Equigua Lab Midterm Review
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
the process of gradual change in a population or species over time
a process that results in changes in the genetic material in a population over time. Reflects the adaptations of organisms to their changing environment and can result in altered genes and noble traits in new species.
Define evolution
gene pool
all the alleles that the individuals in the population carry
the total number of allele frequency
to be able to adapt, survive, and reproduce
what does ‘fitness’ mean?
Taxa
the hierarchical divisions of a species from Kingdom to subspecies
domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
Order of taxa in decreasing inclusiveness
taxonomy
the science of classifying organisms to construct internationally shared classification systems with each organism placed into increasingly more inclusive groupings.
the study of relationships between living organisms & the classification of organisms into groups based upon those hypothesized relationships.
based on similarities and differences
how you can determine how organisms belong to what taxa?
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
states that a population’s allele and genotype frequencies are inherently stable— unless some kind of evolutionary force is acting upon the population, neither the allele nor the genotypic frequencies would change. Assumes conditions with NO mutations, migration, emigration, or selective pressure for or against genotype, plus an infinite population.
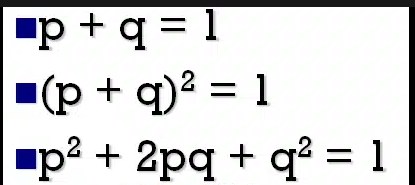
Hardy Weinburg Equations
p = dominant allele
q = recessive allele
p² = homozygous dominant
2pq = heterozygous
q² = homozygous recessive
Speciation
the formation of two species from one original species
the formation of a new and distinct species in evolution
events that lead to speciation
For speciation to occur, two new populations must form from one original population and they must evolve in such a way that it becomes impossible for individuals from the two new populations to interbreed. Biologists have proposed mechanisms by which this could occur that fall into two broad categories. Allopatric speciation (allo- = "other"; -patric = "homeland") involves geographic separation of populations from a parent species and subsequent evolution. Sympatric speciation (sym- = "same"; -patric = "homeland") involves speciation occurring within a parent species remaining in one location.
Situation that occurs when a species is reproductively independent from other species; behavior, location, or reproductive barriers may cause this to happen. Ex: Given enough time, the genetic and phenotypic divergence between populations will affect characters that influence reproduction: if individuals of the two populations were brought together, mating would be less likely, but if mating occurred, offspring would be nonviable or infertile. Many types of diverging characters may affect the reproductive isolation, the ability to interbreed, of the two populations.
Ex: Grasshopper lives in muddy area vs grasshopper living in grass area: both have different breeding schedules and are from different environments
What does it mean when organisms are in reproductive isolation?
A prezygotic barrier
a mechanism that blocks reproduction from taking place. This includes barriers that prevent fertilization when organisms attempt reproduction.
A postzygotic barrier
occurs after zygote formation. This includes organisms that don’t survive the embryonic stage and those that are born sterile.
behavioral isolation
reproduction is affected when there is an absence of specific behavior or if the behavior is not recognized
Ex: Two birds breed and a chick is hatched; however, it does not know how to perform the mating ritual. Eggs never fully develop
geographical isolation
the physical separation of species
Ex: A road is built in the middle of a wetland. Fish on one side of the road are not able to meet fish of the same species on the other side.
mechanical isolation
prevents reproduction because there is an incompatibility of reproductive organs between the 2 organisms. It is a physical barrier.
Ex: 2 insects are not able to mate due to differences in their exoskeletons
ecological/habitat isolation
reproduction is affected because the species population moves to another area. Reproduction with parent species no longer occurs.
temporal isolation
organisms breed at different times during the year (“breeding schedule”)
Ex: 2 species of tree have compatible pollen. One releases pollen in early Spring, the other in late Summer. Pollen is viable for 1 week.
Allopatric speciation
involves geographic separation of populations from a parent species and subsequent evolution
Sympatric speciation
speciation that occurs in the same geographic space
We grouped the lizards based on their analogous and homologous structures.
In the speciation lab, how did you group the lizards? What features did you use to sort out the lizards?
Describe two adaptations of the Anolis lizards and describe in detail how these features are adaptations for Anolis lizards specifically.What were the results of that experiment?
Two adaptations of the Anolis lizards are coloration and toe pads. Coloration allows Anolis lizards to switch to a variety of colors to camouflage & avoid predation. The toe pads on the other hand, are sticky which allows them to climb surfaces and escape predators or find food.
The results were based on a data table which revealed their tail length, body length and leg length.
Review the structure of prokaryotes and be able to list features unique to prokaryotes
flagella: for locomotion
pili: hairlike structures that allows them to attach & transfer DNA
cell wall: encapsulates & protects the prokaryotic cell
Know important roles that prokaryotes play
Prokaryotes: some bacteria are beneficial to humans such as those found in the stomach and intestines. They are probiotics and aid in digestion. Other bacteria are beneficial to plants because they contribute to the nitrogen fixation cycle.
Know the different forms of bacterial cells
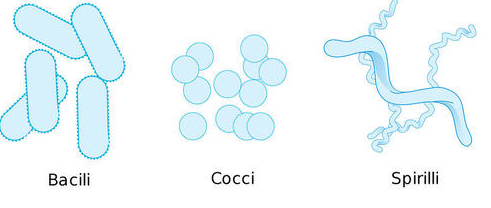
Morphological Species Concept
a concept that relies on structural features and emphasizes groups of physical traits that are unique to each species.
Phylogenetic/evolutionary Species concept
how closely related individuals are evolutionary. They possess certain defining or derived traits.
a concept that defines species as the most irreducible group of individuals that share a common ancestor.
Biological Species Concept
the ability of 2 individuals to successfully reproduce viable, fertile offspring
states that a species is a group of actually or potentially interbreeding natural populations which are reproductively isolated from other such groups.
2 adaptations of Anolis lizards are coloration & toe pads. Specifically, speaking, coloration allows the Anolis lizards to switch to a variety of colors to camouflage and avoid predation. The toe pads on the other hand, are sticky which allows them to climb to surfaces and escape predators or find food.
Describe two adaptations of the Anolis lizards and describe in detail how these features are adaptations for Anolis lizards specifically.
Mechanism of evolution: mutations
a variation in the nucleotide sequence of a genome. A mutation occurs as a result of a deletion, duplication, inversion or translocation. They can change the way DNA is encoded. It could be deleterious or successful and give the organism an advantage thus reproducing and passing these traits onto their offspring.
Mechanism of evolution: gene flow
flow of alleles in & out of a population due to migration of individuals or gametes
Mechanism of evolution: genetic drift
effect of chance on a population’s gene pool
Ex: By chance, some individuals will have more offspring than others—not due to an advantage conferred by some genetically-encoded trait, but just because one male happened to be in the right place at the right time (when the receptive female walked by). It is more frequent in small population
Mechanism of evolution: Genetic drift: founder effect
event that initiates an allele frequency change in part of the population, which is not typical of the original population
Ex: a mexican travels to SK, marries a south korean, & have children
Mechanism of evolution: Genetic drift: bottleneck effect
a sudden event that results in the change of a population’s genome
Natural selection
reproduction of individuals with favorable genetic traits that survive environmental change because of those traits, leading to evolutionary change
Ex: tortoises with long necks were more common on dry lands than short necked tortoises. The long necked tortoises were selected because they could reach more leaves & access X2 food than short-neck tortoises. In times of drought, long necked tortoises had an advantage of obtaining food sources due to this trait. Eventually, long necked tortoises were reproductively successful & passed the long neck trait to their offspring. Over time, only long-necked tortoises were present in the population.