PHARM: Estrogens and Progestins
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
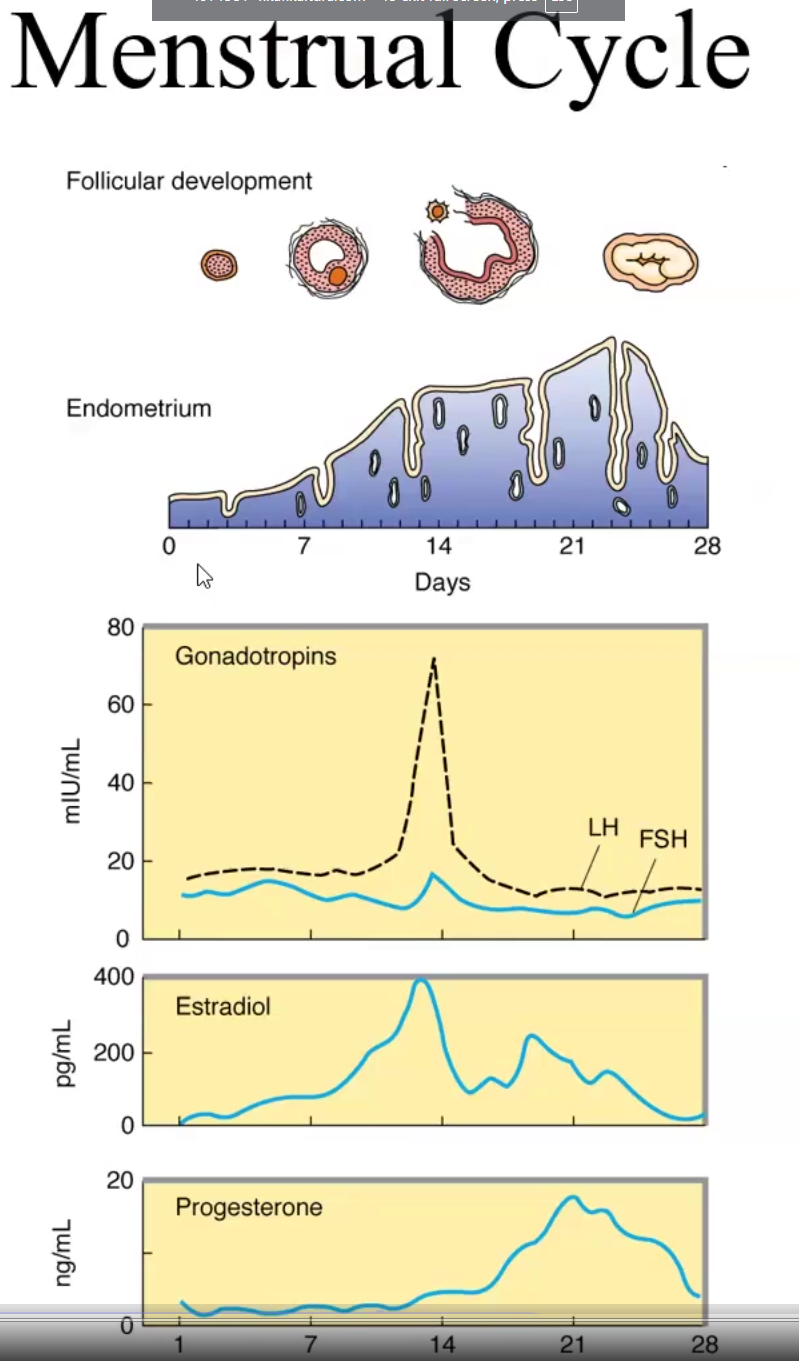
Menstrual Cycle
The ______ Phase is primarily under influence of FSH, while the _______ Phase is primarily under influence of LH.
The follicular phase secretes ______ while the luteal phase secretes
What happens in the follicular phase
What happens in the Luteal Phase
Menstrual Cycle
The Follicular Phase is primarily under influence of FSH, while the Luteal Phase is primarily under influence of LH.
The follicular phase secretes estrogen while the luteal phase secretes estrogen&progesterone
In the follicular phase the follicle matures
In the Luteal Phase, the corpus luteum forms and ovulation occurs, if not fertilized it degenerates into corpus albicans and the endometrium sheds
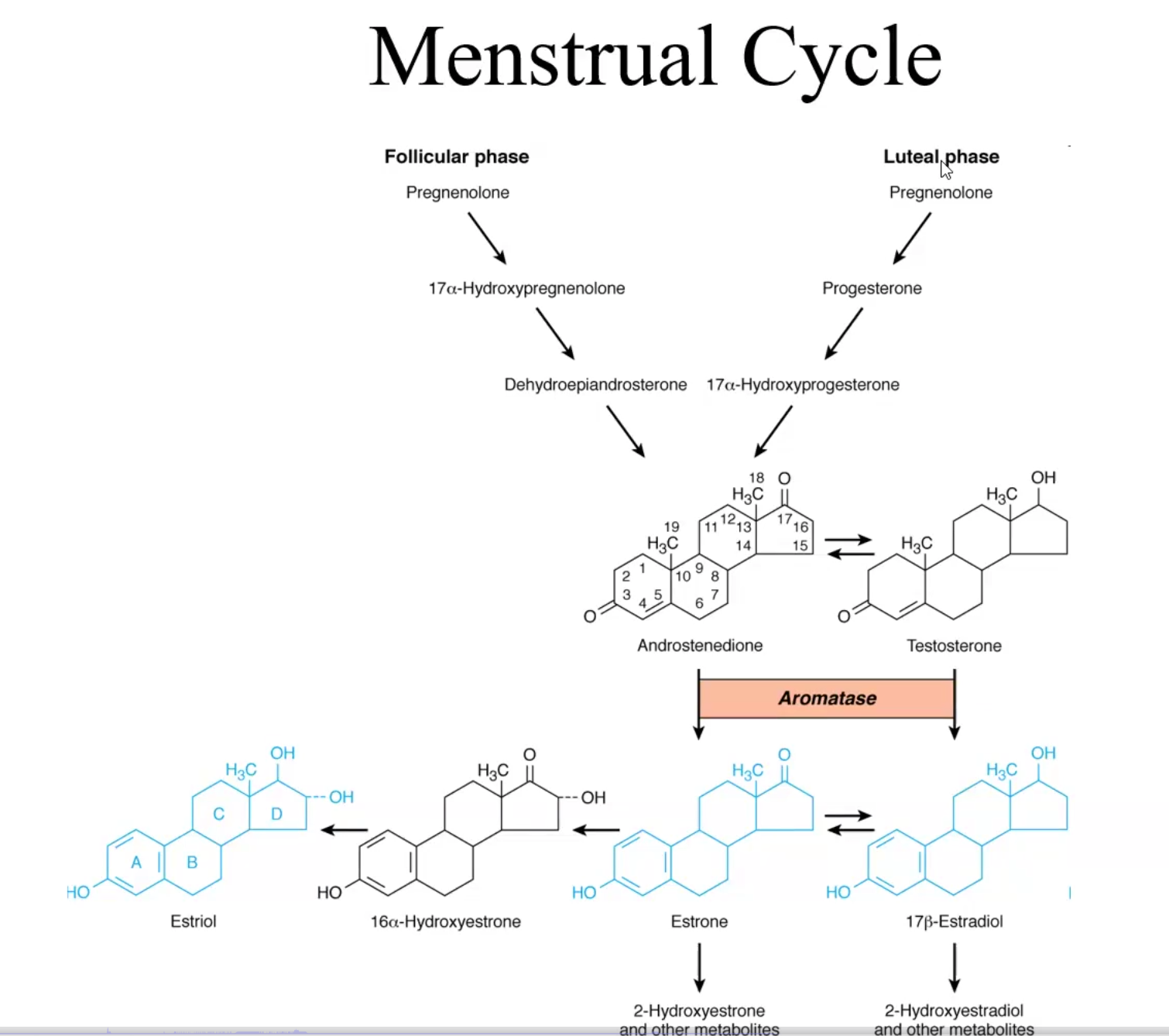
What enzyme mediates the conversion of testosterone into estradiol as well as androstenedione into estrone?
Aromatase, which creates an aromatic ring
Genomic Mechanism of action of Estrogens and Progestins
Passively diffuse into target cells
Bind to nuclear/cytoplasmic PR (A or B) or nuclear ER (alpha or beta)
Binding triggers receptor conformation and releases stabilizing/chaperone proteins Hsp90 and Hsp 70
Hormone-receptor complex dimerizes into homo/heterodimers
Activated dimer enters nucleus
Binds ERE or PRE nucleotide sequence and regulates gene transcription
Note: This process alters both transcription and translation → makes it slow acting but long acting
Natural Estradiol Pharmacokinetics
Physiological effect
Pharmacokinetics
Prescription Options
Clinical use + Combination therapy
Adverse Effects
Physiological effect:
Normal maturation of female, maintaining reproductive structures
Secondary sexual characteristics
Develop endometrial lining
Continuous exposure can cause abnormal hyperplasia
Lack of estrogen leads to osteoporosis
Increases plasma triglycerides and HDL, decreases plasma cholesterol and LDL levels
decreases risk of heart attack
Enhance coagulability of blood, can lead to thrombosis
Increase salt and water retention
Pharmacokinetics: Inactivated by hepatic first-pass metabolism so they have poor oral bioavailability
Thus natural is not used for contraception but used for hormone replacement therapy (menopause and 1ry hypogonadism)
n circulation binds to SHHG and albumin
Doses must be educed in hepatic dysfunction
Prescription Options of Estradiol by brand name:
Natural: well absorbed in all routes, poor oral bioavailability
P.o: Estrace
Micronized to avoid FPM and are administered p.o
IM: Delestrogen and Depo-Estradiol
Transdermal patch: Vivelle DOT, Climara, Alora, Minivelle, menostar
This route avoids first-pass metabolism and systemic effects such as clotting, strokes, MI
Vaginal insets: Estring, Imvexxy, Femring, Vagifem, Divigel
Same as transdermal
Topical gel: Elestrin and Estrogel
Synthetic Estrogens: used as oral contraceptives because they are modified to increase oral bioavailability; highly lipophilic and stored in adipose tissue
Steroidal:
Ethynyl estradiol
Mestranol
Non-steroidal:
Dinestrol
Diethylstilbestrol
Clinical use + Combination therapy:
HRT, Dysmenorrhea, Contraceptives, osteoporosis prophylaxis, hypogonadism, menopause, reduce heart attack risk, increase libido, dysfunctional uterine bleeding,
Menopausal Women w/ intact uterus → estrogen + progestin (to prevent cancer from uterine hyperplasia)
Prefest (p.o): Estradiol +Norgestimate
Activella (p.o and td): Estradiol + Norethindrone
Climara Pro (td): Estradiol + Levonorgestrel
Angeliq (p.o): Estradiol + Drospirenone
Prempro, Premphase): Conjugated estrogens + medroxyprogesterone
Hypogonadism and Menopausal women without uterus (add a progestin for intact uterus)
Menest (p.o): esterified estrogens (these are from horses and less potent but less side effects) (+ progestin if uterus is intact)
Cavaryx, EEMT (p.o): Esterified estrogen + Methyltestosterone (for libido, not progestin)
Not indicated for primary hypogonadism
Premarin (p.o or vaginal): conjugated equine (also from horse) estrogen mixtures
Also for abnormal uterine bleeding and atrophic vaginitis
Adverse Effects:
nausea, vomiting, postmenopausal bleeding, breast tenderness, mastalgia, edema, hypertension, thromboembolism, gallbladder disease, cholestatic jaundice, endometrial hyperplasia, endometrial cancer, migraines, vaginal infections
Contraindications: Estrogen-dependent neoplasms, undiagnosed genital bleeding, endometrial hyperplasia, Liver disease, thromboembolic disorders, heavy smokers, pregnancy
Progestins/
Physiological effect
Pharmacokinetics
Prescription Options
Clinical use
Adverse Effects
Physiological effect
Produced in ovaries, testes and adrenal gland\
Influences alveolar development, prepares uterus to receive the egg
In high concentrations inhibits gonadotropin release due to negative feedback
Decreases HDL, Increases LDL, increases risk for MI
Pharmacokinetics: Progesterone has limited oral bioavailability thus micronized form must be used for p.o administration
Synthetic progestins are more stable and more durable
Prescription Options:
1st gen: Medroxyprogesterone
2nd gen Norgestrel, Levonorgestrel (Plan B), Norethindrone
Androgenic and metabolic side effects
3rd gen: Norelgestromin, Norgestimate, Etonogestrel, Etonogestrel, Desogestrel, Dienogest
Least systemic effects
4th gen: Drospirenone (similar to spironolactone)
Used for treating premenstrual dysphoric disorder because of its anti mineralocorticoid activity
Combination therapy
Clinical use of synthetic: Hormonal contraception, HRT, Endometriosis, Endometrial carcinoma, dysfunctional uterine bleeding
Adverse Effects:
Edema, depression
Androgenic effects: thromboembolic events, decreased HDL, acne, hirsutism (male pattern hair), weight gain
Contraindications: Breast/cervical/uterine or vaginal cancer, history of thromboembolic disease, stroke, MI, thrombophlebitis, hepatic disease, undiagnosed vaginal bleeding
Selective Estrogen Receptor (ER) Modulators (SERMs)
Physiological effect
Pharmacokinetics
Prescription Options
Clinical use
Adverse Effects
Tamoxifen: nonsteroidal, p.o
Physiological effect: ER antagonist in breast tissue and ER agonist in bone → osteoporosis tx and prophy, increases HDL, and decreases risk/treats breast cancer
ER agonist in endometrium → Increases endometrial cancer risk
Pharmacokinetics:
HL: 7-14hrs
Hepatic clearance, excreted in bile
Adverse effects: hot flashes, nausea, vomiting, risk of venous thrombosis and endometrial cancer
Raloxifene: second gen SERM
Physiological effect: ER antagonist in breast, ER agonist in bone → osteoporosis tx and prophy, increases HDL only PREVENTS breast cancer and DOES NOT cause endometrial cancer!
Pharmacokinetics: nonsteroidal, p.o
HL: >24hr
Glucocoronidate in the liver and excreted in bile
Adverse effects: venous thrombosis, leg cramps and hot flashes
Anti-Estrogen SERM: Clomiphene: fertility drug
Physiologic effect: fertility drug that induces ovulation
Selectively antagonizes hypothalamic and pituitary ER, thus preventing negative feedback from estrogen → Continued release of FSH and LH
Also acts as an antagonist to ER receptors
Adverse effects: hot flashes, ovarian cyst formation, ovarian hemorrhage due to enlargement
Anti-Progestin
Physiological effect
Pharmacokinetics
Prescription Options
Clinical use
Adverse Effects
Mifepristone: abortifacient drug during first 10 weeks of gestation; contraceptive off-label
Physiologic effect: PR antagonist and GR antagonist
Clinical use: induce therapeutic abortion, combined with Misoprostol to induce contractions
Adverse effects: uterine bleeding, incomplete abortion
Danazol: tx endometriosis
Physiologic effect: partial agonist that binds to PR, GR and AR but not ER; inhibits gonadal function
Adverse effects: weight gain, edema, decreased breast size, acne, hirsutism, changes in libido
Aromatase Inhibitors
Physiological effect
Clinical use
Anastrazole, letrozole, Exemestane: tx of advanced breast cancer in Tamoxifen-resistant tumors
Physiologic effect: Inhibits conversion of testosterone into estradiol
Pure Estrogen receptor Antagonist
Physiological effect
Clinical use
Physiological effect: Completely gets rid of estrogen because tamofixen-resistant breast cancer moves ER receptor to membrane and are much more sensitive to small amounts of estrogen to feed themselves
Clinical use: treats breast cancer in Tamoxifen resistant breast cancer pt