Glencoe Biology: Chapter 12
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What is DNA?
the genetic "code" that figures out what makes you, you
What does DNA stand for?
deoxyribonucleic acid
3 main parts of DNA?
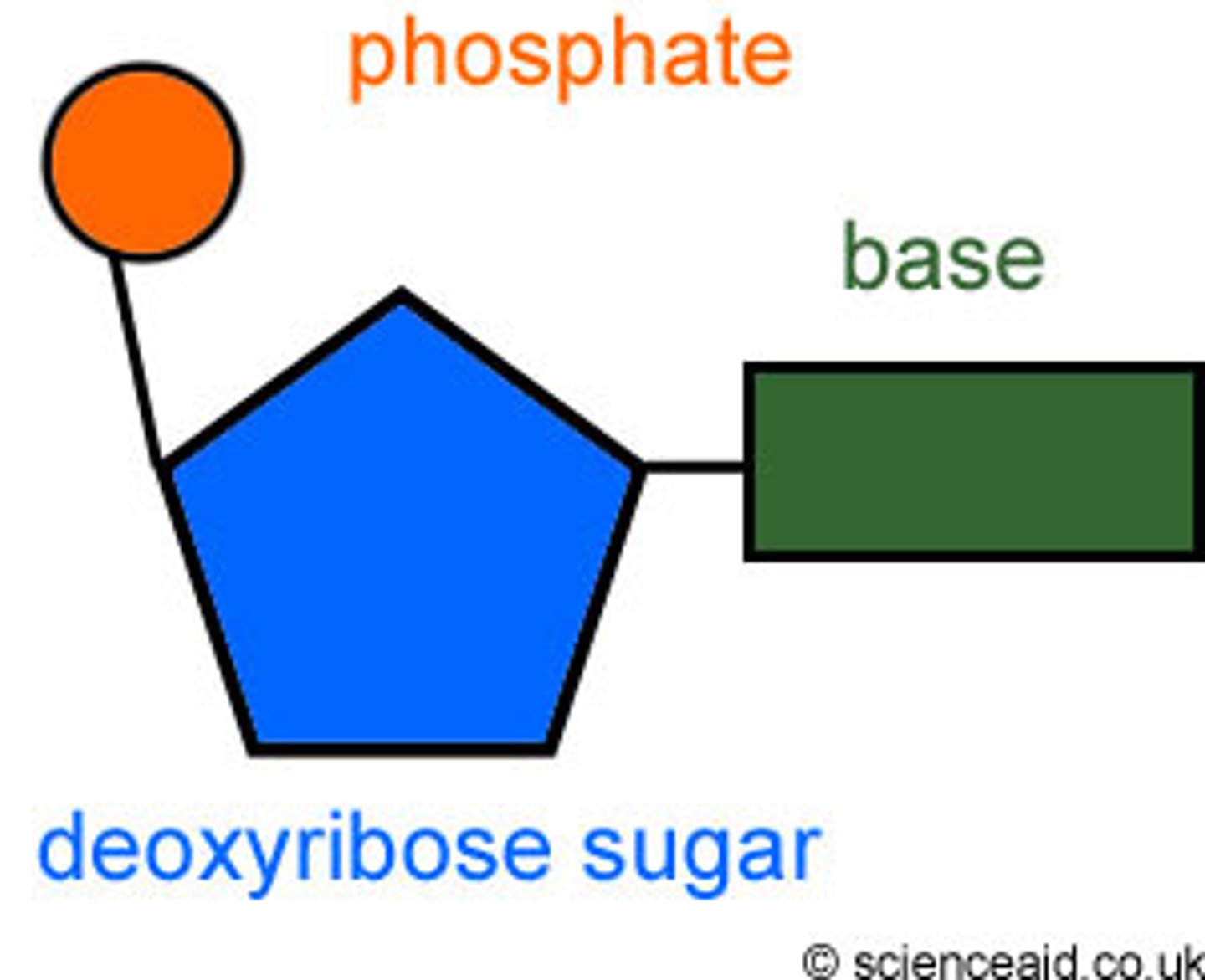
sugars, phosphates, and nitrogen bases
What is the backbone for DNA?
phosphates and sugars
Replication for DNA
the DNA ladders get "unzipped" and a new side is formed to complete it; the 2 sets of DNA are identical
What are base pairs for DNA?
adenine and thymine; cytosine and guanine
Who were Watson and Crick?
two scientists who discovered the construction and communicationof DNA and called it the double-helix
What is in a nucleotide?
1 phosphate, 1 sugar, and 1 nitrogen base
What are the 3 types of RNA?
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
What is the "m" in mRNA?
messenger
What is the "t" in tRNA?
transfer
What is "r" RNA?
ribosomal
What is protein synthesis?
process that describes how enzymes and other proteins are made from DNA
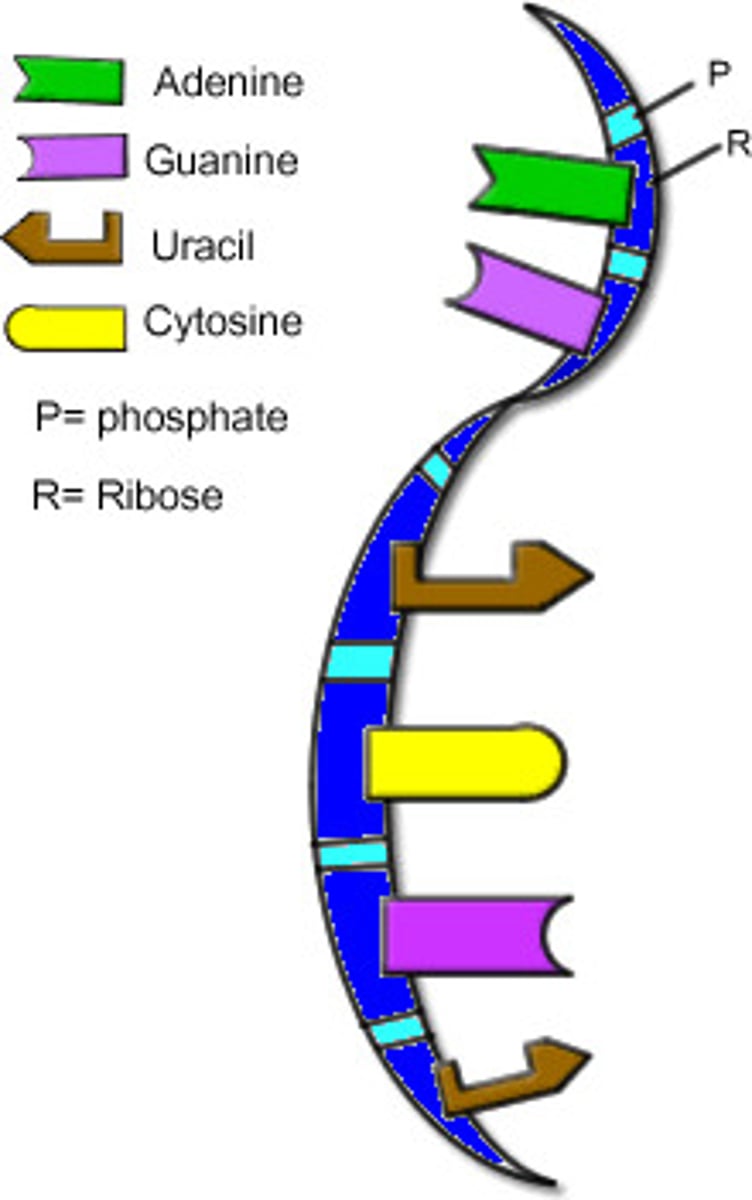
How does RNA differ from DNA?
ribose sugar instead deoxyribose, uracil replaces thymine, single strand instead of double strand
What does mRNA do?
makes a template for sequencing nitrogen bases in replication
What does tRNA do?
transfers short RNA molecules used for transporting amino acids to prepare place on the mRNA template
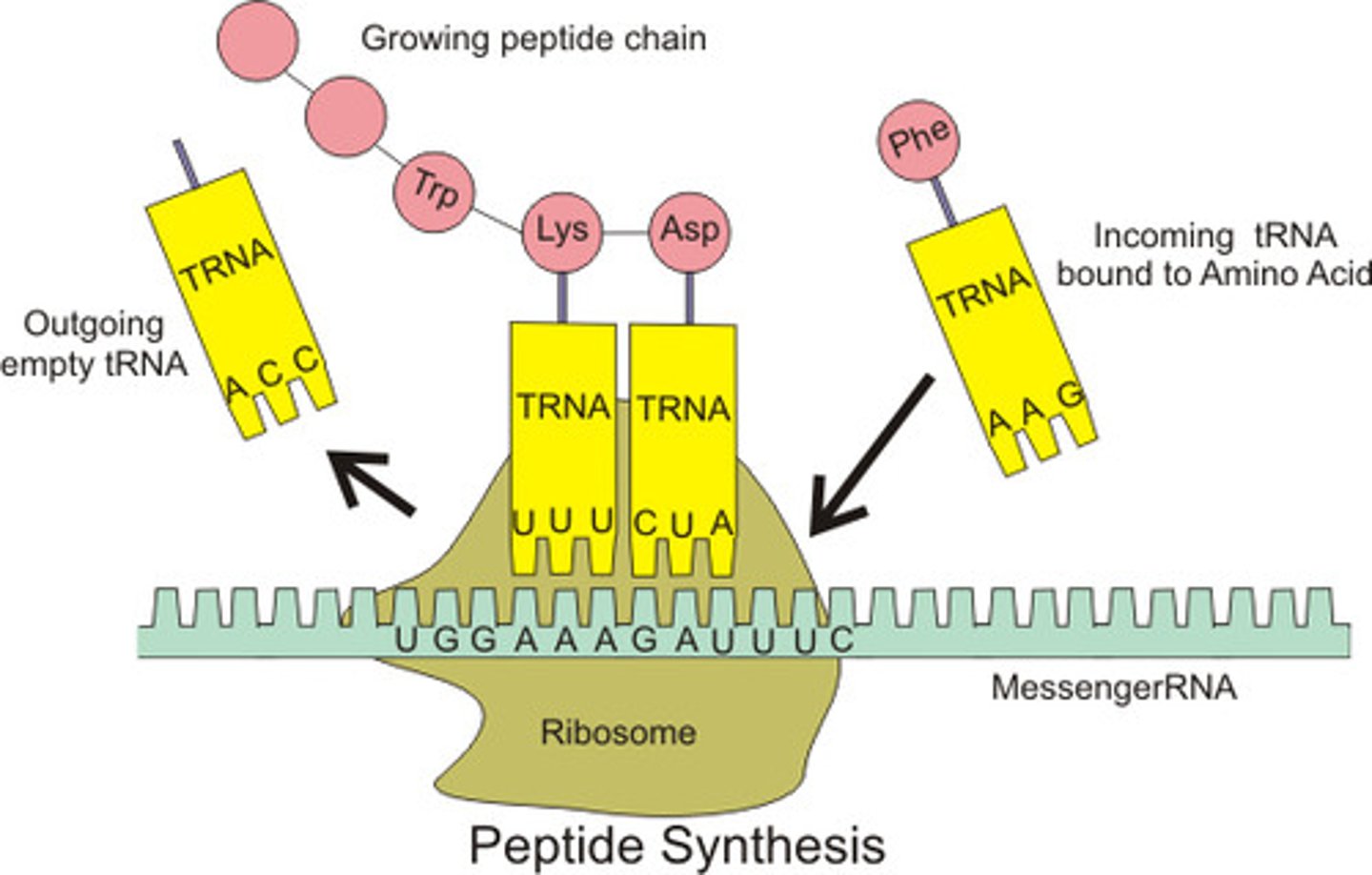
What does rRNA do?
site where protein synthesis occurs in ribosomes
What are building blocks of protein?
amino acids
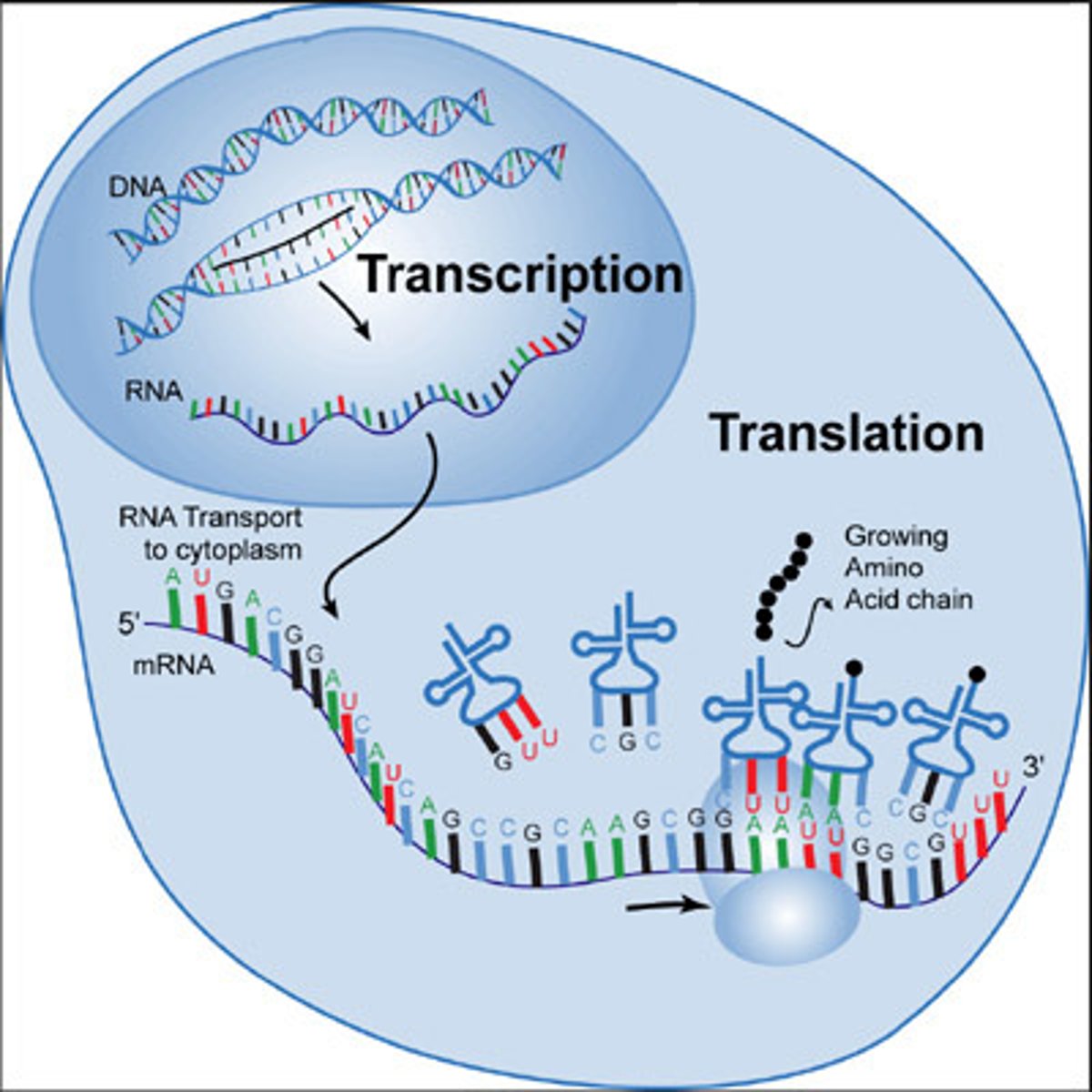
What is the process of transcription?
the process of RNA copying DNA to make codons
Where does transcription take place?
in the nucleus
What is a codon?
3 nitrogen bases paired together
What is the process of translation?
process that reads the message carried on the mRNA to assemble amino acids
Where does translation take place?
in ribosomes
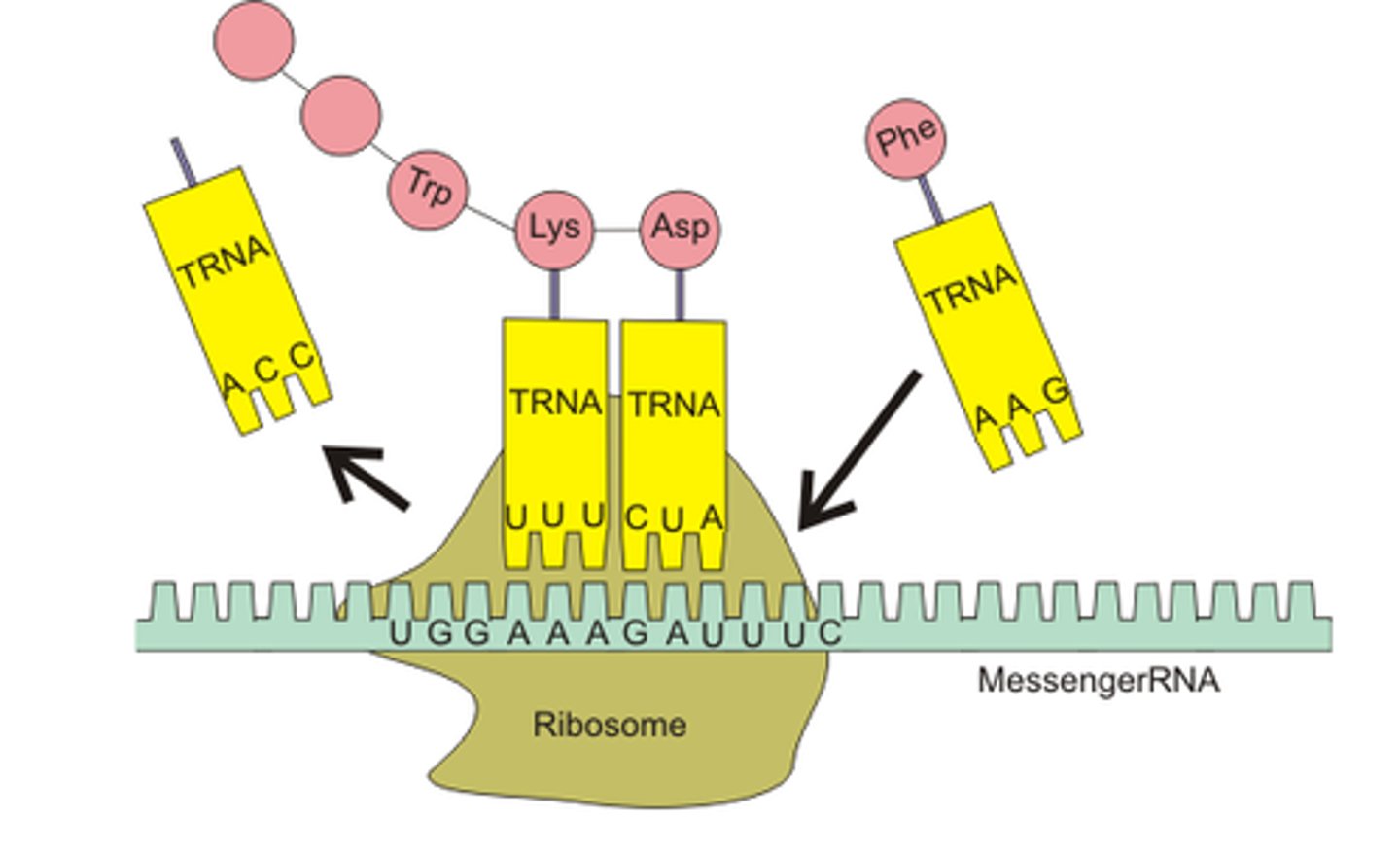
How many bases are in 1 codon?
3
How many amino acids are there?
22
How many amino acids do our bodies make?
2
Codon "AUG" is what type of codon?
initiation codon
Codons "UAA, UAG, and UGA" are what types of codons?
stop codons
What is a protein made up of amino acids?
hemoglobin
When did Watson and Crick discover the construction and communication of DNA?
1953
What prize did Watson and Crick win for discovering the construction and communication of DNA?
Nobel Peace Prize
How often do mistakes in the DNA code occur?
rarely
What is a mutation?
permanent change in a cell's DNA
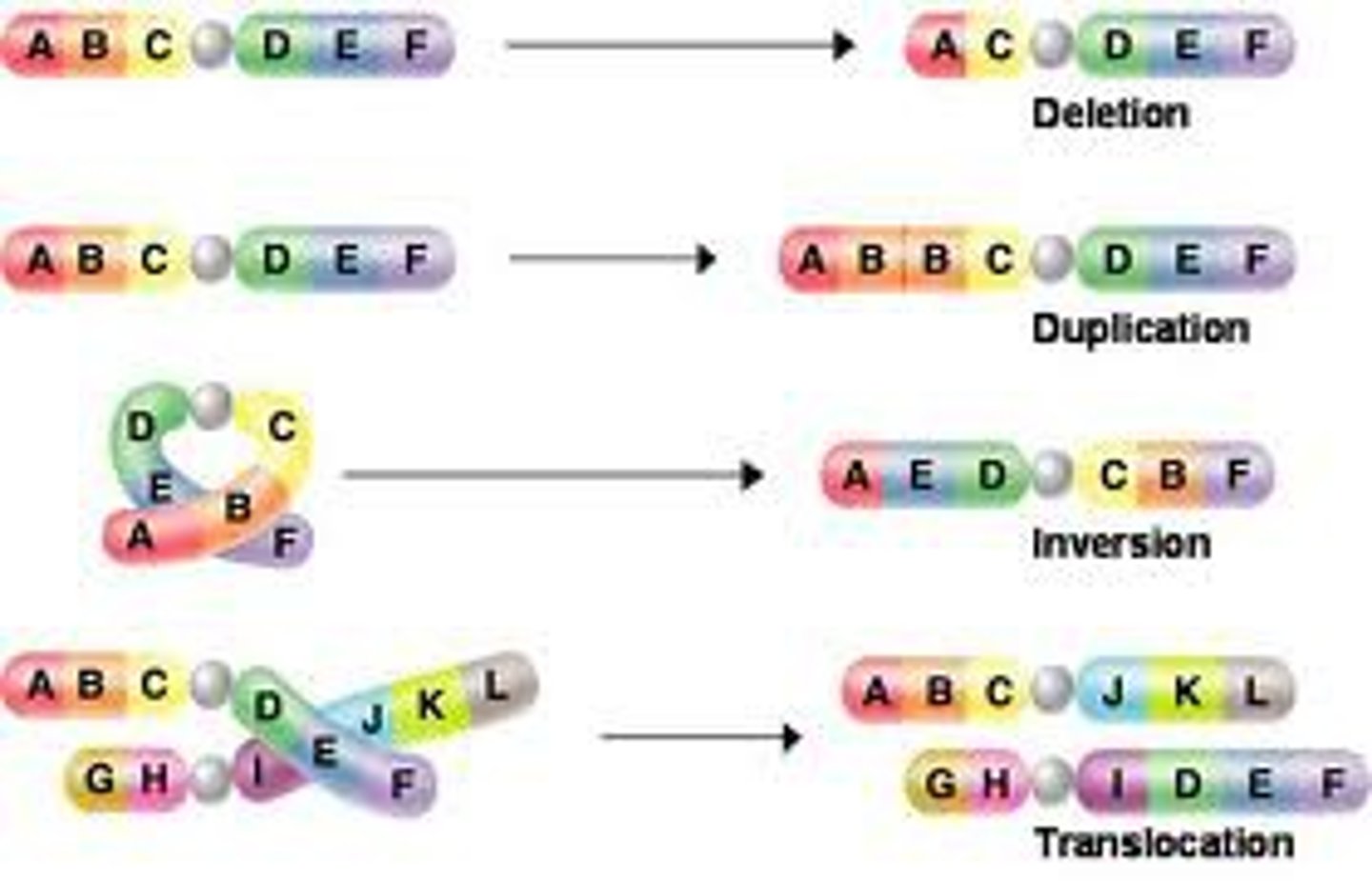
What can happen if your DNA code has a point mutation ?
a chemical change in 1 base pair and can cause a genetic disorder
What is a point mutation?
a chemical change in one base
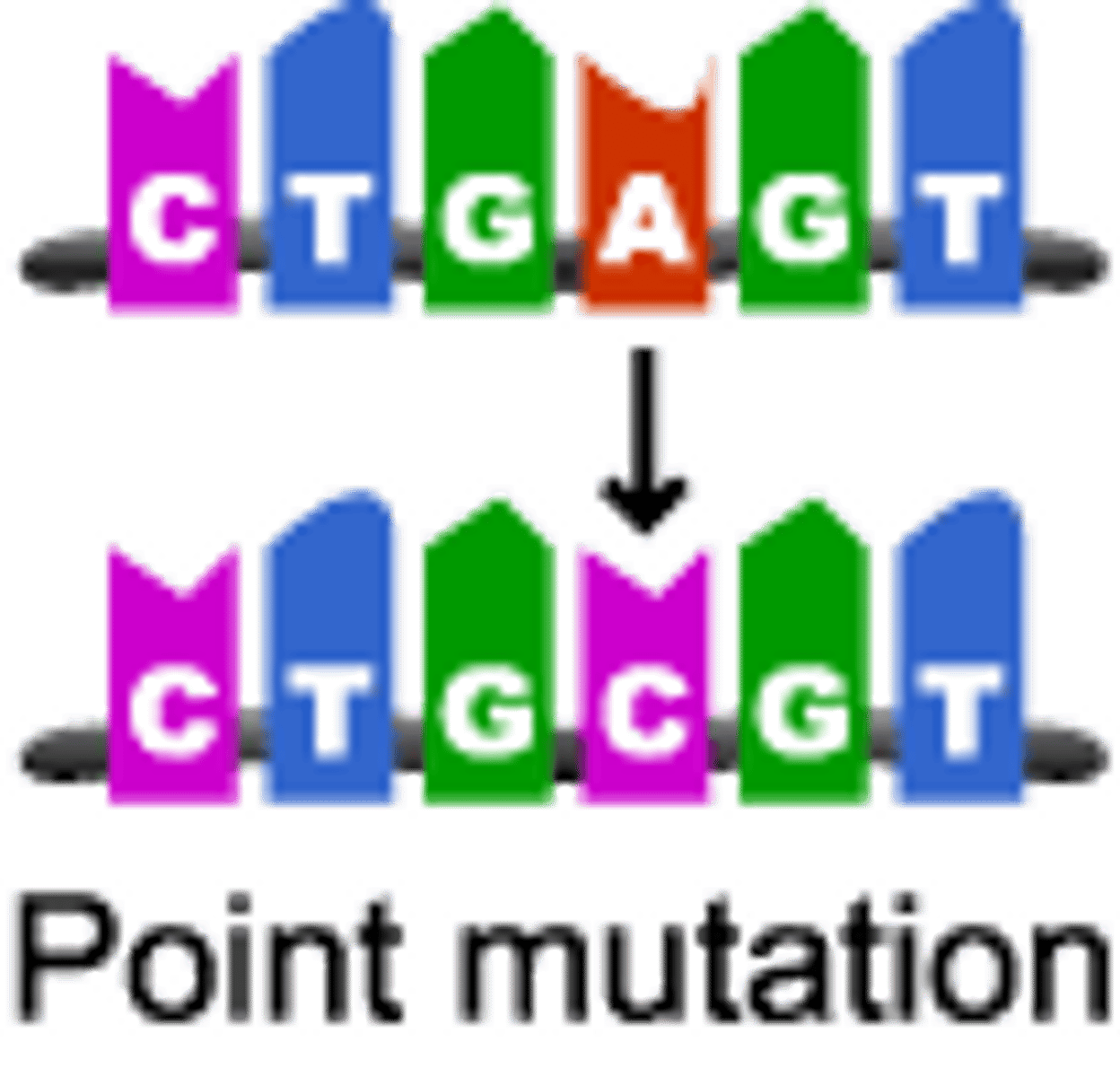
What is a substitution?
one base is exchanged for another in point mutations

What is the problem with point mutations?
this could make a completely different protein than needed
What are 2 more types of mutations that have to deal with frameshift mutations?
insertions and deletions
What is a frameshift mutation?
involves the gain or loss of a nucleotide in the DNA sequence
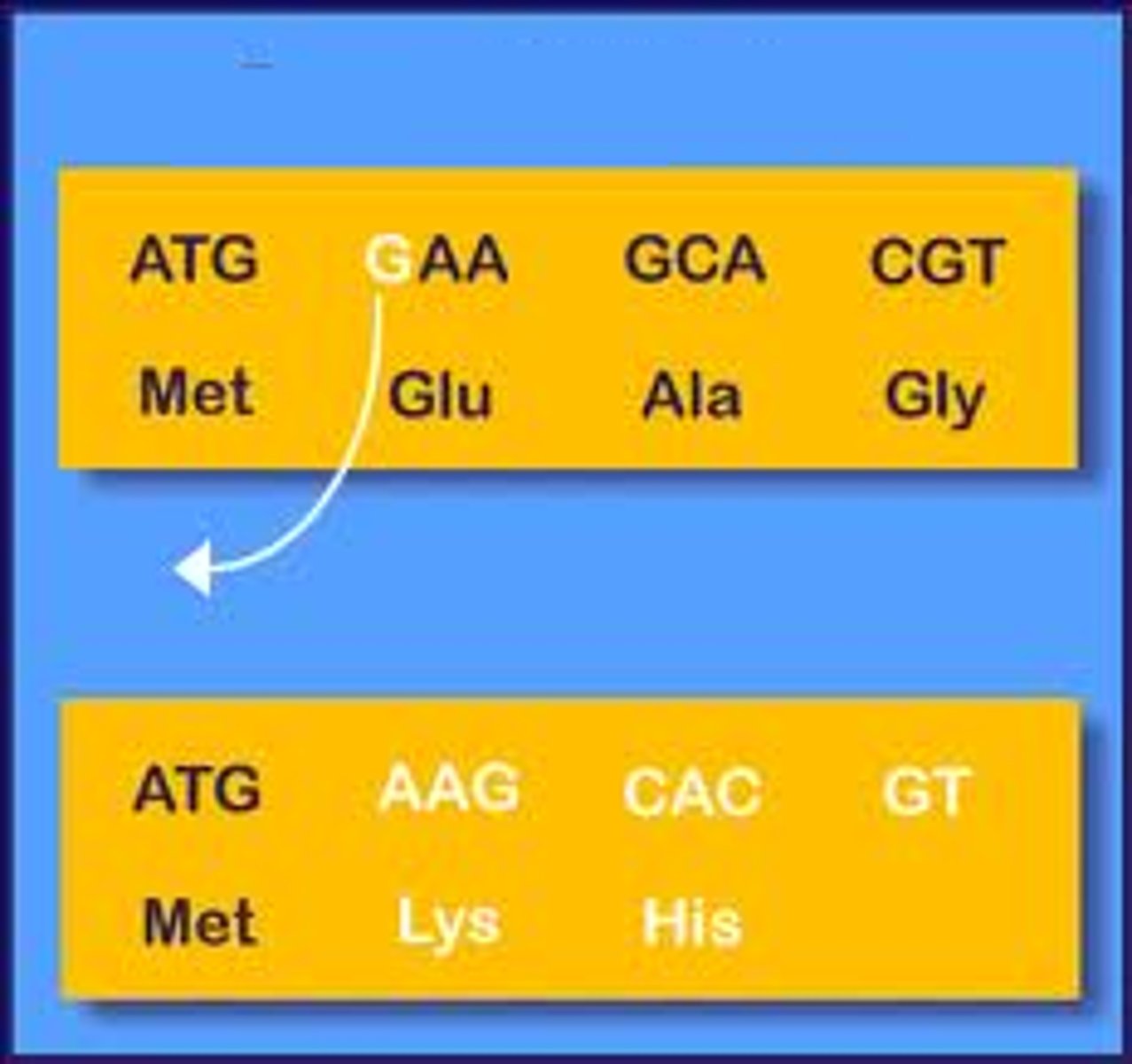
What is the gain of a nucleotide called in frameshift mutation?
insertion
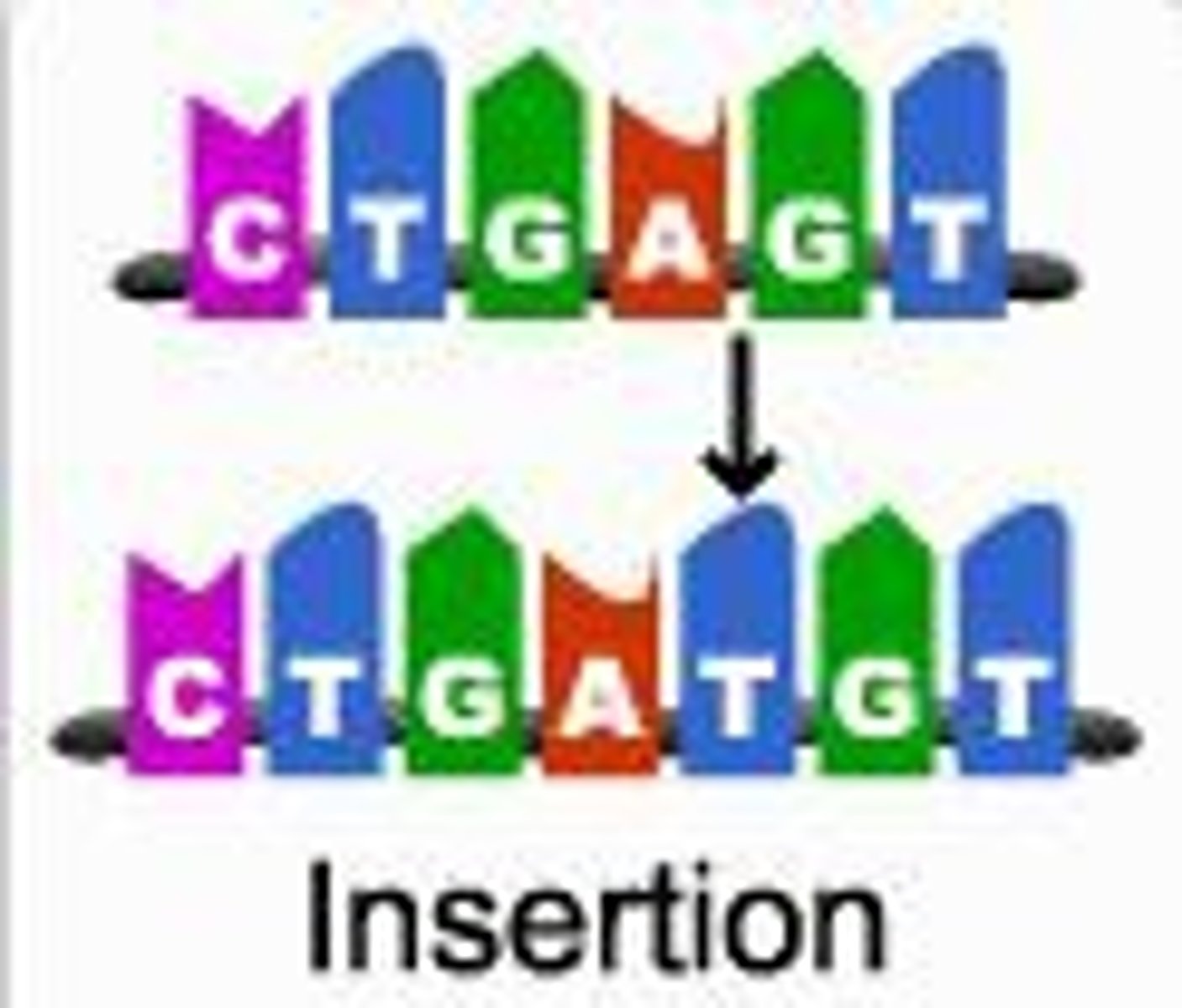
What is the loss of a nucleotide called in frameshift mutation?
deletion

What is the problem with frameshift mutations?
the entire DNA strand's code is changed, and produces different proteins
What are the 2 types of mutations?
point mutations and frameshift mutations
How is cystic fibrosis characterized?
abnormally thick mucus filled lungs, intestines, and pancreas
What are the 3 causes of mutations?
insertions and deletions/change in a base, certain chemicals that change the structure of the bases, radiation
What are the 3 BIG processes?
replication, transcription, translation
How many bases does one person have?
3 million
What percentage of our DNA is identical to cauliflower?
50%
What percentage of our DNA is identical to each other?
99%
What percentage of our DNA makes us different from everyone else?
1%
What percentage of our DNA is identical to primates?
95%
How many types of nitrogen bases are there?
4
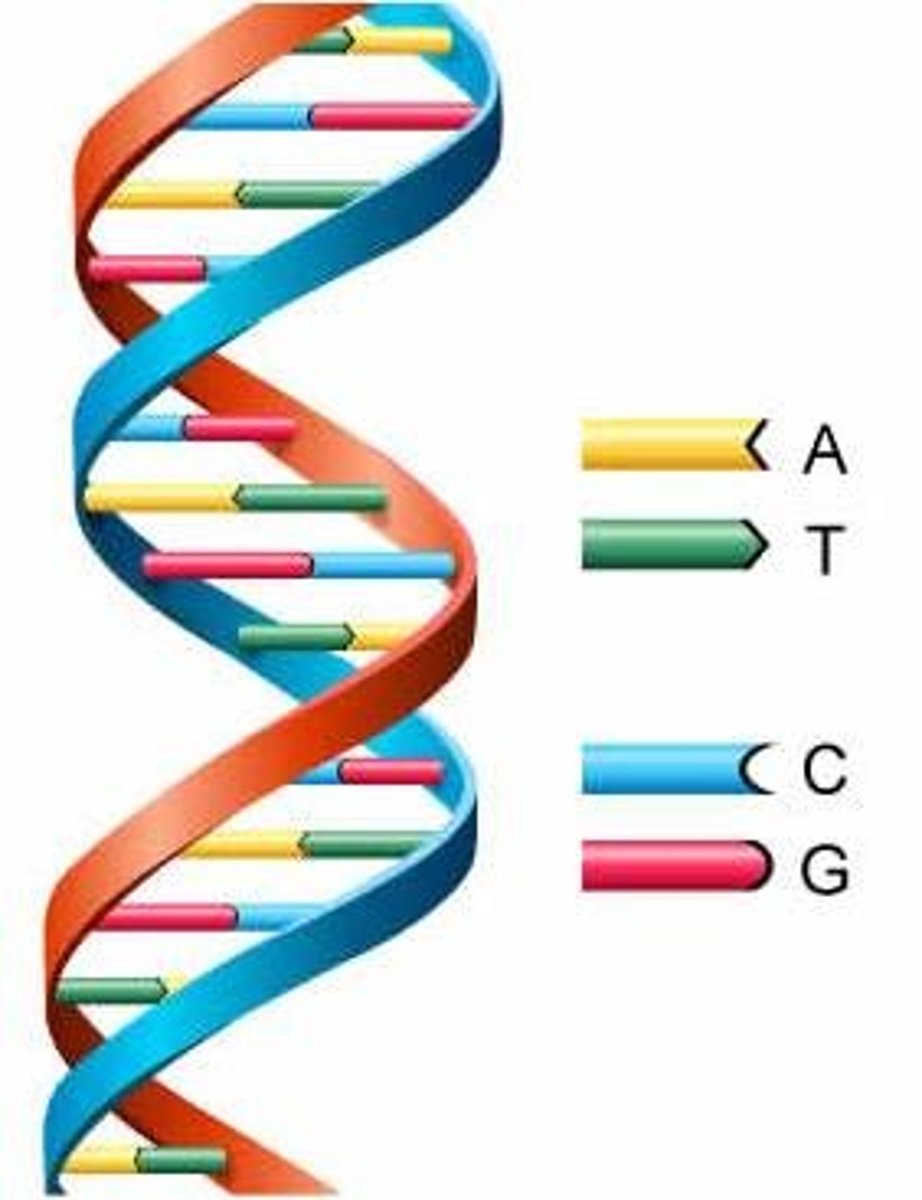
What are the names of the nitrogen bases?
adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine
What are the sides of the DNA ladder made of?
phosphates and sugars
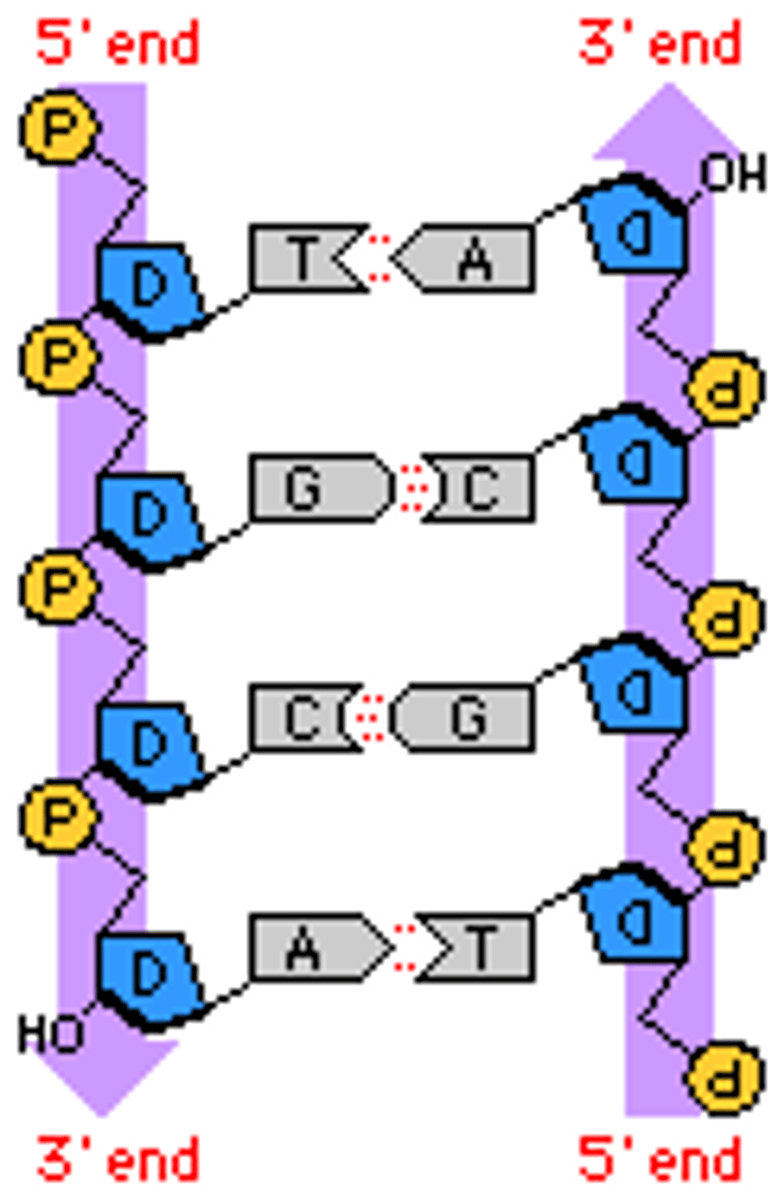
What are the steps of the DNA ladder made of?
nitrogen base pairs
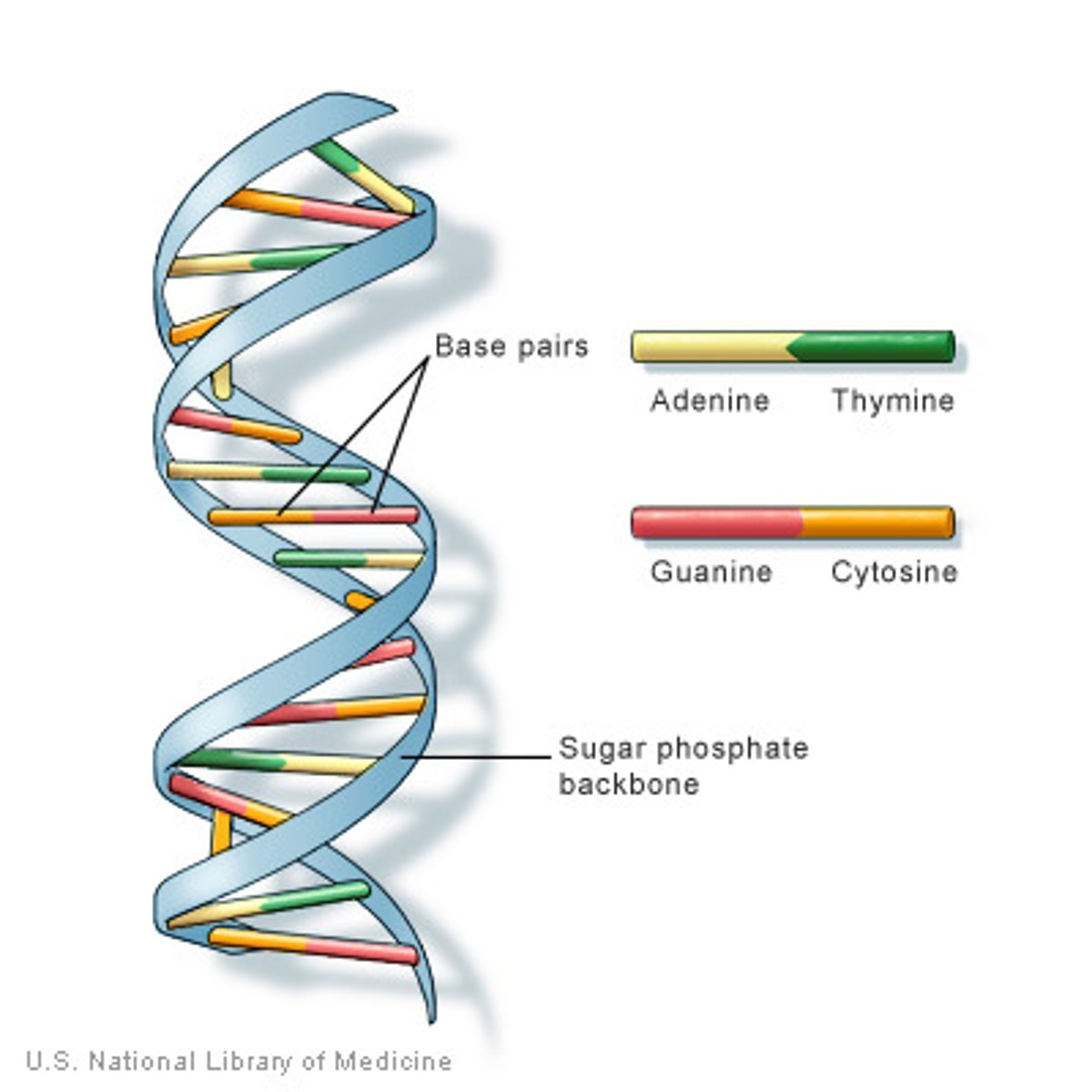
What kinds of bonds hold the nitrogen bases together?
weak hydrogen bonds
TRUE OR FALSE
The process of DNA replication results in a copy of the original strand of DNA
true
TRUE OR FALSE
The final result of DNA replication is two copies of the original DNA strand
true
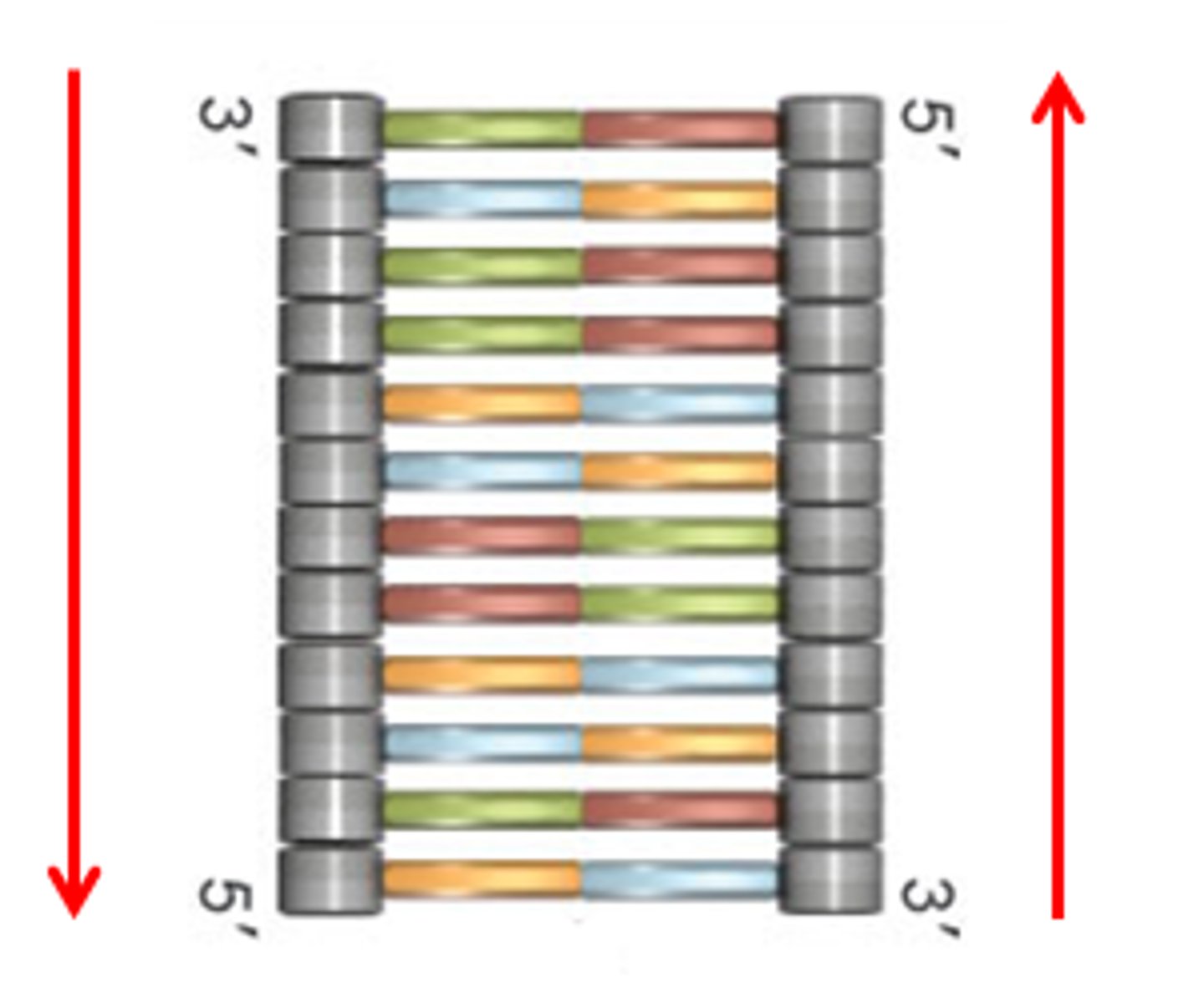
What does it mean that DNA is antiparallel?
one end of a strand is 3' and the other being 5'. the other strand being 5' at one end and 3' at the other end
What are the 3 characteristics of DNA?
genetic code, includes 4 nitrogen bases, sides of ladder made of phosphates and sugars
Why is the sequence of nucleotides so important?
it determines the proteins being made
What are the 4 steps in DNA replication?
DNA starts to unzip, mRNA comes in and pairs the nitrogen bases, the 2 sides join together, 2 identical DNA strands are produced
Is it possible that mutations can be repaired?
yes
Why is it harder to fix mutations?
it is newer technology and it's really expensive
TRUE OR FALSE:
Cancer is a type of mutation due to uncontrolled cell growth
true
What type of mutation is this? 2 ANSWERS
AUG|CAA|AAG|UAG
AUC|AAA|AGU|AG?
frameshift mutation or deletion
What type of mutation is this?
AUG|CAA|AAG|UAG
AUG|CAG|AAG|UAG
substitution
What type of mutation is this? 2 ANSWERS
AUG|CAA|AAG|UAG
AUG|CCA|AAA|GUA|G??
frameshift mutation or insertion
Central Dogma
refers to all living organisms. It states that DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. Hershey and Chase discovered that the genetic material is found in DNA, not protein.