aphg unit 5.1-5.12
1/61
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
subsistence agriculture
food production to feed a farmers family or community, uses manual labor, small scale, mostly in LDCs
commercial agriculture
mass production of food for sale (think commerce), uses machinery, large scale, more common in MDCs
intensive agriculture
requires greater amnt of labor/capital relative to the amnt of space being used
extensive agricultural
requires fewer amnt of labor/capital relative to the amnt of space being used
pastoral nomadism
agriculture based on the herding of domesticated animals
extensive subsistence farming
located in asia and africa in the arid climate areas
products include cheese milk and wool
relevant terms include transhumance and developing countries
shifting cultivation
agriculture using slash and burn techniques and regular rotation sites
extensive subsistence farming
located in the americas asia and africa in tropical climates
products include crops firewood and timber
relevant terms include human-environment interaction possibilism and developing countries
intensive subsistence - wet rice dominant
agriculture involving the regular application of intensive labor
intensive subsistence agriculture
located in south east asia and india in tropical climates
products include rice
relevant terms include double cropping terraces and developing countries
intensive subsistence - not wet rice dominant
agriculture involving the regular application of intensive labor
intensive subsistence agriculture
located in east and south asia in continental climates
products include millet soybeans sorghum potatoes wheat and barley
relavant terms include double cropping terraces and developing countries
plantation
agriculture practice where cheap labor is used to grow cash crops
intensive commercial agriculture
located in the americas africa and asia in tropical climates
products include cotton sugar coffee rubber and exotic fruits
relavant terms include cash crops forced migration slavery and developing countries
mixed crop and livestock
fattening up animals through crops to sell them
intensive commercial farming
located in the us europe asia and africa in temperate climates
products include meat milk eggs and crops
relavant terms include crop rotation agribusinesses feedlots and developed countries
dairy farming
raising cows to market dairy goods in the market
intensive commercial farming
located in india and the us in cold mid latitude climates
products include milk and cheese
relavant terms include milkshed agribusiness and developed countries
grain farming
growing grain products for sale to be made into products for human consumption
extensive commercial farming
located in china india and us in temperate climates
products include wheat barley and corn
relavant terms include agribusiness and developed country
ranching
commercial grazing of livestock
extensive commercial farming
located in the americas australia and asia in semiarid/arid climates
products include meat beef chicken and pork
relavant terms include rural areas agribusiness and developed country
mediterranean farming
growing specialized crops in a climate like the mediterranean region
intensive commercial agriculture
located in the mediterranean region chile south africa and california (basically any place that has the mediterranean climate)
products include olives grapes and pistachios
relavant terms include horticulture agribusiness and developed countries
market gardening
growing of highly profitable crops for sale
intensive commercial farming
located in florida and asia in temperate climates
products include fruits and medicinal plants
relavant terms include horticulture commercial gardening truck farming agribusiness and developed countries
clustered/nucleated
type of rural settlement pattern, most common in europe parts of africa and north east us, its when settlements are grouped together
they are the result of communal farmland, leaving land open for farming, and residents having easier access to services if their settlements were grouped this way
dispersed
type of rural settlement pattern, most common in the midwest and west of us, it’s when settlements are spread out
they are result of gov land policies, individual pioneer families setting up their farms in the homestead act, and independently owned farms
linear
type of rural settlement pattern, common in quebec french america louisiana, it’s when settlements are in organized lines
they are a result of access to a resource like a river and farmers building along a water way or road for easier transportation
metes and bounds
type of survey method, it was introduced by the british and its most common in north east us, it uses natural physical features of a landscape to demarcate pieces of land - leads to irregular shapes
township and range
type of survey method, it uses an imposed grid pattern and was made by the homestead act, territory in west us use this type of survey method
long lots
type of survey method, used mainly by the french, it’s when there are strips of land around a river or road, also called ribbon farms
first agricultural revolution
occured ~8000-14000 years ago and was the shift from hunter-gatherers to to agricultural societies, farming and domestication was invented
east asia
a crop hearth where rice and millet originated
sub saharan africa
a crop hearth where sorghum yams millet and rice originated
latin america
a crop hearth where beans potatoes cotton and corn/maiz originated
south west asia
a crop hearth where barely wheat lentil and olives originated
southwest asia
the animal domestication hearth taht domesticated the most important animals such as cattle goat and sheep and pig
silk road colombian exchange trade
how agriculture diffused
second agricultural revolution
happened at the same time as the industrial revolution, it marked an increase in population and food production with the aid of new technology
resulted in better diets which lead to high life expectancies
the beginning of commercial farming
positives of second agricultural revolution
new technology made farming easier, reduced the number of animal labor, no land is unused, barbed wire is invented, higher yields, better diets, and higher life expectancy
negatives of second agricultural revolution
increased pollution and co2 emissions, decline in soil nutrients and human labor, and an increase in the amnt of pesticides used
four crop rotation system
an agricultural practice where four different crops are planted in a sequential order over four seasons or years on the same land to improve soil health and reduce pests
green revolution
the third agricultural revolution, occurred around 1960s-now, it introduced high yield seeds mechanized farming and increased chemical usage
norman bourlaug
father of the green revolution
crossbreeding
mating two diffenrt breeds to make a desirable trait - leads to hybrid plants
genetically modified organisms
an organisms genome is altered to get specific traits that allow for increased production of livestock and crops
positives of the green revolution
increased food production and economic growth, reduction of global hunger and production costs, and the green revolution allowed for LDCs to have higher yields
negatives of the green revolution
decreased jobs for women, unequal development, decline in family farms - they can’t compete, monoculture farming, water contamination, soil degradation/depletion
agribusiness
the economy of agriculture
monocropping farming
growing one crop in a large scale over a wide area (reduces biodiversity)
bid rent theory
theory that value of land is affected by its relationship/distance to the market
more wanted land that is closer to the market is higher cost which means less land is bought - results in intensive farming
less wanted land that is farther from the market is less costly which means more land is bought - results in extensive farming
economies of scale
large scale farming results in bulk purchasing for less money, results in higher yields, basically when production is high the cost of production is low
technological advancements
will lead to the cost of operating to be high but also increases efficiency, also increases the carrying capacity of the land bc of higher yields
commodity chain
complex network that connects production places with distribution to consumers in steps
ex: farm gate → transport → processing → manufacturing → transport → retailers/exporters
slash and burn
type of agricultural practice that alters the landscape, when trees are cut and land is burned, results in deforestation soil depletion and soil erosion
terrace farming
type of agricultural practice that alters the landscape, when terraces are built, results in hills becoming like steps and soil erosion
irrigation
type of agricultural practice that alters the landscape, when water systems are built, results in depletion of water sources
pastorol nomadism
type of agricultural practice that alters the landscape, it’s when herds are taken to graze, results in overgrazing which results in soil erosion and desertification
draining wetlands
type of agricultural practice that alters the landscape, when wetlands are drained for agriculture, results in a decrease in biodiversity and habitats for animals and increases in storm and flood damage
pollution
an effect of a agricultural practices that affects the environment, occurs when there is increased demand for meat or increase in the usage of chemicals or fossil fuels
soil salinization
an effect of a agricultural practices that affects the environment, process where salt builds up in the soil bc water evaporates quickly bc plants can’t absorb the water, is happening more bc land is being drained of water (ex the aral sea)
desertification
result of overgrazing, when the area becomes like a desert
deforestation
an effect of a agricultural practices that affects the environment, increases greenhouse gases and soil erosion and decreases biodiversity
organic farming
healthier farming that doesn’t use harsh chemicals or gmos and is also more sustainable
value added speciality crops
something different that enhances a procducts value (ex strawberries into strawberry jam)
fair trade
fair everything! workers are getting paid fair and it also promotes sustainability
local farmers market
more sustainable than large scale cooperation farming as there is less pollution as less transportation is used bc the market is local
community supported agriculture
a system that is set up where farmers support one another and people commit to buy from that farm
food deserts
areas with little to no access to healthy nutritious food, can occur in MDCs and LDCs, causes more health problems rates, basically when there is no fresh food/supermarkets within a walkable distance
aquaculture
farming on the water (ex fishing)
von thunen model
model that was used to reduce land and transportation costs while maximizing profits
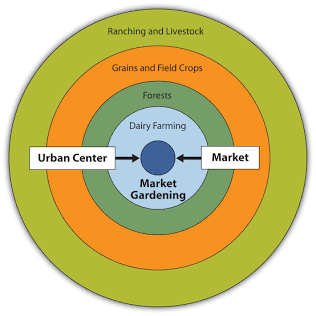
assumptions of the von thunen model
assumptions include that all land is flat, only one single market (disproved through the global market), all land has equal access to the market, farmers want to maximize their profits, all land has similar characteristics