Peripheral Nervous System and Spinal Cord (Part 1)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
brain and spinal cord
Central Nervous System (CNS)
nervous structures outside of brain and spinal cord (e.g. nerves and ganglia)
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
specific type of communication between the CNS and structures in the body in the form of electrical impulses and chemical or electrical signals that travel through the PNS
innervation
Afferent innervation that reaches conscious awareness
sensory innervation
Efferent innervation that causes a structure to do something (e.g. causes muscles to contract, glands to secrete)
Motor innervation
nerve cells; transmit innervation in for of electrical impulses and chemical or electrical signals
Neurons
sensory
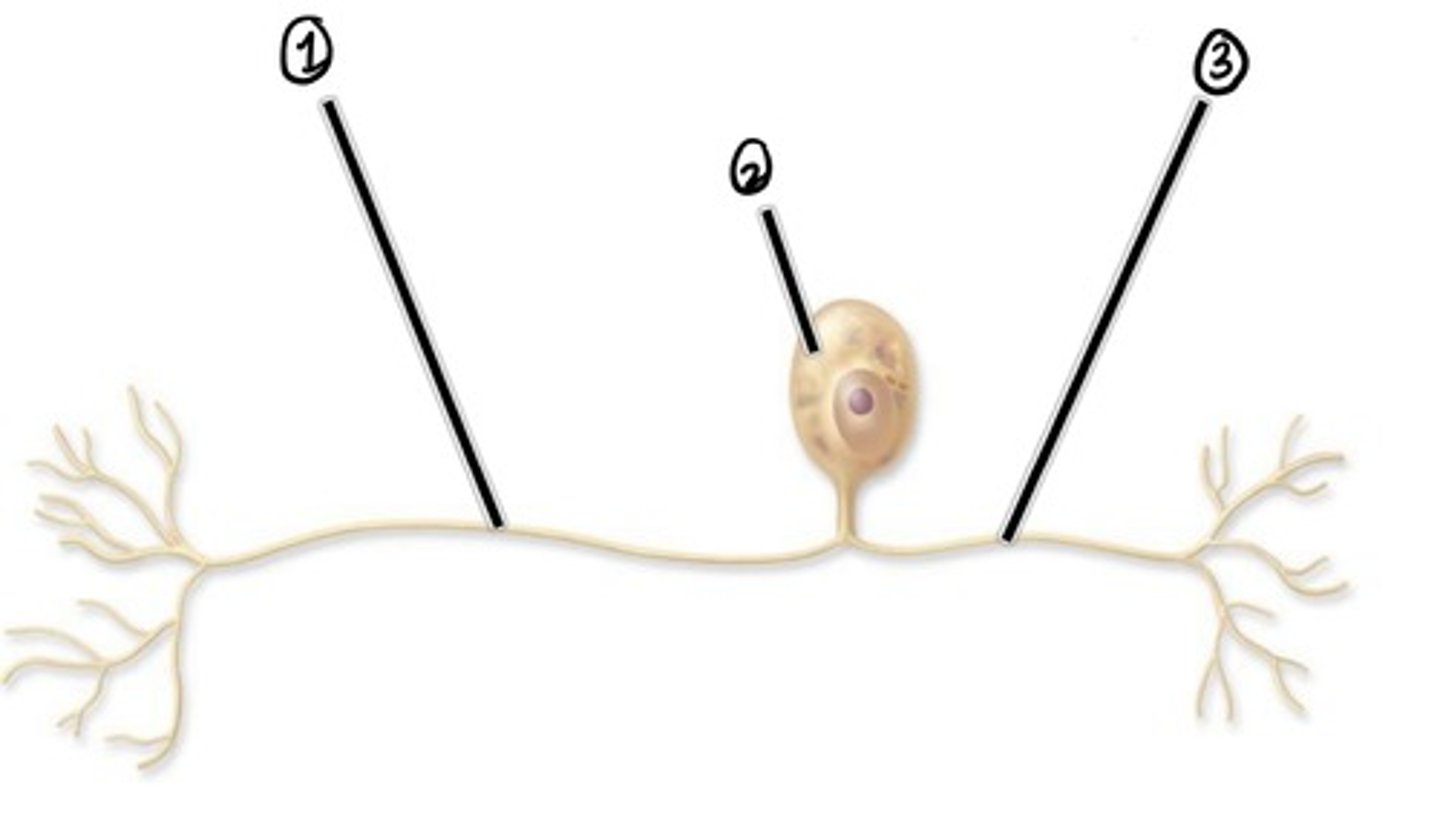
what type of nerve cell is this?
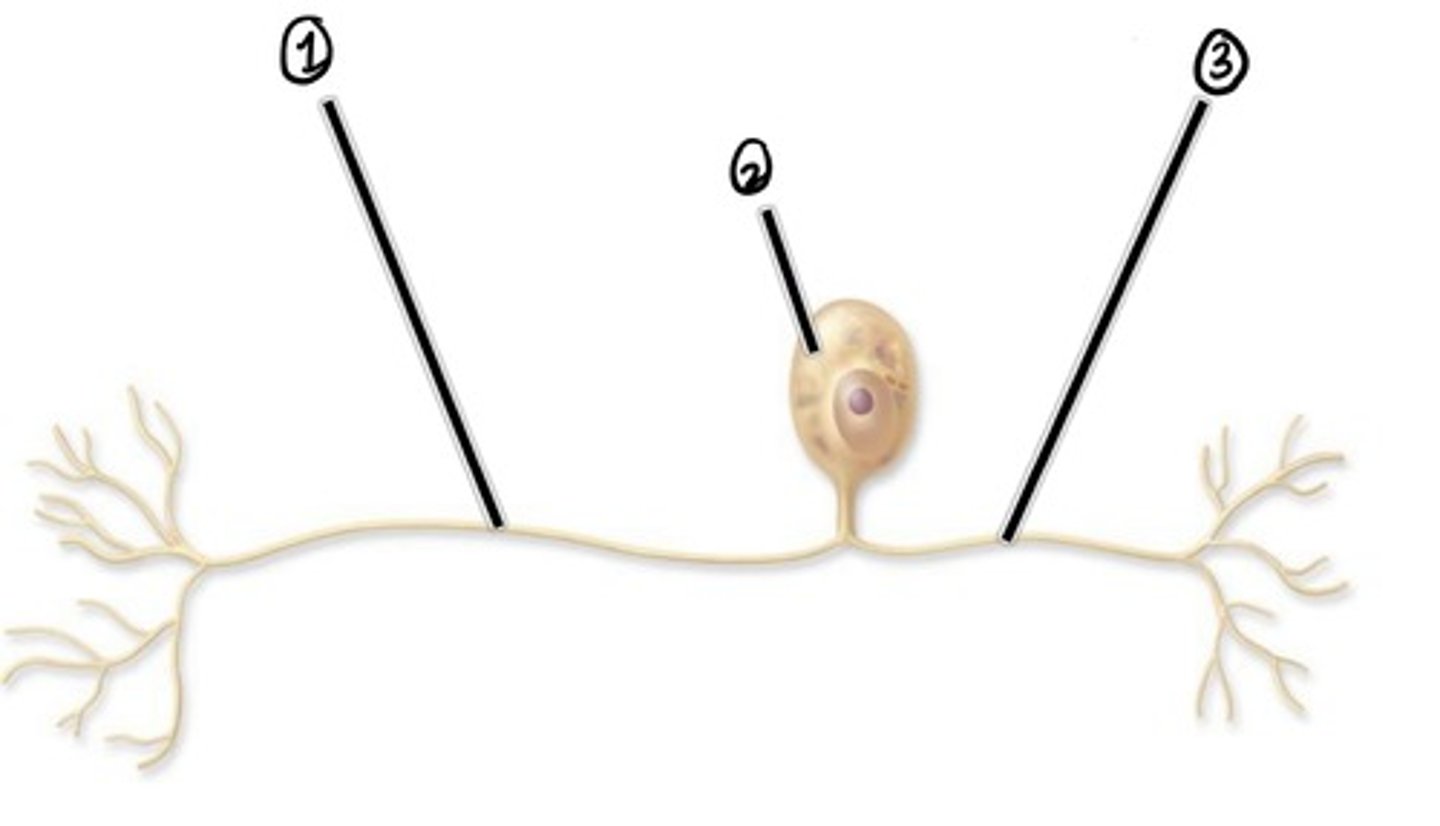
Peripheral Process (carried impulse to cell body)
Assuming the direction of impulse is left to right, what is 1
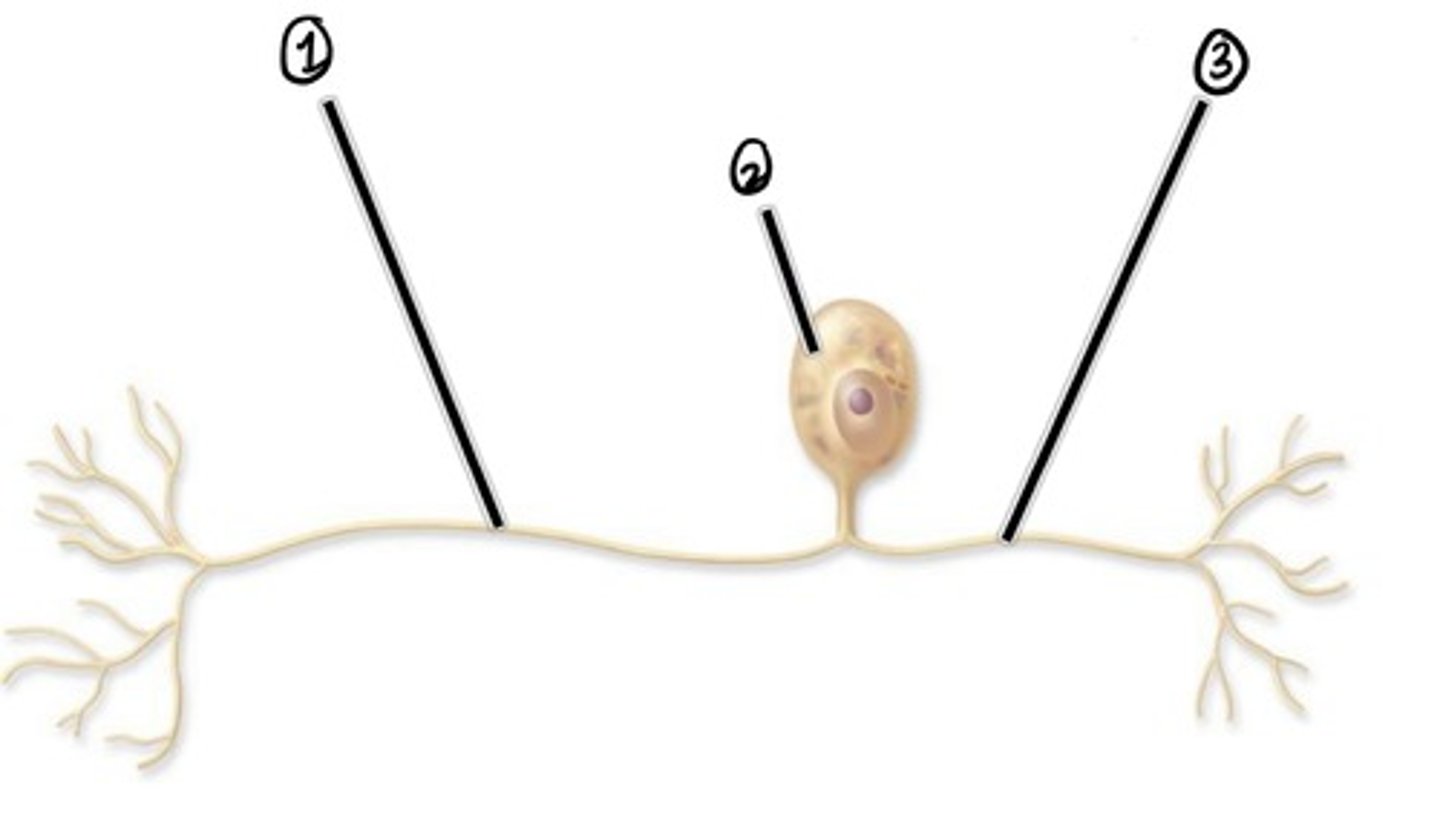
cell body
Assuming the direction of impulse is left to right, what is 2
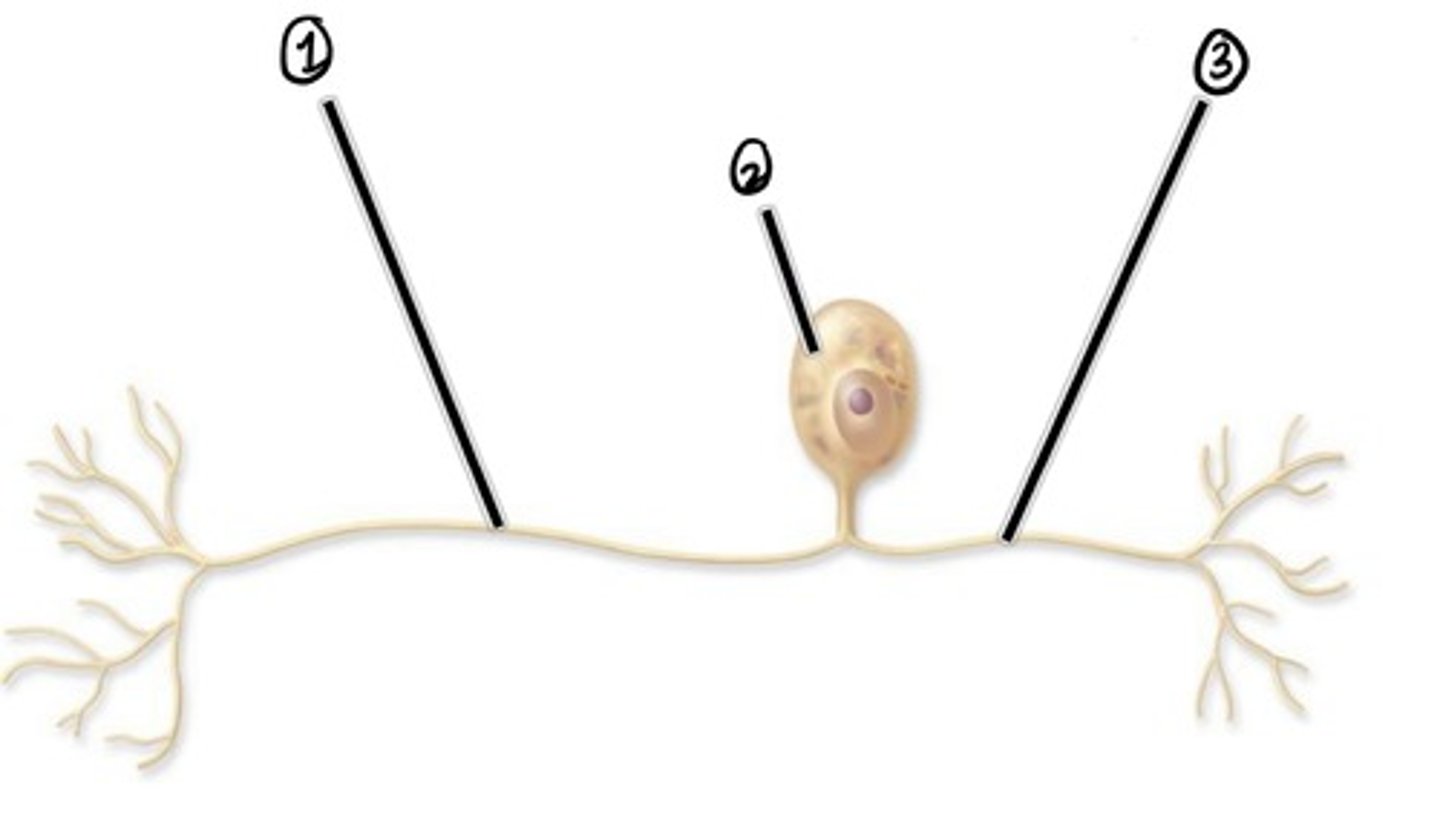
central process (carries impulse from cell body)
Assuming the direction of impulse is left to right, what is 3
motor
what type of neuron is this?
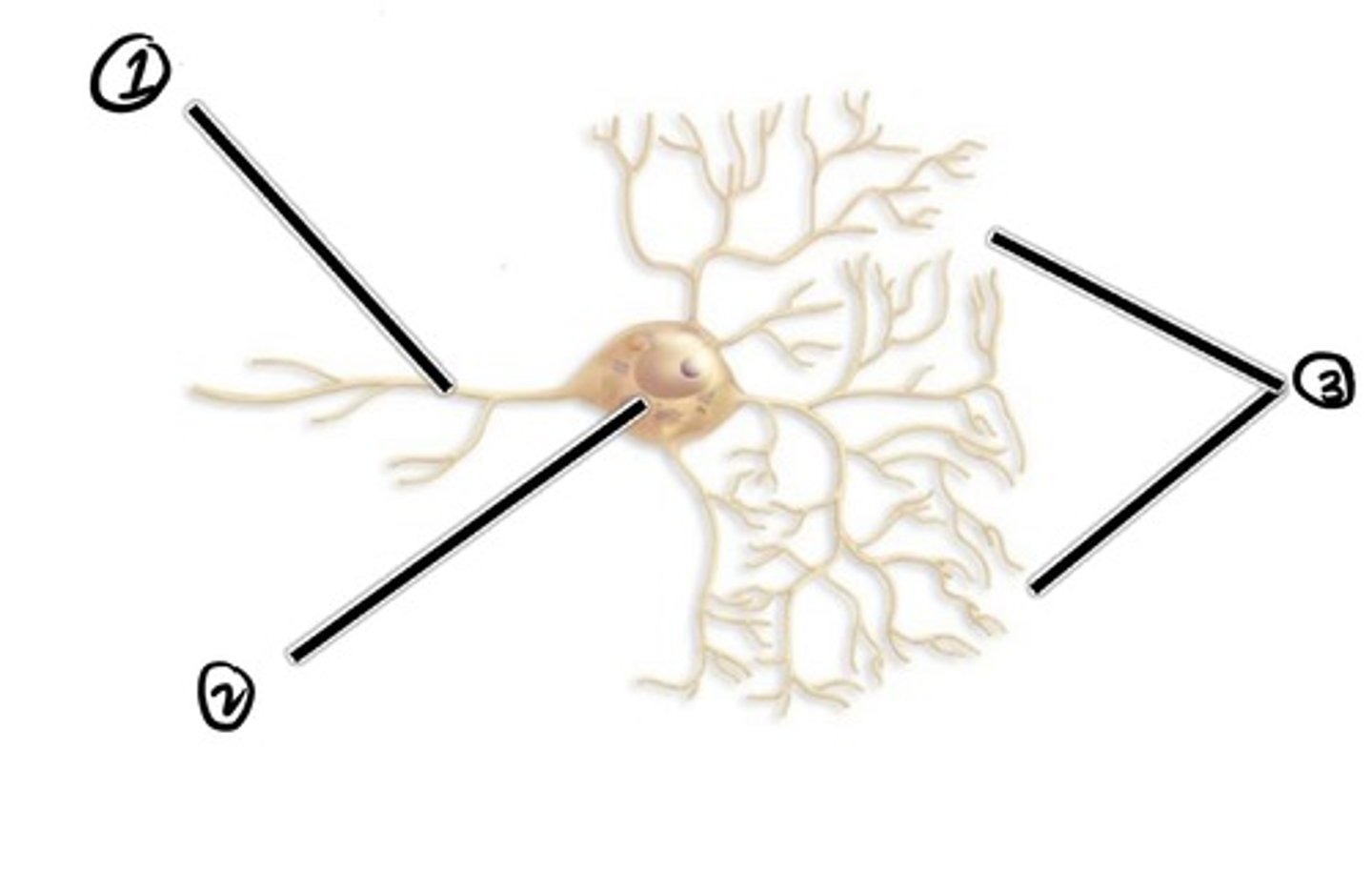
Axon (carried impulse from cell body)
assuming the direction of impulse is right to left, what is 1
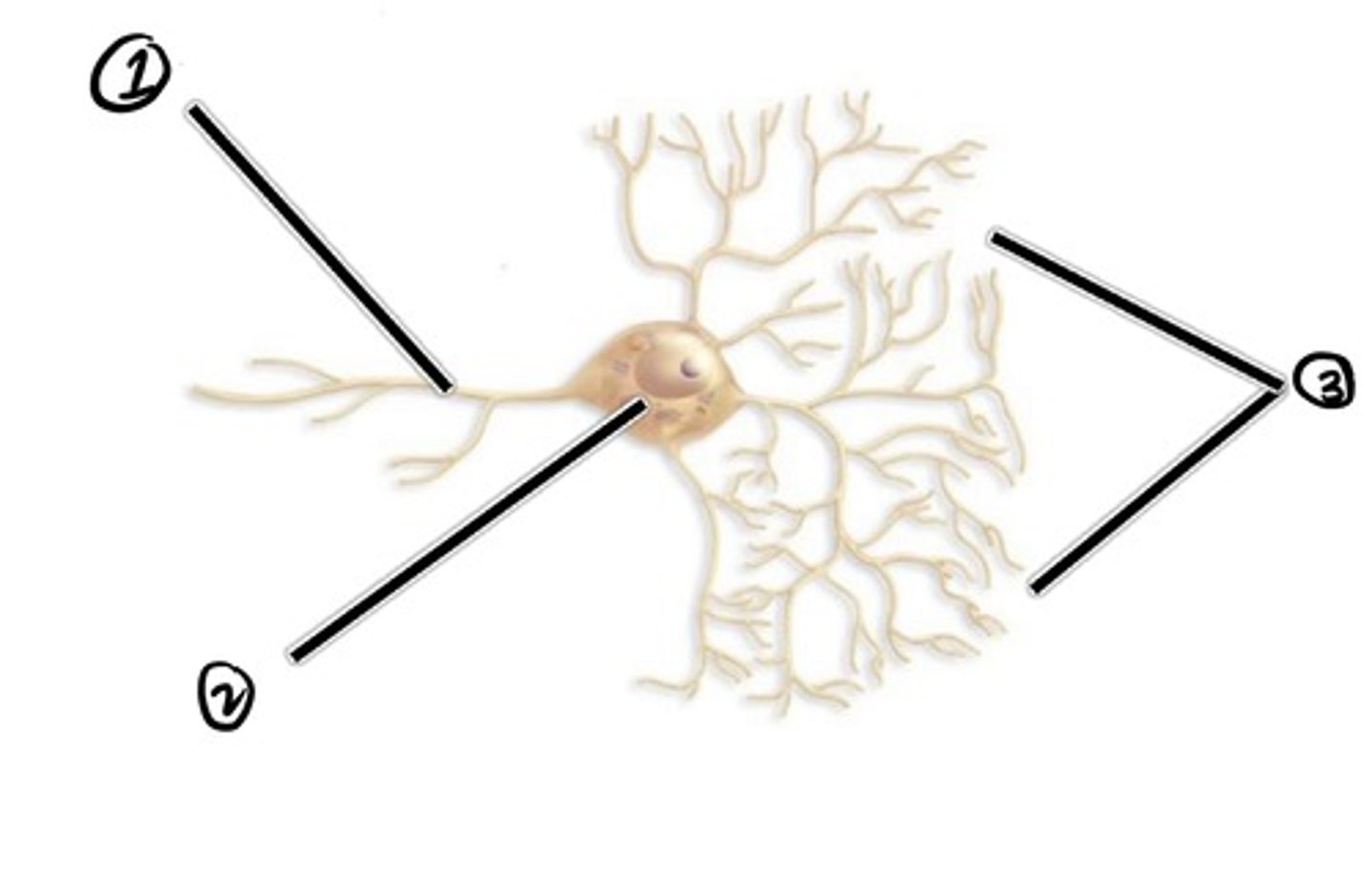
cell body
assuming the direction of impulse is right to left, what is 2
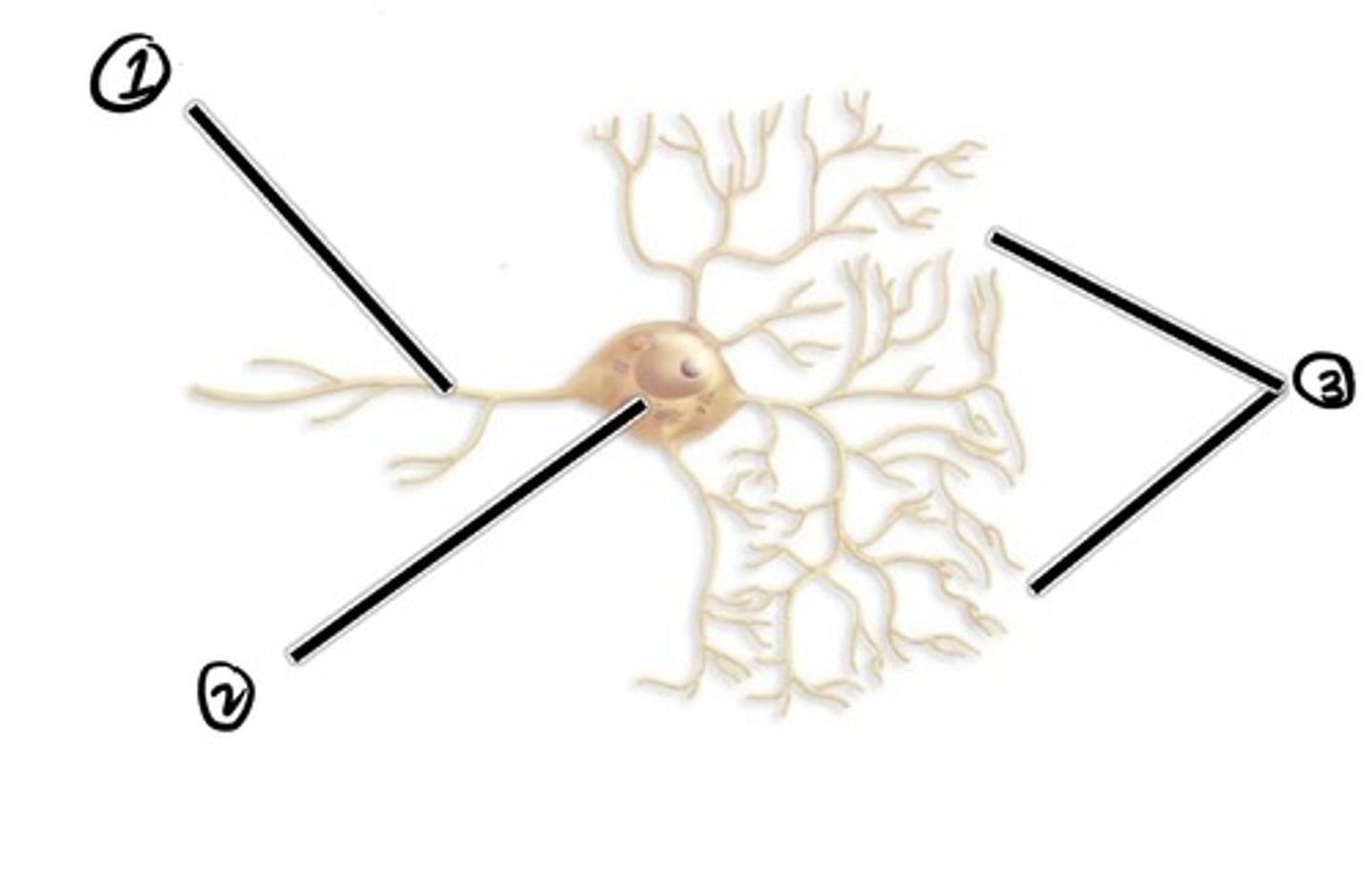
dendrites (carries impulse to cell body)
Assuming the direction of impulse is right to left, what is 3
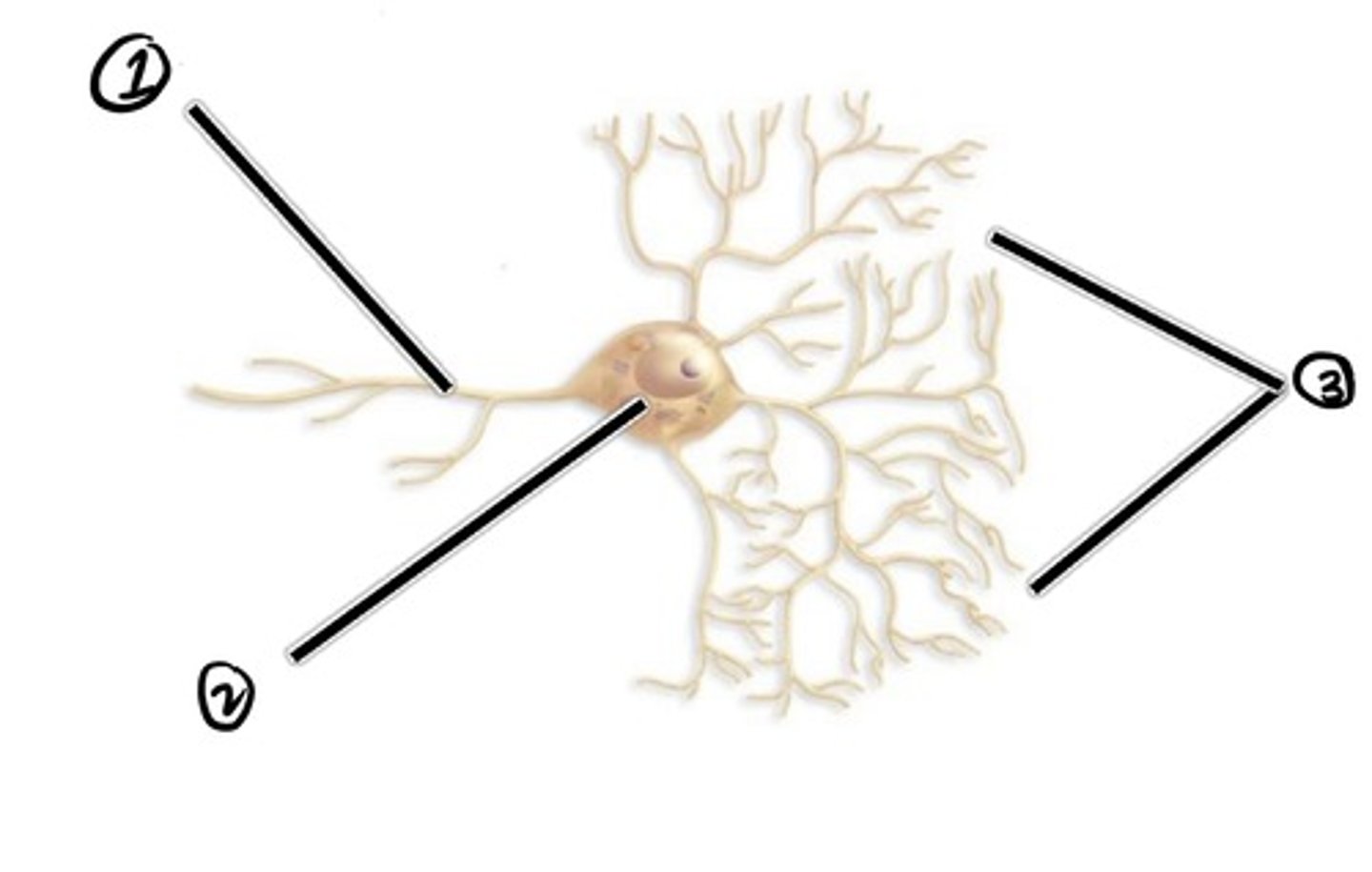
location where one neuron transmits its impulse to another cell
synapse
sheath surrounding long fibers of neurons that speeds up conduction of impulses (most neurons in the PNS have this)
myelin sheath
a fiber that has a myelin sheath
myelinated fiber
a collection of neuronal fibers surrounded by connective tissue in the PNS
nerve
a collection of neuronal cell bodies surrounded by connective tissue in the PNS
Ganglion (plural: ganglia)
parts of CNS that are mainly comprised of myelinated fibers
white matter
parts of CNS that are mainly comprised of neuronal cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers
gray matter
structures comprised of somatic tissue and associated fascia
somatic structures
somatic tissue
skeletal muscle, bone, skin, and other associated connective tissues are ____________ tissue
structures comprised of visceral tissue and associated fascia (includes internal organs)
visceral structures
visceral tissue
smooth and cardiac muscle and glands are __________ tissue
skin, superficial fascia, deep fascia, skeletal muscle, bone
somatic structures that form the body wall
internal organs and associated structures
visceral structures in the body cavity
glands (e.g. sweat), arrector pili muscles, and smooth muscle in blood vessels
visceral structures in the body wall
visceral sensory (visceral pain), somatic sensory, sympathetic, parasympathetic, and somatic motor
the 5 types of innervation
carry somatic innervation (among other types) for somatic structures if body wall (below the head)
spinal nerves
segment of spinal cord that gives rise to a single pair of spinal nerves
spinal cord segment/ level
31
there are _____ spinal nerve pairs
C1-C8
cervical nerves (quantity/name)
T1-T12
thoracic nerve pairs (quantity/name)
L1-L5
lumbar nerve pairs (quantity/name)
S1-S5
sacral nerve pairs (quantity/name)
Co1
Coccygeal nerve pair(s) (quantity/name)
dorsal horn
what is 1
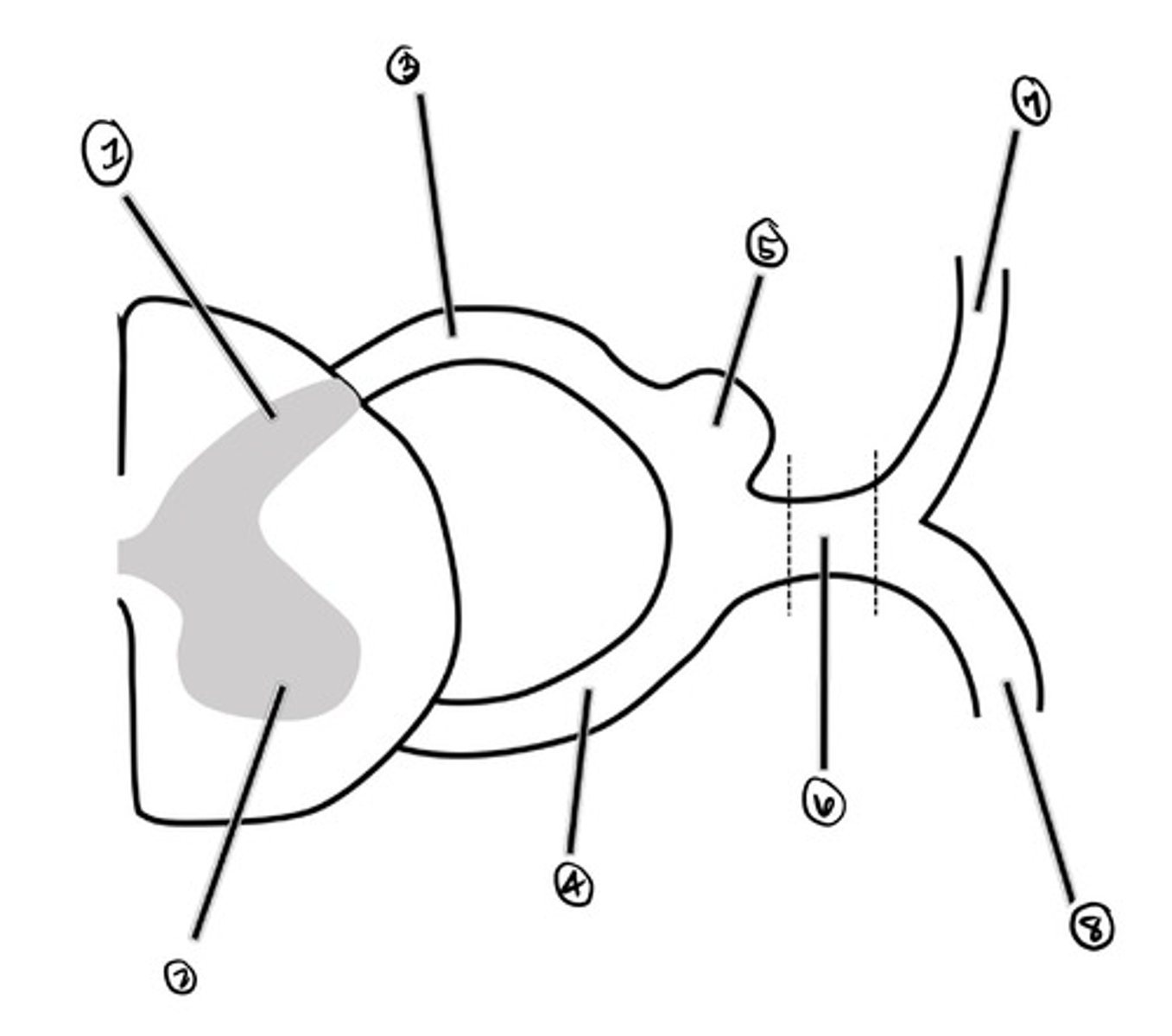
ventral horn
what is 2
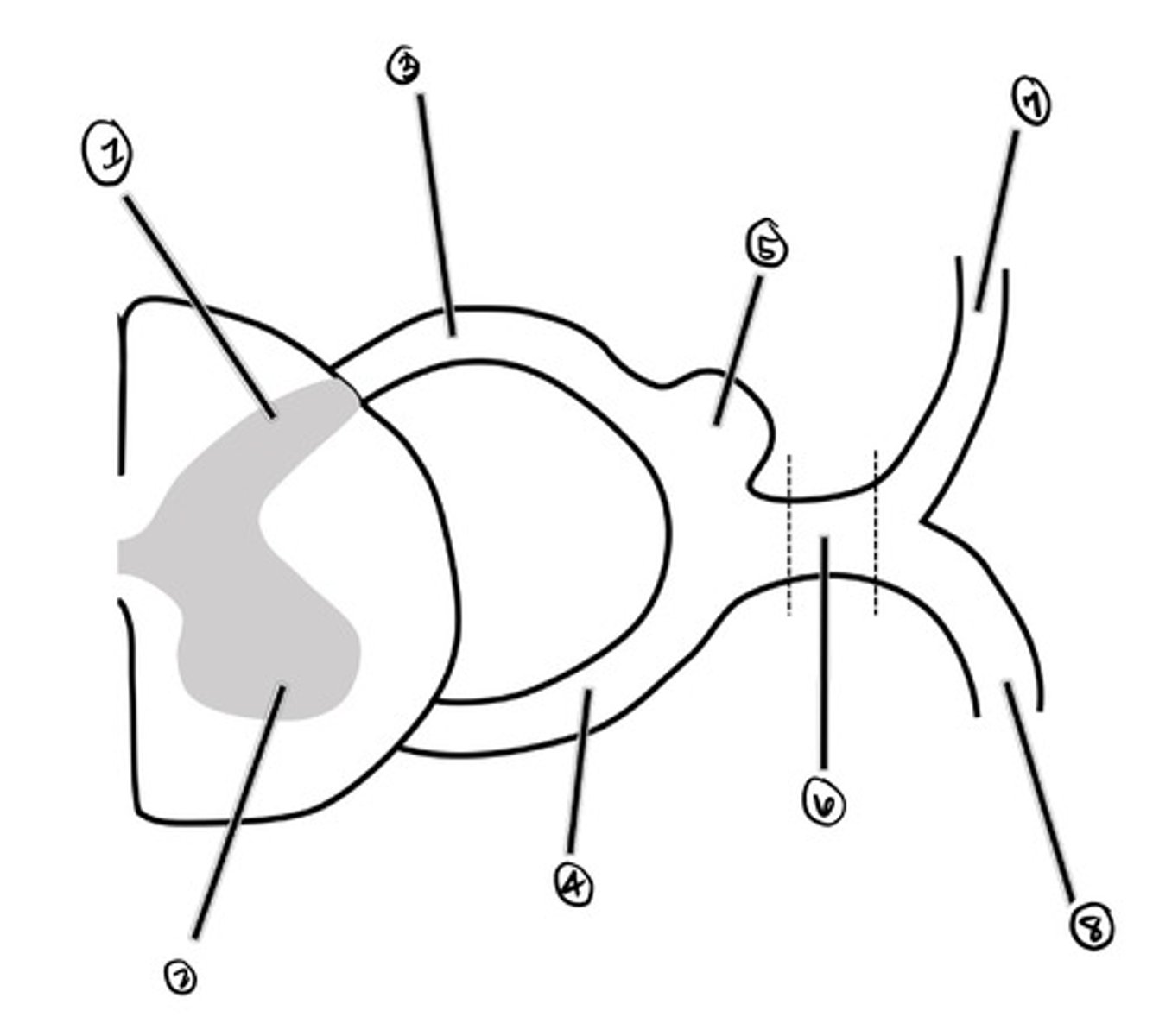
dorsal root
what is 3
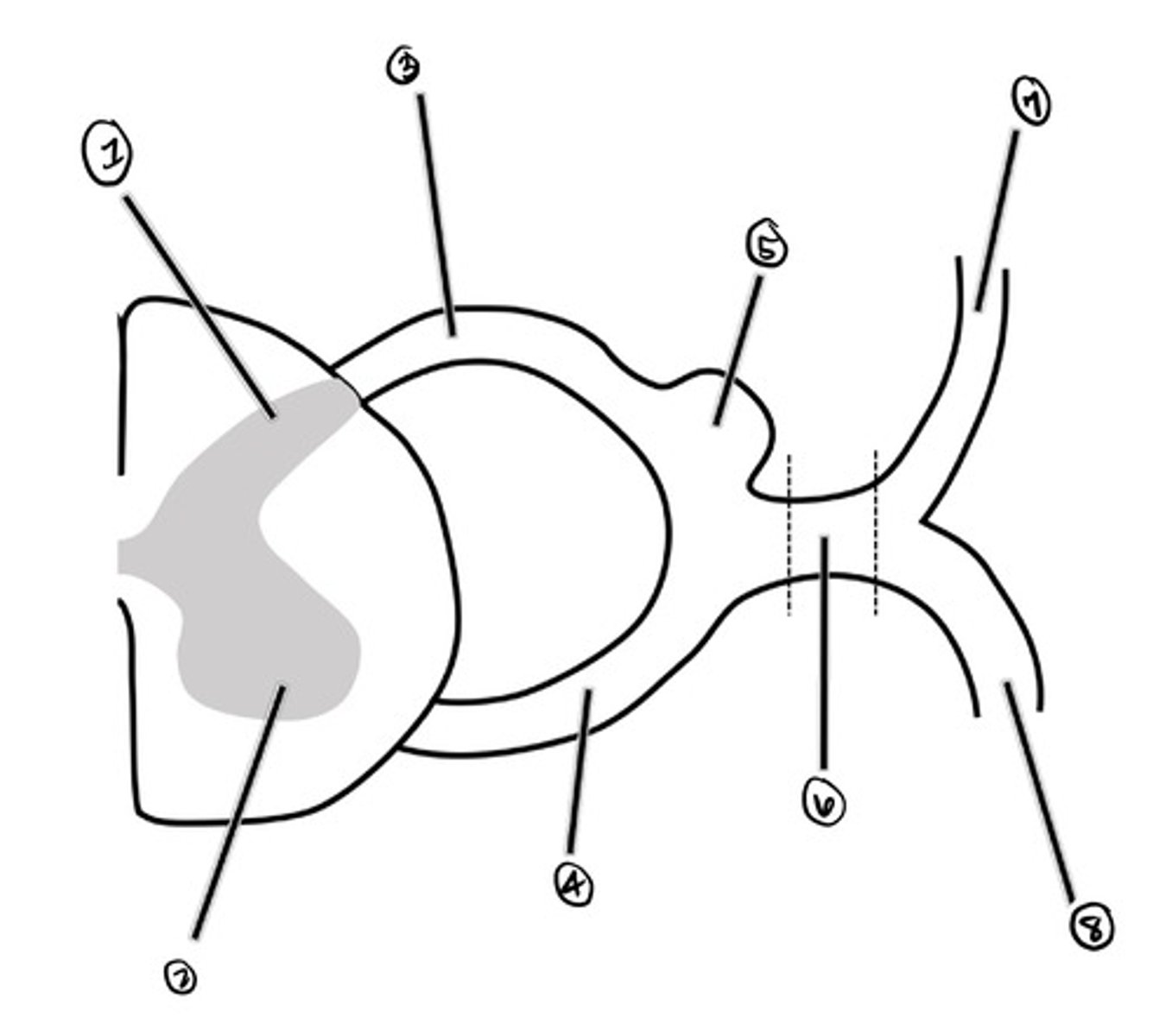
ventral root
what is 4
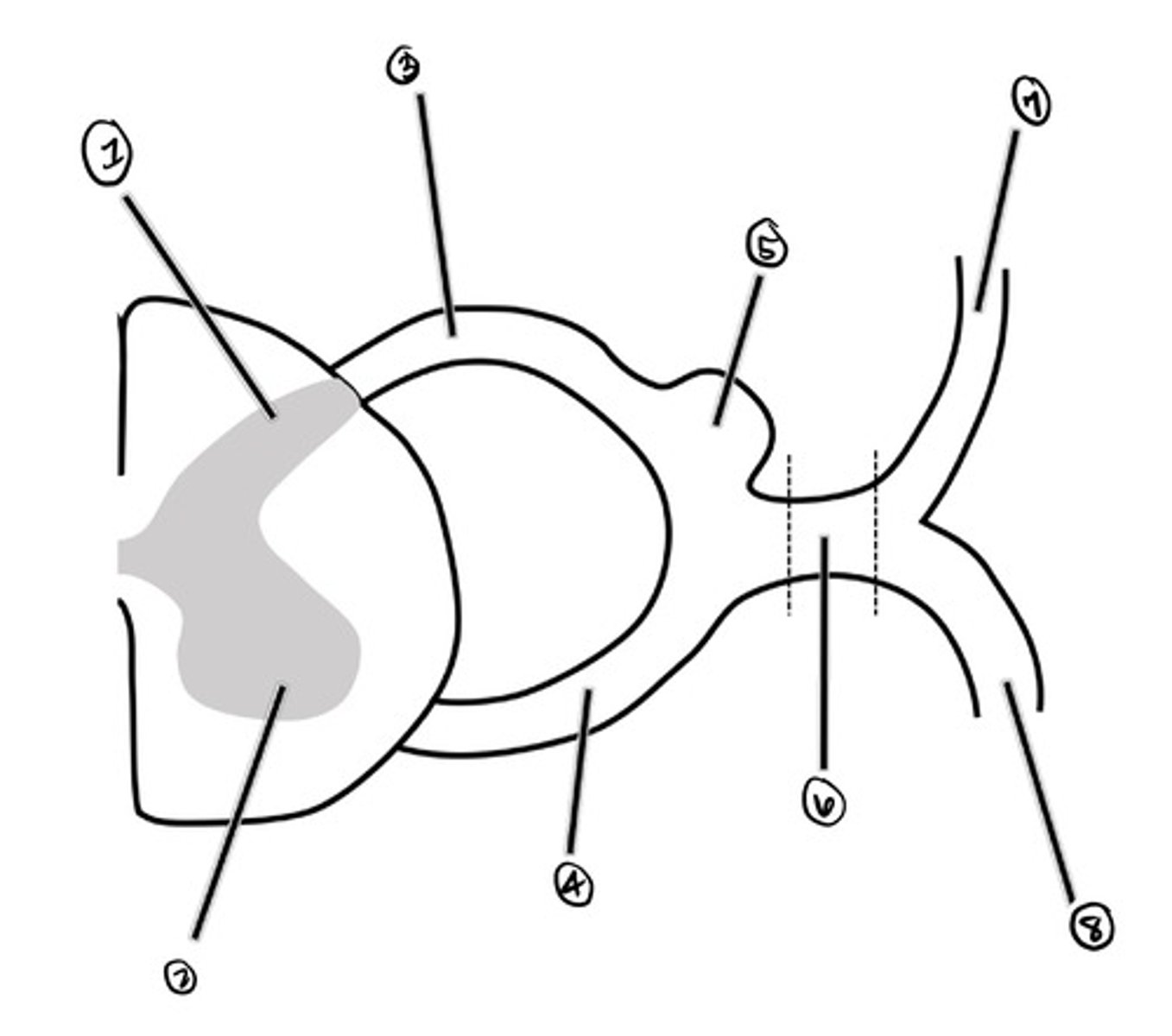
Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG)
what is 5
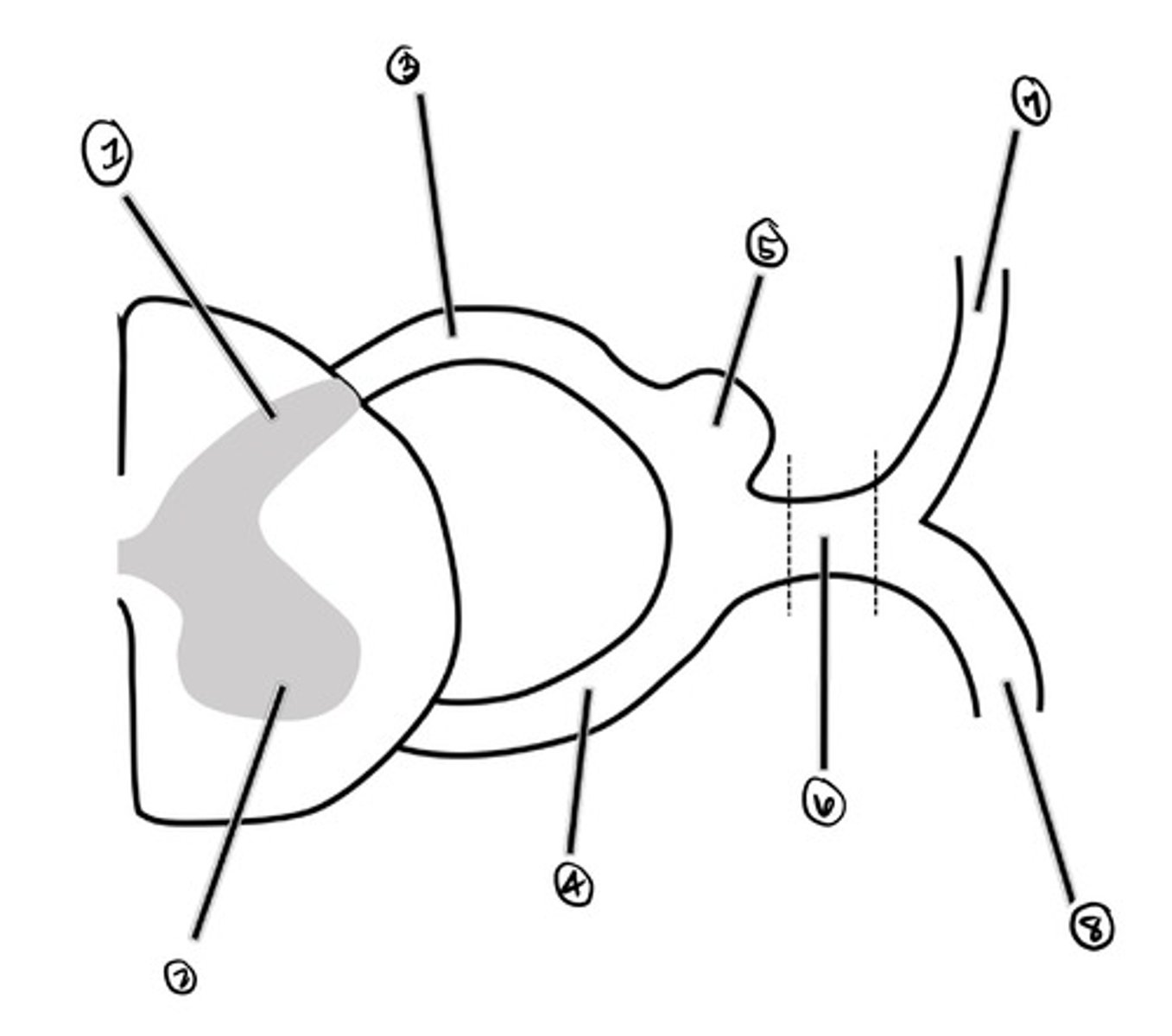
spinal nerve
what is 6
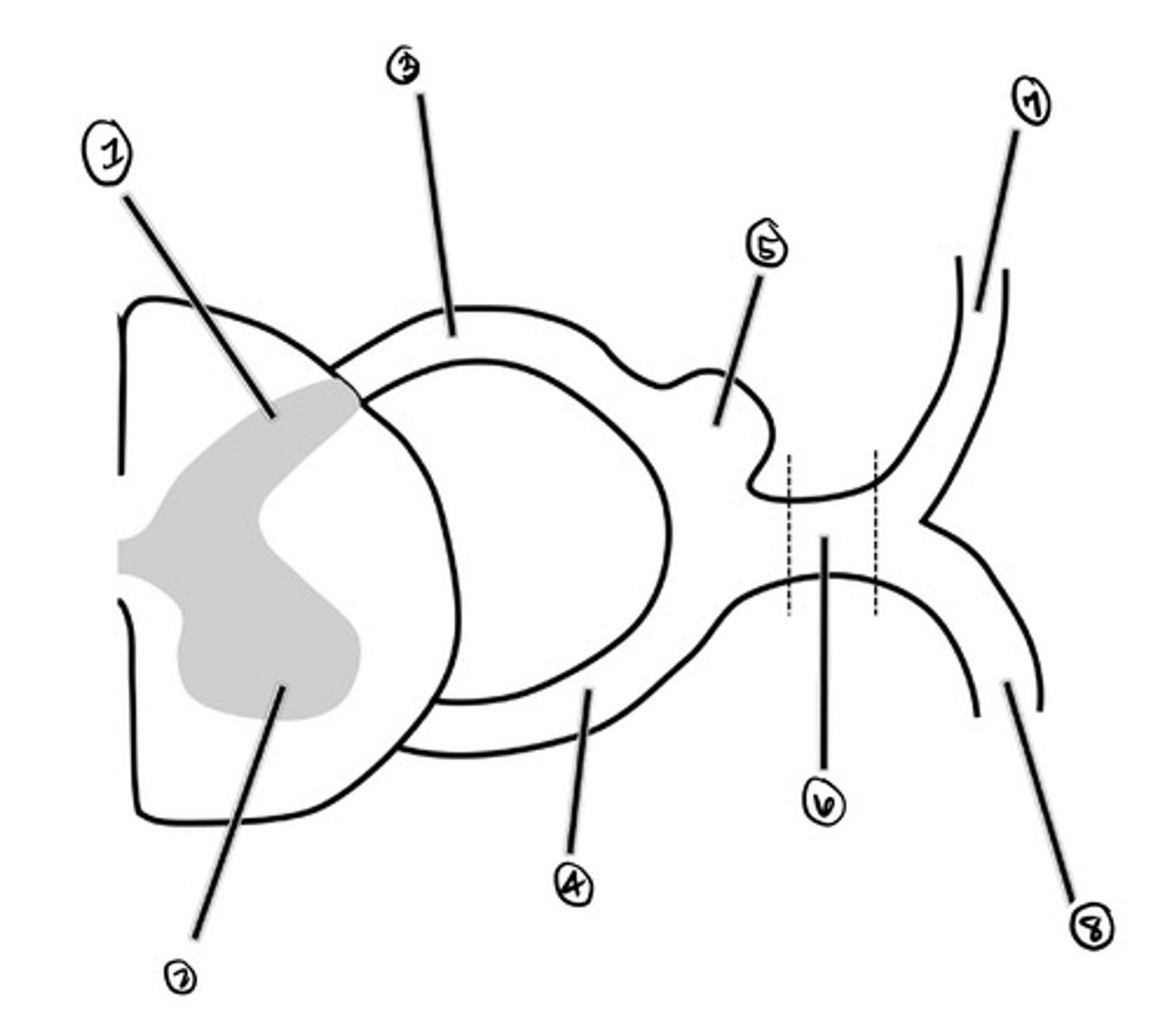
dorsal ramus
what is 7
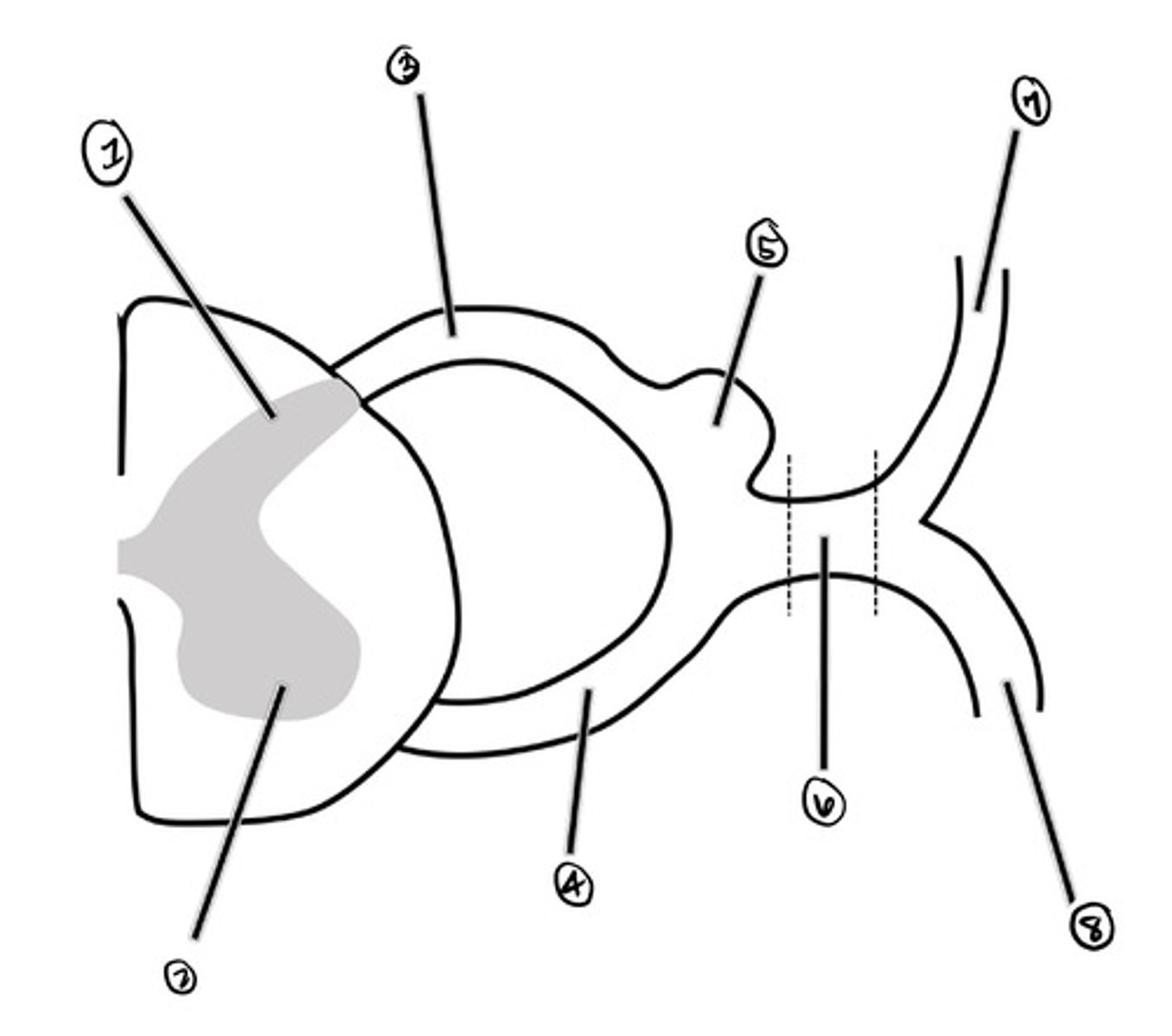
ventral ramus
what is 8
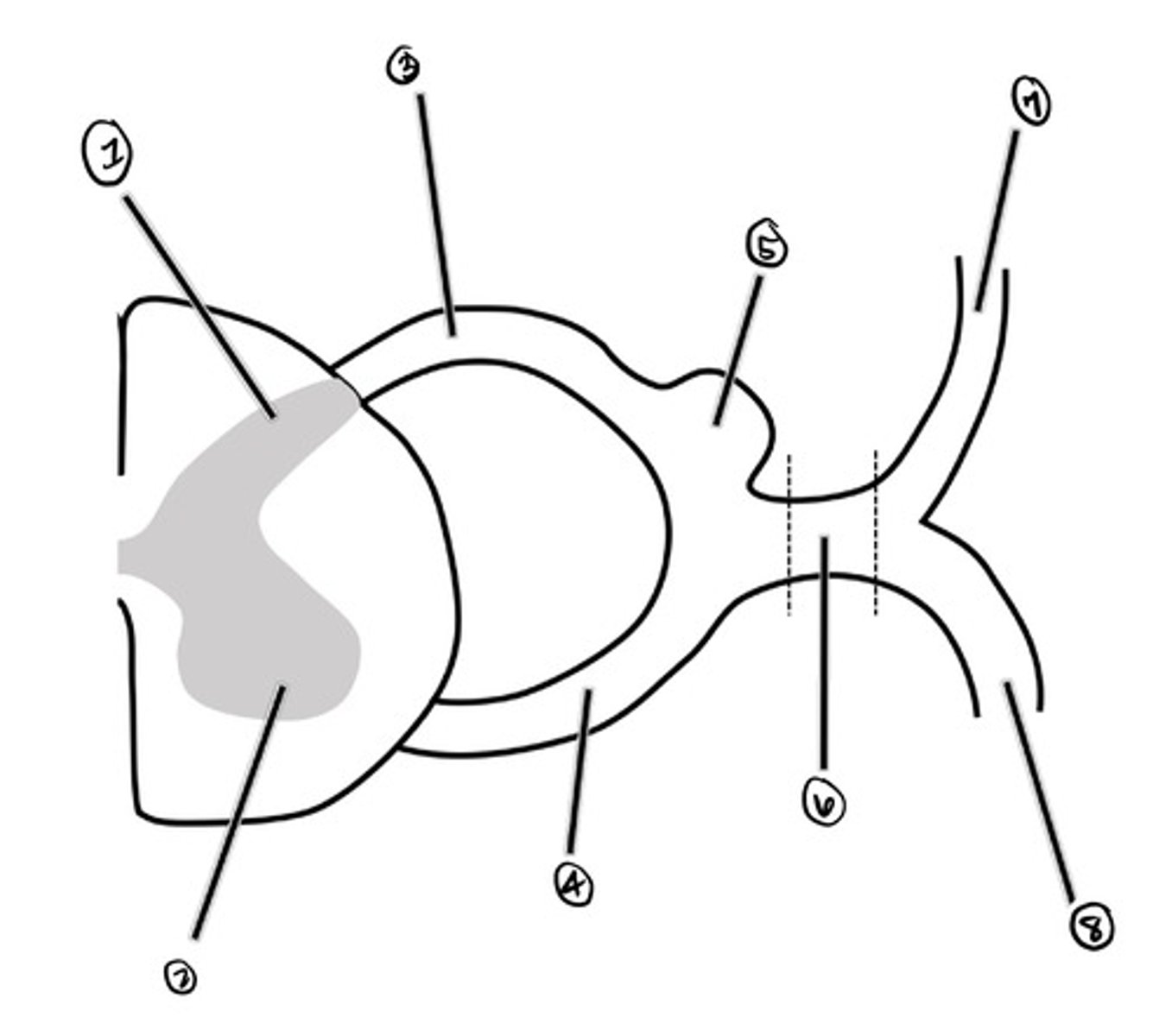
a strip of skin that receives somatic sensory innervation from a particular spinal cord segment; names according to spinal cord segment
Dermatome (adult)
paired sequential blocks of embryonic tissue on either side (left and right) of the developing spinal cord
somites
31
there are _____ pairs of somites
part of the somite that will contribute to development of skin and skeletal muscle of body wall
dermomyotome
contributes to skin (dermis)
dermatome (embryonic)
develops into skeletal muscle
myotome (embryonic)
epaxial division
the dorsal portion each embryonic dermatome/myotome set separates into is called the
hypaxial division
the ventral portion each embryonic dermatome/myotome set separates into is called the
dorsal ramus; ventral ramus
each spinal nerve corresponding to the dermatome/myotome sets separates into a dorsal branch (aka the ____________) and a ventral branch (aka the ________________)
epaxial division
the dorsal ramus will innervate the structures developed from the ________________ division
hypaxial division
the ventral ramus will innervate the structures developed from the ______________ division
Dermatome: skin along central back
Myotome: intrinsic back muscles (ONLY)
The epaxial dermatome and myotome derivatives are....
dorsal ramus
structures derived from the epaxial division are innervated by the...
Dermatome: skin of body wall (INcluding limbs, EXcluding skin of central back)
Myotome: Skeletal mucles (INcluding limbs, EXcluding intrinsic back muscles)
The hypaxial dermatome and myotome derivatives are....
ventral ramus
structures derived from the hypaxial division are innervated by the...
True
True of False: a single muscle derived from multiple myotomes can be innervated by several myotomes corresponding spinal nerve
the origin of sensory innervation; specialized sensory structure that sends an impulse in response to a stimulus (Can originate in both epaxial and hypaxial derivatives with the goal destination being the CNS)
Receptor (Somatic Sensory)
the destination of motor innervation; the structure that is being innervated (can target both epaxial and hypaxial muscles- originating from the CNS)
Target (Somatic Motor)
ventral horn (cell body) -> [ventral root -> spinal nerve -> ventral ramus](Axon) -> hypaxial muscles (target)
Somatic motor pathway to hypaxial muscles
ventral horn (cell body) -> [ventral root -> spinal nerve -> dorsal ramus](Axon) -> epaxial muscles (target)
somatic motor pathway to epaxial muscles
hypaxial structures (receptors) -> [ventral ramus -> spinal nerve -> dorsal root](peripheral process) -> DRG (cell body) -> dorsal root -> dorsal horn
somatic sensory pathway from hypaxial structures
epaxial structures (receptors) -> [dorsal ramus -> spinal nerve -> dorsal root](peripheral process) -> DRG (cell body) -> dorsal root -> dorsal horn
somatic sensory pathway from epaxial structures
one neuron pathway
somatic innervation is a _______ neuron pathway
ventral horn
somatic motor cell bodies are located in the
dorsal root ganglion
somatic sensory cell bodies are located in the
localized
Somatic sensory pain in the diaphragm is.... (Exception to typical somatic sensory)