BN Week 2 Vocab
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Neuron/nerve cell
the basic unit of the nervous system, each composed of receptive extensions called dendrites, an integrating cell body, a conducting axon, and a transmitting axon terminal
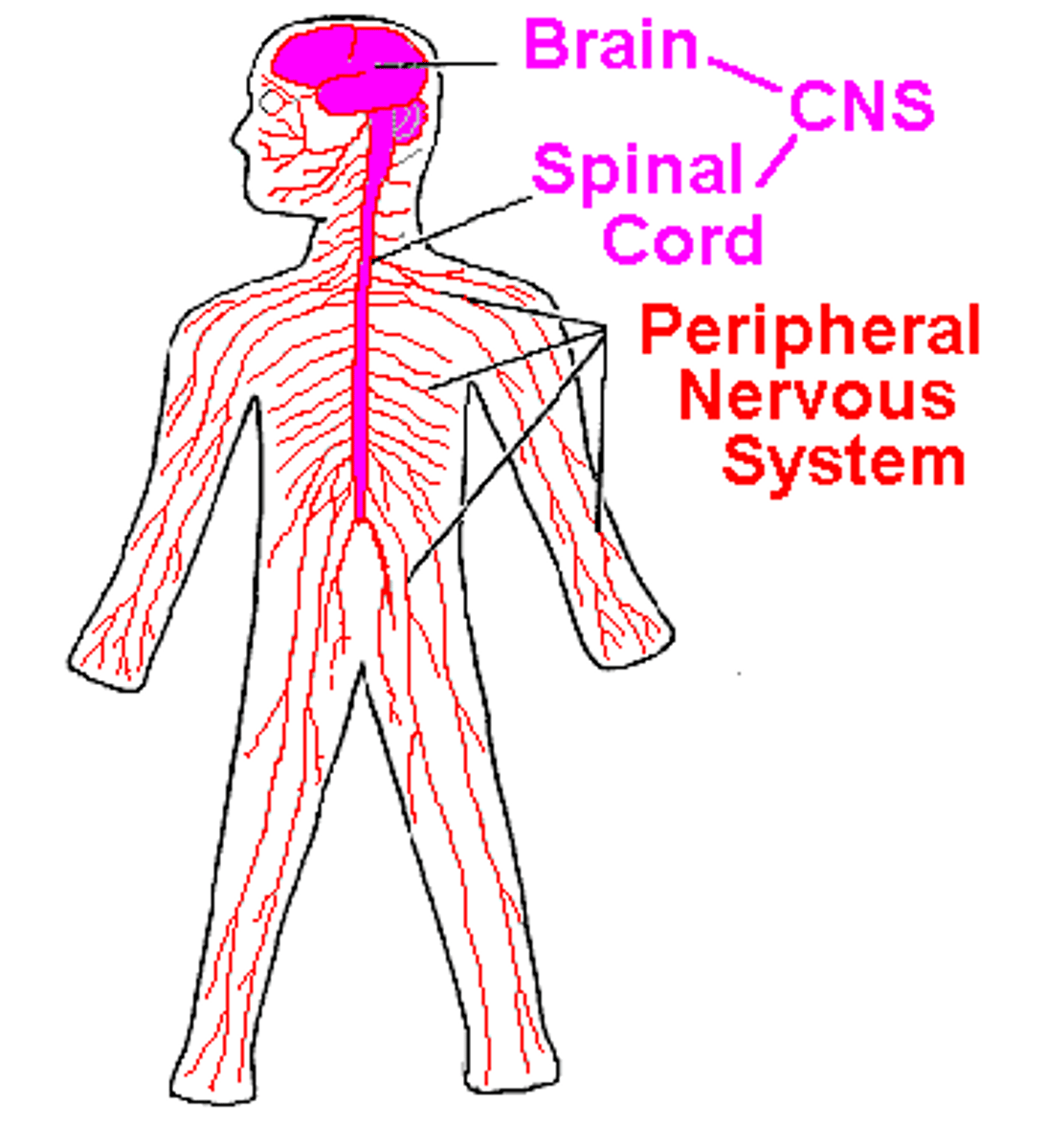
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The portion of the nervous system that includes all the nerves and neurons outside of the brain and spinal cord
Dendrite
Long, thin tree-branch structure that receives info, many branch out of a singular soma
Dendritic spines
Short outgrowths that increase the surface area available for synapses, highly plastic (can grow/ shrink/ be destroyed)
Input zone
the part of a neuron that receives information from other neurons or from specialized sensory structures (vis dendrites from a neurotransmitter, then relayed to soma)
Soma/Cell Body/Perikaryon
Central area for integration of info and decision making regarding to send the signal down the axon (location of organelles and nucleus)
Integration zone
The part of a neuron that initiates neural electrical activity (axon hillock)
Axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body (myelin sheath and nodes of ranvier help conduct the electrical signal to axon terminals/boutons)
Conduction zone
Conduct an electrical signal to carry info from point A to point B (from soma to axon terminal/boutons)- happens on the axon
Axon terminal/boutons
-Presynaptic terminal
- Bulbous endings of axon, releases neurotransmitters to relay info to postsynaptic cell
Active zone
Region in the presynaptic bouton that regulates release of chemicals/neurotransmitters for communication with the neuron on the postsynaptic side
Myelin Sheath
A layer of fatty tissue (lipids) segmentally encasing the axon; enables greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
-Stops leakage of electrical current
-Discontinuous (nodes of raniver)
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath that increase the efficiency of conducting an electrical impulse
-Allows action potential to move quickly down axon
Synpase
The gap between the terminal buttons of the presynaptic cell and either postsynaptic neuron's dendrites, dendritic spines, soma, or another cell
- Can appear anywhere on the postsynaptic cell depending on its function
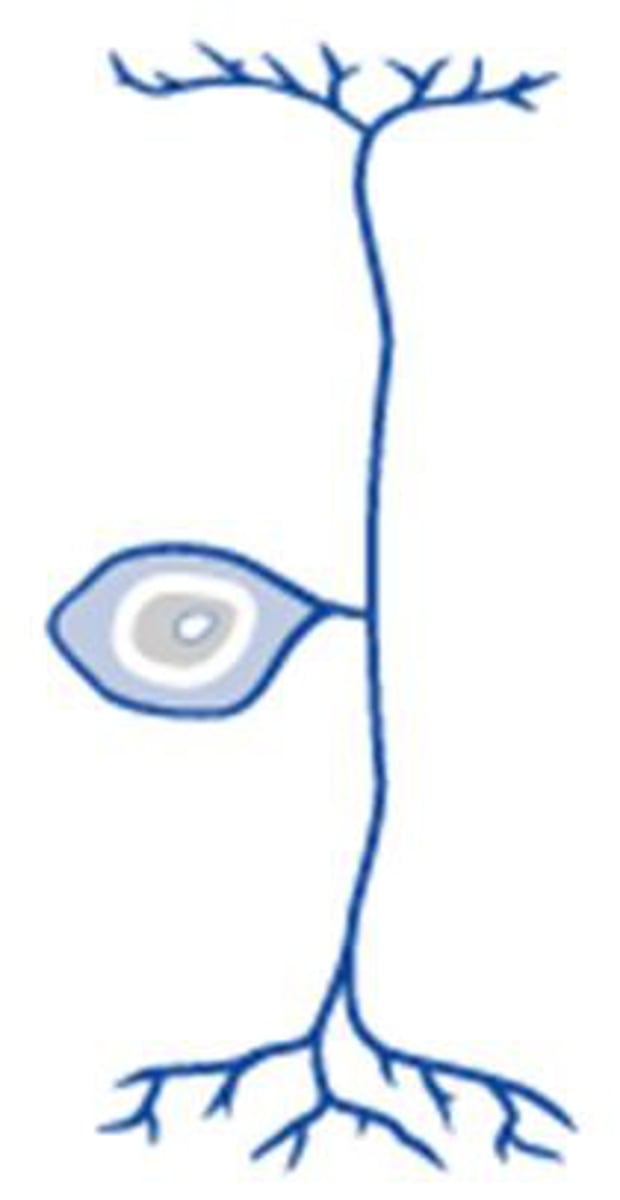
Unipolar neuron
A nerve cell with a single branch that leaves the cell body and then extends in two directions; one end is the receptive pole, the other end the output zone
-Typically only touch info (very simple in structure and therefore function)
Axon hillock
The cone-shaped region of a neuron's axon where it joins the cell body; typically the region where nerve signals is generated
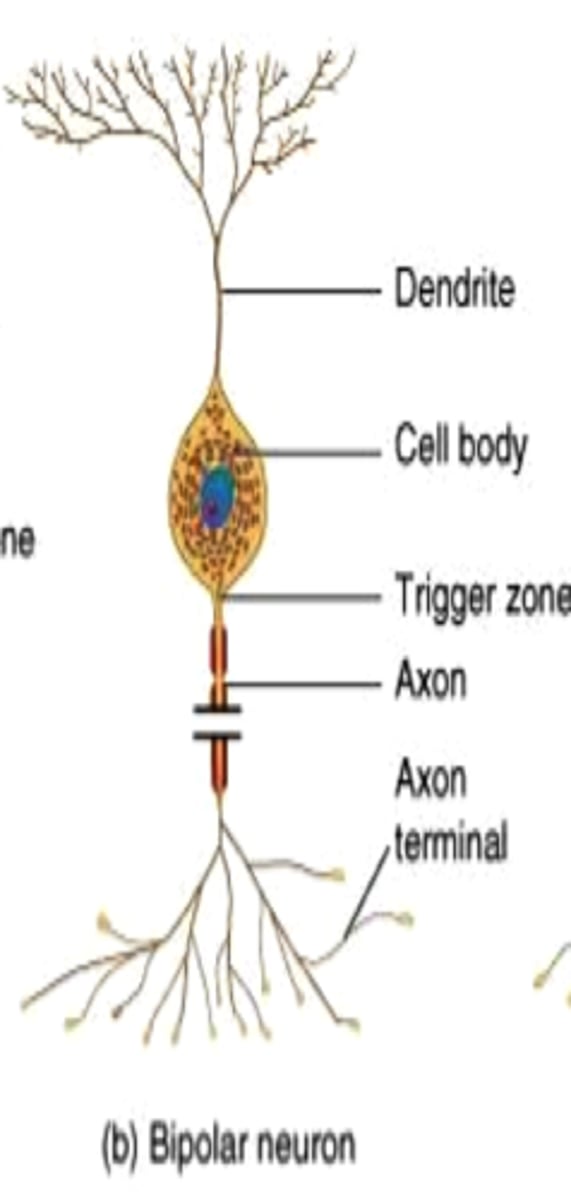
Bipolar neuron
A nerve cell that has a single dendrite at one end and a single axon at the other end
-Common in sensory systems (vision)
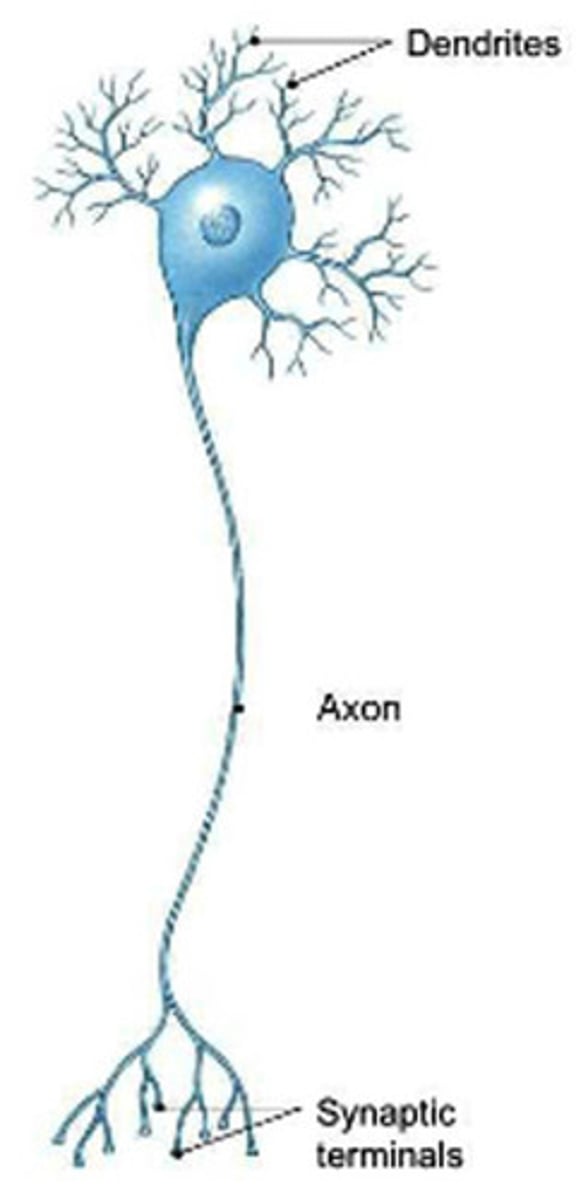
Multipolar neurons
A nerve cell that has many dendrites and a single axon
-Most common type of neuron
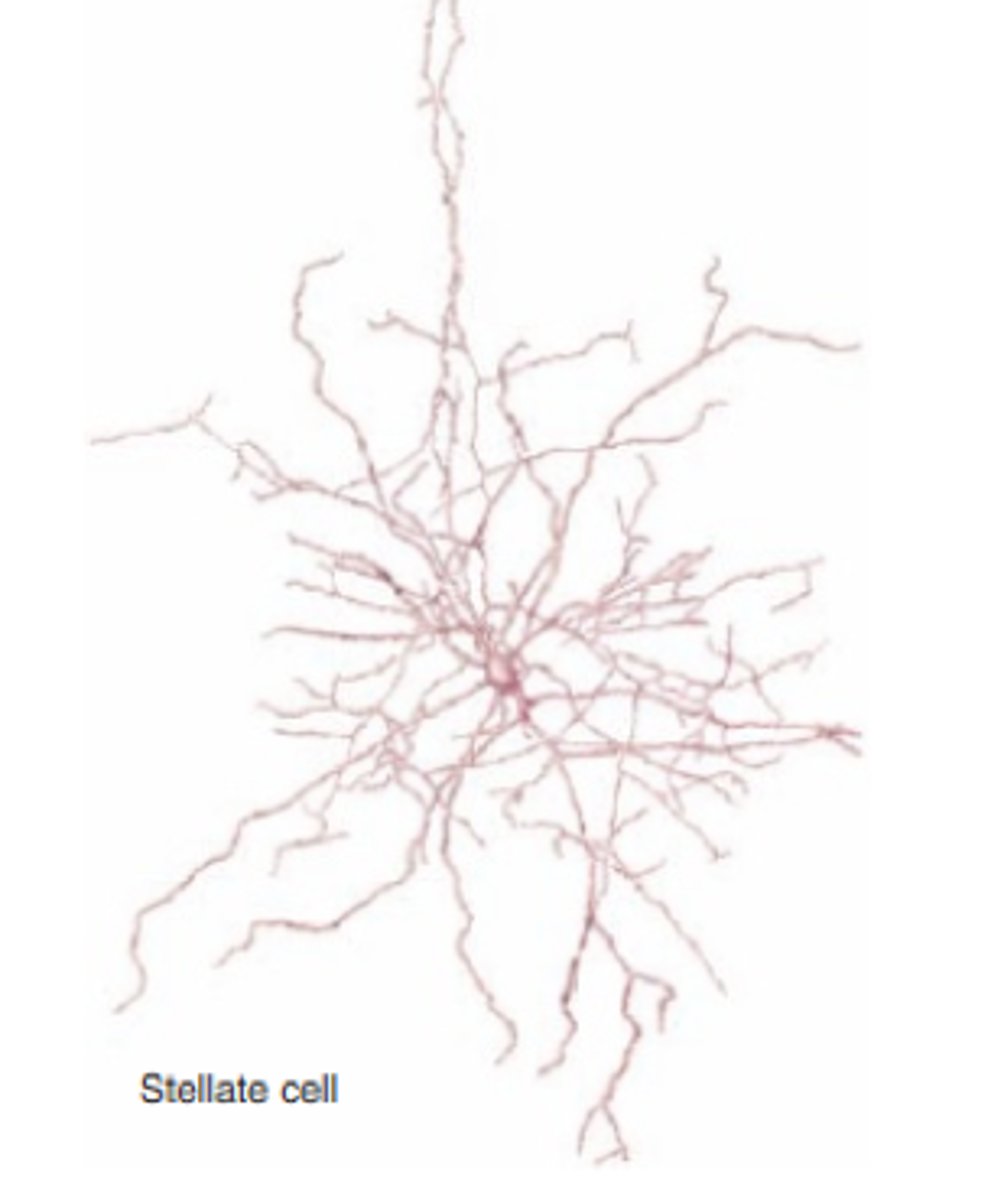
Stellate neuron
A neuron characterized by a radial, star-like distribution of dendrites
-Multipolar neuron
-Found in CNS
Fusiform neuron
An atypical pyramidal neuron
-Multipolar
-Located in the cerebellum
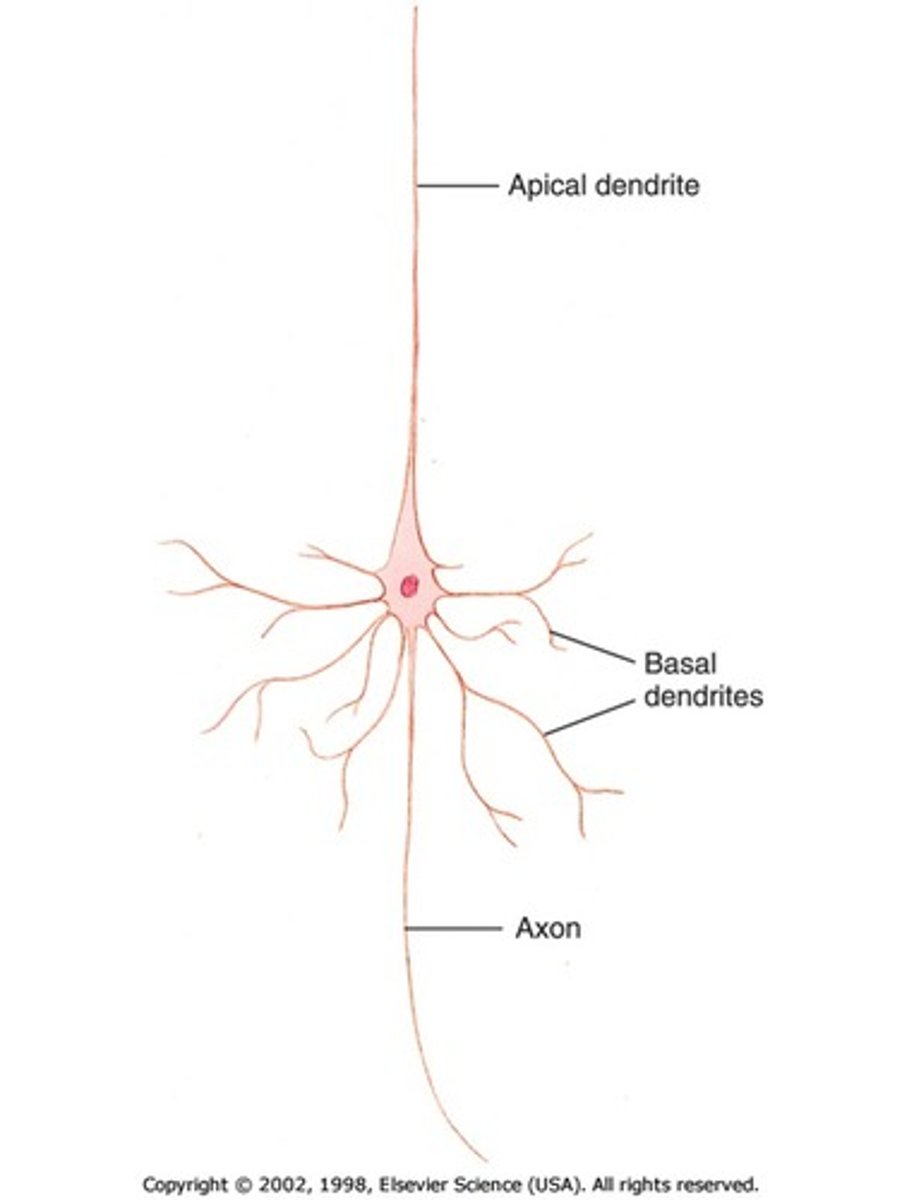
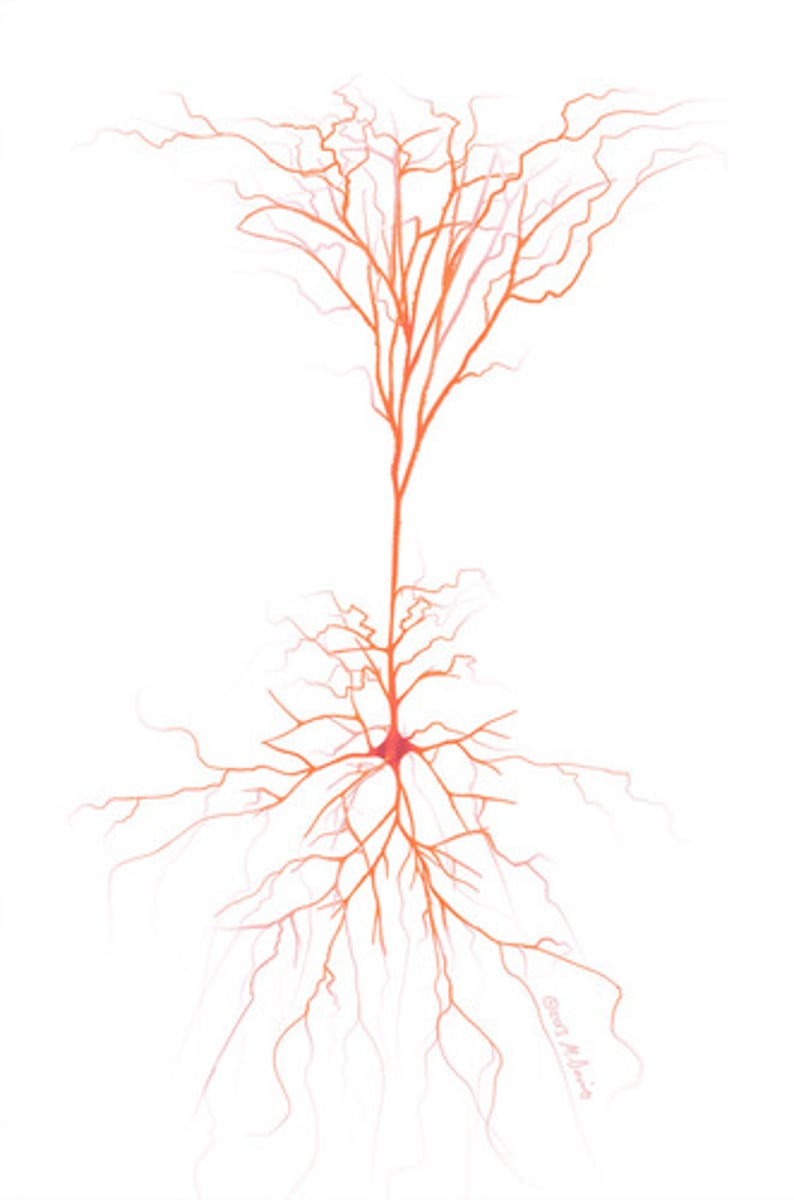
Pyramidal neuron
Pyramid shape with multiple dendrites (apical dendrite extends from the tip of neuron, basal dendrites extend from the sides)
-Most common neuron in the cerebral cortex
-Multipolar neuron
Motor neuron
A neuron that sends an impulse to a muscle or gland, causing the muscle or gland to react based on info from spinal cord and brain
Sensory nerves
Nerves that carry information from the sense receptors to the spinal cord and brain.
Afferent
Bring info towards a structure
-ARRIVE
- EX: Sensory neurons, postsynaptic cell
Efferent
Bring info away from a structure
-EXIT
-EX: Motor neurons, presynaptic cell
Interneurons
CNS neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
Output zone
Axon terminals at the end of the axon, that once electrical signal is received, release neurotransmitters to communicate info to postsynaptic cell
Synapatic vesicles
Membrane bound structures that hold neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons to relay information
Receptors
In neurons, specialized protein molecules on the postsynaptic membrane; neurotransmitters bind to these molecules after passing across the synaptic cleft to relay information
Postsynaptic density (PSD)
Protein dense specialization attached to the postsynaptic membrane
-Dendrites, dendritic spines, axon, soma, etc
-Anywhere the neuron can receive a signal there will be PSD (area of a lot of receptors
Light microscope
An optical instrument with lenses that refract (bend) visible light to magnify images of specimens.
-Shines light on signal
Laser scanning microscopes
- use laser light to scan object point by point into one image
- Focuses on one thing not an entire sample
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM)
A technique that uses a laser excites fluorescent to get a 3D image of the entire specimen
Electron microscope
A microscope that focuses a beam of electrons to magnify objects (can magnify very small things bc electrons are small and can fight between things to illuminate them)
Live imaging
Use of a fluorescent microscope to observe a fluorescently tagged fusion protein
Gila
Cells found throughout the nervous system that provide various types of support for neurons (structural, nutrient, etc)
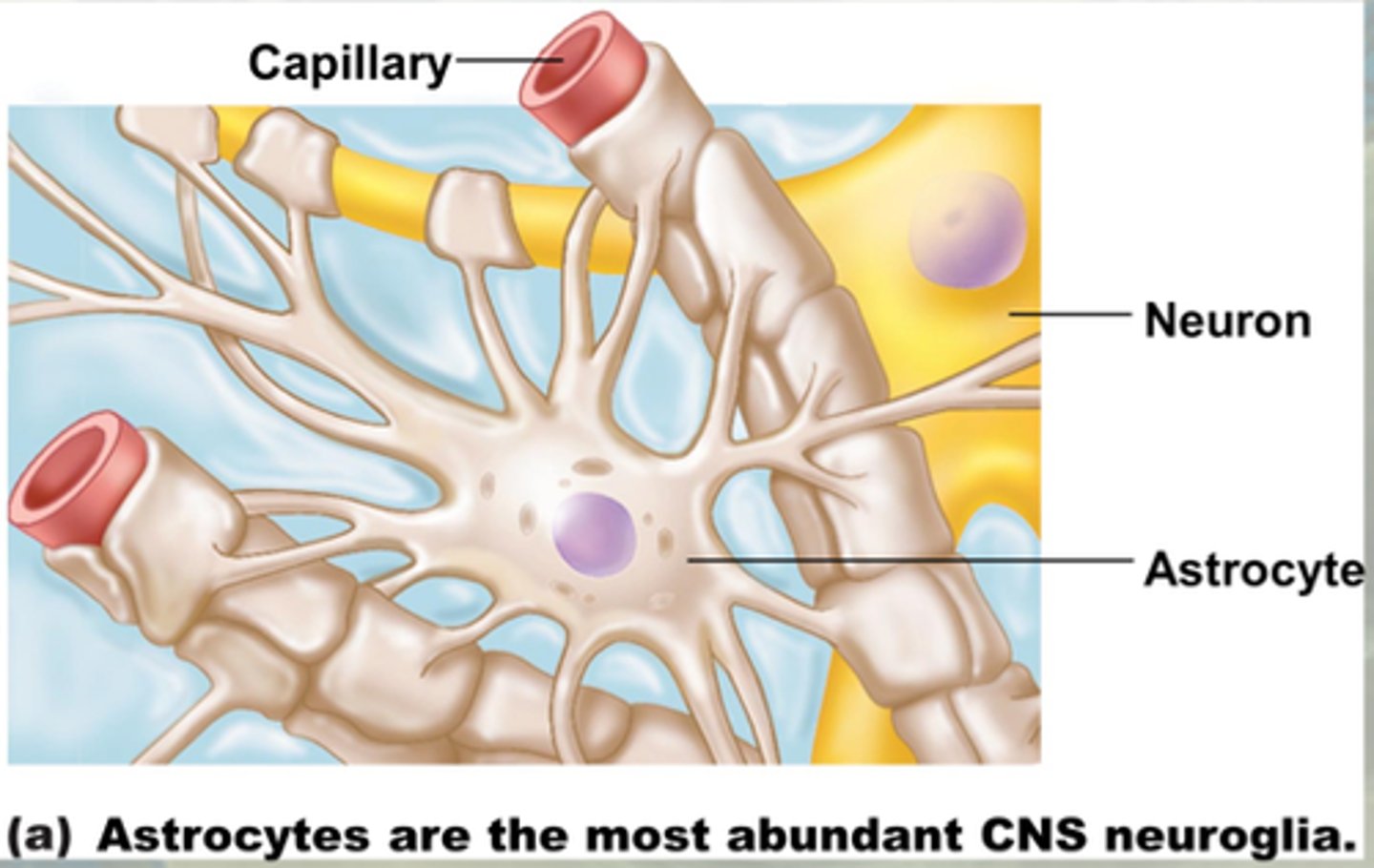
Astrocyte
A type of glial cell that transports water and salts from capillaries
-Regulate blood flow in brain (by enlarging o restricting blood cell size)- based on surrounding neuron activities (more active will need more nutrients i.e. blood)
-May play a role in formation of synapse & synaptic transmission and communication
-Most abundant in the CNS
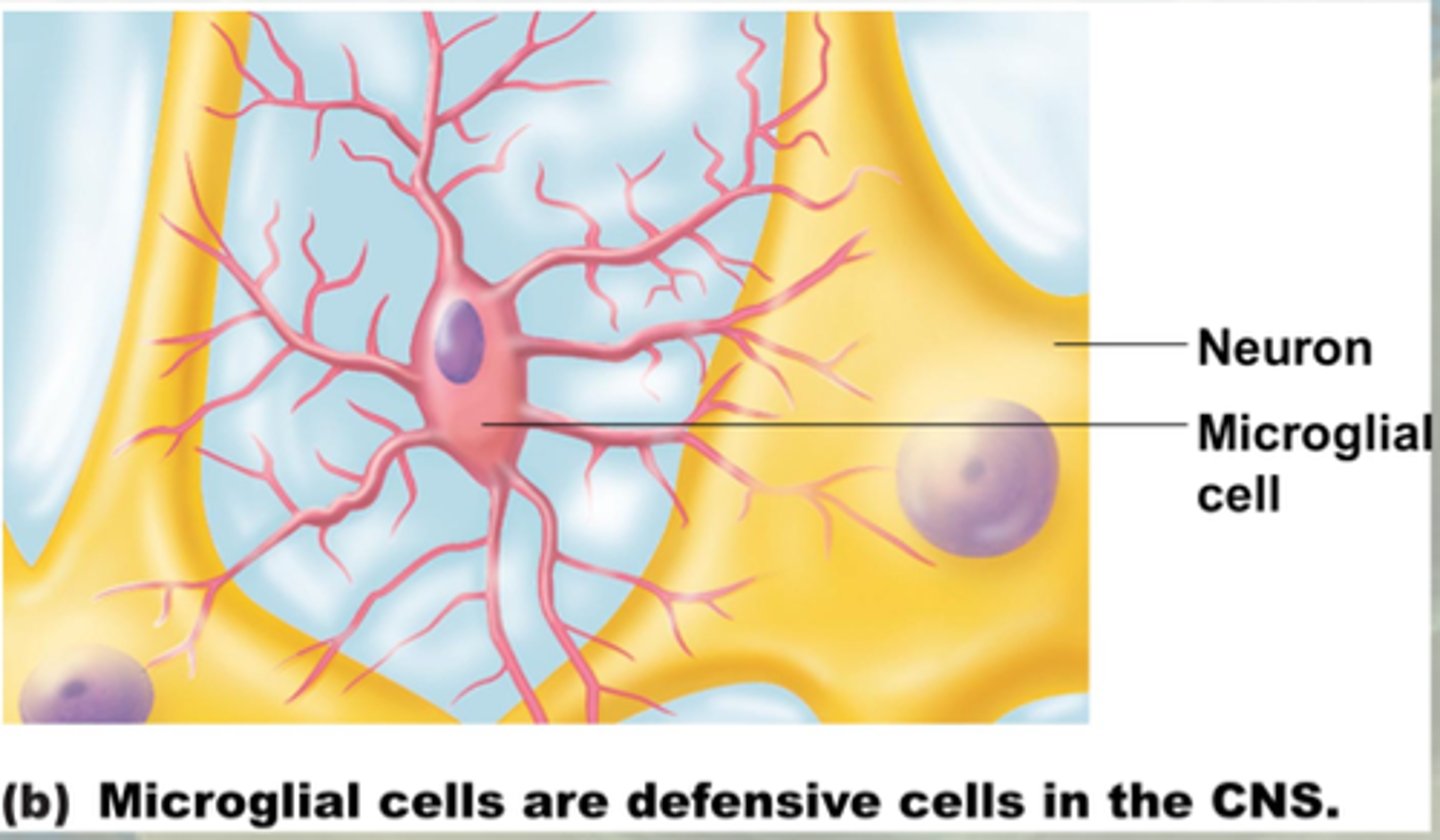
Microglial cell
A type of cell that functions as a phagocyte in the nervous system to remove debris left by dead or dying neurons and glia
-Preforms endocytosis and digestion
-May have a role in synapse formation
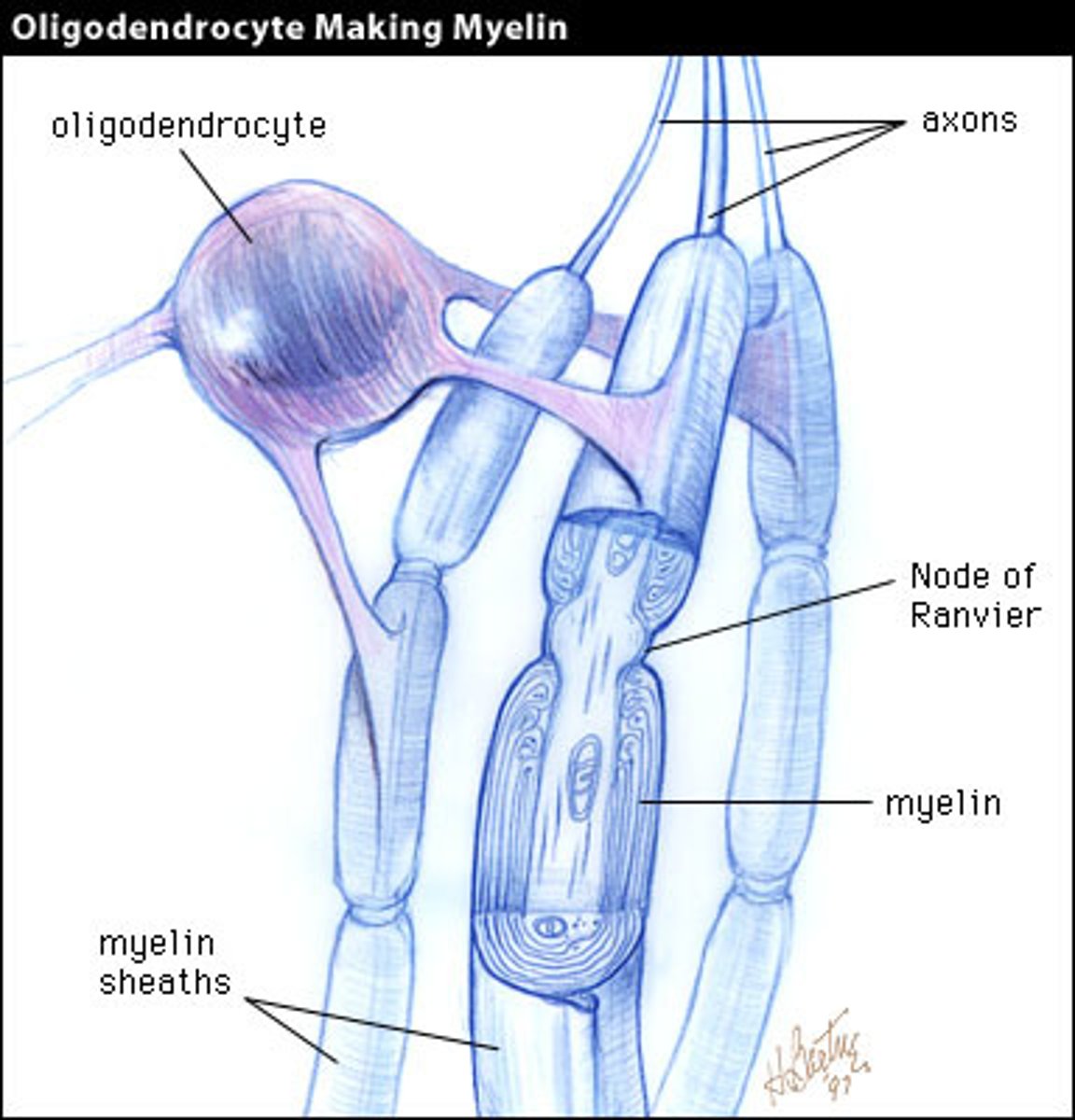
Oligodendrocytes
Type of glial cell in the CNS that wrap axons in a myelin sheath.
-75% of glial cells
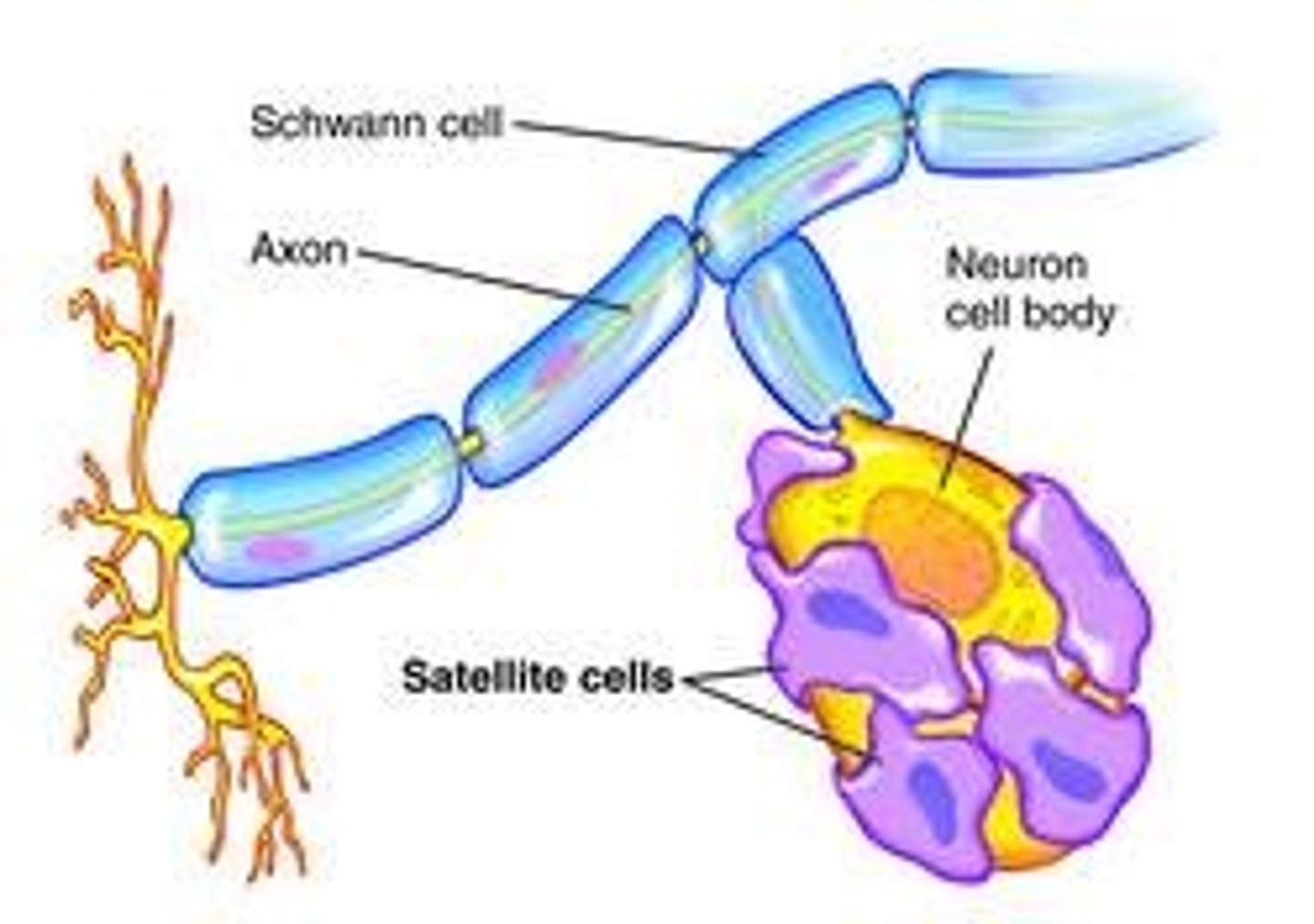
Schwan cells
Create a protective myelin sheath around neurons in the PNS
-Multiple schwann cells myelinate one axon
Myelination
The formation of a fatty sheath around the axons of a neuron
- Some short axons don't have myelin
- Process continues throughout life
Radial glia
Guide the migration of neurons and their axons and dendrites during embryonic development
-Zipline to final destination
Blood-brain barrier (BBB)
A barrier between the circulatory system and the central nervous system that establishes a privileged blood supply, restricting the flow of substances into the CNS
-Small, non-polar substances can pass through (passive transport)- CO2, O2
-Large, polar substance need help passing through (active transport)- glucose and amino acids
Endothelial cells
Cells lining the blood vessels that controls the flow of substances and fluid into and out of a tissue
-SPECIALIZED in the CNS
-Extra defensive, with no gaps, and is not porous as it is in other parts of the body
-Reinforces the BBB
-Astrocytes reinforce these cells
Passive Transport (Diffusion)
A process that requires no energy to move molecules down their concentration gradient(from high to low concentration)
-Small, nonpolar molecules
Active transport
Energy-requiring (ATP) process that moves material across a cell membrane against the concentration gradient
(low to high)
-Large, polar molecules
Neuroanatomy
study of the structure or organization of the nervous system
-Founded on the concepts of localization and connectionism
-Focuses on large scale things (can be seen with your eyes)
Hierarchical vs. Network
Systems are overlaid over simpler ones vs. equally weighted units working cooperatively
-Way to look at neuroanatomy
Serial vs Parallel
separation and sequence of different pathways (i.e., sensory -> motor) vs. simultaneous multiple levels of processing of related information
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord
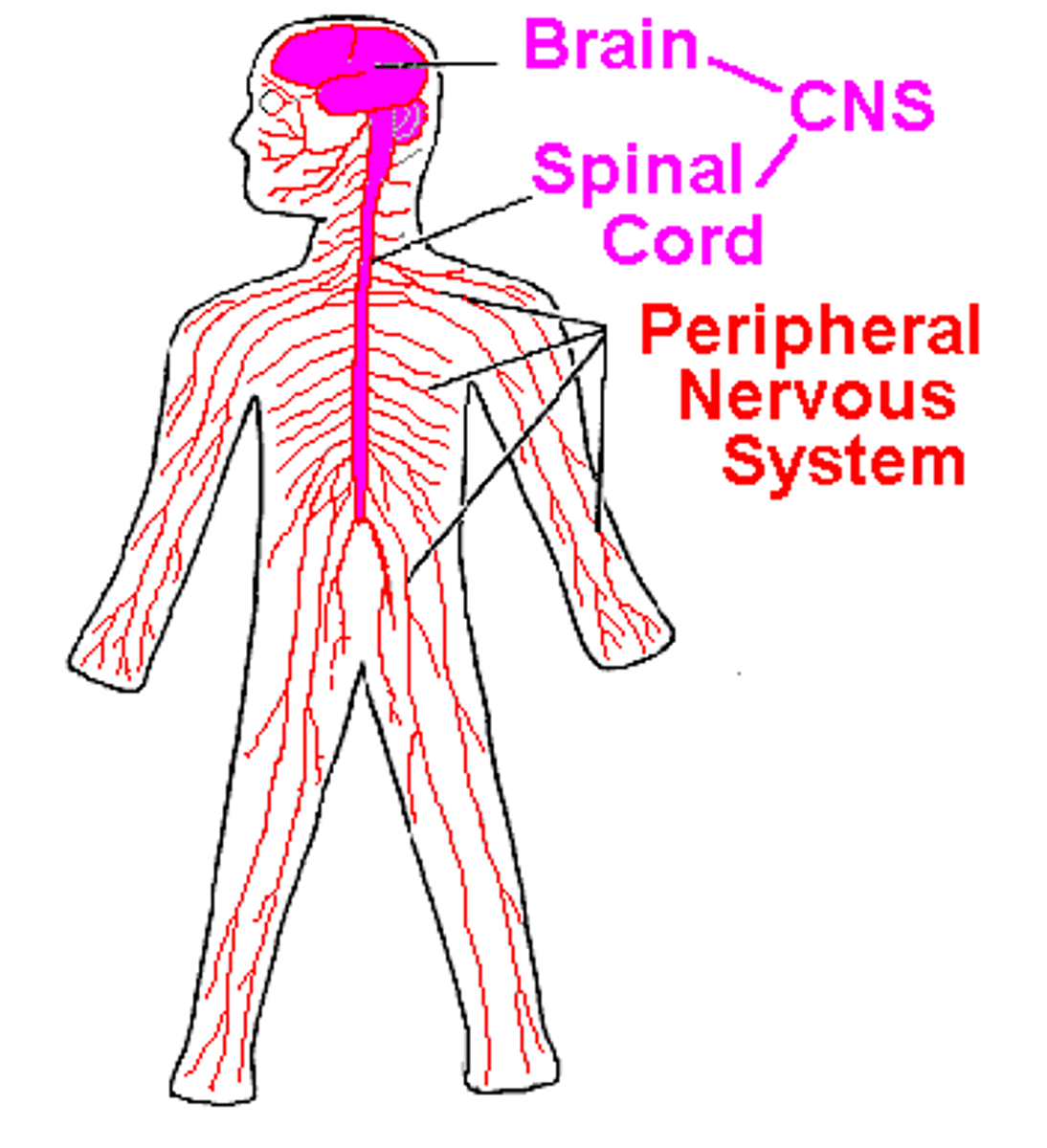
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body
-Everything but the brain and the spinal cord
Somatic nervous system
The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
-Things under your conscious control
Autonomic nervous system
The part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs to regulate automatic behaviors of the body to maintain homeostasis
-2 subcategories; sympathetic (arouses) and parasympathetic (calms)
Homeostasis
Property of a system that regulates its internal environment for maintain stable constant condition (pH, blood sugar, etc)
sympathetic nervous system
Network of sympathetic ganglionic neurons that prepares the organs for increased activity (increase heart rate & blood pressure)
-Fight or flight response
-Active in stressful situations
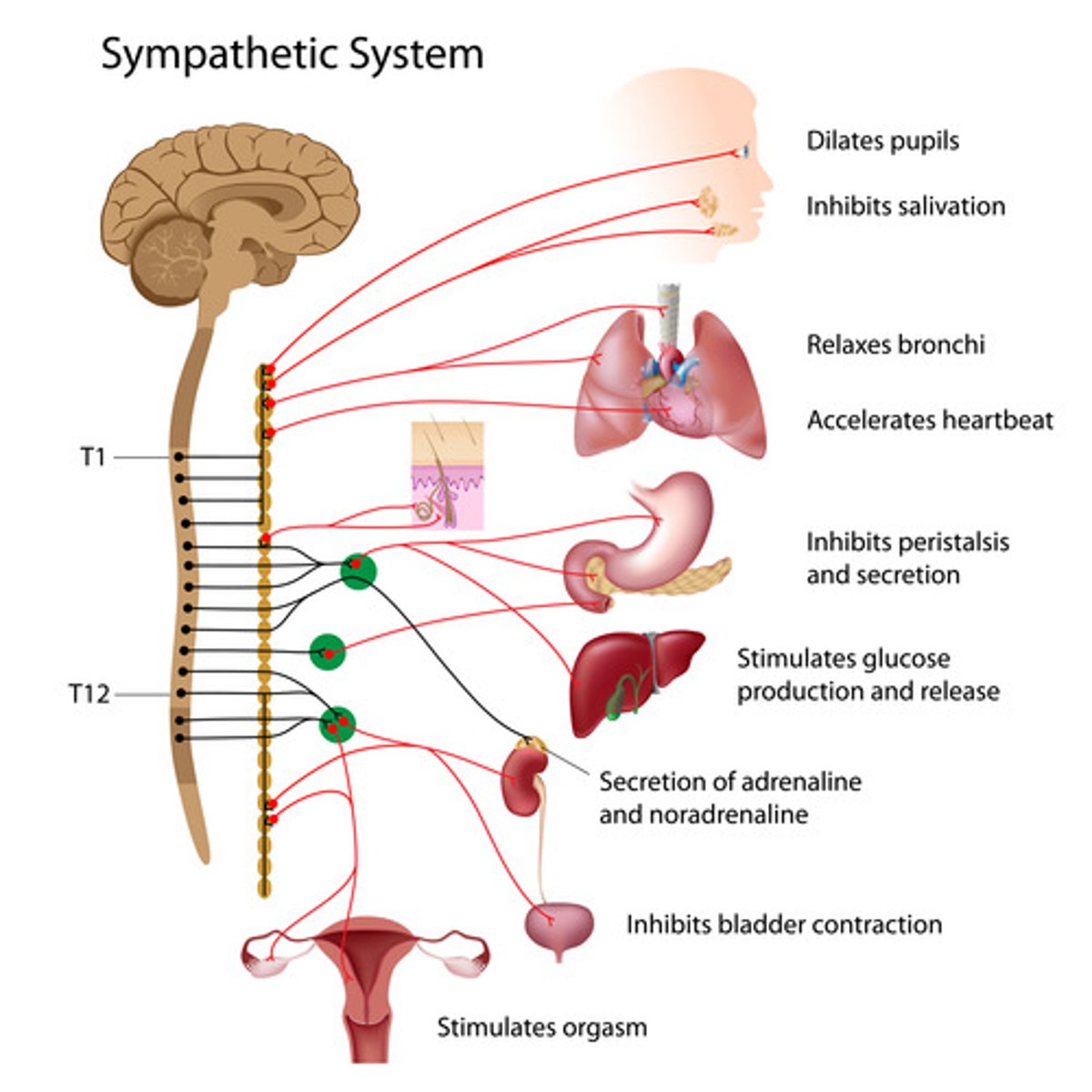
Sympathetic preganglionic neurons
Originate in the thoracic and lumbar region of the spinal cord (middle/ medial)
-Axons are very short (faster communication) which allow for faster response in a high stress environment
Norepinephrine
Chemical neurotransmitter of the sympathetic nervous system to communicate to the postganglionic neurons in high stress situations to arouse/alert
sympathetic postganglionic neurons
Long, postsynaptic neurons that transmits message to target neurons
Parasympathetic nervous system
The division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
-Located on both sides of the sympathetic nervous system
-Is active during rest
Parasympathetic preganglionic neurons
Long neurons that originate from the cranial and sacral part of the spinal cord (top and bottom)
-Do not need a fast response like in the SNS so axons are longer
Acetylcholine
Chemical neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic NS that enables learning, memory, and triggers muscle contraction
Parasympathetic postganglionic neurons
Short neurons that attach directly to target (organs)
Spinal cord
A major part of the central nervous system which conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain
-Middle man that conveys info from brain to PNS
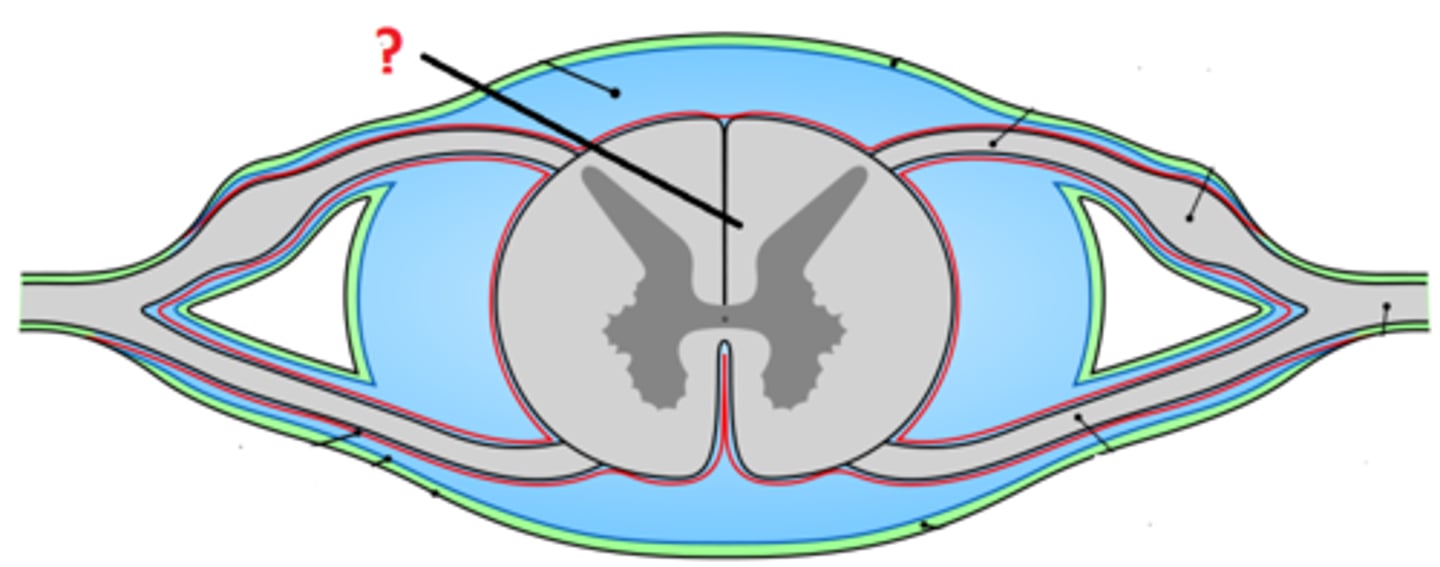
Gray matter
Brain and center of spinal cord tissue that appears gray with the naked eye; consists mainly of neuronal cell bodies (nuclei) and lacks myelinated axons
-Processes information (bc it has the soma)
White matter
White tissue in the brain and spinal cord that is made up of myelinated axons
-Myelin is a lipid which is a white-fatty substance
-Carries info from gray matter to spinal cord (in the brain)
Segmentation
Each part of the spinal cord send sensory info to the brain and receives motor commands to send to certain parts of the body
Dorsal root ganglion
Contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons that bring information from the PNS to the spinal cord
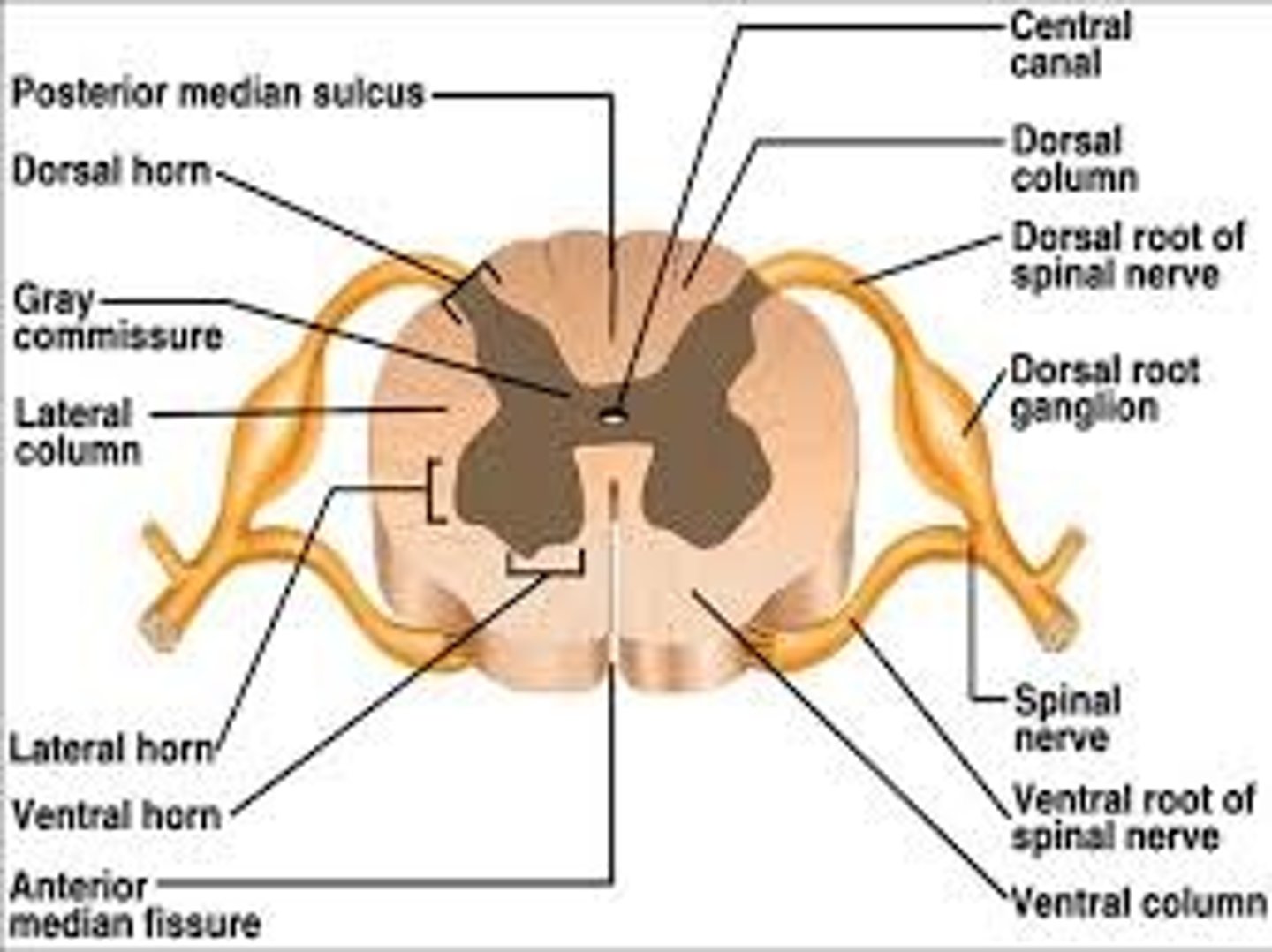
Ventral root ganglion
Contains cell bodies of motor neurons which outputs motor commands from the brain to the PNS
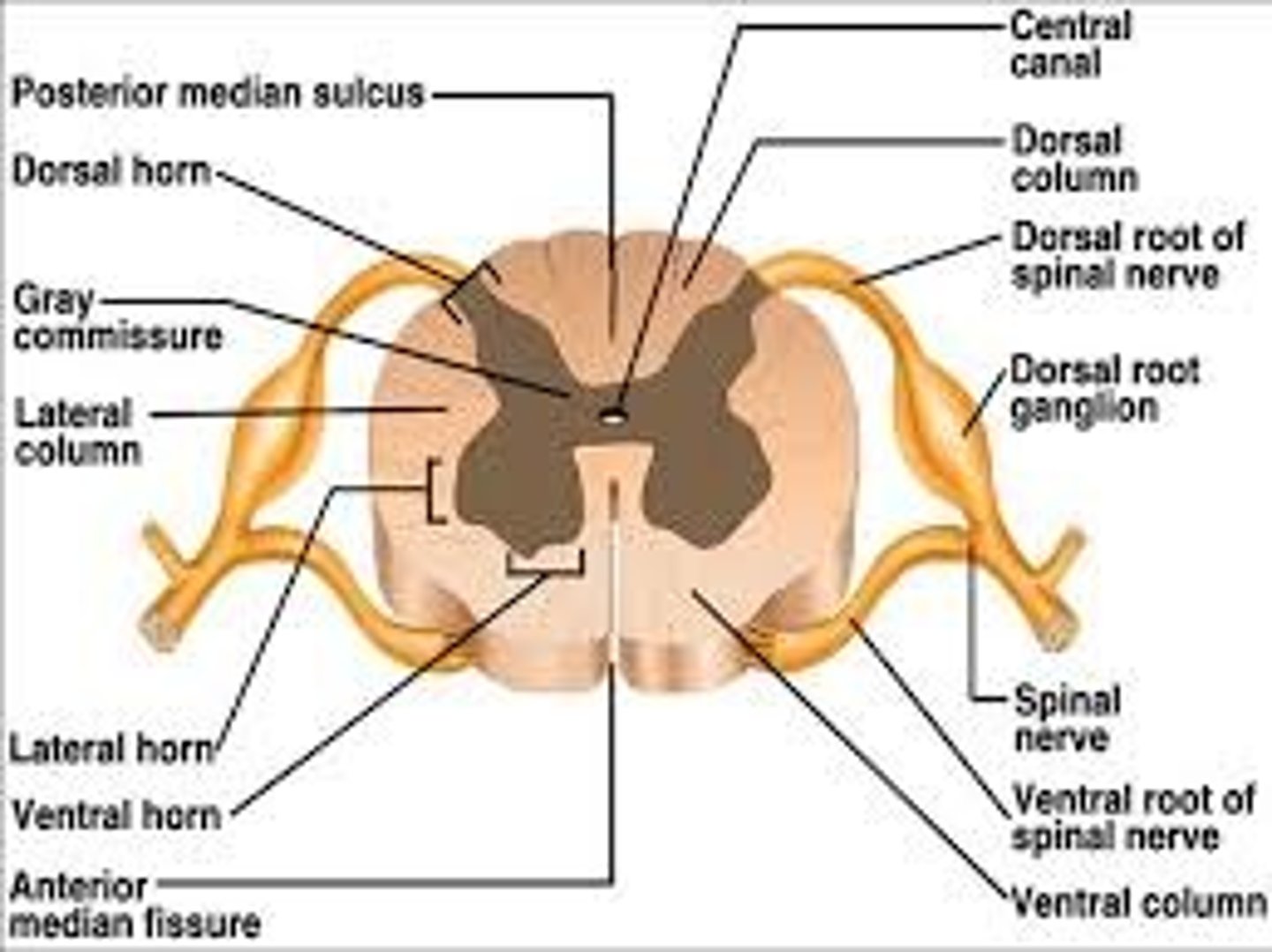
Ganglion
Collection of nerve cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system
-ONLY IN PNS
-In CNS it is called the nucleus
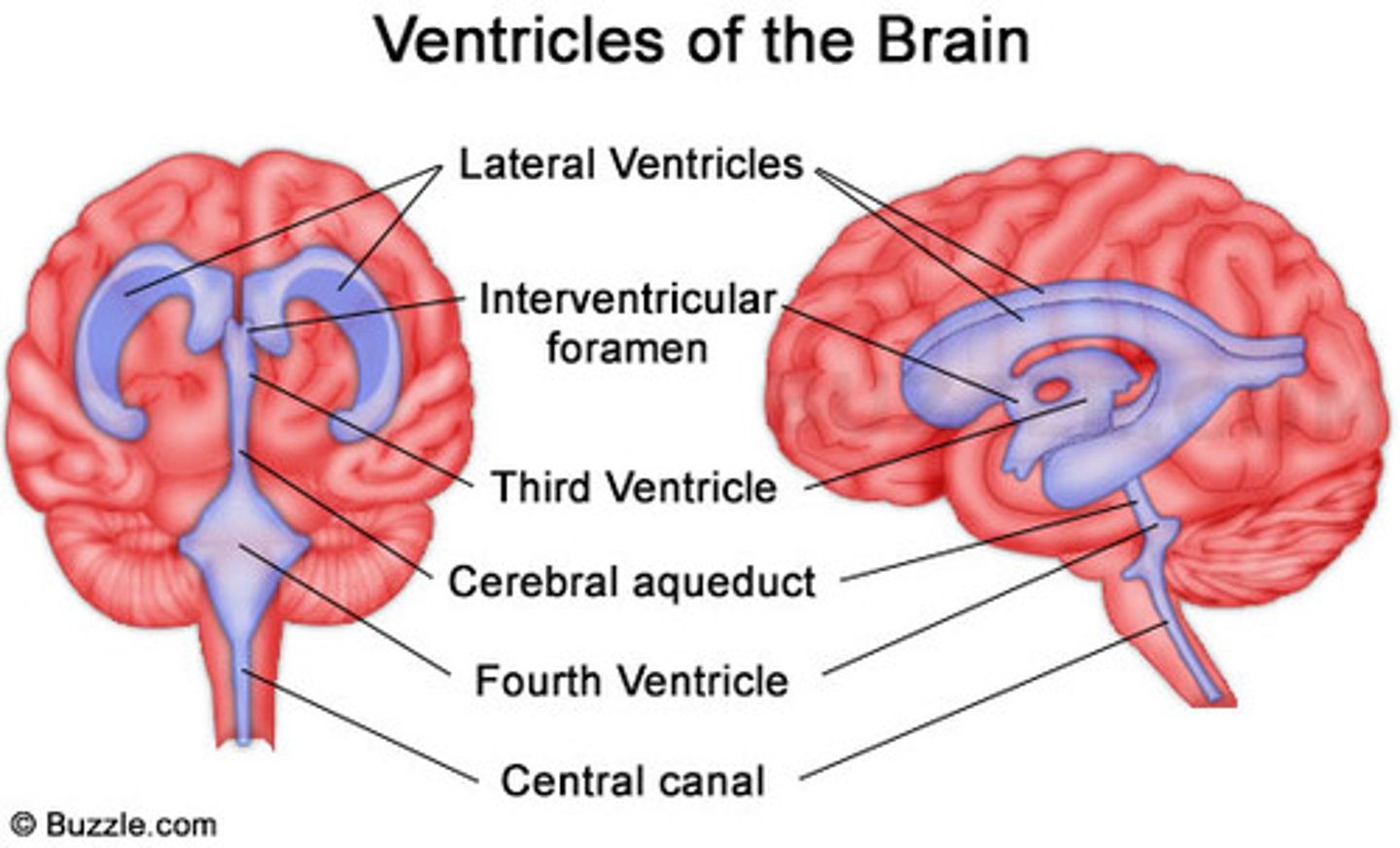
Central canal
A fluid-filled channel in the center of the spinal cord
Ventricles of the brain
Canals in the brain that contain CSF
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
plasma-like clear fluid circulating in and around the brain and spinal cord
-Shock absorption
-Storage of hormones/nutrients
Meninges
3 protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
-PAD, forms a pad for the brain
Dura mater
Outermost meninge, thickest and most protective
Arachnoid space
Spider-web layer that connects the maters, contains blood vessels and CSF to maintain pressure
Pia mater
Innermost layer that lays on top of the brain, thinnest and most delicate layer
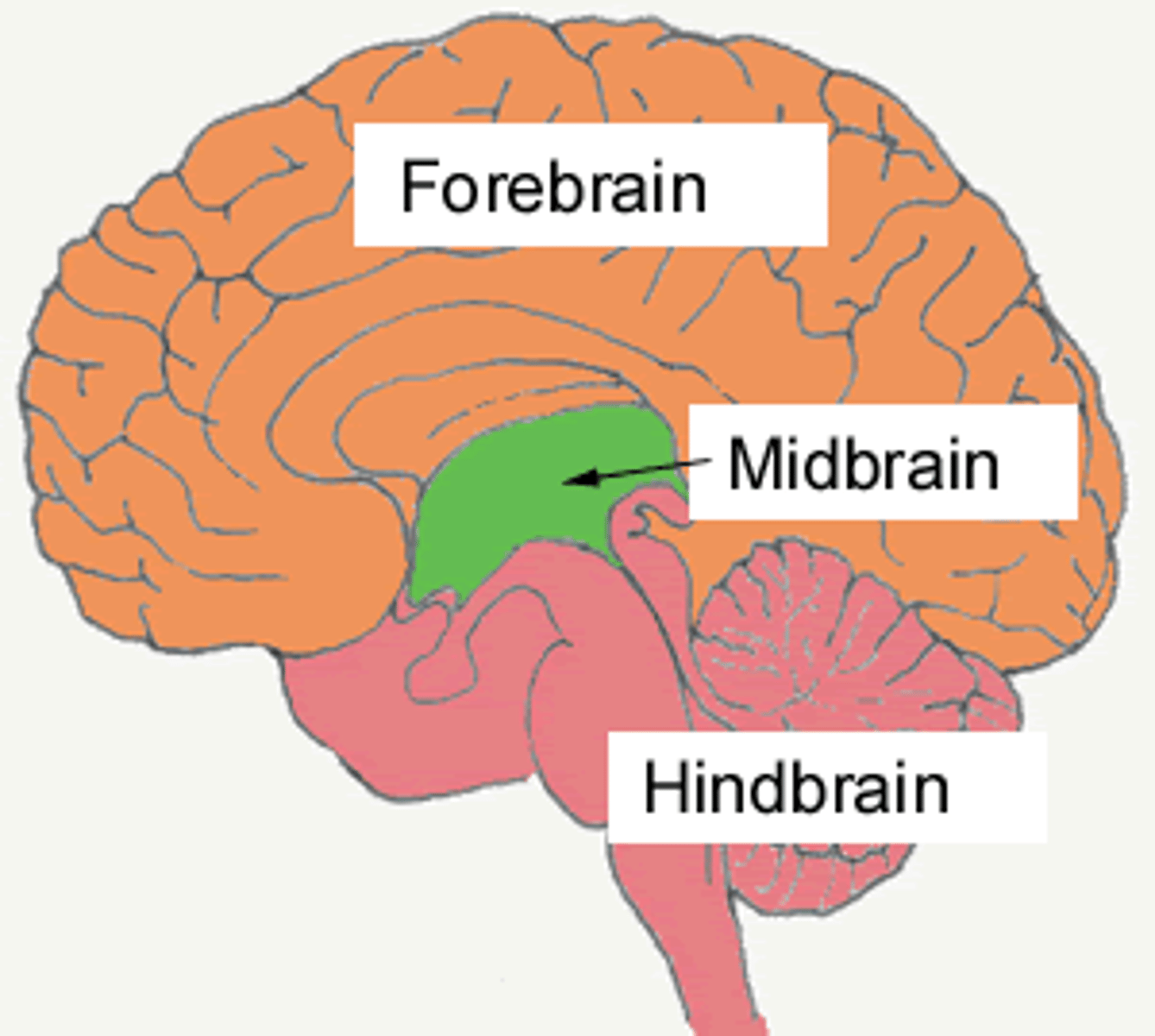
Forebrain
Most dominant and anterior part of the brain
-Contains the diencephalon and telencephalon
Diencephalon
part of forebrain, composed of hypothalamus and thalamus (di means 2, structures)
Telencephalon
part of the forebrain, contains the basal ganglia and limbic system
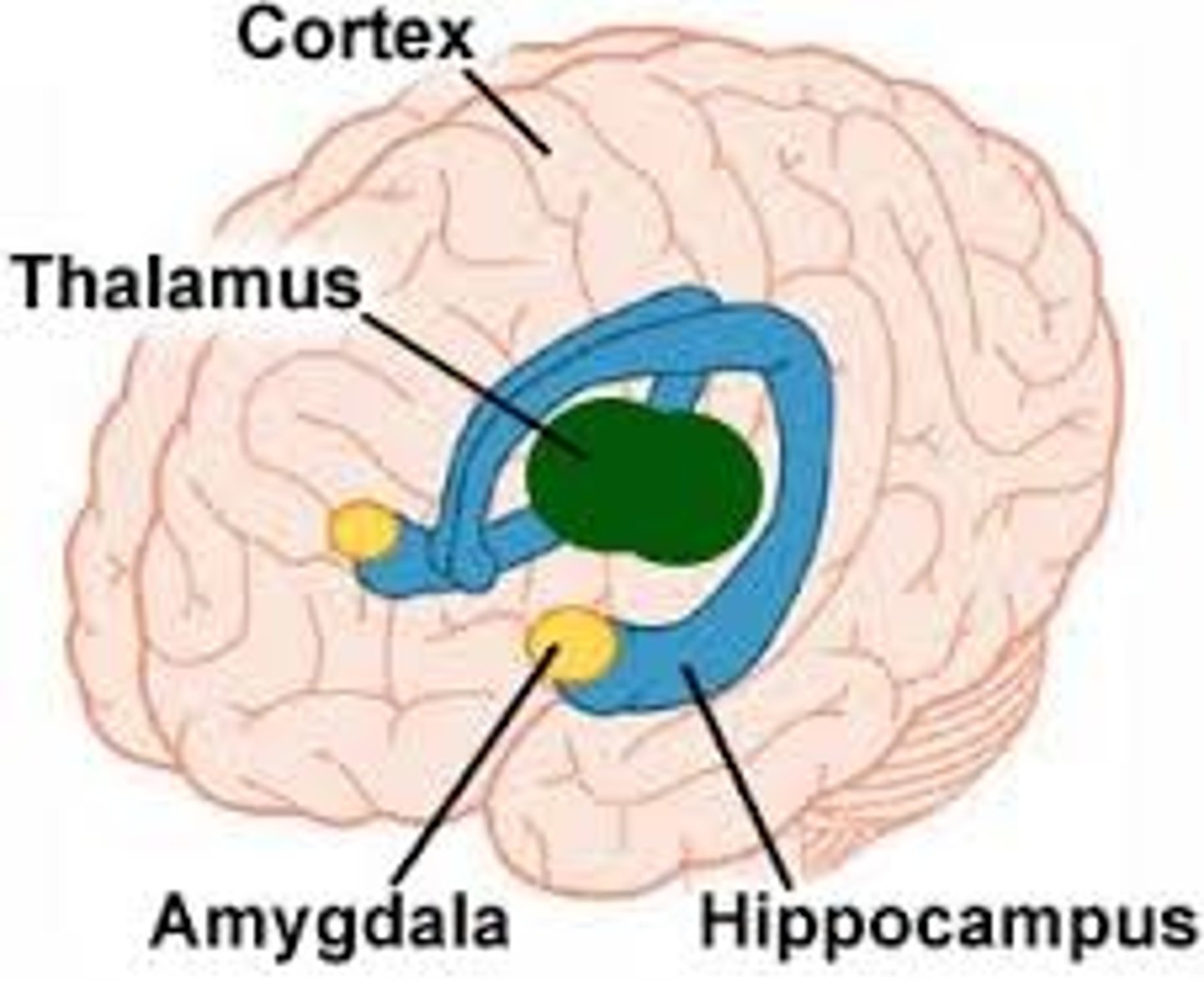
Hypothalamus
Bilateral structure that surrounds the 3rd ventricle, conveys messages to pituitary gland to control endocrine function, as well as neural projections to different brain regions, maintains homeostasis (eating, drinking, reproduction, defense, etc)
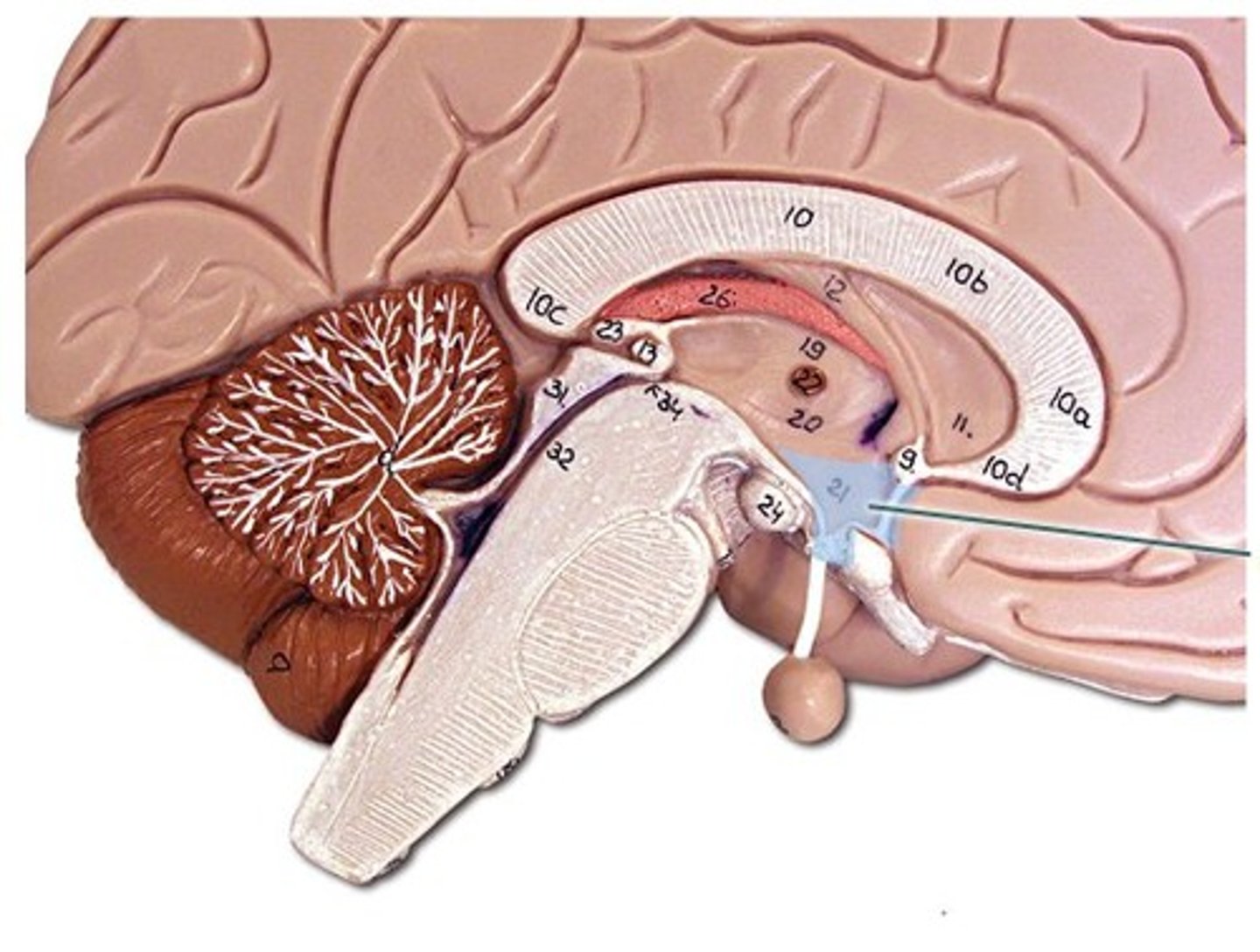
Pituitary gland
Hormone producing glad apart of the endocrine system and controlled by the hypothalamus (not apart of forebrain)
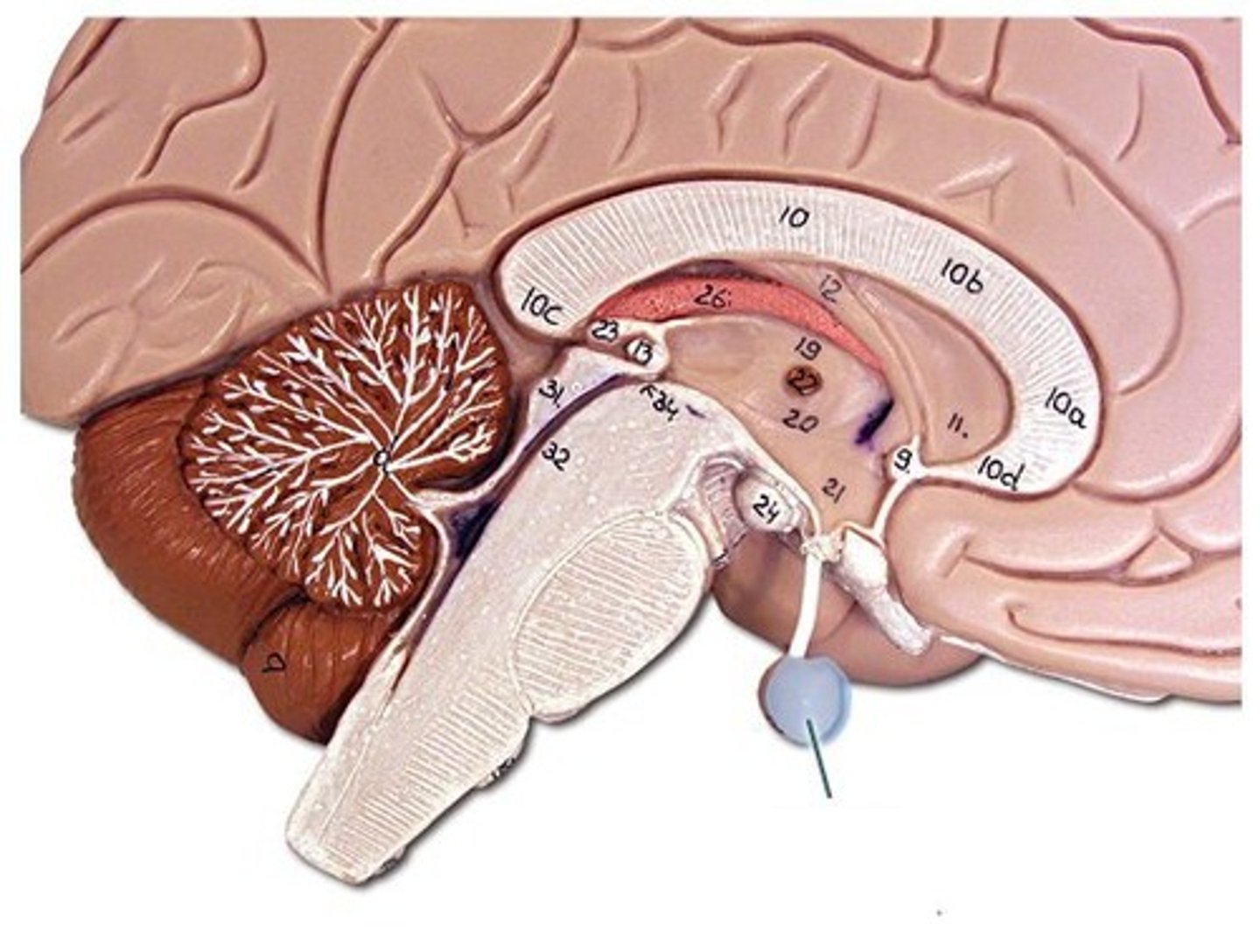
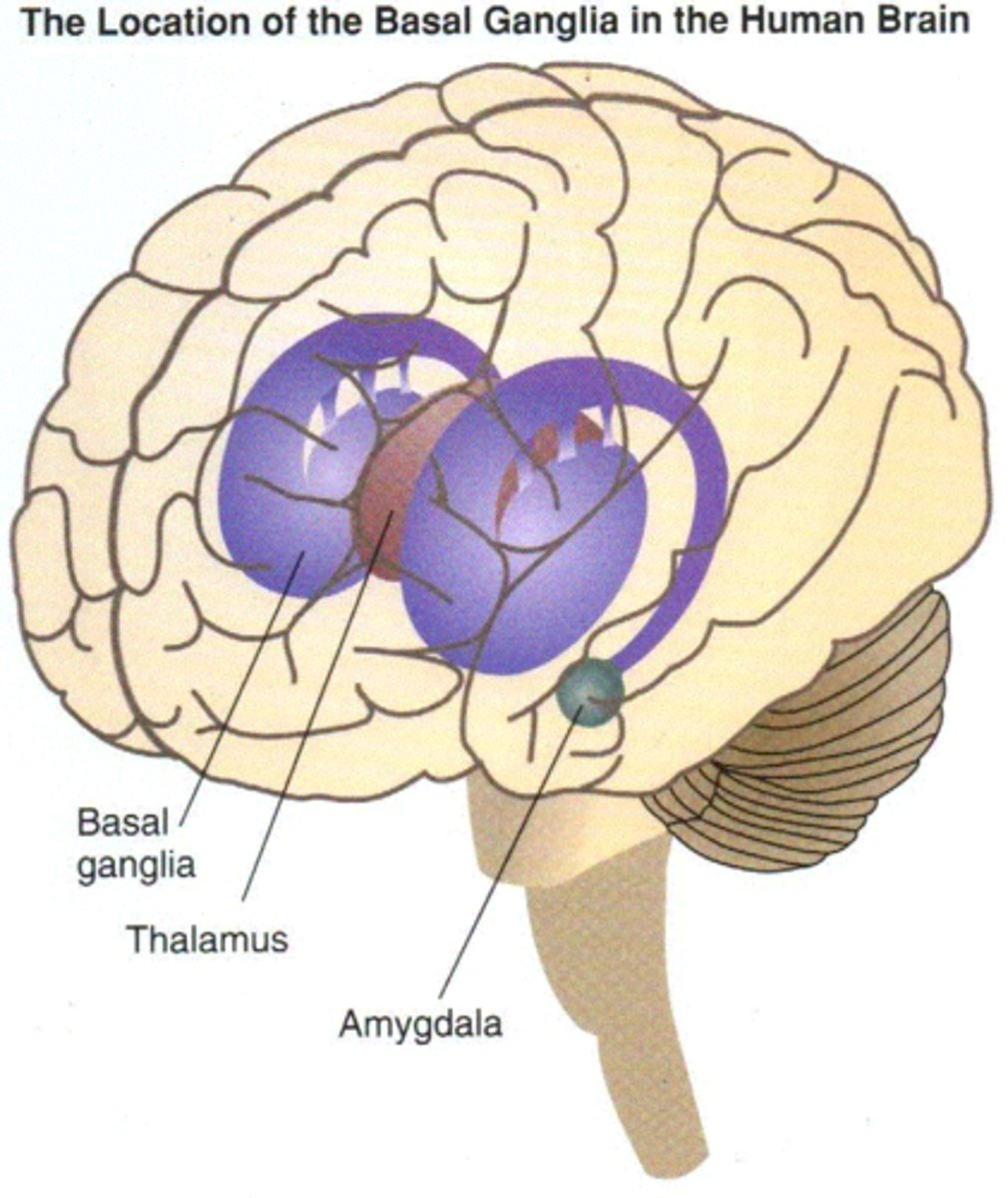
Thalamus
Switch board of the brain, relays info from the brain stem and hypothalamus to the cortex
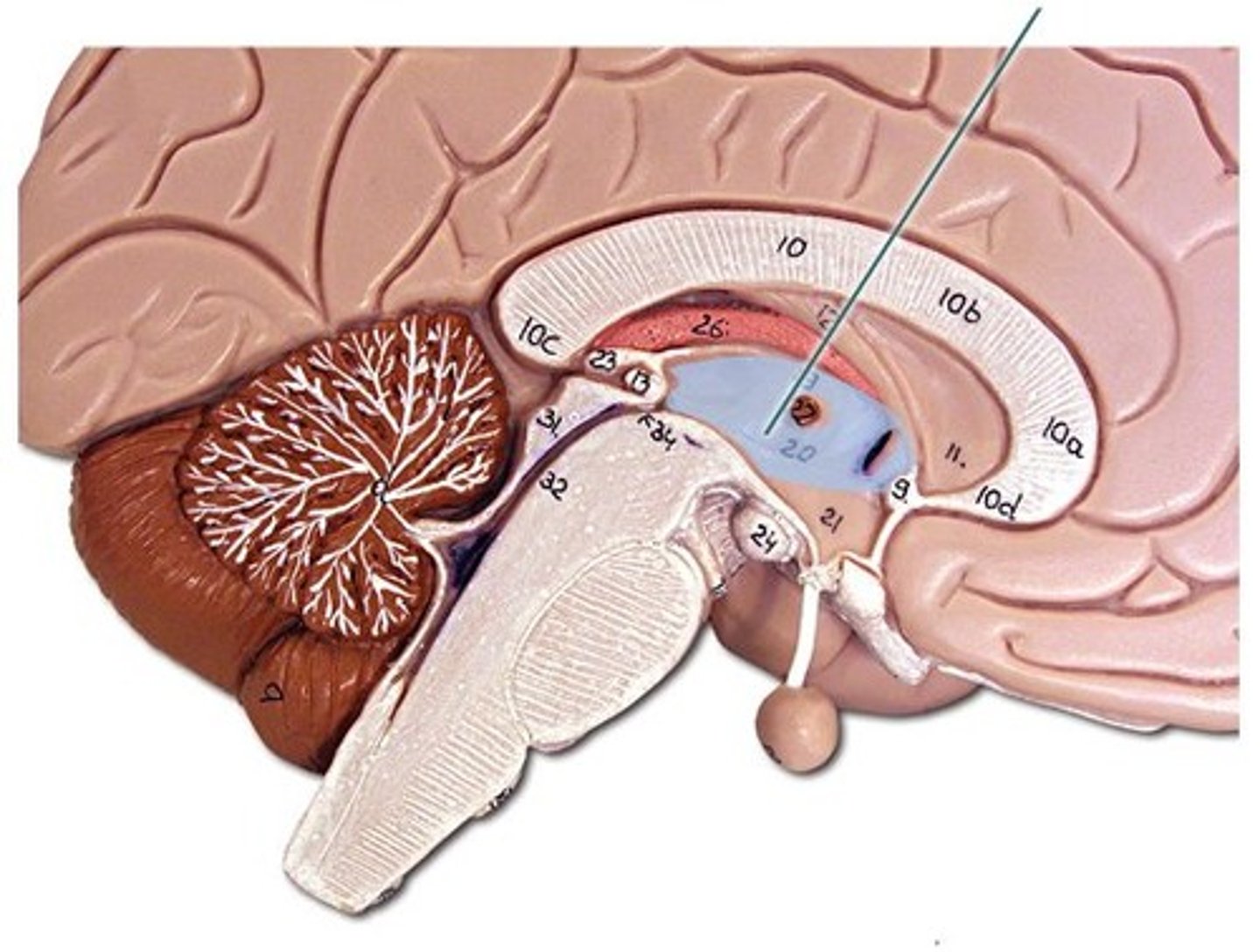
Basal ganglia
not actually ganglia (bc apart of the CNS), helps with voluntary movement, procedural learning, and learned behaviors/muscle memory (lesser role in memory and emotional expression), 3 parts
-Caudate nucleus
-Putamen
-Globus pallidus
Limbic System
consists of interlinked structures that support emotion, behavior, motivation, long term memory, and smell
-Consists of the hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala, and cingulate gyrus of cerebral cortex
Hippocampus
Located between the thalamus and cerebral cortex, does memory consolidation(short and long term), spatial learning (where things are, how to get there in your head)
-Contains the:
-Entorhinal cortex
-Dentate gyrus
-CA3
-CA1
-Sibculum
-Pathways between things:
-Preforant
-Mossy fiber
-Schaeffer collaterals
NEED TO KNOW HOW TO DRAW THIS
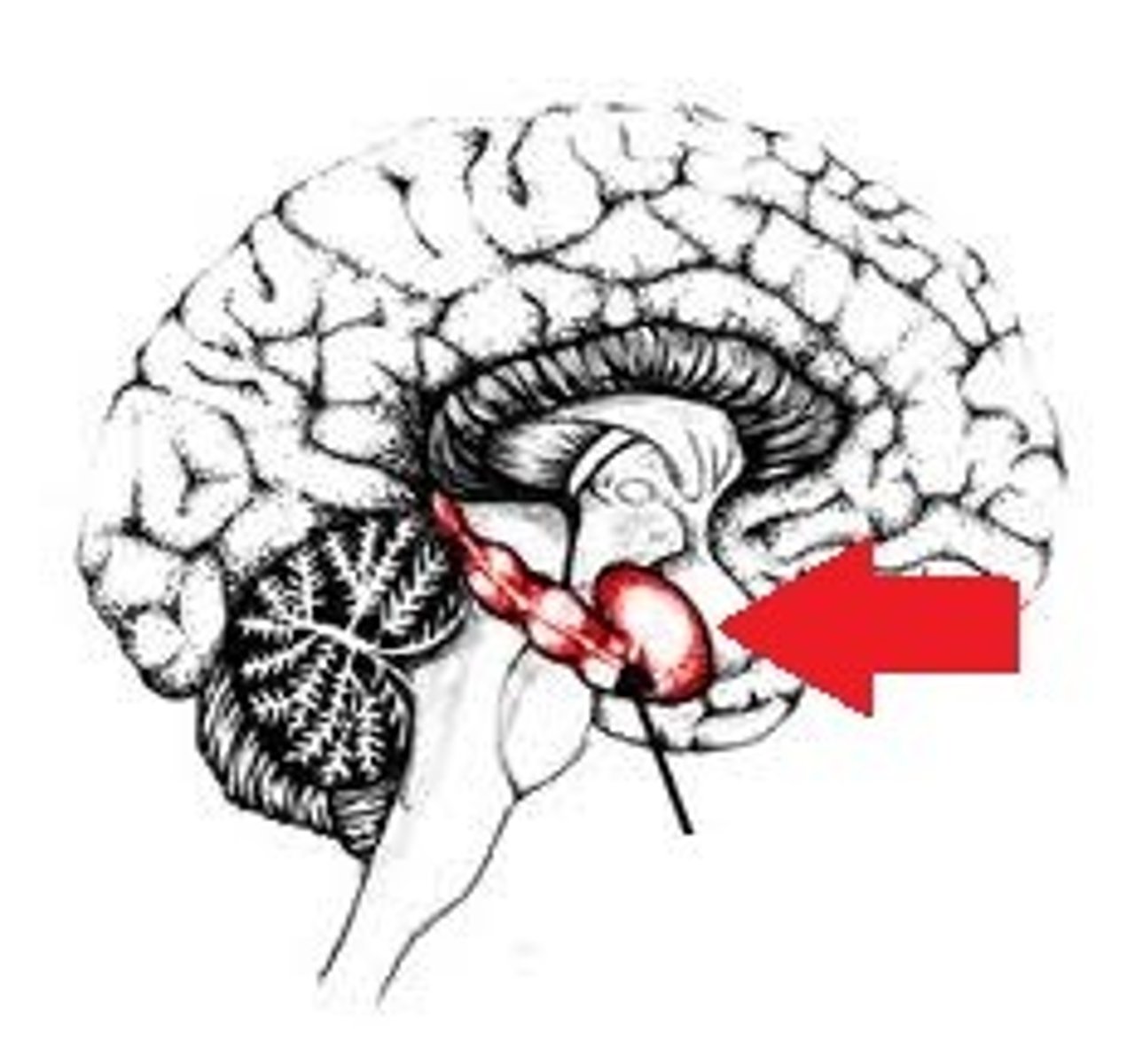
Amygdala
Nuclei (bundle of nerves) in the base of temporal lobe, produces emotion, mostly fear and defensive responses (fight or flight)
Contains the:
-Lateral amygdala
-Basolateral amygdala
-Central nucleus of amygdala
-info moves lateral to medial and comes from auditory cortex and auditory thalamus
NEED TO KNOW HOW TO DRAW THIS
Midbrain
(mesencephalon) middle part of brain, contains the mesencephalon
Mesencephalon
part of the midbrain, contains the superior and inferior colliculus
Superior and inferior colliculus
bilateral structure (4 bumps) on the top of the midbrain, process/ orients visual (superior) and auditory (inferior) stimuli for reflexive action
-Put together they are called tectum
Tectum
superior and inferior colliculi together
Hindbrain
(rhombencephalon) posterior, contains the myelencephalon and metencephalon
Myelencephalon (medulla)
Part of the hindbrain located above the spinal cord, responsible for vital, automatic processes (vomiting, salvation, coughing, sneezing, breathing, heart rate, etc)
-Most cranial nerves connect to the medulla
(control face, neck, head regions)
Cranial nerves
12 cranial nerves (pair for left and right of body), control sensory and motor (connect to brain or medulla) without spinal cord
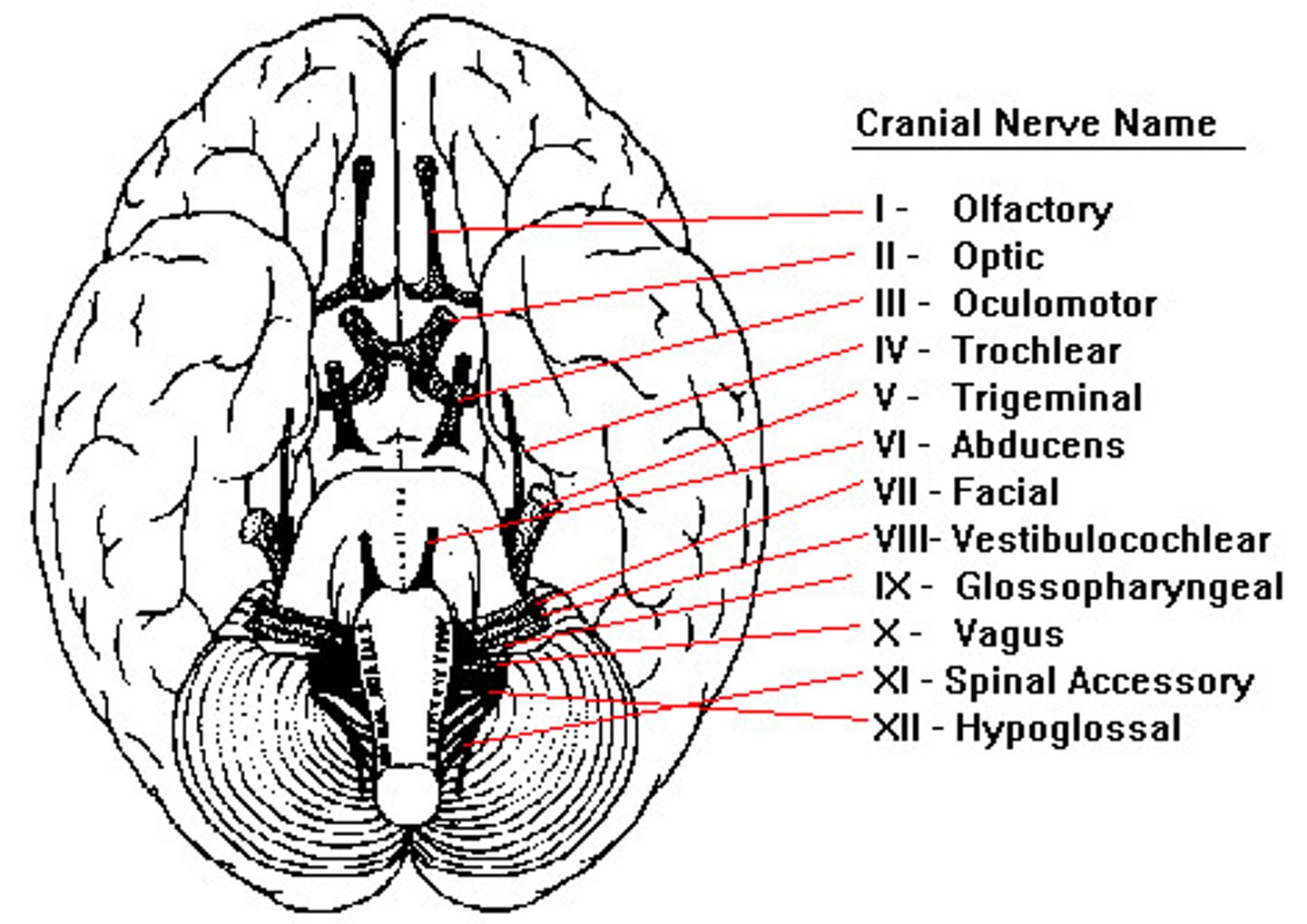
Olfactory nerve (I)
sense info (smell) and sends to brain
Optic nerve (II)
on the back of each eyeball, sends visual info to brain
Vagus nerve (X)
information from internal organs and motor control of internal organs
Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
balance and hearing
Metencephalon
part of hindbrain, develops into cerebellum and pons
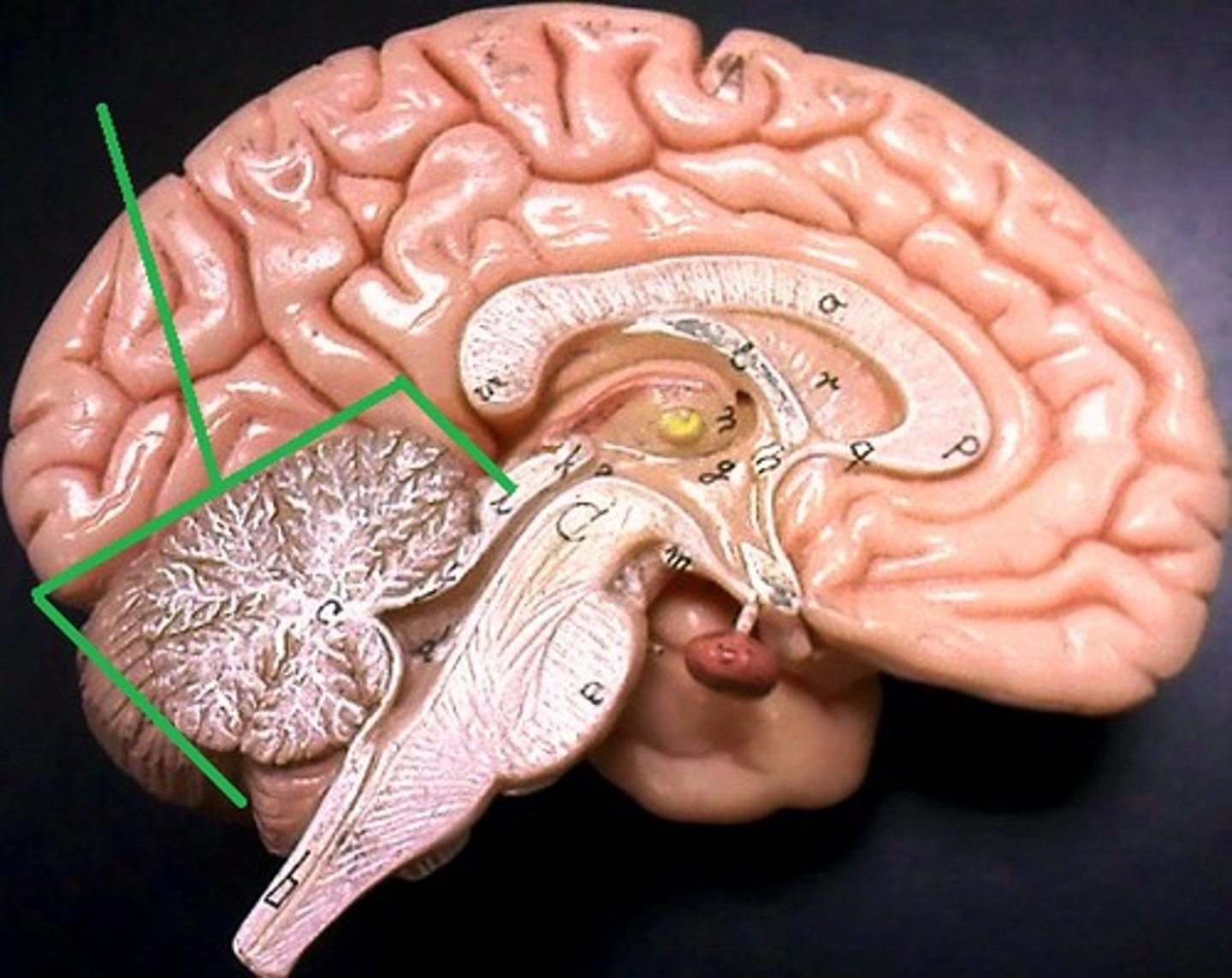
Cerebellum
Regulates motor movement, balance, and coordination
-"Small brain"
-Highly folded to increase SA