"Probably napping" OHS quiz 1
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
What is the clinical term for the "moist epithelial lining of the oral cavity"?
mucosa
the depression between the nose and upper lip, extraorally, is called the
philtrum
what is the function of palatine tonsils
responsibile for removing toxins
The correct terminology for the underside of the tongue is________?
ventral surface
Where is the retromolar pad found?
behind mandibular third molars
What is the area called where the root meets the crown?
cementoenamel junction
What is the difference between the anatomical and clinical crown?
Anatomical crown: whole crown that is covered by enamel (covered by gingiva or not)
Clinical crown: part of the crown that is visible in the mouth (above the gingiva)
What is the area called on the root of a tooth where the nerves enter the tooth?
apex
What is the most densely mineralized and hardest tissue in the body?
enamel
What type of stimulus does nerve tissue respond to?
pain (Pain is the only response the nerve of the pulp/root canal can emit once stimulated)
If the cusp is the mountain what is the "valley" area called?
fossa (depression or concave area)
What do you call the spaces between teeth that help to reduce occlusal (biting) forces?
embrasures
vestibule
space between the lips/cheeks and the teeth
transverse ridge
when two triangular ridges connect
vermillion broder
outline of lips
labial commissures
where corner of upper and lower lips meet
uvula
hangs from posterior margin or soft palate
retromolar pad
dense pad of tissues behind mandibular 3rd molars
palatal torus
bony projection that is on palate (maxilla and mandible)
osteoblasts
bone building cells
osteoclasts
bone resorbing cells
buccal mucosa
mucous membrane lining cheek
main functions of teeth
incisors -to cut
canines- to tear
molars - to grind
which premolar can have 3 cusps?
mandibular 2nd premolar
trifurcation
3 roots present (16,17,26,27)
bifurcation
2 roots present (24/14)
hypercemenosis
excess cementum on outside of root
Cause?
- trauma
-inflammation
-developmental effect
Treatment?
-more conservative
dilaceration
unecpected root curvature
supernumerary roots
extra root
periodontal ligament (PDL)
support structure found between cementum on the root and the alveolar bone
what teeth normally have no distal contact and has the most varied form?
3rd molar
What can happen if too much pressure is applied too quickly when moving teeth during orthodontic treatment?
root resorption
maxillary first molar
6 year molar
First permanent tooth to erupt in the mouth
the Cusp of Carabelli
rhomboid shape
divergent roots
ankylosis
tongue tie- lingual frenum is short and attached close to the tongue
structure of teeth
crown, root, joined by CEJ
enamel, cementum, dentin
hard tissue
soft tissue
pulp
enamel
its strength is resistant to wear but consider excessive mechanical and/or chemical effects
protects against bacteria, mild acids, tooth decay
smooth surface - easy to self clean
outer covering of crown
colour varies in thickness
most densely mineralized and hardest tissue in the body
dentin
main portion/bulk of tooth
underlying structure on crown AND root
second hardest tooth structure
70% inorganic; 30% organic
cementum
outer covering of the root
has voids that expose dentin
provides attachment sire for periodontal ligament
thin at cervical line but increases near apex
3rd hardest tooth structure
65%inorganic;23% organic , 12% water
pulp
sensation area of tooth
pulp cavity
entire cavity within the tooth, including pulp canal and pulp chambers
pulp chambers
where nerve lives
cavity in the centre of the tooth that normally contains the major portion of the dental pulp. the pulp canal lead into the pulp chambers.
pulp horn
extension of pulp tissue into a thin point of the pulp chamber in the tooth crown
developmental grooves
lines where lobes join (highway)
pits
pinpoint depression found in grooves (potholes)
How is the division of quadrants different than the divisions of sextants?
4 quadrants, 6 sextants
When an anterior tooth first erupts what are the ridges called on the incisal edge?
mamelons
when is the period of mixed dentition?
6-12 years old
What is the sequence for naming teeth?
1. dentition
2. arch
3. quadrant
4. tooth name
What is the smallest and most symmetrical of all permanent teeth?
mandibular central incisors
which tooth has the widest crown mediodistally of any permanent anterior teeth?
maxillary central incisors
Differences between maxillary and mandibular canines
max canines have the longest roots
max canines are wider
eruption date: max 11-12 years; mand 9-10 years
mandibular canines may be bifurcated
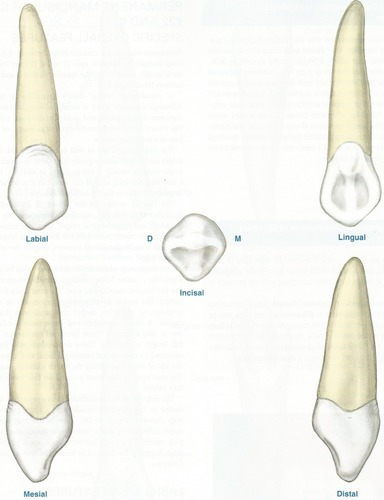
maxillary central incisor
Eruption: 7-8years
"The widest out of the centrals"
Mesio-incisal edge is 90 degrees
Disto-incisal edge is rounded
Triangular in shape
Mesial greatest cervical curvature
Single conical root
Slants lingually
Cingulum is off center to distal
Lingual groove may be present
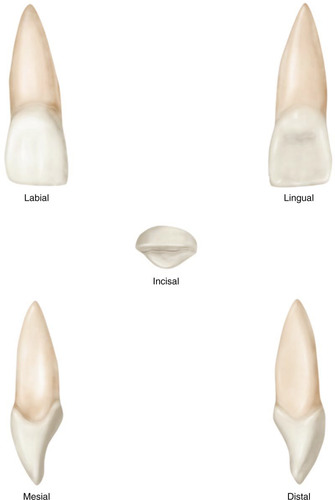
maxillary lateral incisor
Eruption between 8-9 years
Root is longer than central incisors
More rounded
More convex labially
More Pronounced mesial cervical
Resembles central but smaller and but all features are more pronounced
Deeper lingual groove
Deeper fossa
More prominent cingulum
Curves to the distal
Longer root then max

maxillary canine
Eruption: between 11-12 years
Root has blunt apex, distal curvature
Shallow labial grooves
Well developed lingual
Note 2 fossae
Developmental depressions may look like two roots
Wider labio-ligually
Mesial slop is shorter
4 ridges: labial,lingual, mesio-incisal, disto-incisal
1 cusp
Cusp tip in line with long axis
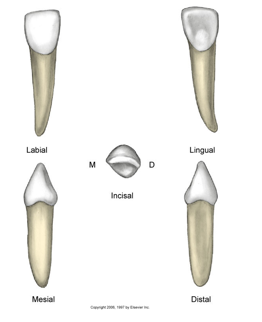
mandibular central incisors
Eruption: 6-7 years
Not conical in shape
lingual pits
Wider labio-lingual
Incisal edge is lis lingual in relation to the long axis and Slants labially
Edge is usually rounded
Labial is very smooth
Cervical line more curved
mandibular lateral incisors
Eruption: between 7-8 years
Slightly bigger, wider, longer
Thicker linguo incisal ridge
Greater mesial cervical curvature
Root is wider, thicker, longer
Sharper mesial angle
Distal lobe is larger, appears rotated on it
Wider labio-lingual
Contact incisal third
More pronounced lingual
More rounded
Deeper developmental grooves
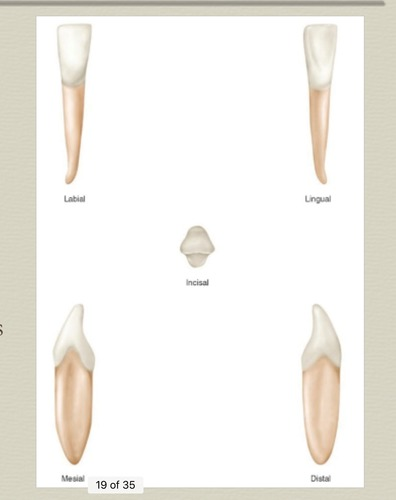
mandibular canine
eruption: 11-12 years old
mesial slop shorter
lingual surface more smooth, less distinct
root shorter than max, longest of mand
narrower than max
thinner lingual ridges
wider labio-lingually
cusp tip lingually inclined, slants lingually
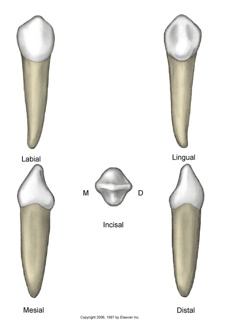
How many roots does the maxillary first premolar have ?
2 roots
How is the maxillary second premolar different than the maxillary first premolar?
more rounded, less angular
buccal cusps shorter, less pointed
lingual cusp larger
which premolar can have 3 cusps?
mandibular 2nd premolar
how many roots does a permanent molar have?
3 roots
How is the mandibular first molar different from the mandibular second molar?
First molar erupts @ age 6, 5 cusps vs 4 for second
Mandibular 1st Premolar
eruption 10-12 years
always smaller than 2nd premolar
resembles canine
mesial cusp ridge shorter
tip of cusps centered
transverse ridge cause 2 fossaes
lingual cusp much smaller/narrower
single rooted; very occasionally two roots
buccal outline longer than lingual crown tilts lingually
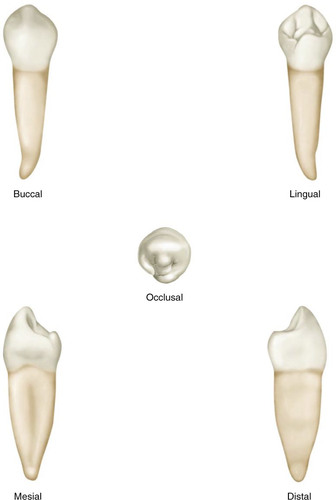
mandibular 2nd premolar
eruption 11-12 years
always larger than 1st premolar
2 cusp type - single lingual lobe
3 cusp type - 2 lingual cusps from 2 lobes
longer toot than 1st premolar
apex curves distally
no tendency to bifurcate
higher marginal ridges - functions like molar
mesial marginal ridge higher than distal
buccal cusp shorter than 1st premolar
more developed lingual cusp
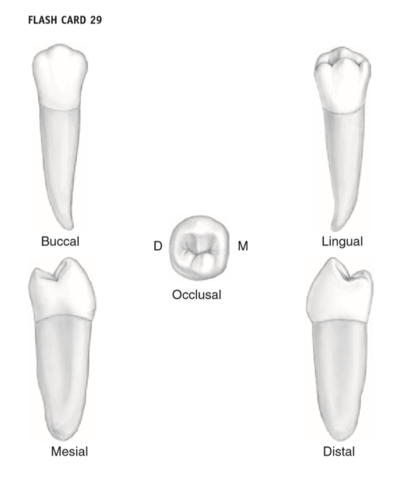
maxillary 1st premolar
eruption 10-11 years
similar to max canine
buccal cusp centered over root
more curved CEJ
lingual cusp shorter than facial cusp by 1mm
more shallow distal marginal groove less curved CEJ
hexagonal shape
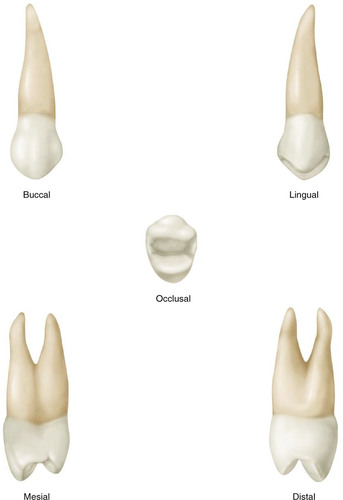
maxillary 2nd premolar
eruption 10-12 years
ovoid shape
buccal cusp not as long as 1st premolar/less pointed
lingual cusp longer than 1st premolar
lingual cusp almost as long as buccal
looks more like molar-more rounded less angular
no developmental groove or depress on mesial
usually single rooted/occasionally bifurcated
CEJ both same pattern but flatter
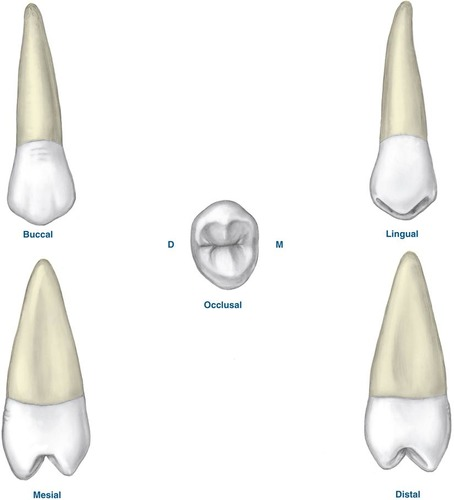
maxillary first molar
Eruption: 6-7 years
MB cusp is broader
DB cusp is sharper & longer
Rhomboidal outline sides unequal in length: DM ridge is shorter
MM Ridge is longer
Root Trunk is "shortest of all the molars"
Larger divergent roots than 2nd molar
palatal root is longest
Roots 2x length
Furcations 3-M, 4-B, 5-
Largest teeth in max arch - 1st tooth to erupt in max arch
5cups, 2 buccal, 3 lingual afunctional, "cusp or carabelli"
CEJ - mesial is more curved/ distal is straighter
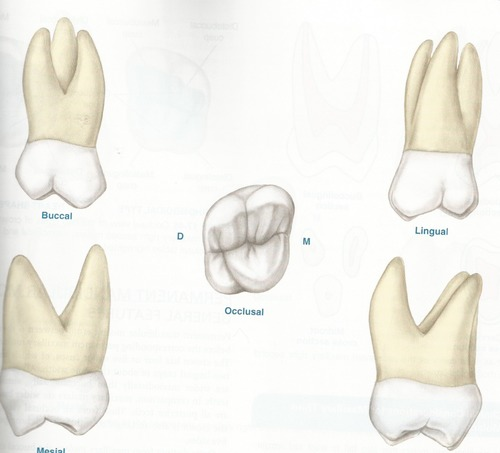
maxillary 2nd molar
"12 year molars"
Smaller DB cusp
Buccal groove farther distal than 1st molar
Roots are smaller & more closely together
Buccal Roots are equal length
Root trunk longer so furcation is less cervical
Shorter occlusalcervically, Narrower mesiodistally
increase supplemental grooves
lingual pit usually present
smaller and shorter DL cusp- sometimes not present
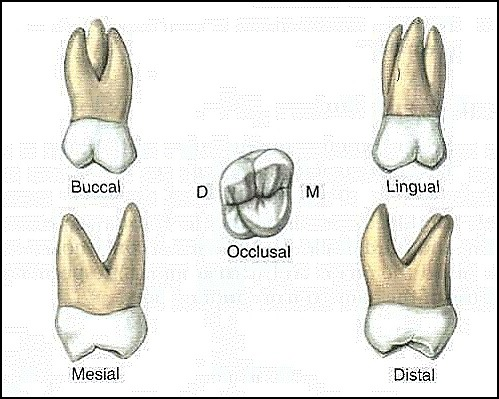
maxillary 3rd molar
Eruption: 17-21 years
smaller in all crown proportions
most wrinkled appearance
shows greatest variation in all max teeth
DB cusp much shorter than MB
DB cusp usually smallest
Tendency to become impacted
Roots tend to fuse
DB root is shortest
Lingual root is longest
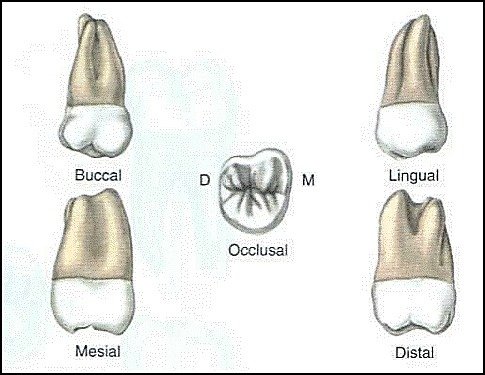
mandibular first molar
Eruption: 6-7 years
Narrow at cervical 3rd
Convex at middle and occlusal 3rd
5 cusps
MB cusp largest ; D cusp smallest, sharpest - all functional
MB & DB same height
MB groove - pit
DB grooveCEJ- 1mm higher on mesial and lingual
Largest of all mand teeth 1st permanent to erupt
Lingual cusps are higher than buccal
Root trunk shortest of man molars, furcations are more cervical
Bulge in cervical 3rd
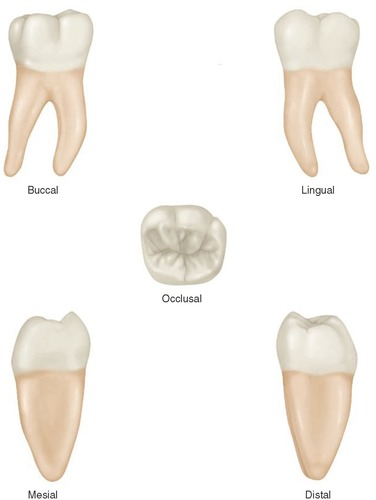
mandibular 2nd molar
Eruption:11-13
Buccal groove between buccal cusps
4 cusps nearly equal size
lingual cusps are higher than buccal
Ususally smaller than 1st mand molar
not as long M/D , short C/O
Mesial root is broader
Same as 1st molar- mesial and distal profiles are more curved
Rectangular outline
longer trunk than 1st molar so less cervical
Lingual groover between lingual cusps - pit
mandibular 3rd molar
eruption 17-21 years
smaller than 2nd molar
2 buccal cusp, 1 buccal groove
shows variation in dimensions
more supplementary
groove-wrinkled
Teeth with two or three roots have an unbranched area called the
root trunk
What characteristics of a root aid in support of the tooth
1. width of roots
2. shape of roots
3. length of roots
4. # of roots
5. Concavities
6. Direction of PDL fibers
slight movement of tooth is called?
mobility
What an infected tooth is exposed to heat, what can cause pain?
gas
is cementoma painful? Where would it typically be seen?
no (benign), found on mandible and in the molar region
There can be more than one opening at the apical region of a root, if these orifices are on the lateral surface of the root what are these called?
accessory root canals
Which teeth have one root?
incisors, canines
mand 1st premolar
mand 2nd premolar
which teeth have two roots?
mandibular molars
max 1st premolar
max 2nd premolar
which teeth have 3 roots?
max molars
apex
end of root
anatomic root
area of tooth below CEJ dentin covered by cementum
periapical foramen
opening in apex where blood vessels and nerves enter pulp cavity
what would cause the tooth root to be exposed?
Periodontal disease, recession, trauma, pathology
Ways to stimulate nerves
dehydration
root decay
root resorption
abrasion
friction
anoxia
lack of oxygen
injuries that could affect pulp of teeth
Repeated procedures
Large carious lesion/dental filling close to pulp
trauma
exposure
cracked tooth
best predictor of loss of vitality?
cold
pain response to cold
nerve alive but badly inflammed
Alveolar mucosa
-the lining of cheeks
-loosely attached and moveable
-reddish in color from blood vessels under thin unattached mucosa
fordyce granules
Misplaced sebaceous glands
Appearance: yellowish in color embedded in the mucosa
Found on:
Labial mucosa Inner portion of the lips
Buccal mucosa Inner cheek
exotoses
excess bony growth
Alveolar process of the maxilla and mandible - cortical plate (compact bone)
Localized developmental growths of normal bone with a hereditary etiology.
May be single, multiple, unilateral or bilateral
Usually in the canine, premolar to molar region
Covered by normal oral tissue
hard palate
Anterior portion has transverse ridges of epithelial and connective tissue known as RUGAE
Covered in keratinized epithelium
Wide, narrow, have a high arching curvature (vaulted) or flat in its contours.
soft palate
Posterior portion of palate
Non-keratinized tissue
Contains adipose tissue and minor salivary glands
Submucosa thin and firmly attached to muscles for speech and swallowing
Mucosa and muscles function as one unit
palatine tonsils
Masses of lymphoid tissue located between these borders.
maxillary tuberosity
rounded elevation of tissue distal to the last tooth of the maxilla
functions of embrasures
Moves food from contact areas - reduce food impaction
Reduce and dissipate occlusal trauma forces by shunting food