Genetics Exam 1 (DNA Transcription)
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are the major steps of transcription (3)
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Initiation in Prokaryotes (ecoli)
Sigma, subunit of RNA polymerase holoenzyme) positions RNA polymerase core enzyme on the DNA template strand at the transcription start site and disassociates after transcription starts
Elongation in prokaryotes (ecoli)
Reaction is catalyzed by RNA polymerase core enzyme
NTPs (nucleoside triphosphates) added to the 3’ end of the nascent (new) RNA
Termination in prokaryotes (ecoli) (2 mechanisms)
Intrinsic termination
Hairpin structure in RNA causes RNA polymerase to stall
RNA-DNA duplex dissociates due to a weak dissociation between the RNA and DNA
Rho-dependent termination
Hairpin structure in RNA causes RNA polymerase to stall
Rho (helicase) unwinds the RNA-DNA duplex
What does polycistronic means and what does it allow for
one mRNA can encode several proteins
Allows for tight regulation of protein synthesis for proteins that are in the same pathway
Initiation in Eukaryotes
General transcription factors bind to the core promoter
GTFs are named according to the polymerase with which they interact
Ex: TFIIA
GTFs recruit RNA polymerase to form the preinitiation complex (PIC)
RNAP cannot locate a gene on its own
Recruitment of polymerase by GTFs is increased by activators bound to enhancer sequences (we’ll revisit this when we discuss gene regulation)
Elongation in Eukaryotes
RNAP catalyzes NTP addition to the 3’ end of the nascent RNA strand (much like in prokaryotes)
During transcription
5’ m7G cap is added to the mRNA
Introns are spliced out (exons are spliced together) to form one continuous coding sequence
What is the purpose of m7G cap
Attached to mRNA by a 5’-5’ linkage when mRNA is 20-30 nucleotides long
Necessary for translation
Protects RNA from 5’ to 3’ exonucleases
What are the subunits of spliceosome called
snRNP which base pairs at:
5’ splice site
3’ splice site
Branch point A
which:
Loops out intron
Exons covalently bonded together
Introns released as a lariat and likely degraded
Termination in Eukaryotes
mRNA is cleaved at the polyA cleavage site
mRNA is released from the transcription bubble
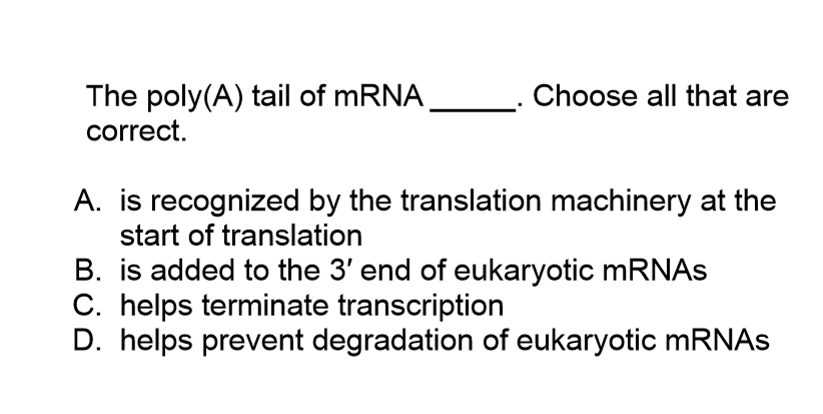
mRNA is polyadenylated
About 250 adenine nucleotides (ATPs) are added to the 3’ end of the RNA by PolyA Polymerase
Called the polyA tail
PolyA tail is coated with protein
Necessary for translation
Protects 3’ end of mRNA from 3’ exonucleases that would otherwise degrade it
Draw transcription bubble
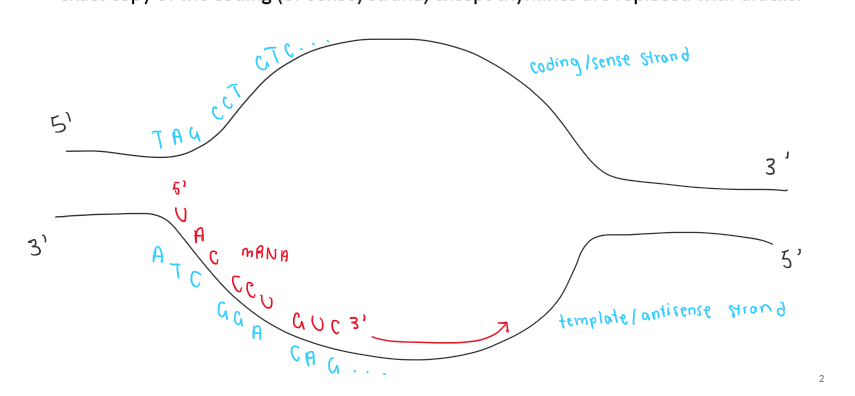
mRNA has the sequence of 5’-AUGUACGGAGGGUAG-3’, What is the sequence of the DNA template strand?
coding: 5’- ATG TAC …. TAG - 3’
noncoding: 3’ TAC ATG…. ATC-5’
answer:
5’- CTA CCC …. CAT-’3
Sigma subunit of bacterial RNA polymerase
bind to bacterial gene’s promoter
is required for RNA polymerization for holoenzyme but not for core
Is NOT required for termination of transcription
Is NOT required for ribosomal binding
Is part of holoenzyme and not the core enzyme
What are the four major differences between prok. and euk. transcription
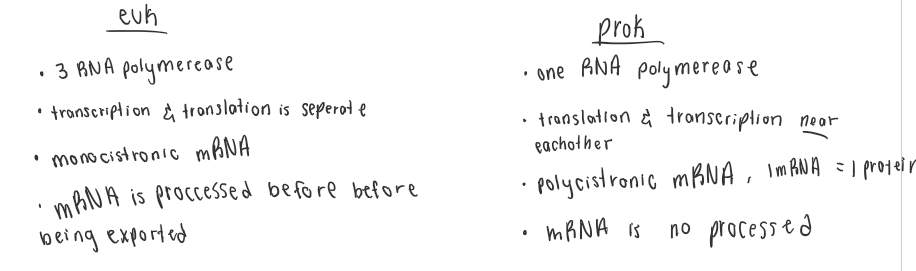
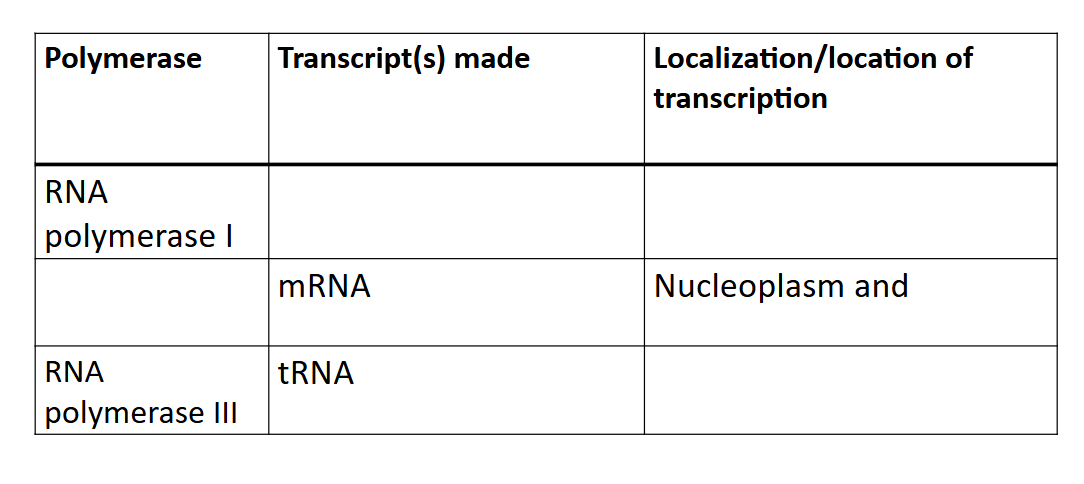
complete the table
Top row: rRNA, nucleoslus, mitchondria, and chloroplast
middle row: RNAP II, mRNA+snRNA
bottom row: tRNA, nucleoplasm
3 main processing steps for euk pre-mRNA to become mature mRNA
1.) Capping of 5’ end, conected with 5’ to 5’ bond
2.) Splicing out intron, splicing tgt extrons
3.) Polyadenylation of 3’ end, adding PolyA tail
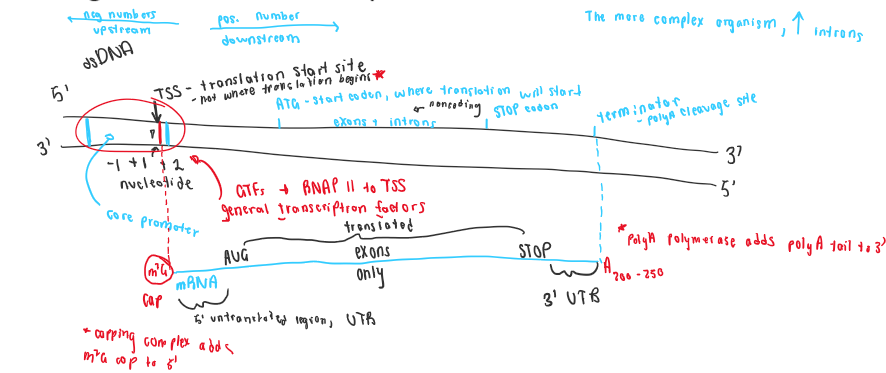

Affects snRNP binding, intron is not spliced out as it will less like complementary base pair






all