MODULE 6: Touch Screens, Gesture, Speech, and Response Time
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What is a touch screen?
An interactive display that allows users to operate a system by directly touching the screen with a finger or stylus.
What devices commonly use touch screens?
Smartphones, tablets, ATMs, and interactive kiosks.
What are the two common types of touch screens based on interaction techniques?
Single-touch screens and multi-touch surfaces.
What is a single-touch screen?
A screen that detects only one point of contact at a time, allowing users to perform one action at a time.
Where are single-touch screens typically used?
In devices like ATMs, kiosks, and older mobile phones.
What limitations do single-touch screens have?
They do not support advanced gestures like pinch-to-zoom or swipe gestures.
What is a multi-touch screen?
A screen that supports multiple points of contact simultaneously, allowing for complex gestures.
What functionalities do multi-touch screens enhance?
They enable dynamic interactions such as pinching to zoom, swiping to scroll, and rotating objects.
Where are multi-touch screens commonly found?
In smartphones, tablets, touch-enabled laptops, and large interactive displays.
What are the two main technologies used in touch screens?
Capacitive and resistive touch technologies.
How do resistive touch screens work?
They consist of two layers separated by a gap; pressure on the top layer creates a change in electrical resistance.
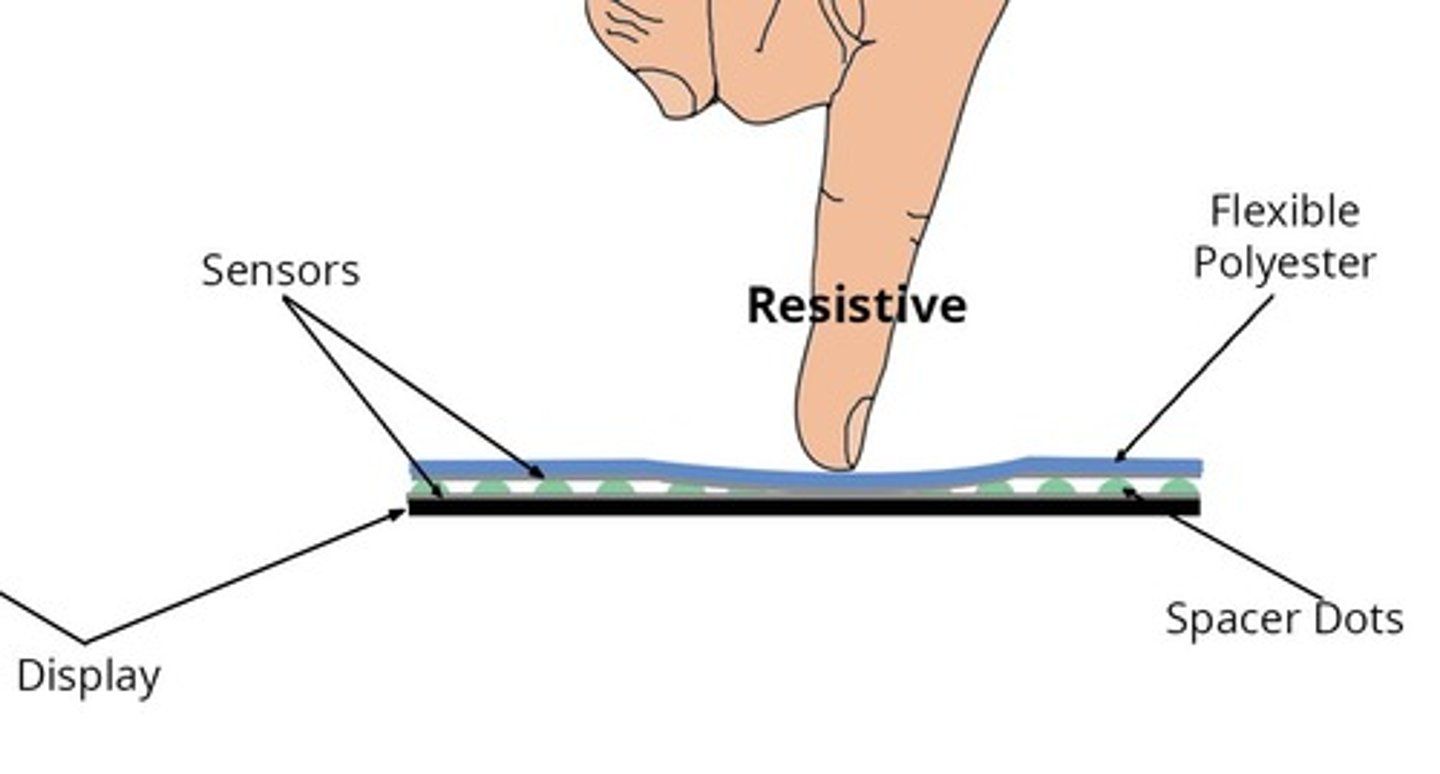
What are the advantages of resistive touch screens?
They work with any object, are less expensive to manufacture, and are more resistant to dust and water.
What are common uses for resistive touch screens?
ATMs, older PDAs, kiosks, and industrial control systems.
What limitations do resistive touch screens have?
They are less sensitive than capacitive screens and do not support multi-touch gestures.
How do capacitive touch screens detect touch?
They use the electrical properties of the human body to detect touch by altering the local electrostatic field.
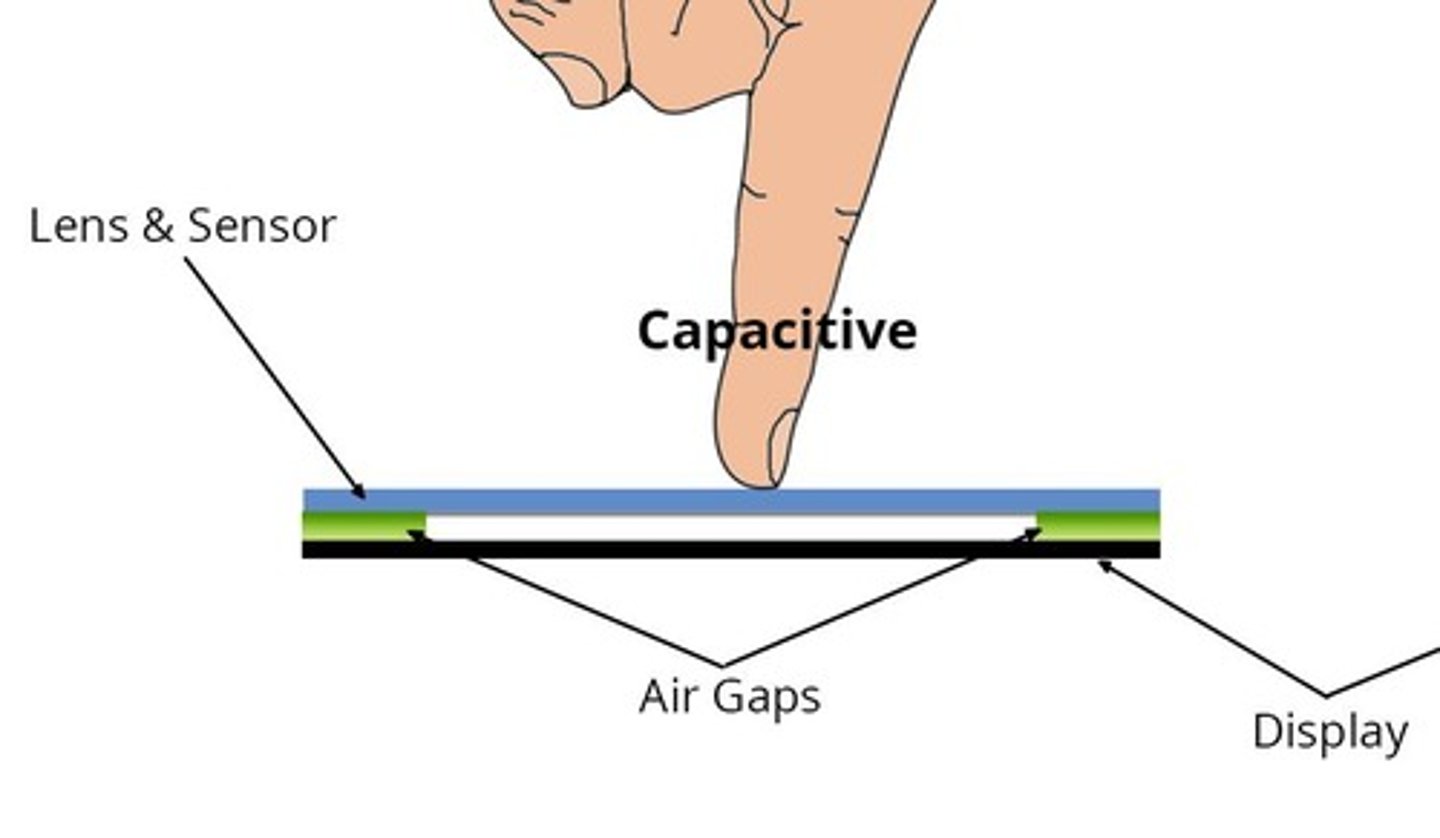
What are the advantages of capacitive touch screens?
They are highly responsive, support multi-touch gestures, and have a transparent material ideal for clear displays.
Where are capacitive touch screens commonly found?
In modern smartphones, tablets, touch-enabled laptops, and interactive displays.
What is the primary difference between capacitive and resistive touch screens?
Capacitive screens use electrical properties for touch detection, while resistive screens rely on pressure applied to layers.
What user experience benefits do multi-touch screens provide?
They offer richer interactions with capabilities like two-finger scrolling, zooming, and rotating.
What is the impact of touch screen technology on user interaction?
It provides a simple and intuitive way for users to interact with systems, enhancing overall usability.
What is the significance of touch screen technology in modern devices?
It has become a standard interface, making devices more accessible and user-friendly.
What are the challenges faced by resistive touch screens in modern applications?
Their limitations in sensitivity and multi-touch capabilities make them less suitable for advanced applications.
What role does touch screen technology play in education and training?
It facilitates interactive learning experiences and enhances engagement through direct manipulation of content.
How has touch screen technology evolved over time?
From basic single-touch interfaces to advanced multi-touch systems that support complex gestures.
What factors contribute to the popularity of touch screens?
Their intuitive nature, versatility, and ability to enhance user experience across various applications.
What are some emerging trends in touch screen technology?
Integration with augmented reality, improved haptic feedback, and advancements in touch sensitivity.
What are capacitive touch screens commonly used in?
Modern smartphones, tablets, touch-enabled laptops, and interactive displays.
What is a limitation of capacitive touch screens?
They do not respond to non-conductive materials such as gloves or plastic styluses.
What is the main difference in touch sensitivity between resistive and capacitive touch screens?
Resistive screens require pressure and work with any object, while capacitive screens are highly sensitive and require a bare finger or capacitive stylus.
Do capacitive touch screens support multi-touch?
Yes, they support multiple touchpoints.
Which type of touch screen is generally more durable?
Capacitive touch screens, as they have scratch-resistant glass.
What is a common application for resistive touch screens?
ATMs, industrial environments, and public kiosks.
What is the 'tap and hold' interaction technique used for?
To select items or trigger specific menus.
What does the 'swipe' interaction technique do?
Moves content by dragging a finger across the screen, commonly used for scrolling or navigating.
What is the 'pinch-to-zoom' gesture?
A gesture involving two fingers moving apart or closer together to zoom in or out, commonly used in map and photo applications.
Why must touch targets be large and well-spaced in touch screen design?
To accommodate the lower precision of a finger compared to a mouse cursor and to minimize the 'fat finger' problem.
What is essential for error prevention in touch screen design?
Making certain actions physically easy to perform, such as hitting a submit button.
How does a touch screen provide feedback to users?
Through immediate visual changes or haptic feedback to confirm that an action was registered.
What is gesture recognition?
An interface technology that allows users to interact with devices through physical movements, such as hand gestures.
What are some applications of gesture recognition in gaming?
Used in systems like Microsoft Kinect to control games with body movements.
How is gesture recognition used in the medical field?
It allows surgeons to manipulate medical images without touching non-sterile surfaces.
What advantage does gesture recognition provide in automotive applications?
Drivers can adjust functions like audio volume using simple hand gestures without physical contact.
What is a key advantage of gesture recognition?
It allows hands-free control, which is particularly useful in hygiene-critical situations.
What is a challenge associated with gesture recognition?
Gesture ambiguity, where gestures can be misinterpreted or confused with accidental motions.
What is a learning curve challenge in gesture recognition?
Not all gestures are universally understood and may need to be explicitly taught to users.
What technology does speech recognition rely on?
It converts human speech into text or actions, enabling hands-free control.
What is a common use of speech recognition technology?
To interact with computers or devices using spoken language.
What is speech recognition particularly useful for?
Scenarios where typing or manual input is difficult, such as while driving, in medical surgeries, or for people with physical disabilities.
How have speech recognition systems evolved over the years?
They have significantly improved in accuracy and functionality, moving from early systems that frequently misinterpreted user input.
What advancements have improved speech recognition systems?
Advancements in machine learning algorithms and natural language processing.
Name three modern systems that utilize speech recognition.
Siri, Google Assistant, and Amazon Alexa.
What are voice command systems?
Devices like Amazon Alexa or Google Home that allow users to control smart home systems and perform tasks using voice commands.
What is a speech-to-text system?
Programs like Dragon NaturallySpeaking and Otter.ai that allow users to dictate text instead of typing it.
What accuracy rate does Dragon NaturallySpeaking report?
An accuracy rate of 99%.
How does speech recognition assist individuals with disabilities?
It allows individuals with visual impairments or other physical limitations to navigate devices or perform tasks more easily.
What is one major challenge faced by speech recognition systems?
Dealing with variations in accents, speech patterns, and background noise.
What limitation do systems like Alexa and Google Home have regarding natural conversation?
They struggle to understand the full nuance of natural human conversations and complex, multi-step requests.
What is a major HCI challenge related to speech recognition?
The visibility of system status, requiring clear feedback to assure users that the system is listening and processing.
What should speech recognition systems do to design for error?
Offer easy recovery options, such as prompting the user for clarification.
What is the keyboard's role in computing?
It is one of the most widely used input devices, essential for text input, coding, or commands.
What are physical keyboards?
Standard keyboards connected to desktop computers and laptops, commonly using the QWERTY layout.
What are virtual keyboards?
On-screen keyboards used on smartphones, tablets, and touch-screen interfaces.
What are specialized keyboards designed for?
Specific uses, such as ergonomic keyboards for reducing strain or gaming keyboards with additional keys.
What advantage do keyboards provide for text entry?
Precision control, making them ideal for writing, coding, or data entry.
How do proficient touch typists benefit from keyboards?
They can type significantly faster compared to virtual keyboards or other input methods.
Why is the layout of a keyboard beneficial for users?
It is highly familiar, reducing the learning curve associated with other input devices.
What does response time refer to in HCI?
The amount of time a system takes to react to a user's input.
Why is minimizing response time important in HCI?
It improves user experience by making interactions feel smoother and less frustrating.
What do users expect regarding feedback when interacting with systems?
Near-instant feedback; delays can cause frustration and interrupt task flow.
What is the importance of real-time feedback in applications?
Quick feedback is crucial in applications like gaming, video conferencing, or emergency response systems to maintain functionality.
How can perceived performance differ from actual performance?
A system's actual performance may be slower than perceived by the user if the interface is designed well, using indicators like loading bars to make wait times feel shorter.
What are Jakob Nielsen's key usability thresholds?
They define how users perceive and interact with a system at different response speeds.
What does a response time of 0.1 seconds signify?
It feels instantaneous to the user, creating a perception of direct causality between action and reaction.
What happens at a response time of 1.0 second?
Users notice a delay but can maintain a continuous train of thought; visual or auditory feedback is necessary.
What is the maximum acceptable response time for holding user attention?
10 seconds; beyond this, users may abandon the task or switch contexts.
What performance metrics are used to evaluate system effectiveness?
Response times, completion times, and error rates are commonly used metrics.
What is Fitts' Law?
A predictive model of human movement that describes the time it takes to move a pointer to a target area.
Who introduced Fitts' Law and when?
Psychologist Paul Fitts introduced it in 1954.
How does distance affect response time in HCI?
The further away a target is, the longer it takes to move the cursor to it.
Why does target size matter in HCI?
Larger targets are easier to hit, reducing the time needed to complete actions and lowering error rates.
What trade-off does Fitts' Law predict?
Users will take less time to interact with large, nearby targets than with small, distant ones.
How should interface elements be designed according to Fitts' Law?
Buttons and icons should be large and placed close to where the user's attention or cursor typically resides.
Why are edge and corner targets more clickable?
Users can quickly 'throw' the cursor toward edges without overshooting, utilizing the screen's physical boundaries.
What is the significance of large touch targets in touchscreen design?
They are easier to interact with, especially on mobile devices where finger size and precision are factors.
How should frequently used items be positioned in a user interface?
They should be closer to the user's starting point and have large clickable areas to reduce movement time.
What factors affect response time in HCI?
The system's processing power, software optimization, network latency, and task complexity.
How does network latency impact user experience?
Delays caused by network latency can lead to poor experiences in interactive applications like online games or video streaming.
How does task complexity influence response time?
Simple tasks yield near-instant feedback, while complex operations take longer due to processing requirements.