AP Biology Structure of Water & Hydrogen Bonding
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
four
number of covalent bonds carbon can form with other elements
hydrocarbons
carbon and hydrogen atoms that are covalently bonded that make them stable and nonpolar
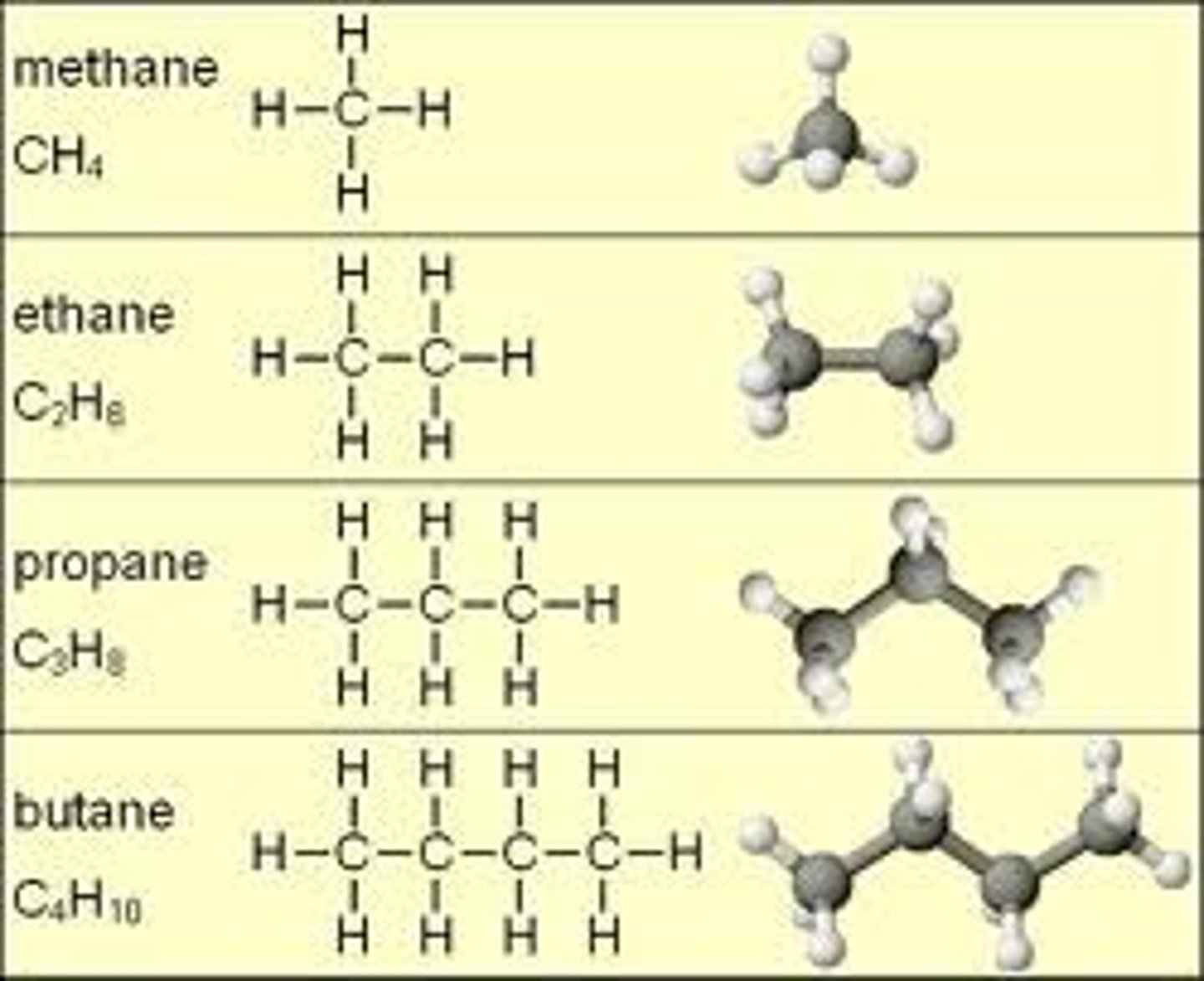
nonpolar
not soluable in water
polar
soluable in water
functional groups
parts of organic molecules that are involved in chemical reactions
charge of the oxygen atom in a water molecule
slightly negative
charge of the hydrogen atoms in a water molecule
slightly positive
high specific heat
property of water in which water changes temperature very slowly with changes in heat due to hydrogen bonding
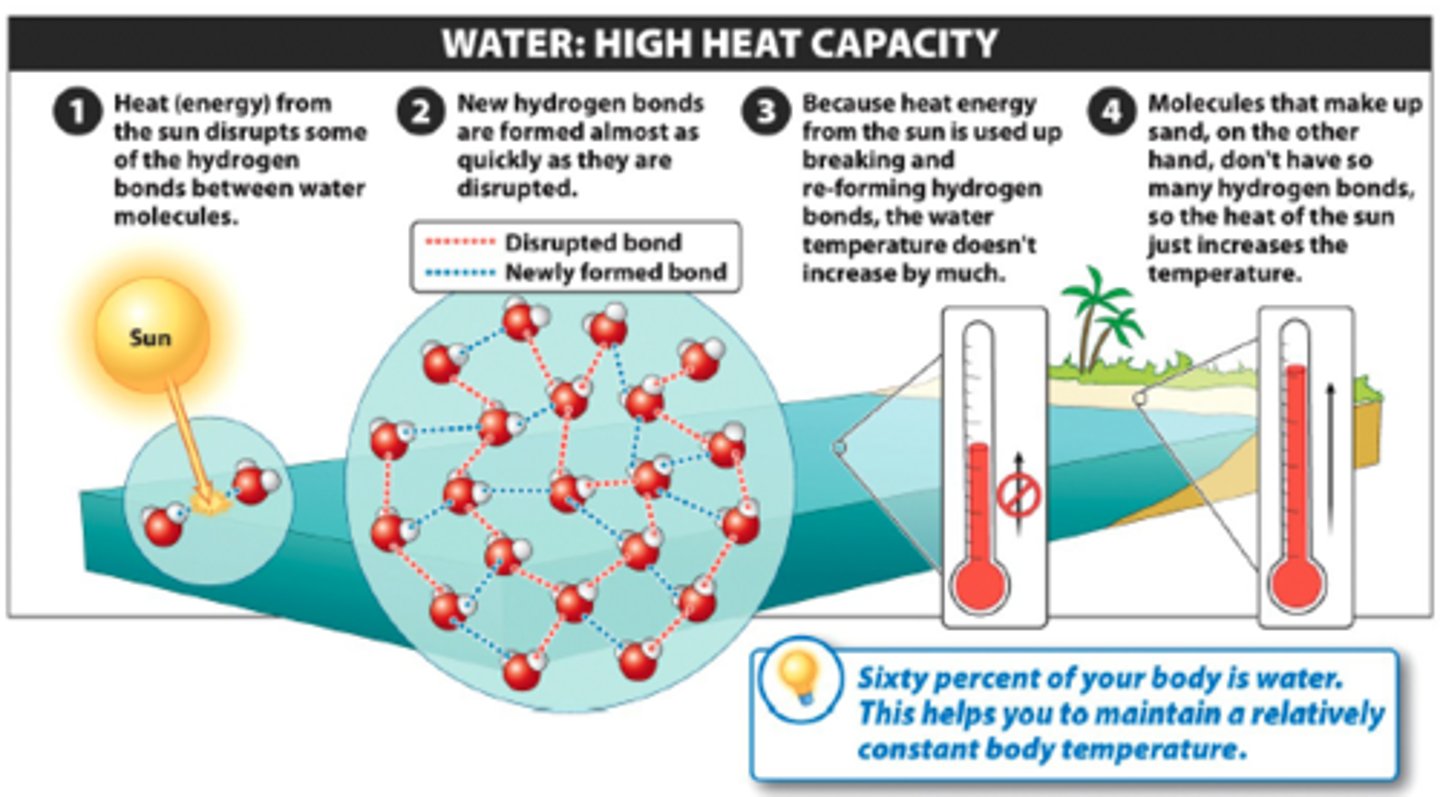
evaporative cooling
water carries the heat it absorbs away in sweat due to its high specific heat
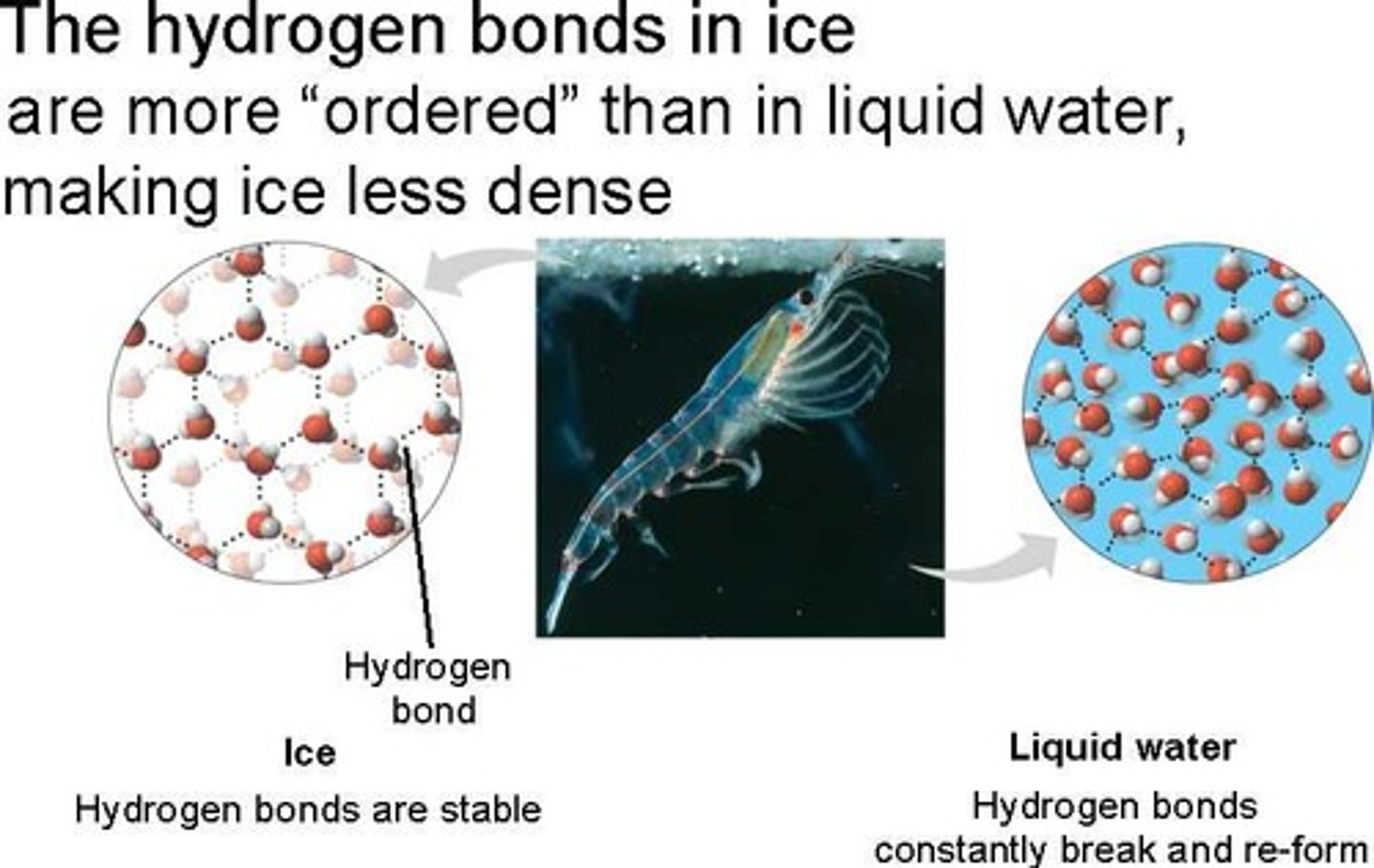
the reason ice floats in liquid water
less dense as a solid; hydrogen bonds form crystalline structure that keeps the water molecules separate
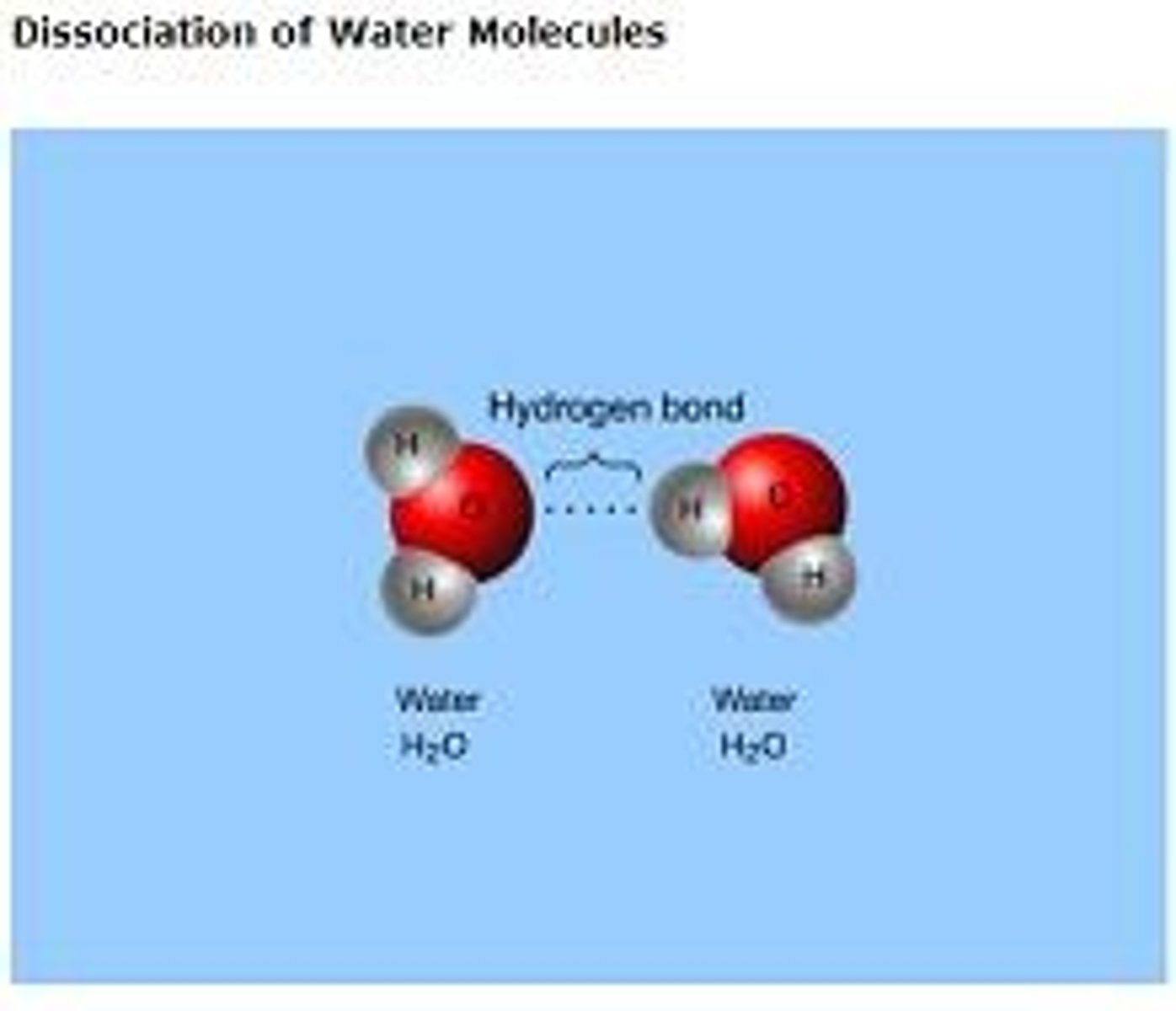
cohesion
the attraction of like substances; water molecules are attracted to other water molecules; this is due to the hydrogen bonding between water molecules
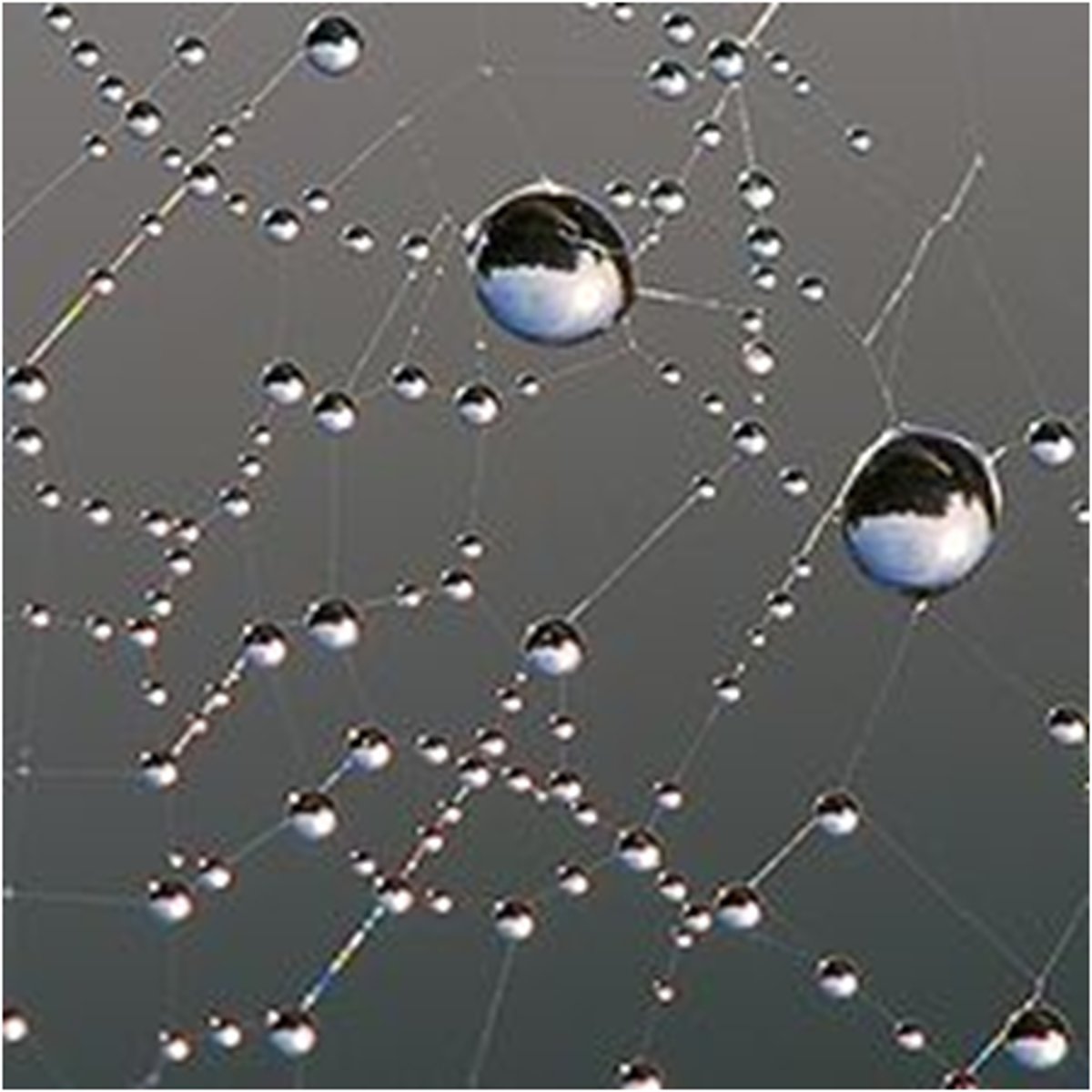
adhesion
the attraction of unlike molecules; water molecules are attracted to other polar surfaces

atom
Smallest form of an element that still displays its particular properties; consisting of a positively charged nucleus and a negatively charged electron cloud.
protons
Atomic particles with a positive charge (+) found in the nucleus of an atom.
neutrons
Atomic particles with a neutral (o) charge found in the nucleus of an atom.
electrons
Atomic particles with a negative charge (-) found outside the nucleus of an atom.
ion
atom becomes charged when it gains or loses an electron
chemical bond
attraction between two atoms by transferring or sharing electrons to attain a stable electron configuration
nonpolar covalent bond
Bond that forms when electrons are shared equally.
covalent bond
Bond that forms when electrons between atoms are shared.
polar covalent bond
Bond that forms when electrons are shared unequally; like that between the oxygen atom and hydrogen atoms in a water molecule