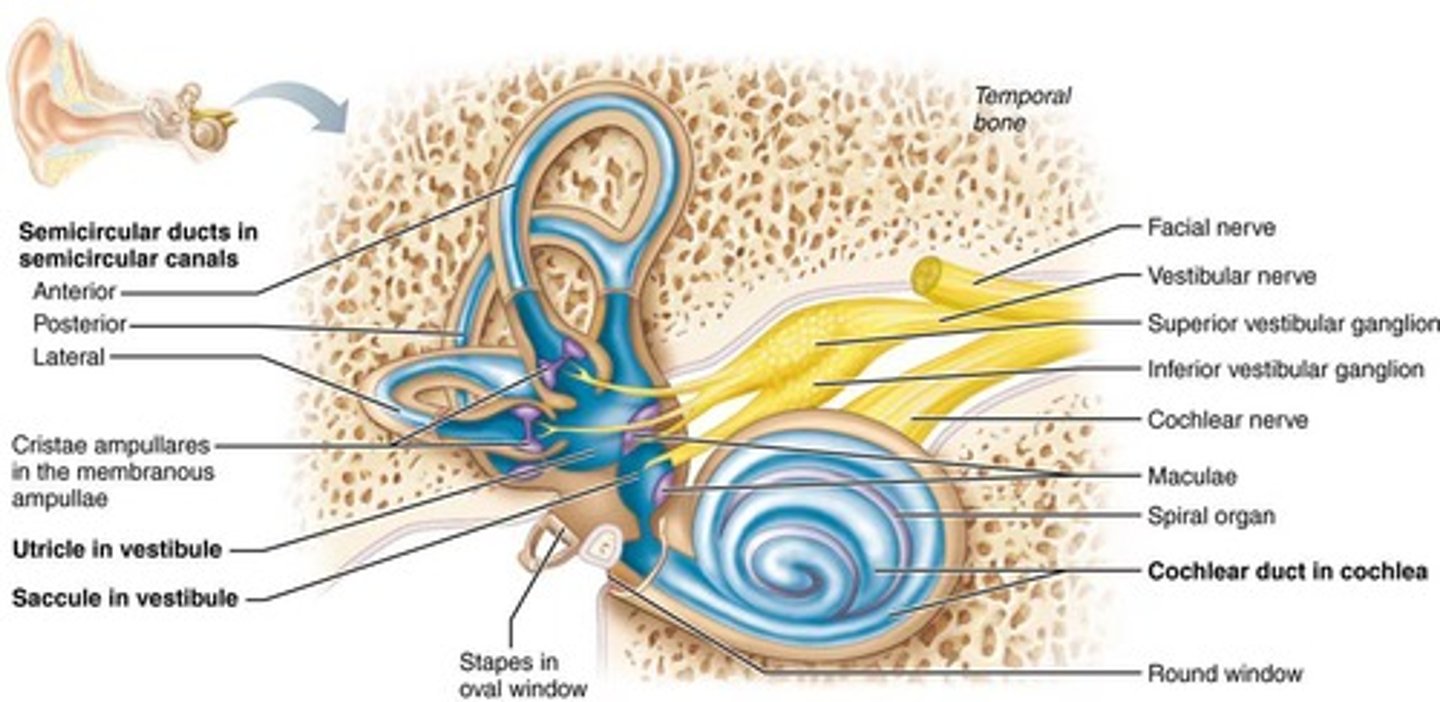
What is the function of the utricle and saccule?
Concerned with balance and position of the head while stationary.
What do the semicircular canals detect?
Rotational movement.