412 Cadaver Lab Exam 2!!!
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
220 Terms
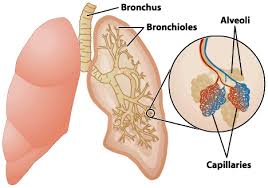
Lungs
organs in the respiratory system responsible for exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment
Parietal pleura
outer layer of pleura lying closer to the ribs and chest wall
Visceral pleura
inner layer of pleura lying closer to the lung tissue
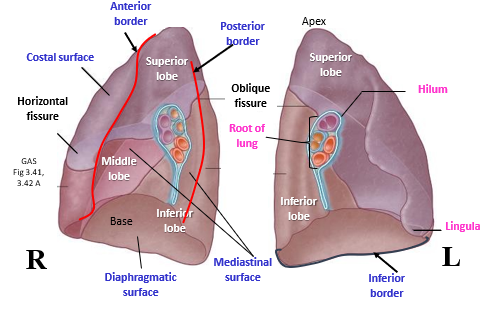
Hilum of lung
midline region where the bronchi, blood vessels, and nerves enter and exit the lungs
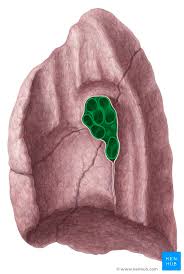
Costal surface of lung
anterior, lateral, and posterior surfaces; pressed against ribs
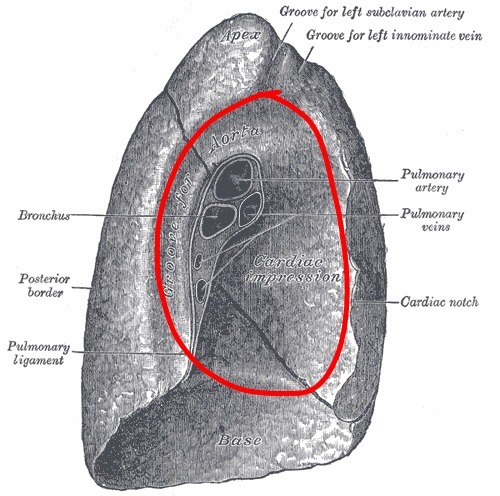
Mediastinal surface of lung
faces medially toward the heart, contains the hilum
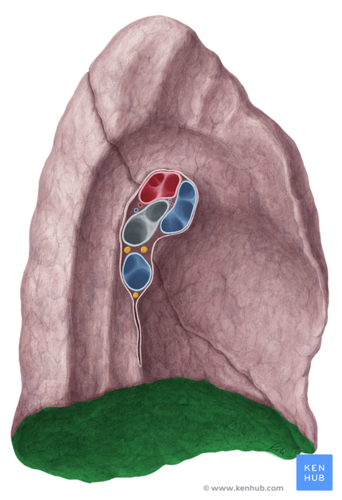
Diaphragmatic surface of lung
wide, inferior surface of the lungs; surface making contact with the diaphragm
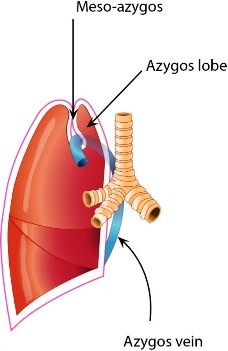
Sulcus of the azygos vein (right lung)
a furrow/groove that accommodates the azygos vein, splits the top of the right upper lobe
Sulcus of the aorta (left lung)
a broad deep groove on the medial aspect of the left lung above and behind the hilum receiving the arch of the aorta and the thoracic aorta
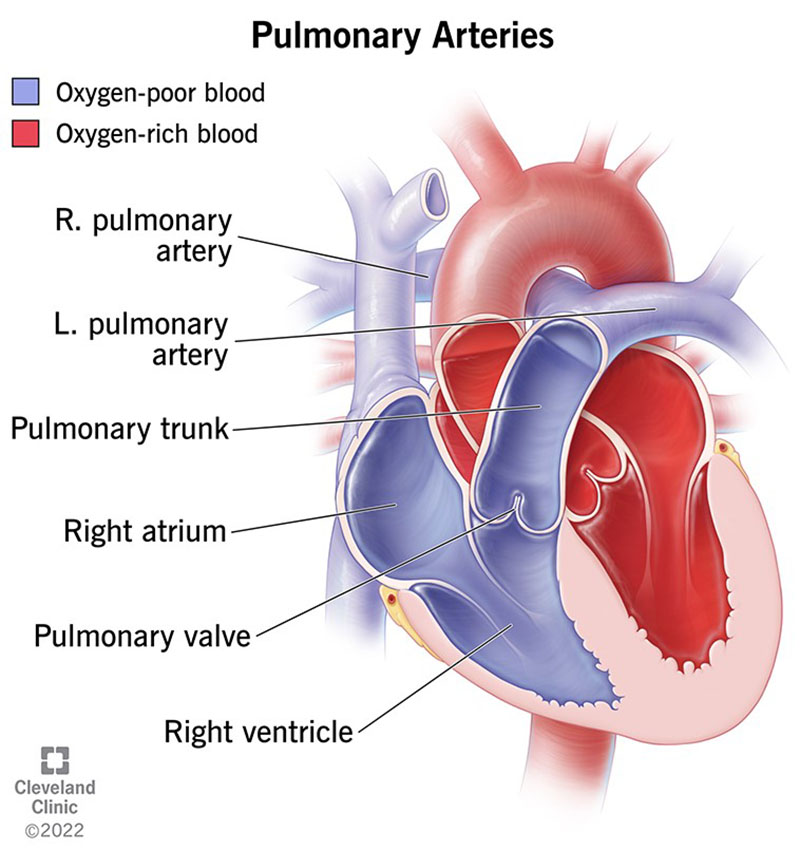
Pulmonary artery (on heart)
artery carrying oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
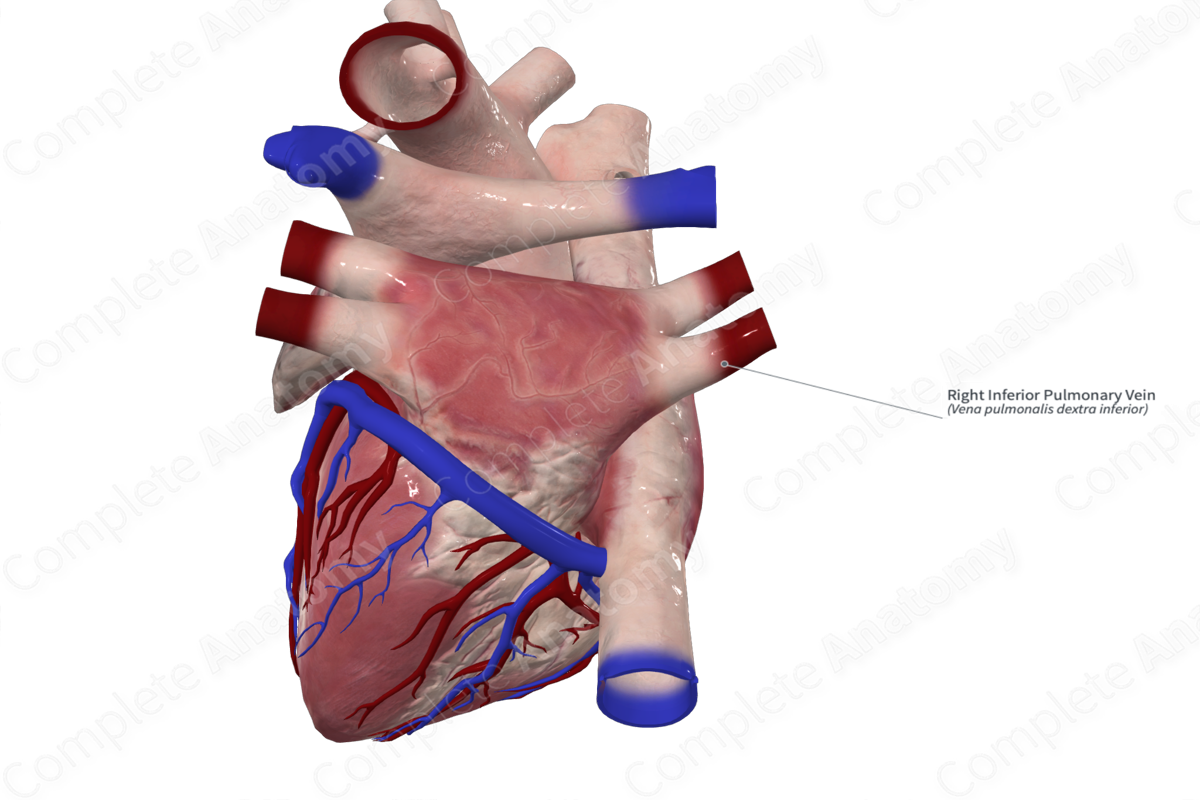
Pulmonary veins (on heart)
carry the oxygenated blood from the lungs into the left atrium of the heart
Primary bronchus
a pair of branches of the trachea that lead to the right and left lung; consist of incomplete rings of cartilage and are lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
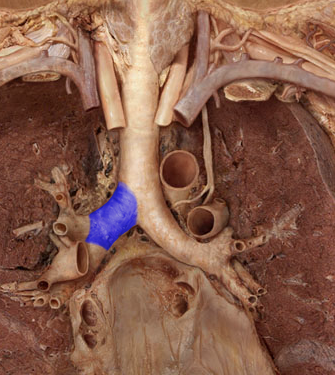
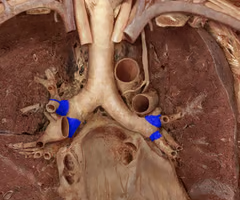
Secondary bronchus
branches of the primary bronchi which supply each lobe of lung; there are 2 in the left lung and 3 in the right lung
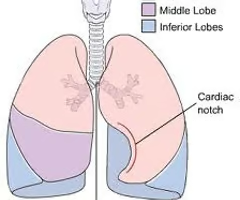
Lobes of lung
superior, middle and inferior - right; superior and inferior - left
Horizontal fissure
separates the superior and middle lobes of the right lung
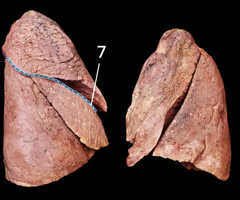
Oblique fissure
separates the superior and inferior lobes of the left lung
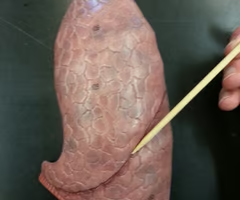
Cardiac notch
lateral deflection of the anterior border of the left lung to accommodate for the heart
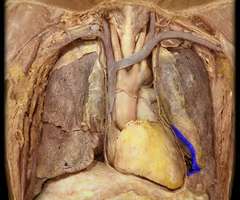
Lingula of left lung
The region of the left lung that corresponds with the right middle lobe, anterior projection of left superior lobe

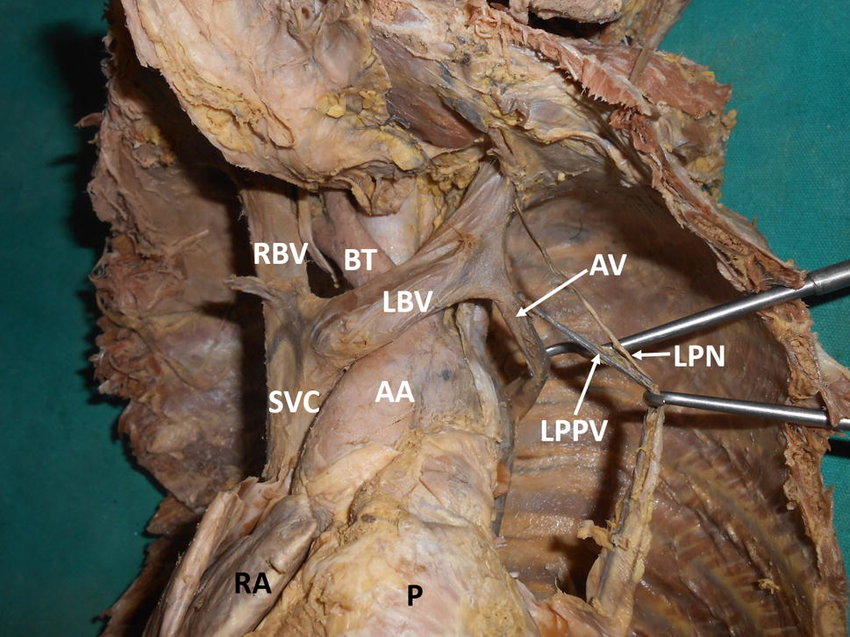
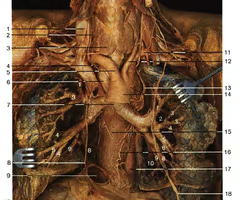
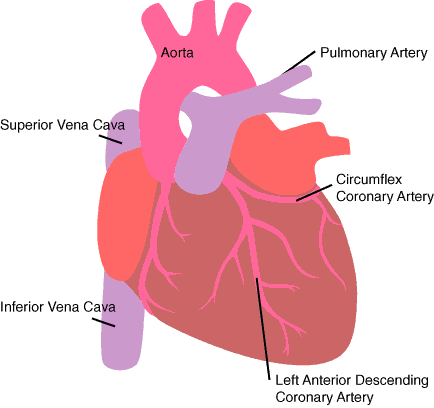
Superior vena cava (in thoracic cavity)
receives blood from the head and arms and chest and empties into the right atrium of the heart
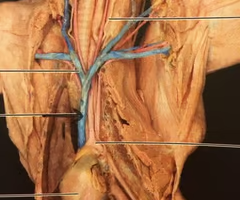
Inferior vena cava ( thoracic cavity)
receives blood from lower limbs and abdominal organs and empties into the posterior part of the right atrium of the heart
Azygos vein
a vessel that drains blood from the chest wall and empties into the superior vena cava, main branch on right side of vertebral column
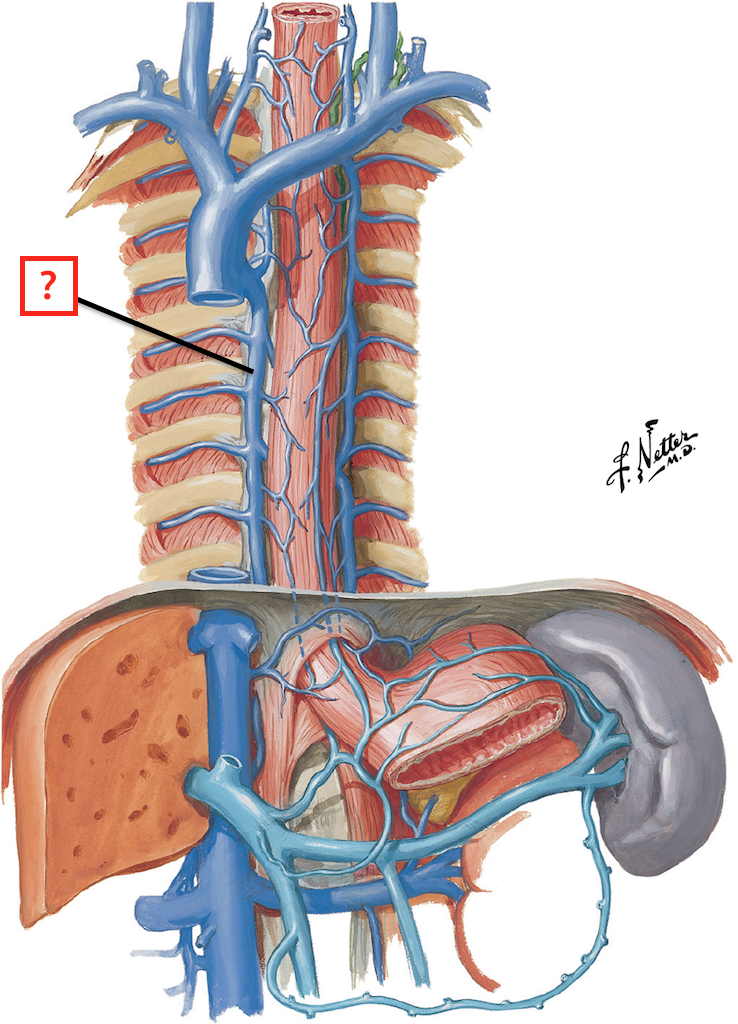
Right and left brachiocephalic veins
drain the head, neck, and upper extremities and unite to form the superior vena cava
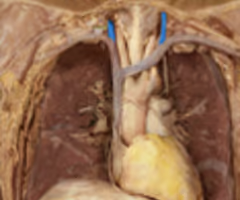
Right and left internal jugular veins
return deoxygenated blood to the heart from the head region
Right and left external jugular veins
not doing
Right and left subclavian veins
carries deoxygenated blood from other smaller veins; carries this blood to brachiocephalic vein
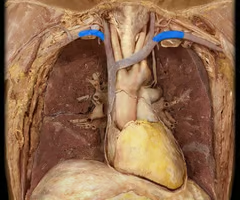
Vertebral veins
serves posterior head, cervical vertebrae, spinal cord
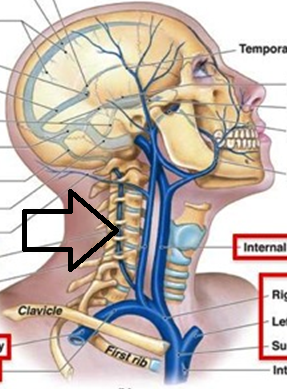
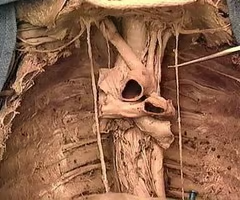
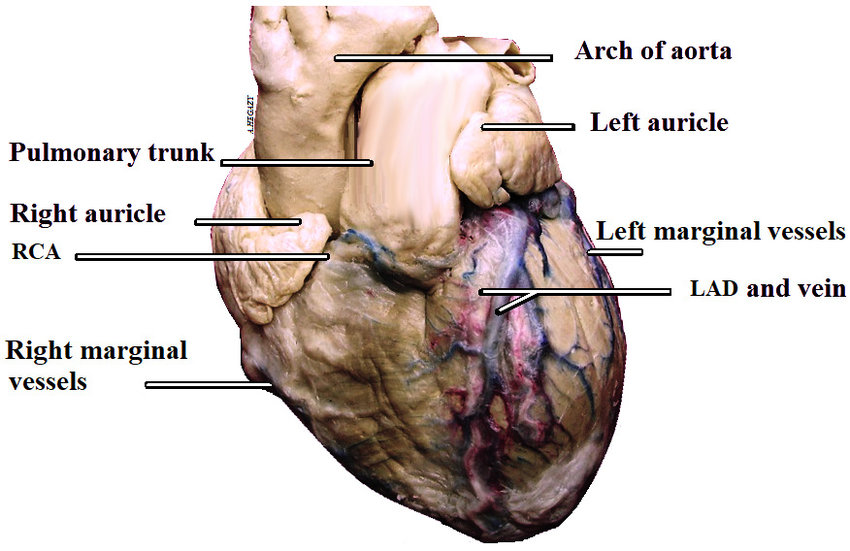
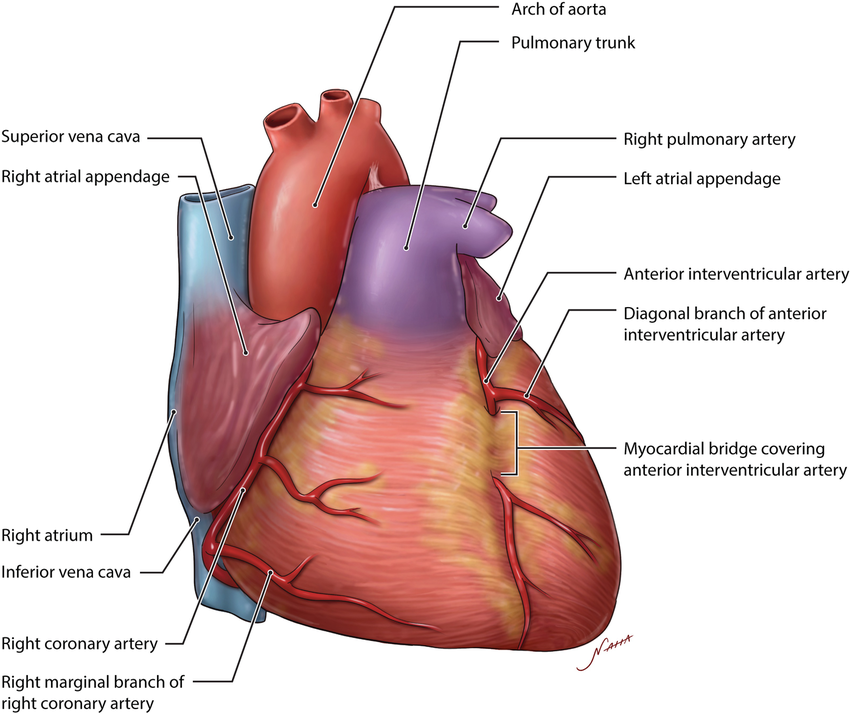
Arch of aorta
most superior portion of the aorta, lying between the ascending and descending segments of the aorta
Brachiocephalic trunk
first large artery arising from the aortic arch, carries oxygenated blood to the neck, head, and right forelimb
Right and left common carotid arteries
carries oxygenated blood; right carotid artery branches off of brachiocephalic artery; left carotid artery branches directly off aorta
Right and left subclavian arteries
carries oxygenated blood; right subclavian artery branches off brachiocephalic trunk; left subclavian artery branches directly off of aorta
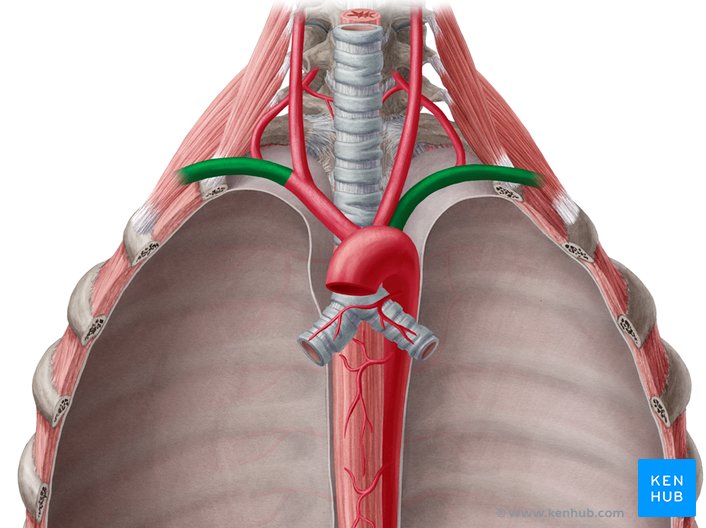
Pulmonary trunk
carries blood from right ventricle to pulmonary arteries
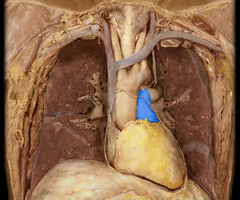
Pulmonary veins (hilum entry)
inferior veins are most inferior holes, superior veins are most anterior holes
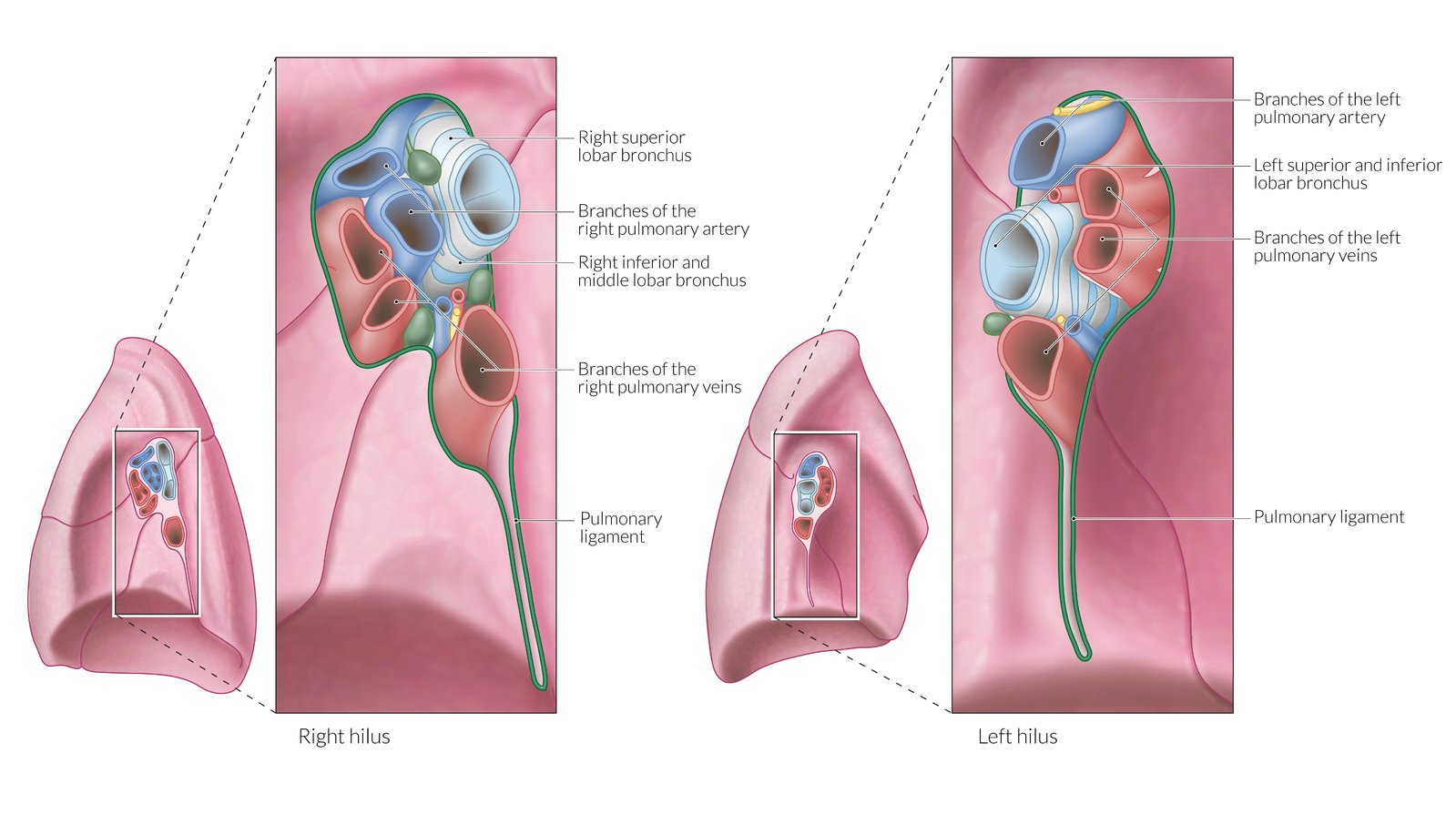
Pulmonary arteries (hilum entry)
left artery in most superior hole (above bronchus), right artery is anterior to bronchus (between right vein)
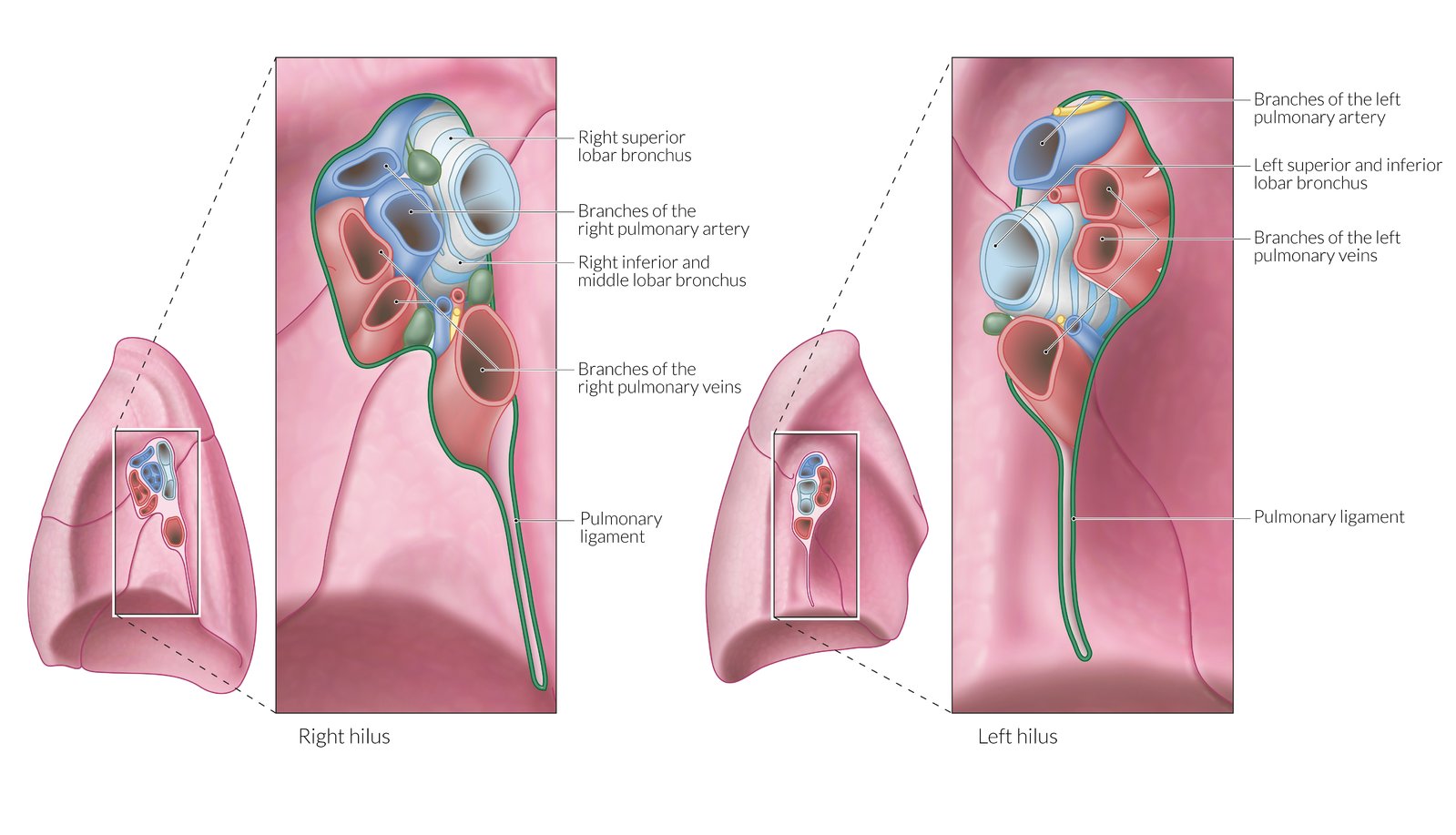
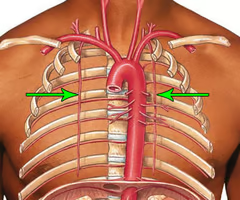
Internal thoracic arteries
from subclavian branches to anterior intercostal arteries
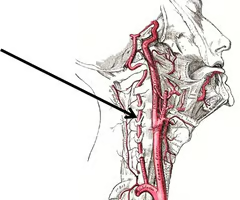
Vertebral arteries
arteries that ascend along either side of the vertebral column through the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae and enter the cranium through the foramen magnum
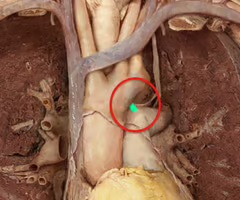
Ligamentum arteriosum
structure is a remnant of a fetal vessel that connected the pulmonary trunk and the aorta (ductus arteriosus)
Right and left vagus nerves
continue from the neck and pass through the mediastinum and parasympathetic supply to visceral structures of the thorax, including the heart
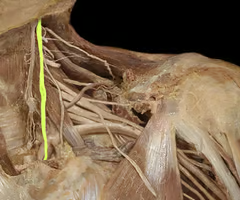
Right and left phrenic nerves
runs along left and right side of heart down to diaphragm
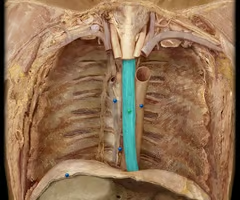
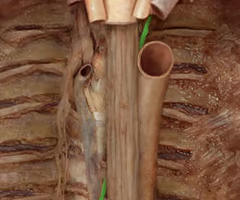
Trachea and bifurcation
cartilage ribbed tube superior to heart, bifurcates into primary bronchi, conducting air passageway
Esophagus
muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach, to right of descending aorta
Thoracic duct (lymphatic)
collects lymph from left head and upper body, and lower extremities; dumps into junction of left subclavian and internal jugular veins
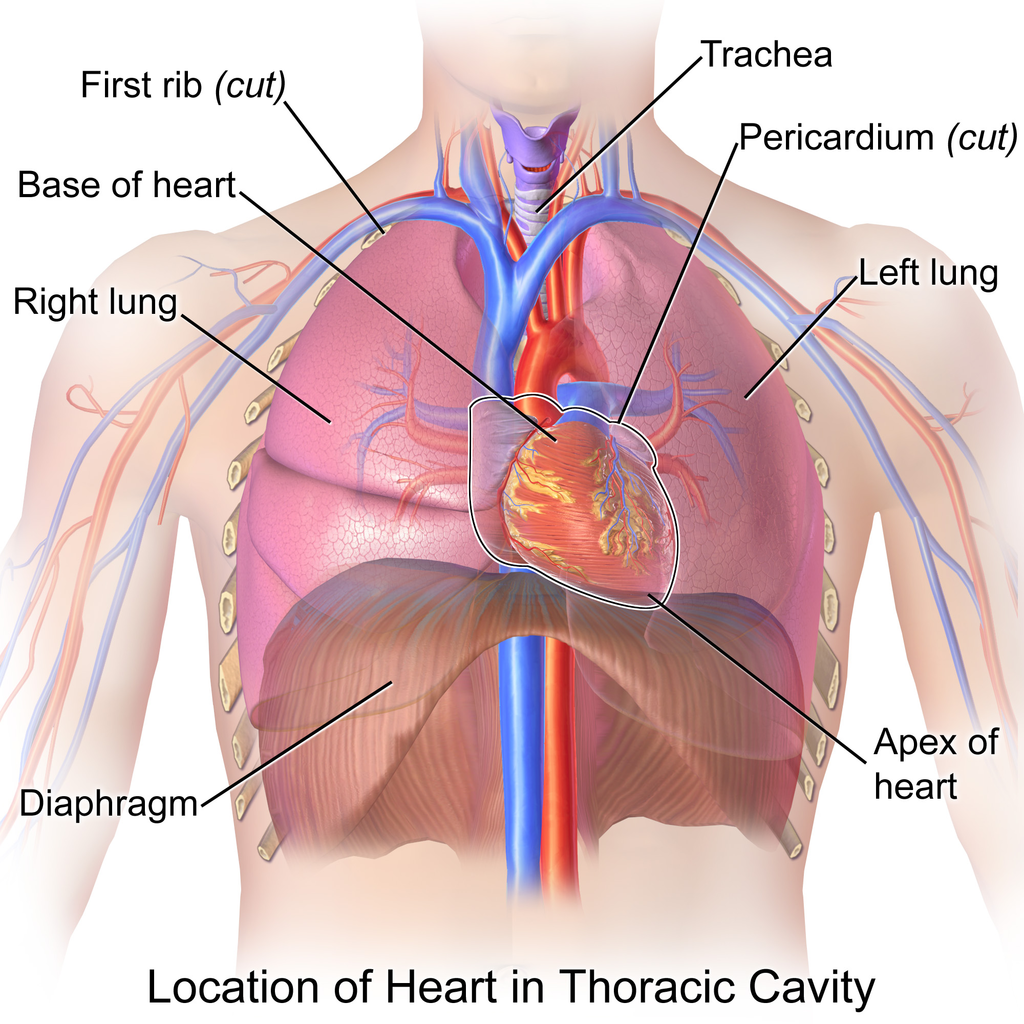
Heart
muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, located in the thoracic cavity between the lungs
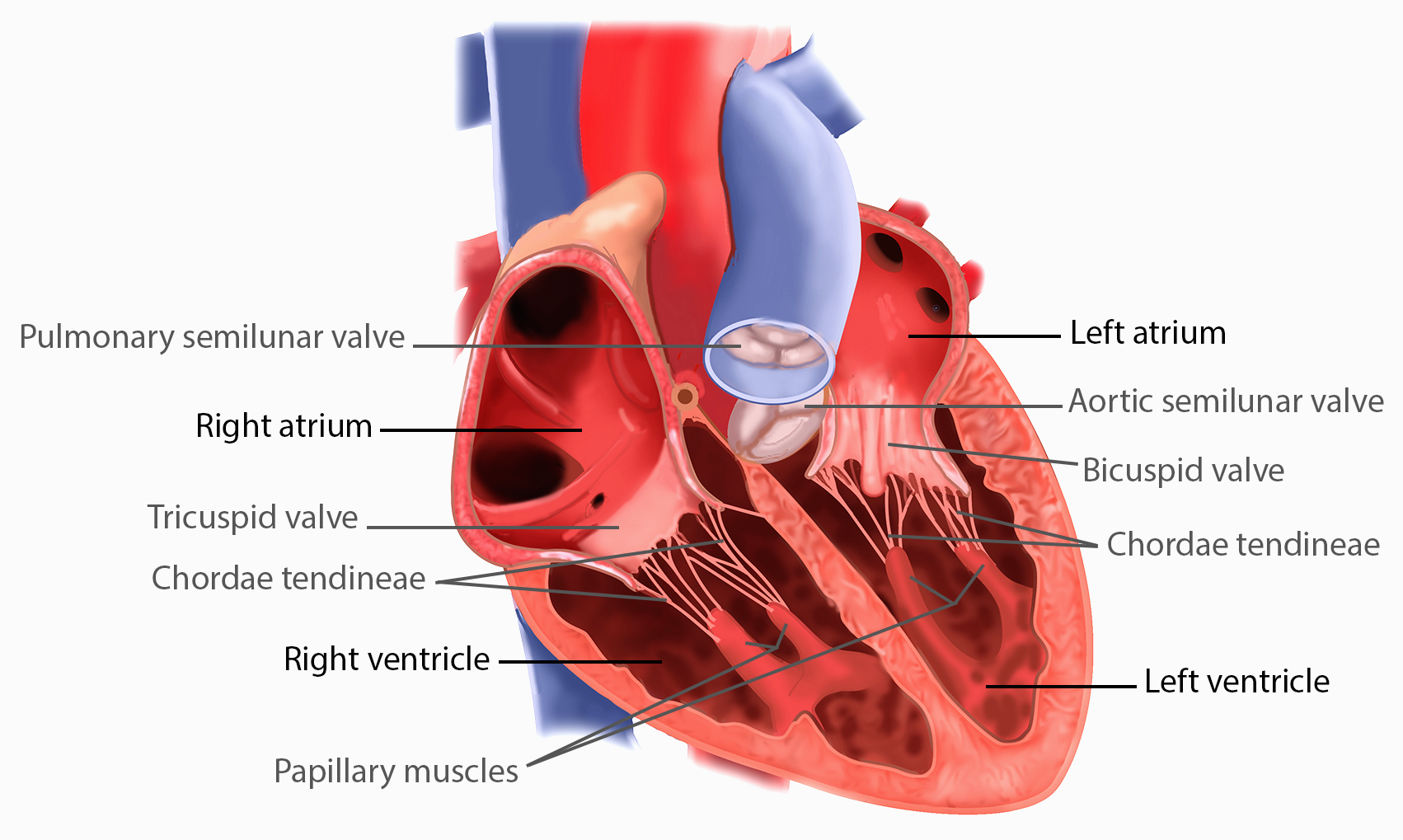
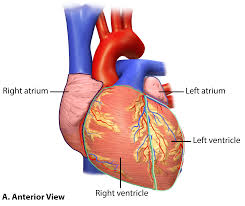
Right and left atria
two superior chambers, receive blood returning to heart; has auricles to enlarge chamber
Right and left auricles
small, earlike projections that extend anteriorly from each atrium, allows additional blood capacity
Right and left ventricles
lower chambers of the heart that pump blood out of the heart
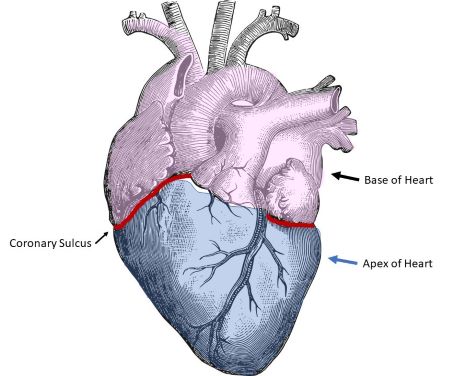
Coronary sulcus
a groove that separates the atria from the ventricles and contains blood vessels
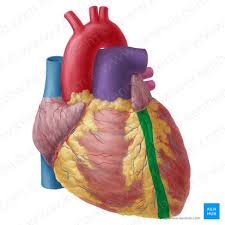
Anterior interventricular sulcus
groove on anterior surface of the heart that separate the right and left ventricles
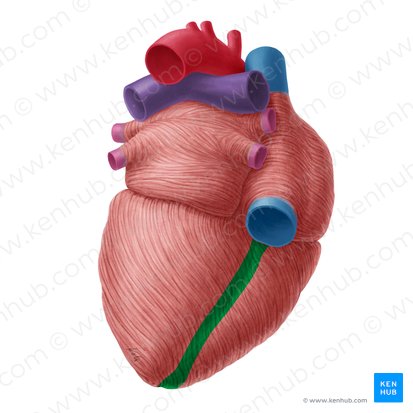
Posterior interventricular sulcus
groove on the posterior surface of the heart that separates the right and left ventricles
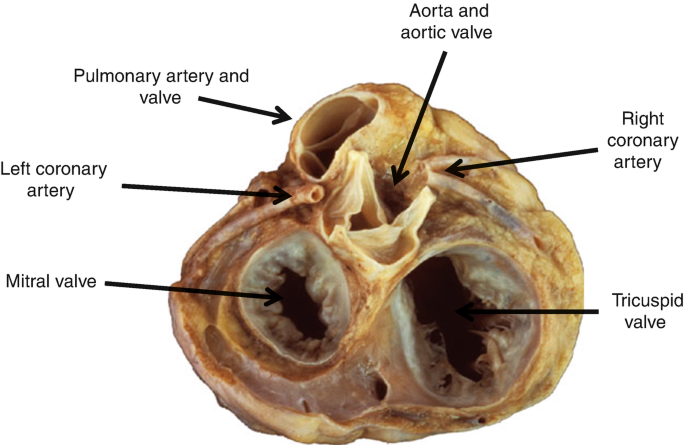
Aorta (on heart)
most center opening on superior aspect of the heart, has the three semilunar valves that prevent backflow back into heart
Superior vena cava (on heart)
a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the right atrium of the heart
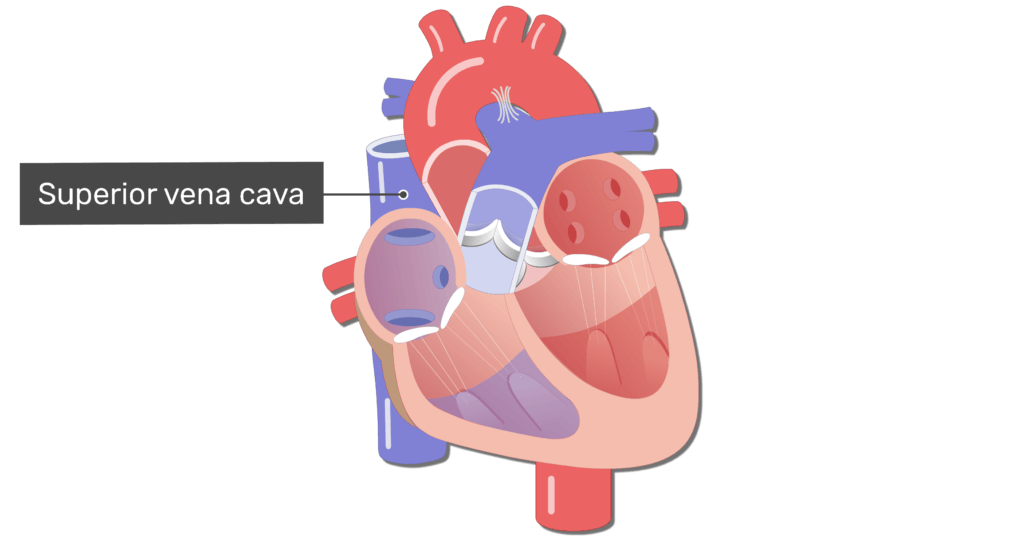
Inferior vena cava (on heart)
a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the right atrium of the heart
Coronary sinus
a large vein that collects deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle itself and drains into the right atrium, in the groove between the left atrium and left ventricle
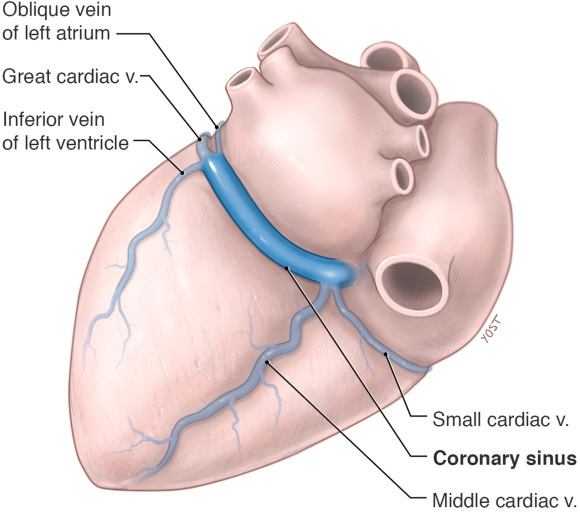
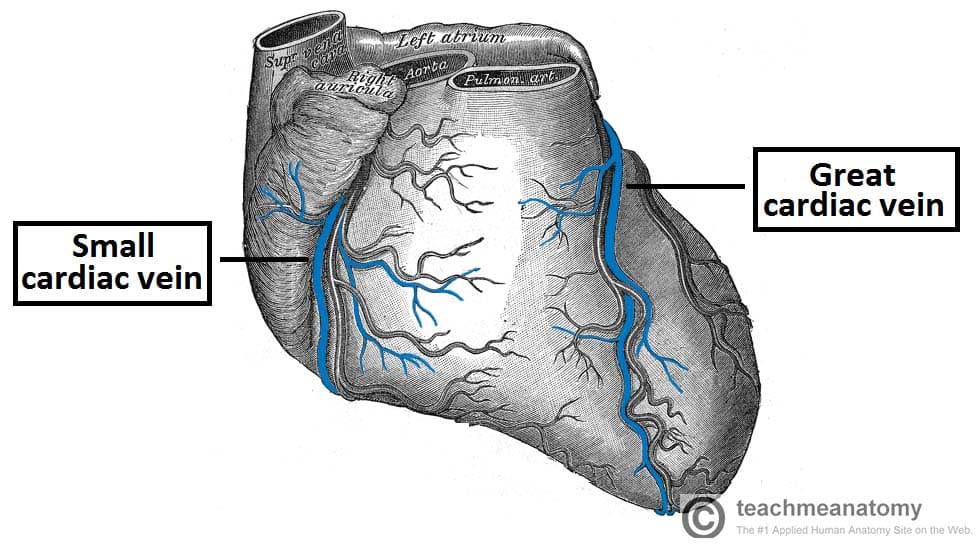
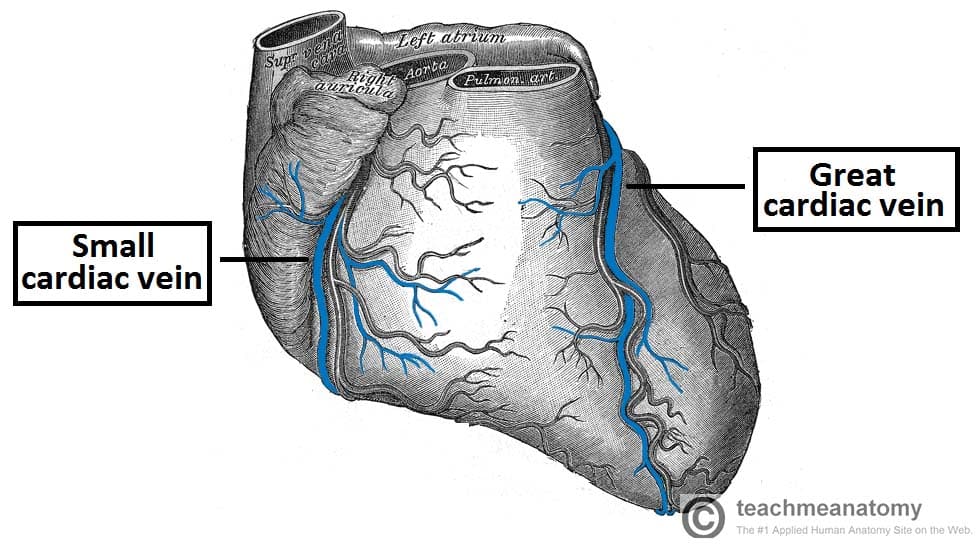
Great cardiac vein
a major coronary vein that originates at the apex of the heart, ascends along the anterior interventricular sulcus, and drains into the coronary sinus
Middle cardiac vein
a major coronary vein that originates near apex of heart, ascends within the posterior interventricular sulcus, and drains into coronary sinus
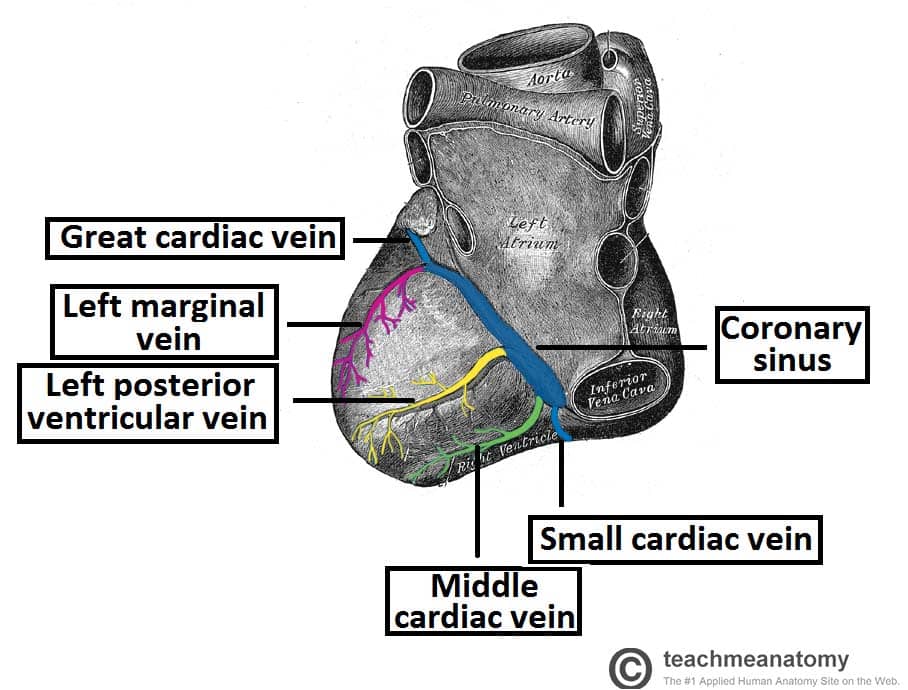
Small cardiac vein
a small tributary of the coronary sinus, draining the inferior and lateral walls of the right ventricle, and runs in the coronary sulcus with the right coronary artery between the right atrium and ventricle, under inferior vena cava
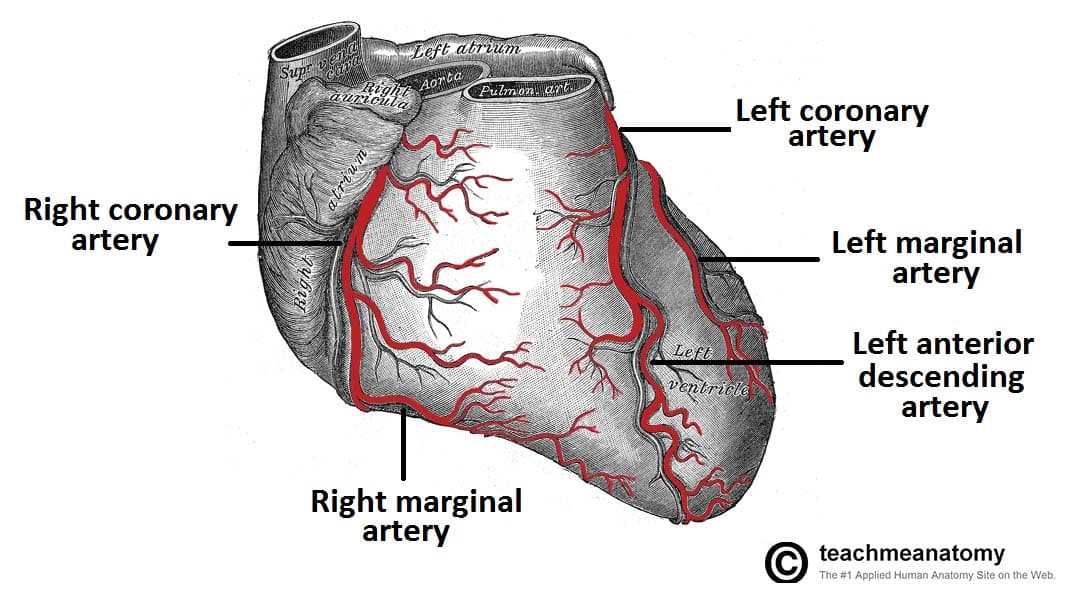
Left coronary artery
supplies blood to the left side of the heart, originates from base of ascending aorta and branches into the anterior interventricular and circumflex arteries
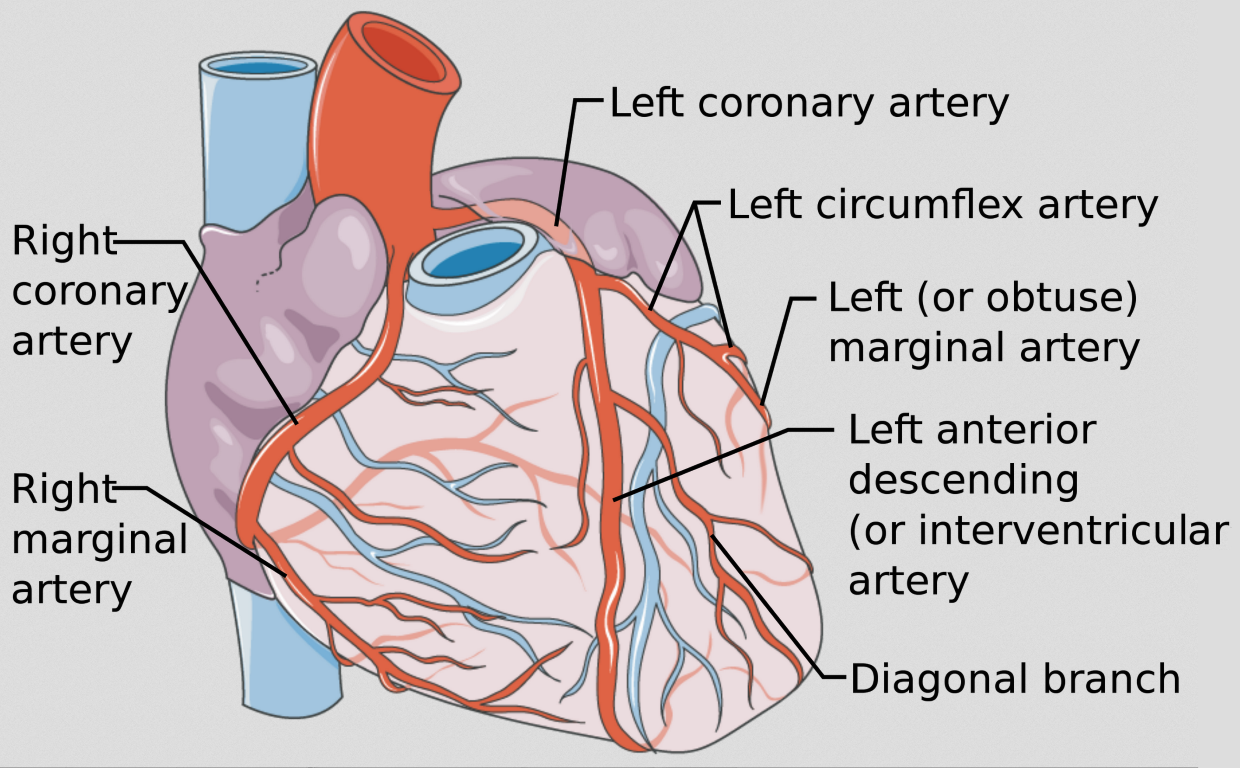
Right coronary artery
originates from the base of the ascending aorta and travels down the right coronary sulcus, branches into the right posterior descending and right marginal arteries
Circumflex artery
branch of the left coronary artery, follows the coronary sulcus around to the posterior side of heart
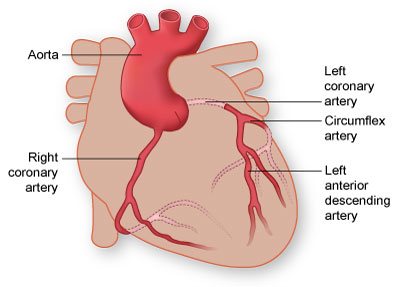
Right marginal artery
first branch off the right coronary artery, located along the right margin of the heart (near inferior vena cava)
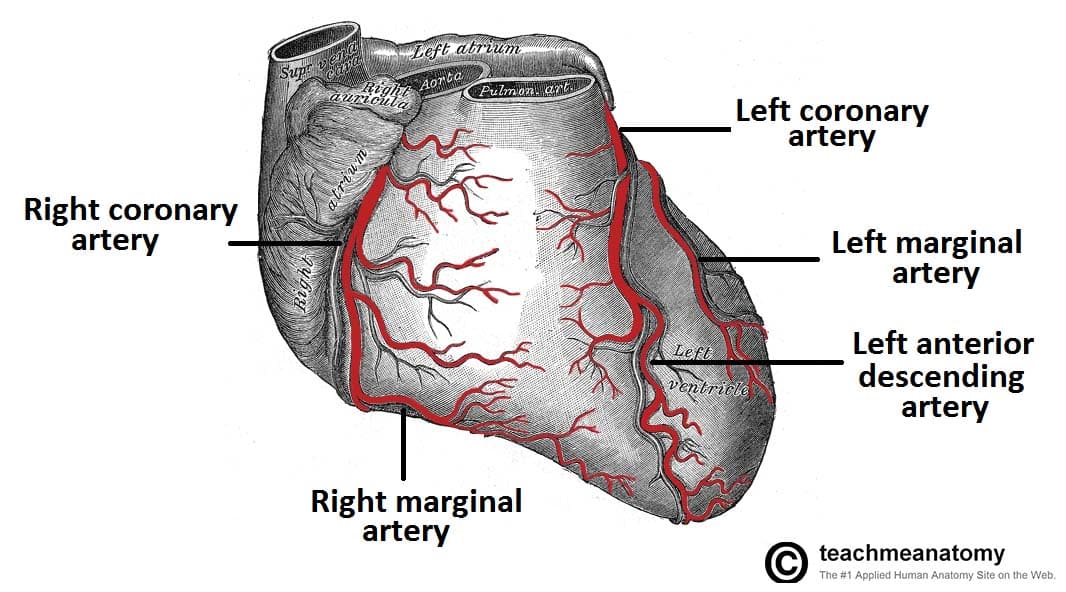
Left marginal artery
a branch of the circumflex artery, travels along the left margin of the heart, towards the apex
Anterior interventricular artery
a major branch of the left coronary artery, descends within the anterior interventricular sulcus towards the apex of the heart
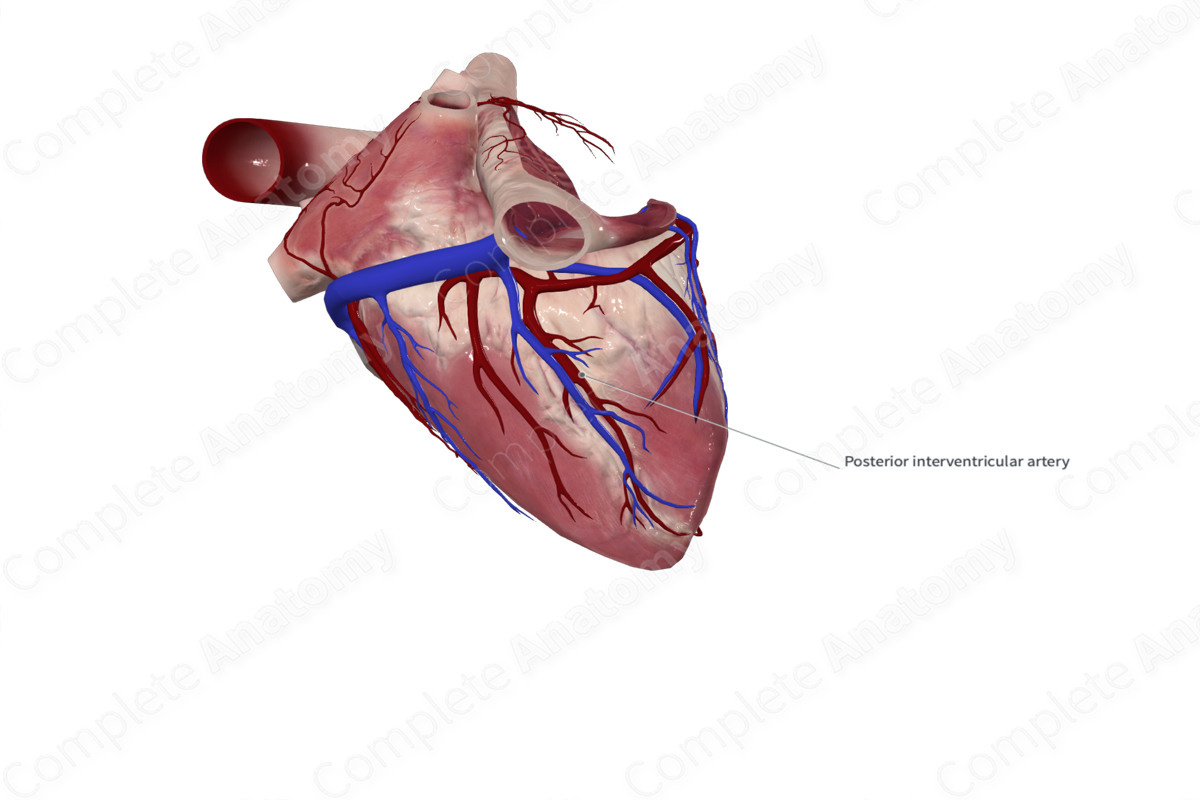
Posterior interventricular artery
a branch of the right coronary artery, it runs in the posterior interventricular sulcus towards the apex of the heart
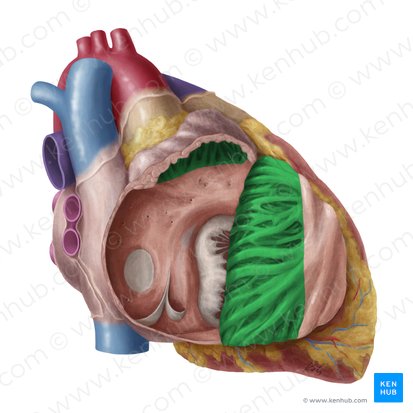
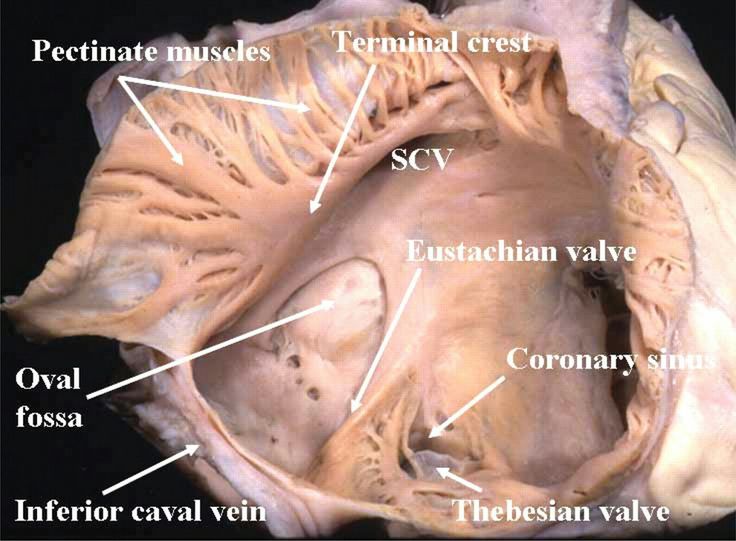
Pectinate muscles (right atria)
muscular ridges found in the right atrium, involved in increasing the efficiency of atrial contraction
Fossa ovalis (right atria)
a depression in the interatrial septum of the right atrium, marking the site of the foramen ovale in the fetal heart, between superior and inferior vena cavae atrial entrances
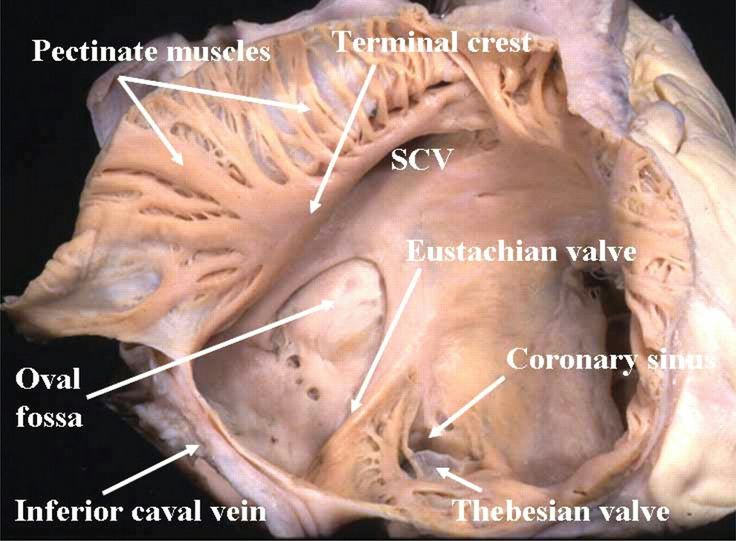
Opening to coronary sinus (right atria)
the opening through which deoxygenated blood from the coronary veins drains into the right atrium, located near the fossa ovalis.
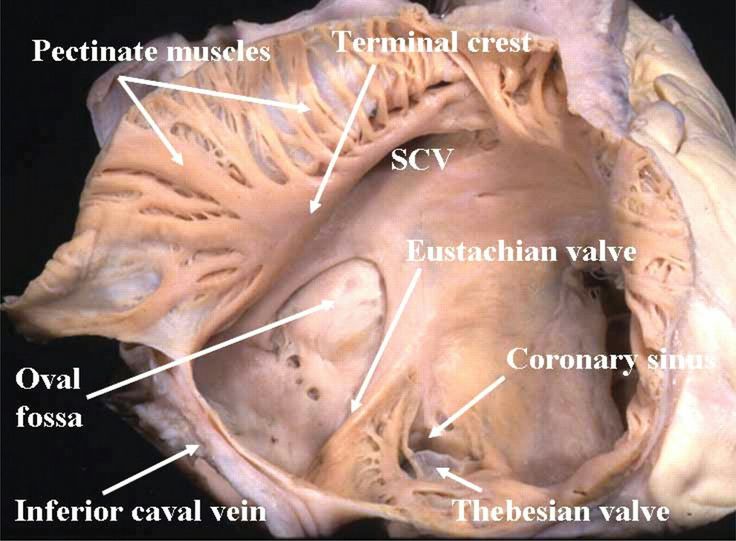
Openings to superior and inferior vena cavae (right atria)
the apertures through which deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the body, located at the posterior part of the right atrium
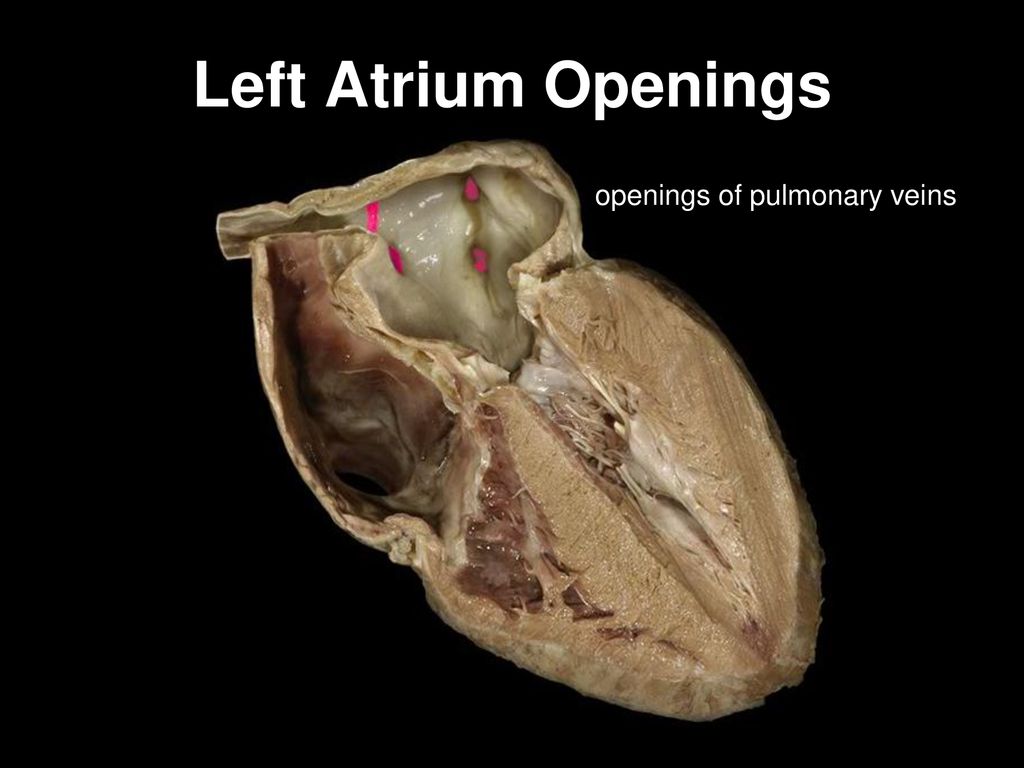
Openings to pulmonary veins (left atria)
the openings through which oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left atrium
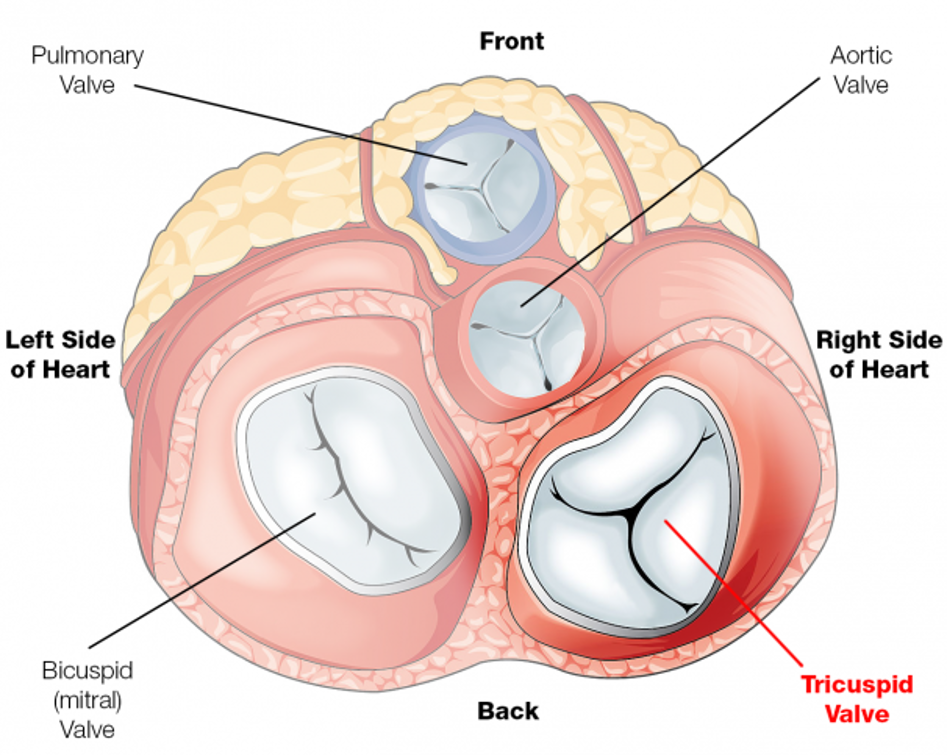
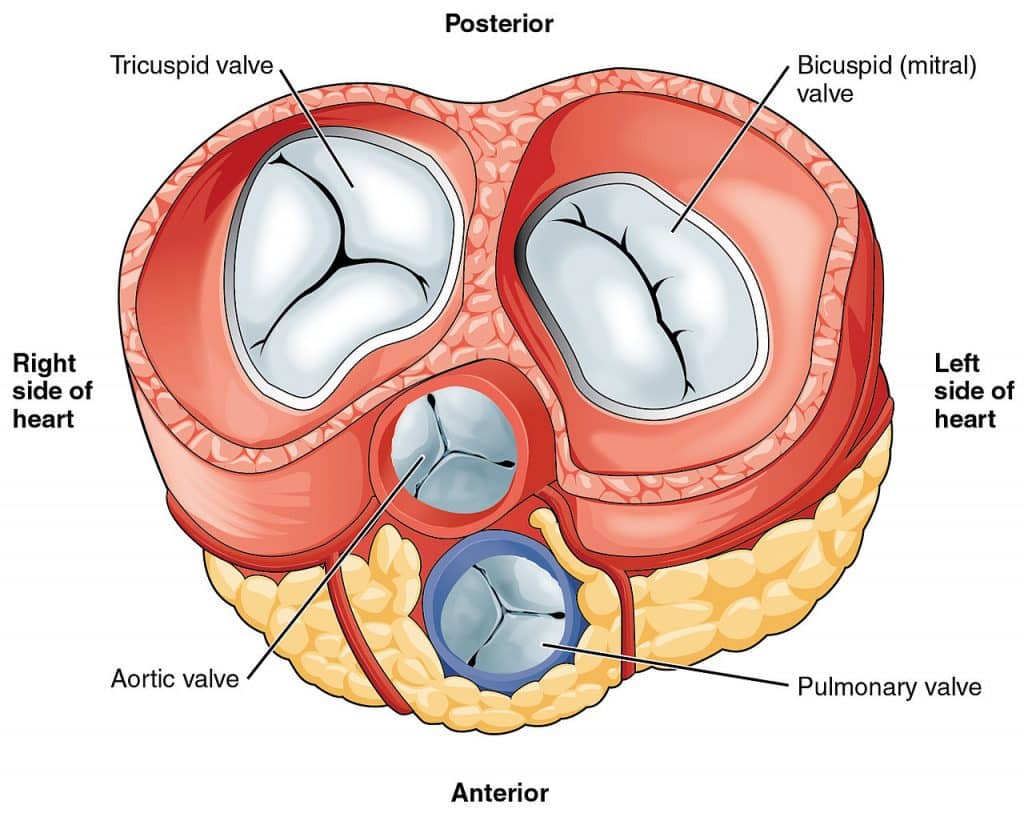
Right AV valve (tricuspid)
valve that separates the right atrium from the right ventricle
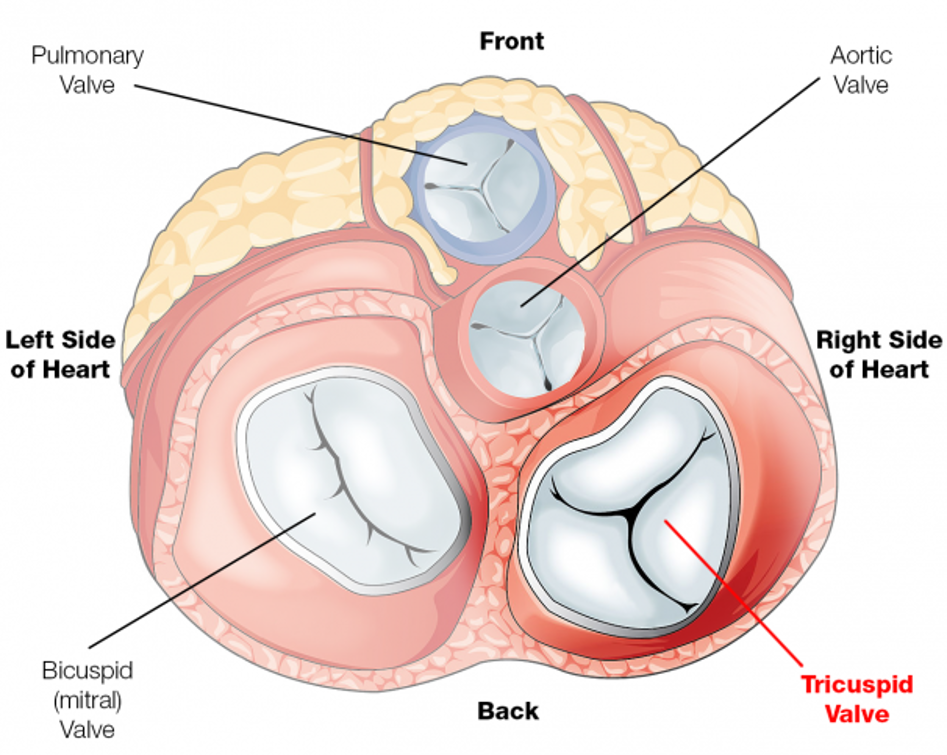
Left AV valve (bicuspid)
valve that separates the left atrium from the left ventricle
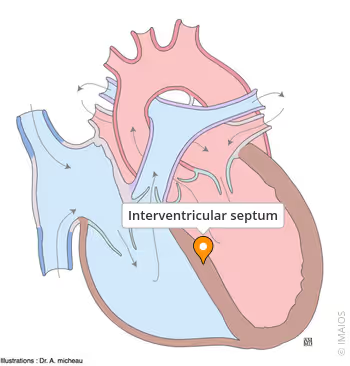
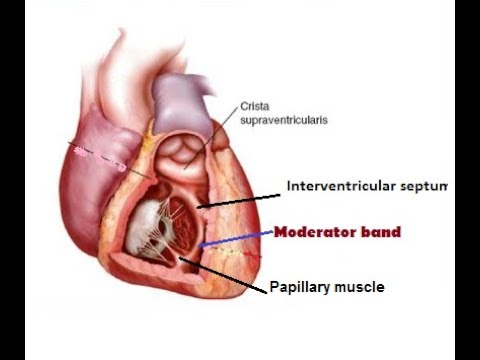
Interventricular septum
muscular partition that separates the left and right ventricles of the heart
Trabeculae carneae
muscle ridges found on the floor of the inner surface of the ventricles that help in contraction
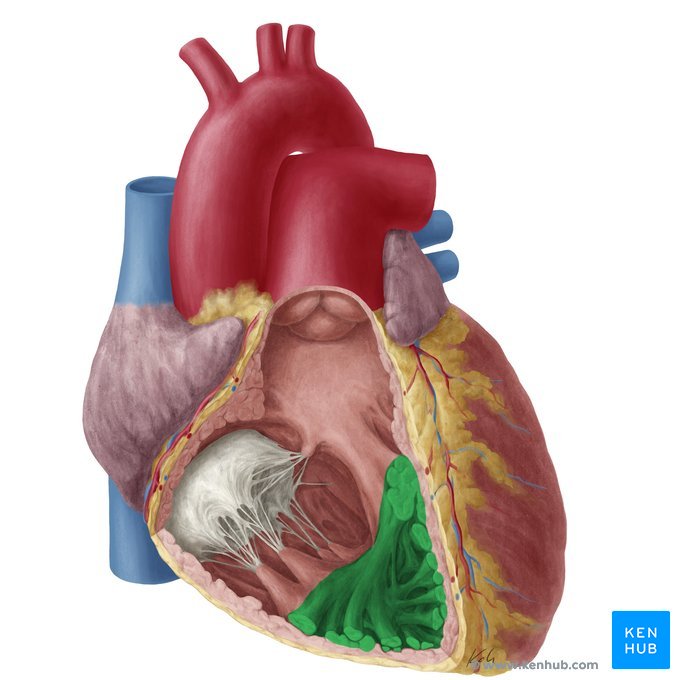
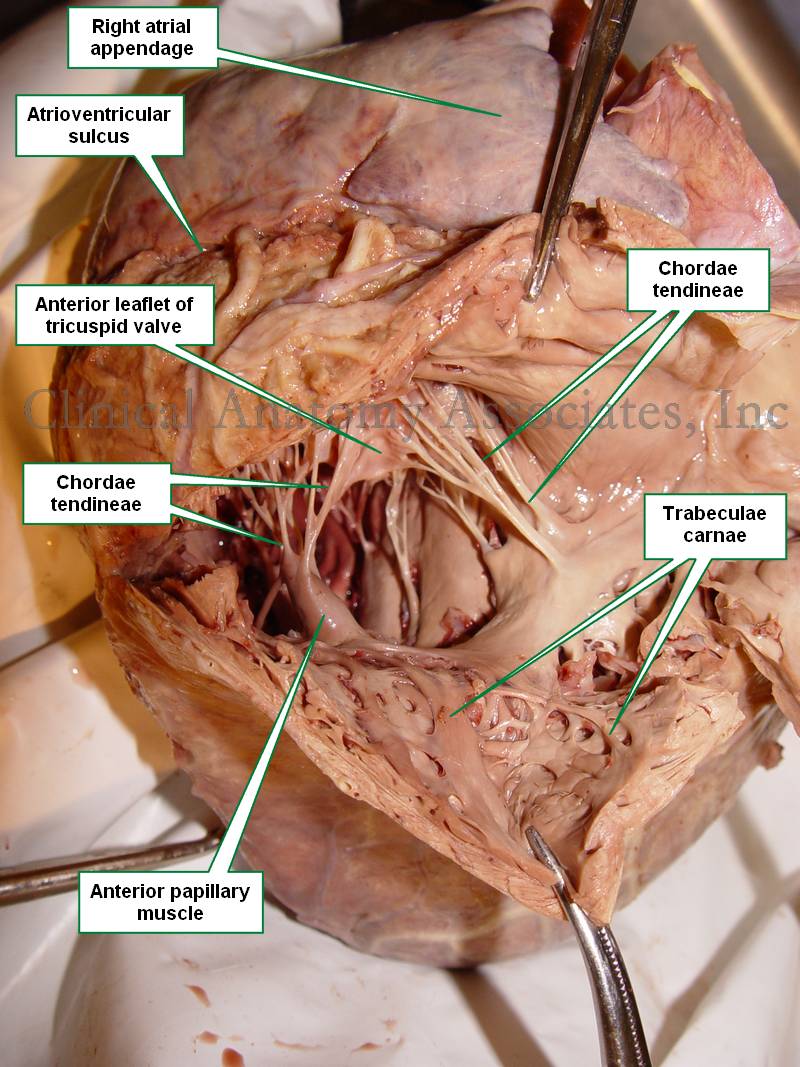
Papillary muscles
small muscles located within the ventricles of the heart that attach to the chordae tendineae and help control the opening and closing of the heart valves
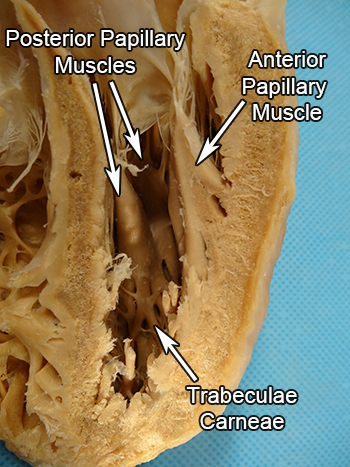
Chordae tendineae
in the ventricles, fibrous cords that connect the papillary muscles to the heart valves
Pulmonary semilunar valve (right ventricle)
valve located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
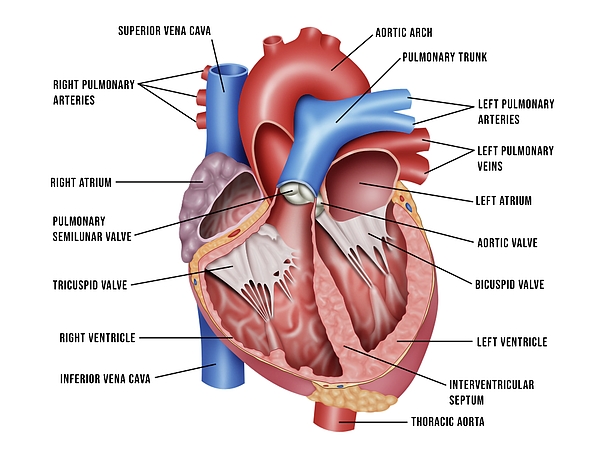
Aortic semilunar valve (left ventricle)
valve located between the left ventricle and the aorta
Moderator band (right ventricle)
band of muscle that extends from the interventricular septum to the anterior papillary muscle
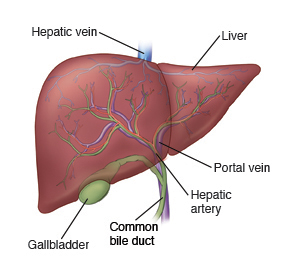
Liver
large organ in RUQ, immediately inferior to diaphragm
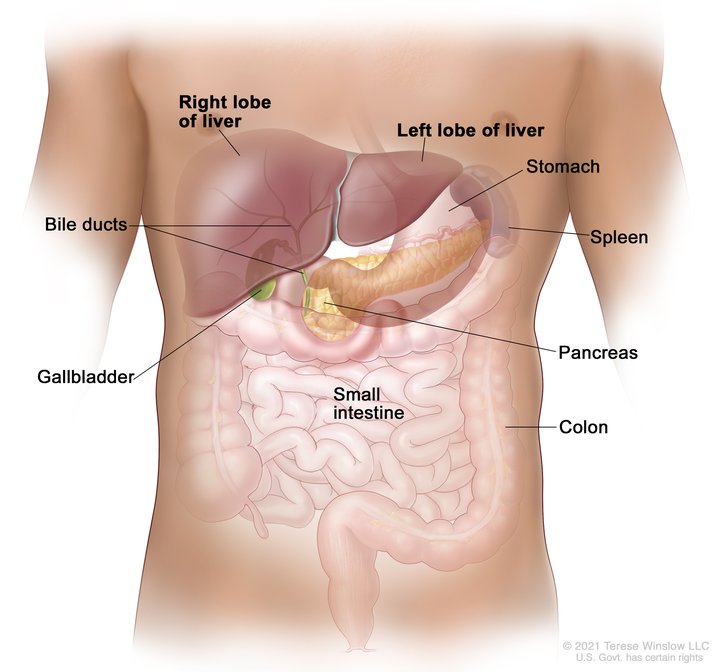
Gallbladder
small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile
Right lobe (liver)
largest lobe of the liver, located on the right side
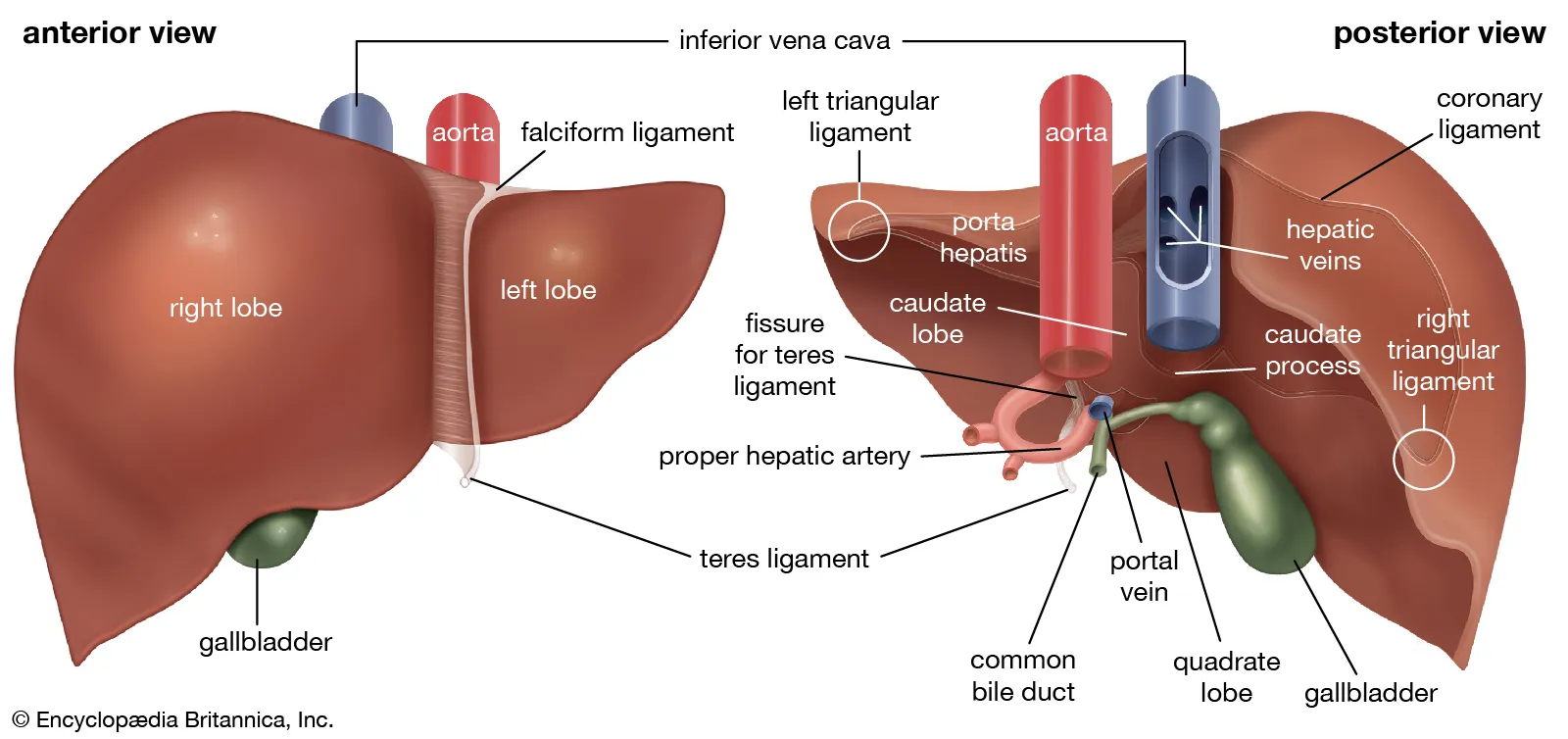
Left lobe (liver)
smaller lobe of the liver, located on the left side
Quadrate lobe (liver)
small lobe of the liver located on the inferior side, between the left lobe and the gallbladder
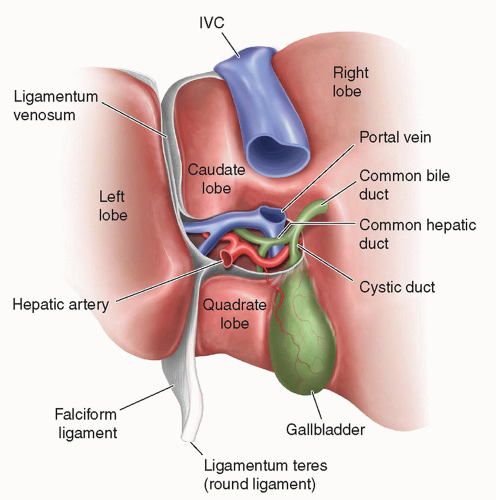
Caudate lobe (liver)
small lobe of the liver situated posterior to the quadrate lobe and near the inferior vena cava, has a tail-like extension.
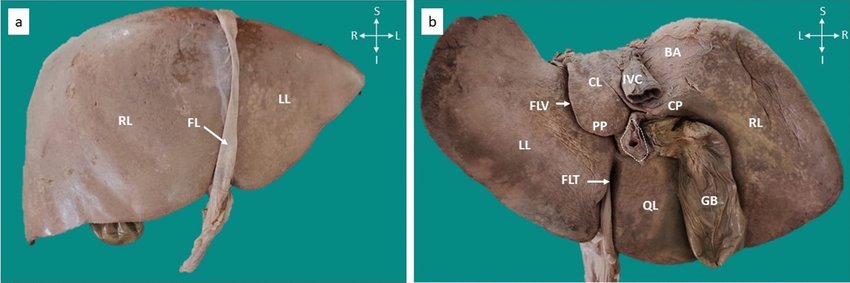
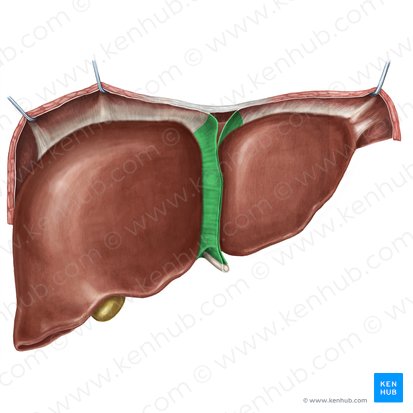
Falciform ligament
thin fold of peritoneum that connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall
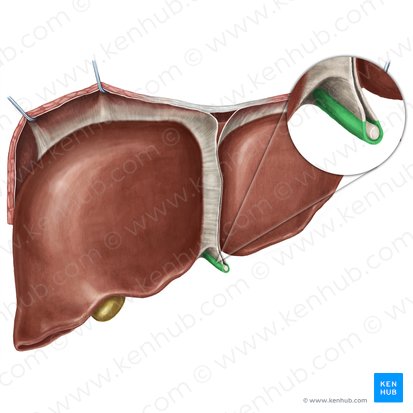
Round ligament
a remnant of the umbilical vein that runs along the free edge of the falciform ligament
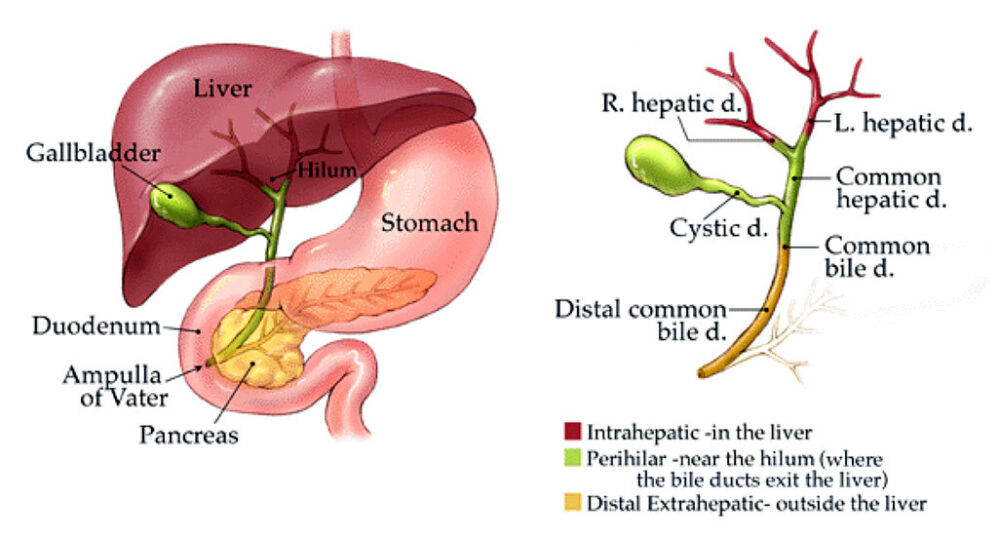
Porta hepatis
the central region of the liver where the hepatic ducts, blood vessels, and nerves enter and exit
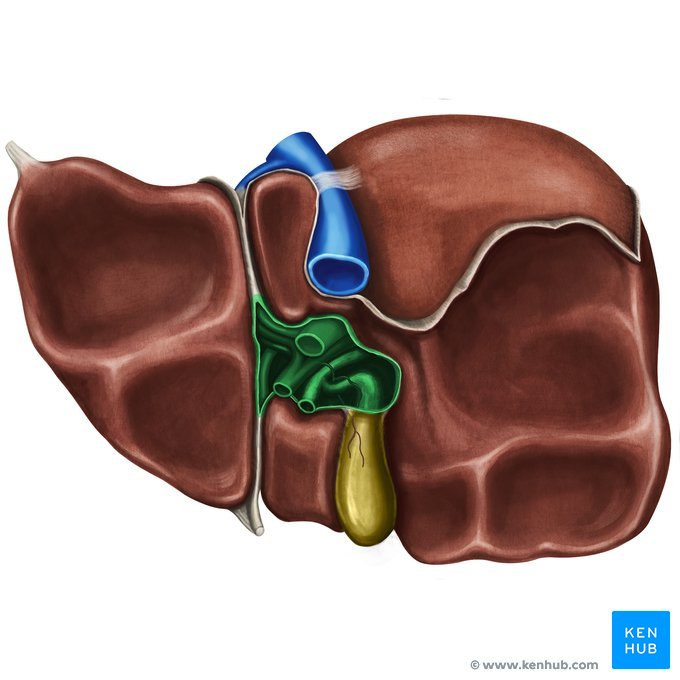
Hepatoduodenal ligament
not doing
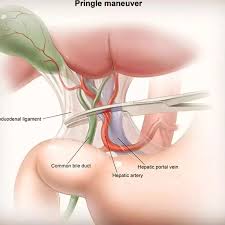
Common bile duct
the duct that carries bile from the liver and gallbladder to the duodenum
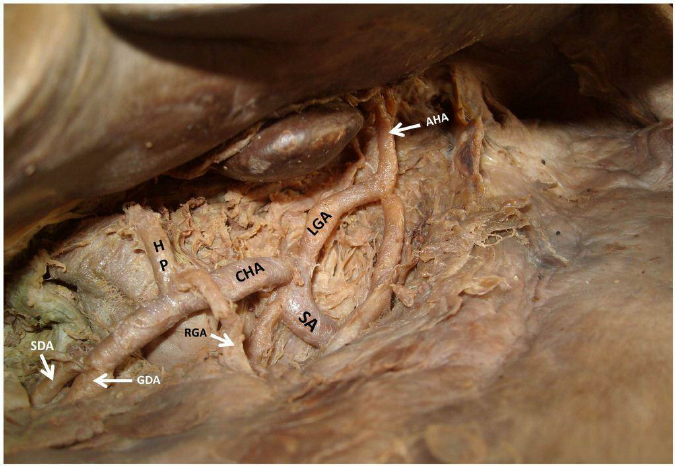
Hepatic portal vein
the vein that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract and spleen to the liver for processing
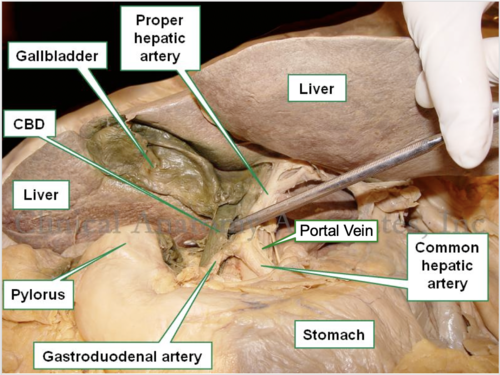
Proper hepatic artery
branches off the common hepatic artery leading up to porta hepatis
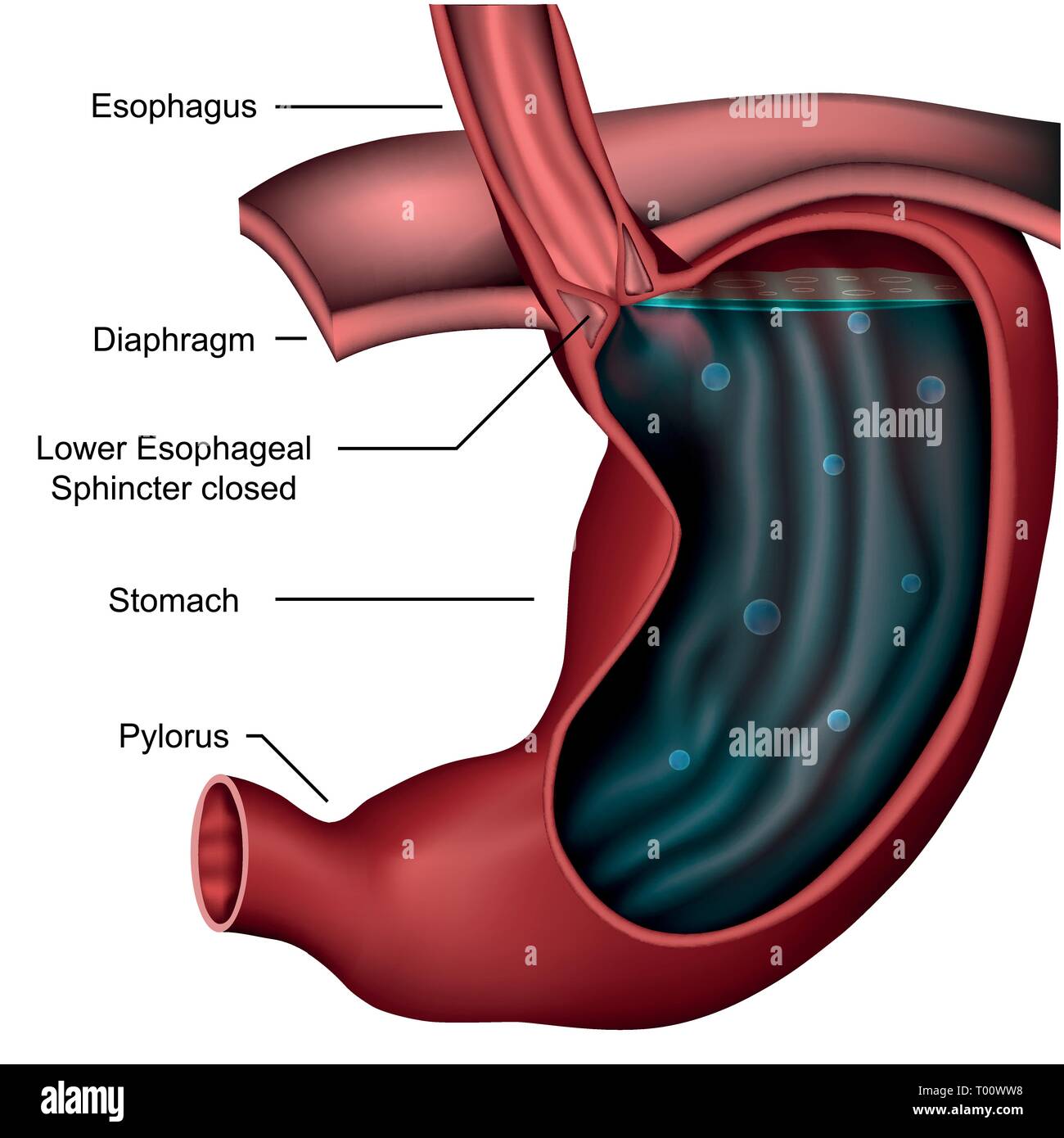
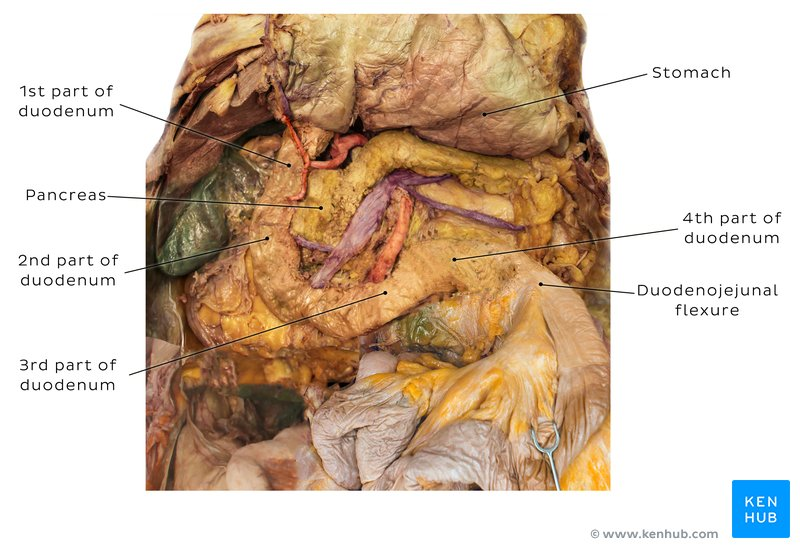
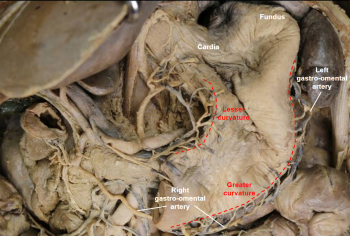
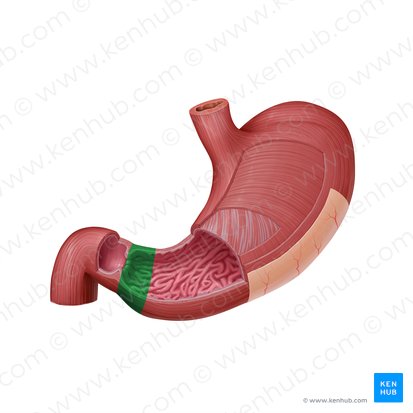
Stomach
organ in LUQ
Greater curvature of stomach
the larger, outer curve of the stomach that extends from the esophagus to the duodenum
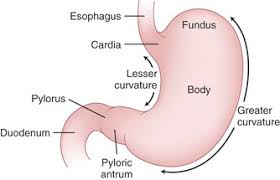
Lesser curvature of stomach
the shorter border of the stomach opposite the greater curvature
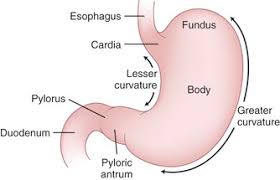
Cardia
the region of the stomach adjacent to the esophagus, where food enters the stomach
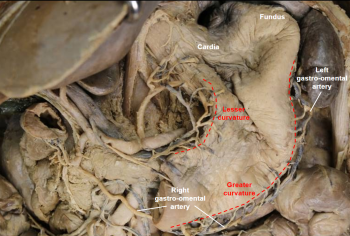
Fundus
the upper, rounded portion of the stomach that lies above the level of the cardiac opening
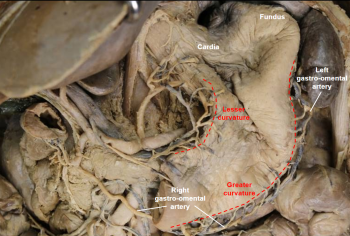
Body of stomach
the main central region of the stomach, located between the fundus and pylorus
Pylorus
the lower portion of the stomach that connects to the duodenum, regulating the passage of partially digested food
Rugae of stomach
the folds in the stomach lining that allow for expansion and increase surface area for digestion
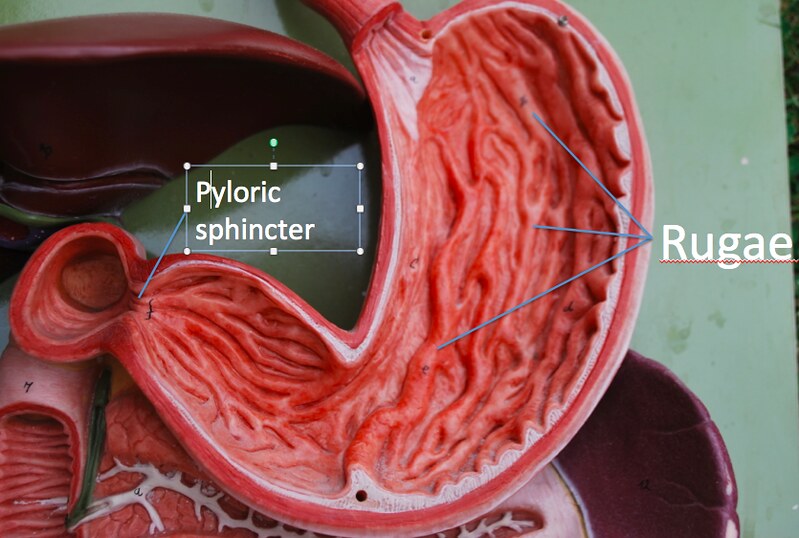
Pyloric sphincter
a muscular valve at the junction between the pylorus and the duodenum
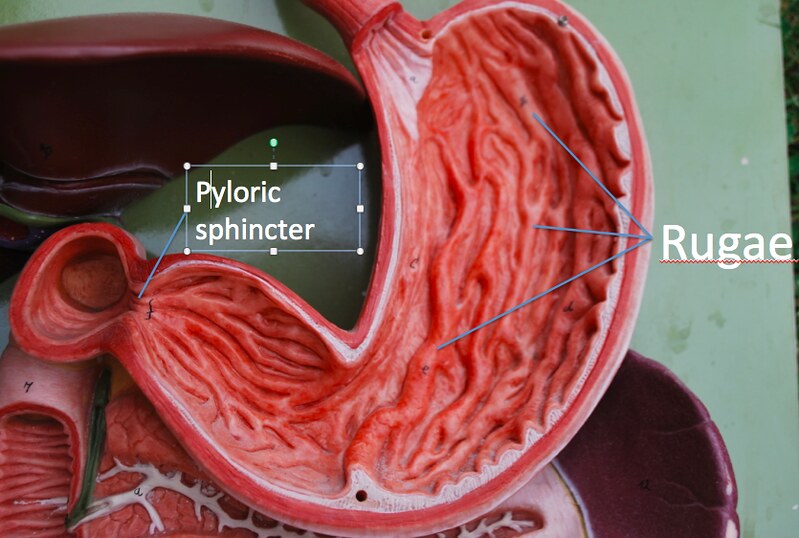
Pyloric orifice
the opening through which food passes from the stomach into the duodenum, located at the pylorus and regulated by the pyloric sphincter
Esophageal/cardiac sphincter
a muscular ring that controls the passage of food from the esophagus into the stomach