Homogenous Hydrogenation - Lecture 6-8
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
activation of dihydrogen by TM, mechanisms, chemoselective and stereoselective reactions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Hydrogenation reaction
favourable dynamics
alkene → alkane
carbonyl → alcohol
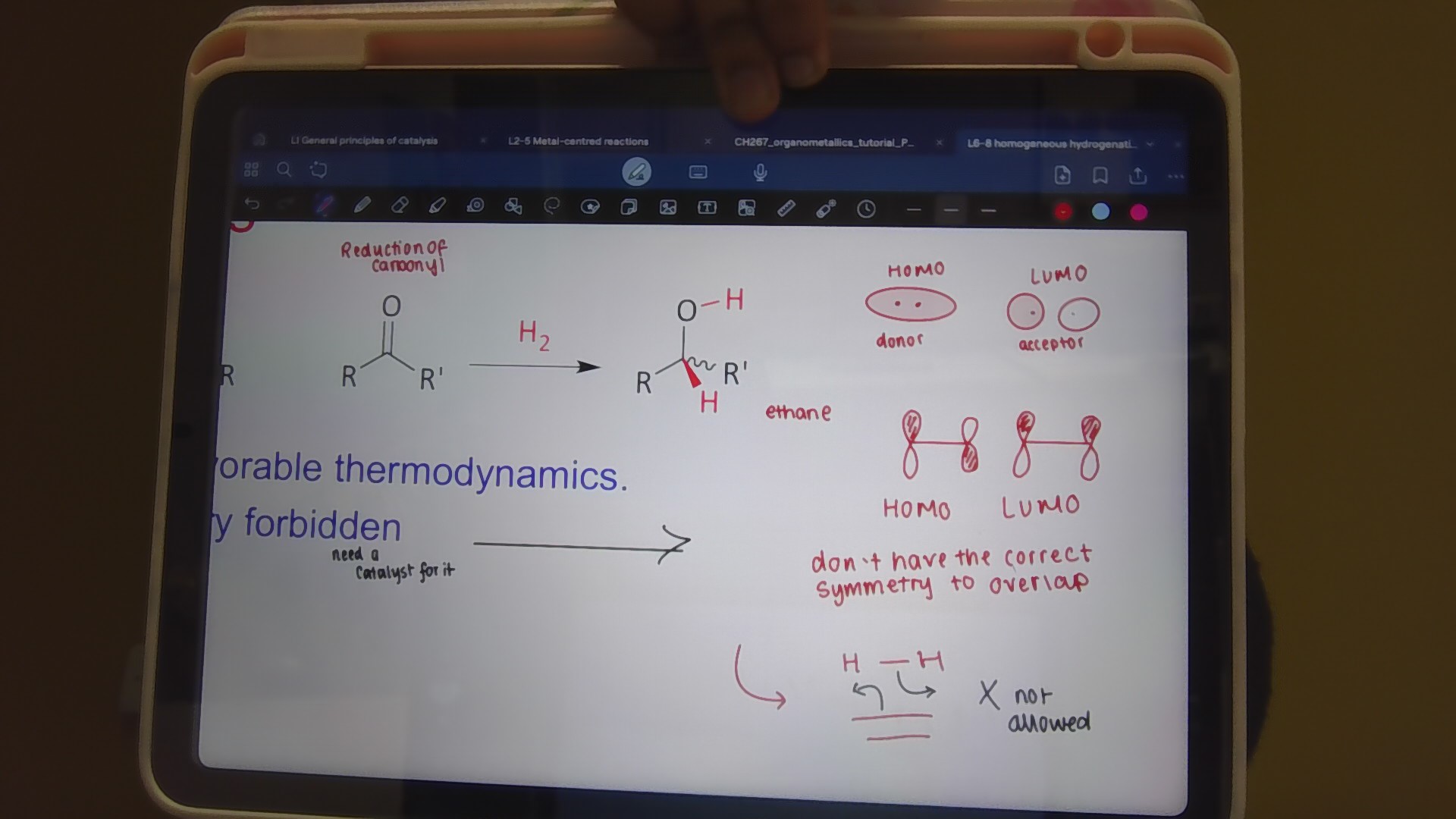
The direct addition of H2 is forbidden why?
symmetry
the HOMO and the LUMO of the dihydride are of the wrong symmetry to overlap with the HOMO and LUMO of the alkene
How to do a hydrogenation reaction?
stoichiometric addition of hydride and proton
LiAlH4 or NaBH4 reduction of ketones and aldehydes (H- then H+)
catalytic activation of hydrogen using transition metals
metal nanoparticles / metal surfaces = heterogenous
single TM centre = homogenous
transfer hydrogenation - extraction of hydrogen from sacrificial molecules
take it from an alcohol
Activation of dihydrogen
very stable molecule
strong and completely non polar H-H bonds
typically require activation with a (reactive) TM
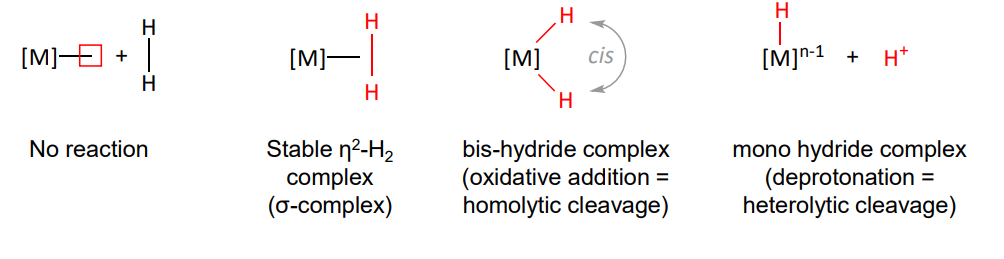
no reaction
stable n2-H2 complex (L)
dihydride complex (X2) - most common
mono hydride complex
A coordinated H2 has ….
weaker bonds
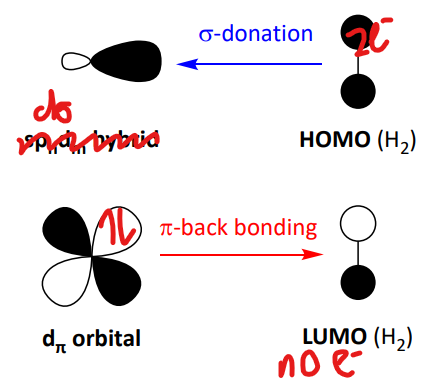
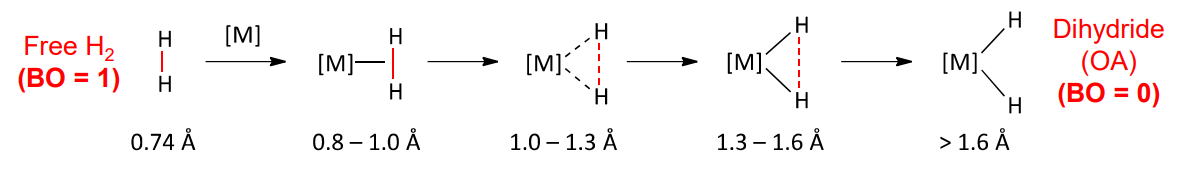
bonding in dihydrogen complexes
formed by both HOMO and LUMO of the H2 with the frontier MOs of TM
results in population of the sigma* orbital of the HH and H-H bond elongation
H-H bond length elongation
pi back donation leads to reduction of H2 bond order
complete donation results in OA of H2
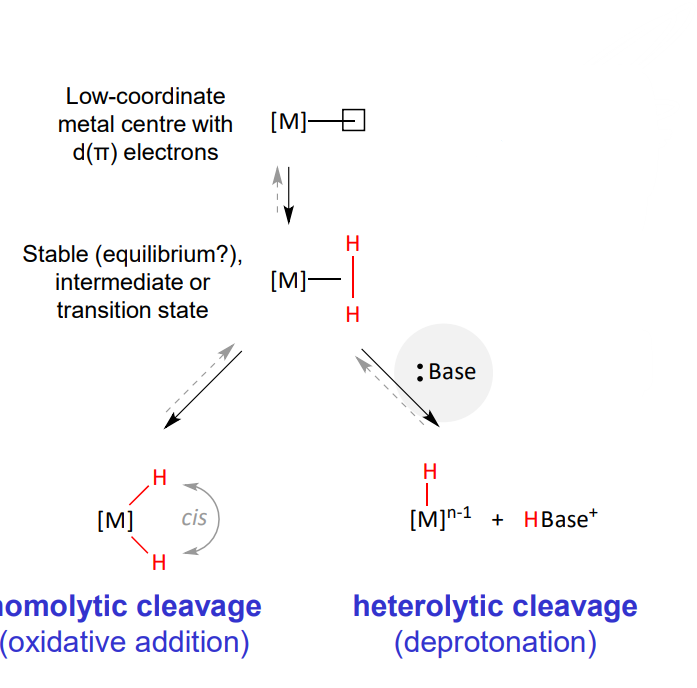
Reactivity of dihydrogen complexes
low coordinate metal centre with d(pi) electrons (free coordination site)
stable intermediate or TS (of metal and dihydrogen)
either
homolytic cleavage via oxidative addition change in VN = +2
heterolytic cleavage via deprotonation by base, change in VN = 0
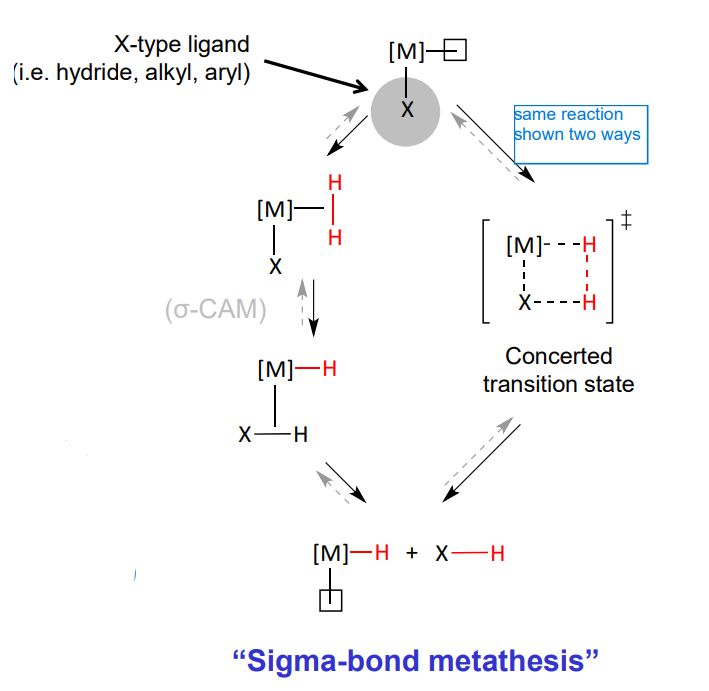
Reactivity of dihydrogen complexes - when there is a x type ligand cis to the free coordination site
x ligand cis to the free coordination site
sigma bond metathesis
concerted transition state
Wilkinson’s pre catalyst
involves OA of H2
common for group 9 metals - before coordination of the olefin
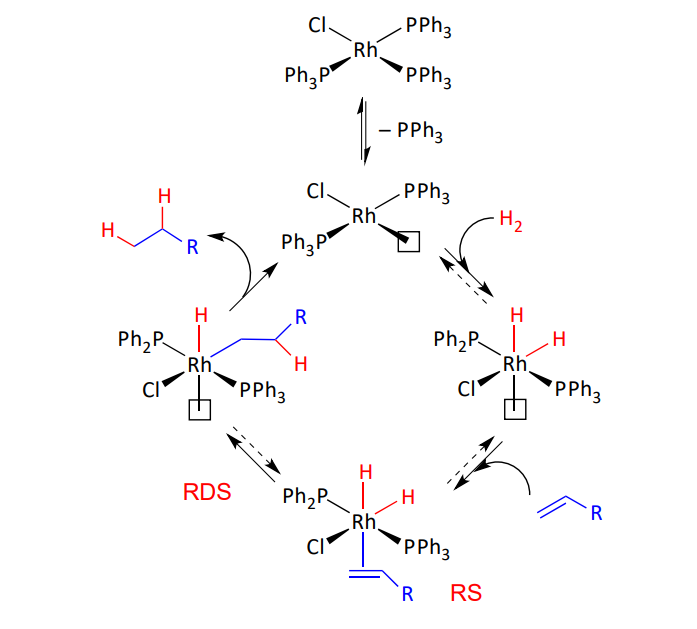
Explain this kinetic pathway of a Wilkinson’s catalyst
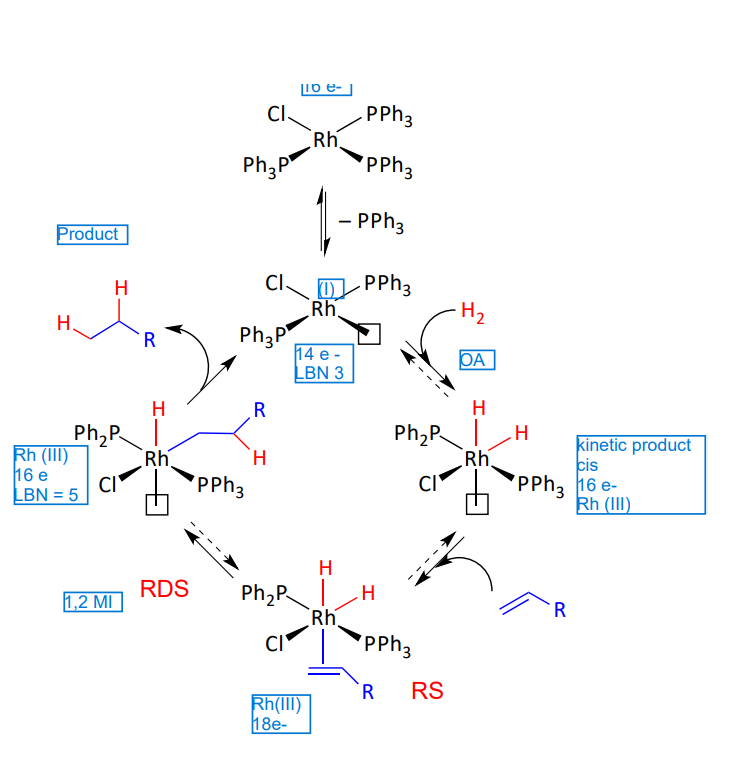
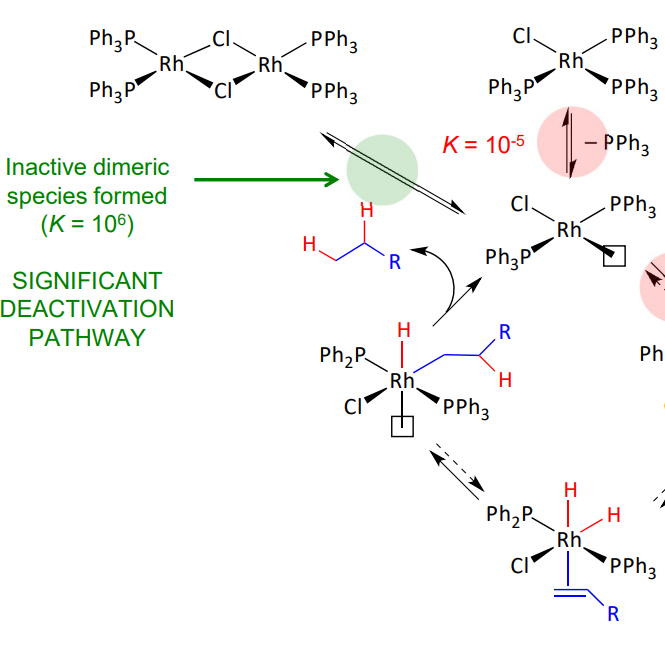
wilkinson’s pre catalyst - deactivation pathway
lone pair on chlorine forms bonds
forms an inactive dimeric species
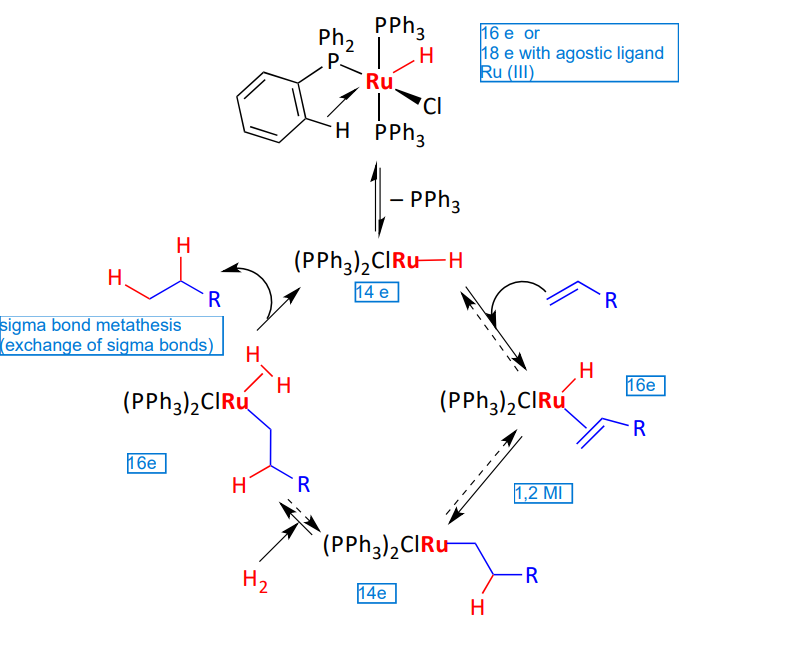
Mono hydride mechanism
single hydride ligand present prior to the coordination of the alkene
no OA
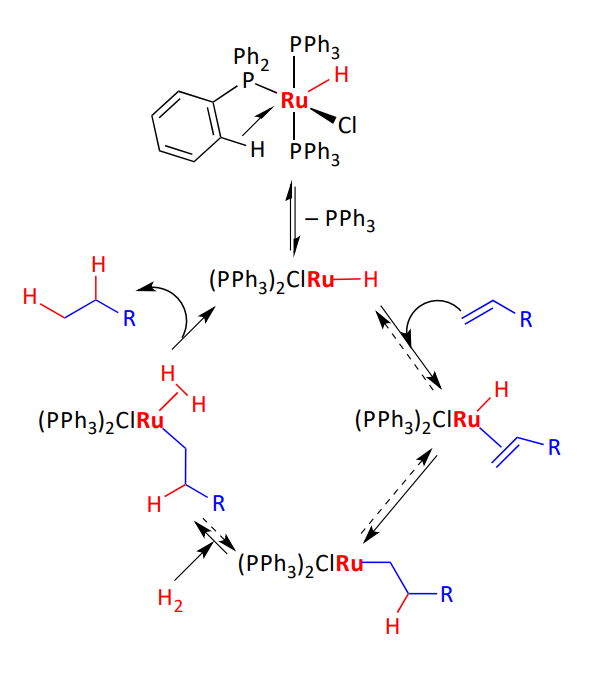
Explain this Mono hydride mechanism
Asymmetric hydrogenation catalysis
ability to control stereochemistry has very important applications
selectivity is reported as enantiomeric excess ee(%) = %major - %minor
Re vs Si face
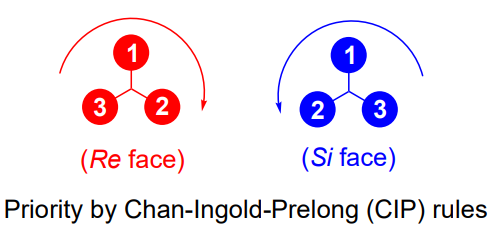
chiral chelating ligands
when you have the product - not enantiomers they are distereoisomers
Control of enantioselectivity
use chiral, enantiopure metal catalyst [m]
![<ul><li><p>use chiral, enantiopure metal catalyst [m]</p><p></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a67bc70c-c3d9-4db9-856b-df299ae02813.png)
Curtin-Hammett principle
If A + B are in fast equilibrium (relative to product formation), then the product composition is determined by the difference G at Ts A and TS B
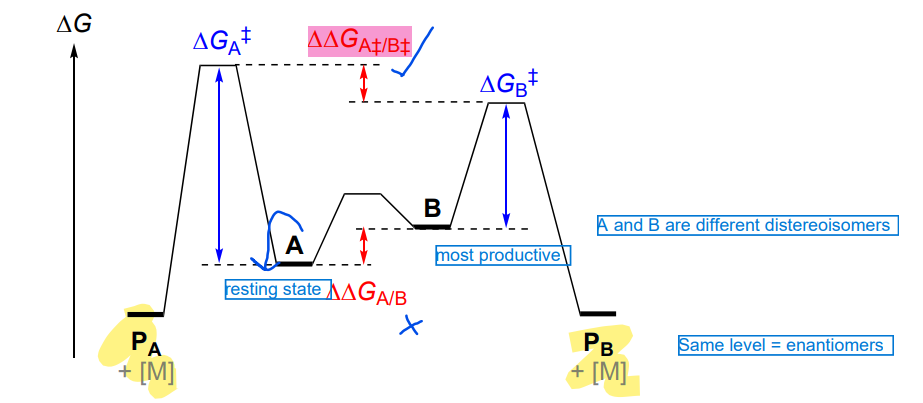
enamide hydrogenation - why is there such different barriers
major diastereomer gives minor product (S) due to forced steric clash
minor diastereomer gives the major product (R) due to minor changes in conformation, lowest barrier
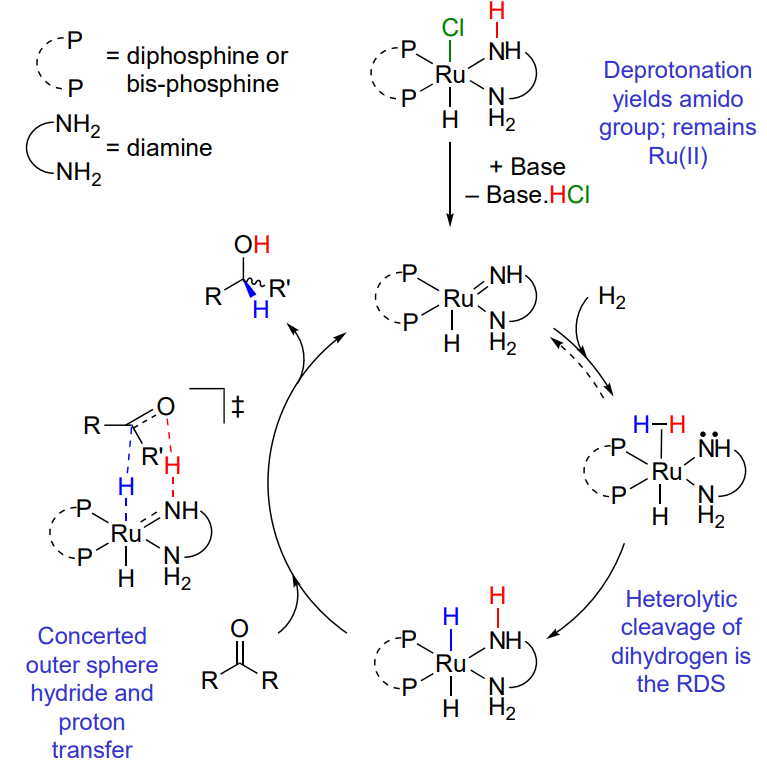
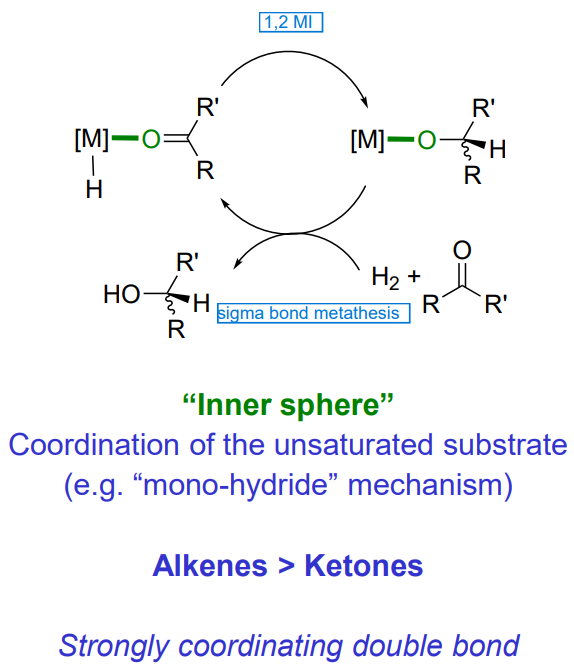
Hydrogenation of carbonyls - Inner sphere
coordination of the unsaturated substrate (mono hydride mechanism - no change in OS or VN)
Alkenes > ketones
strongly coordinating double bond
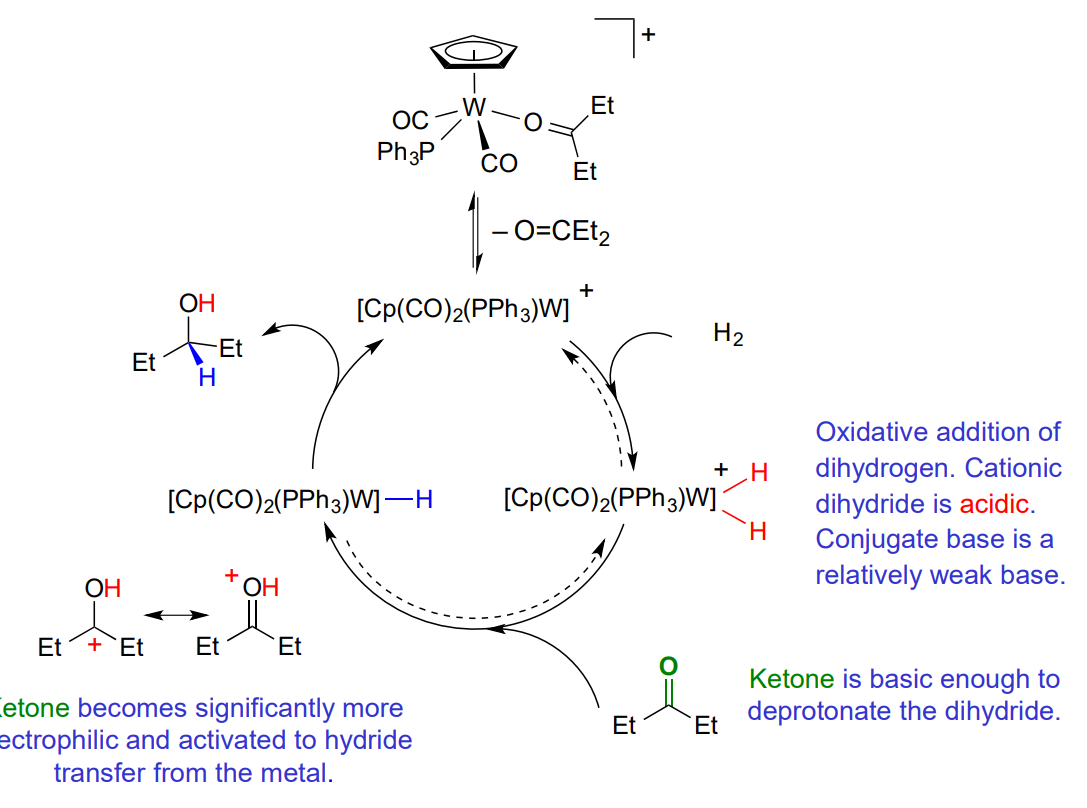
Hydrogenation of carbonyls - Outer sphere
no direct coordination of the unsaturated substrate
ketones > alkenes
polar double bond
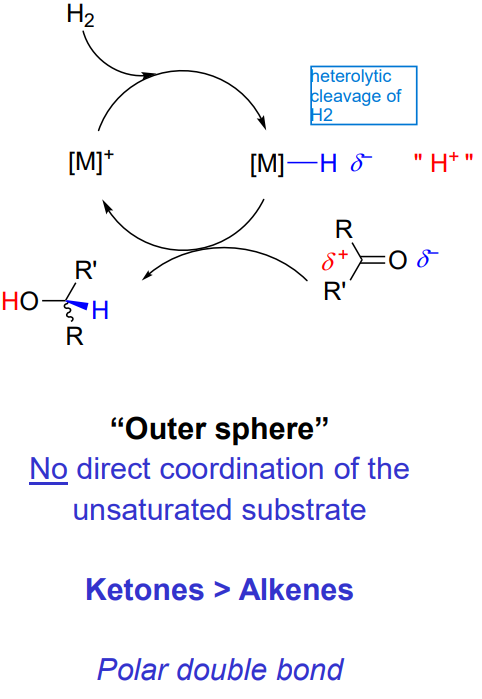
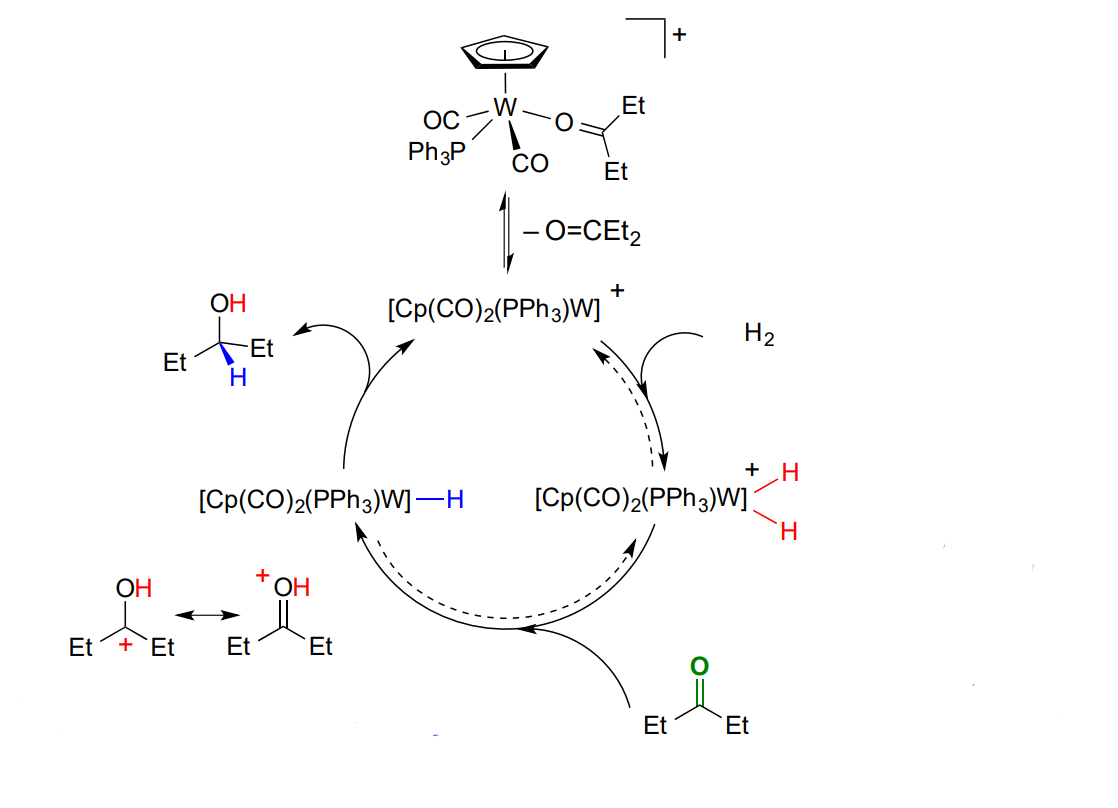
Explain the outer sphere hydrogenation - ionic mechanism
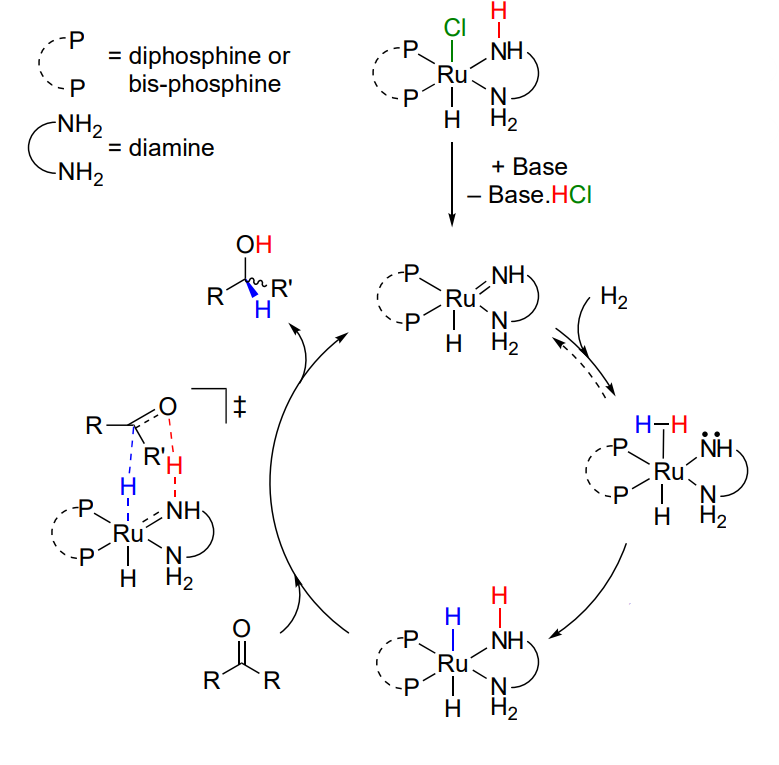
Explain the outer sphere hydrogenation - bifunctional mechanism