Period table quiz
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
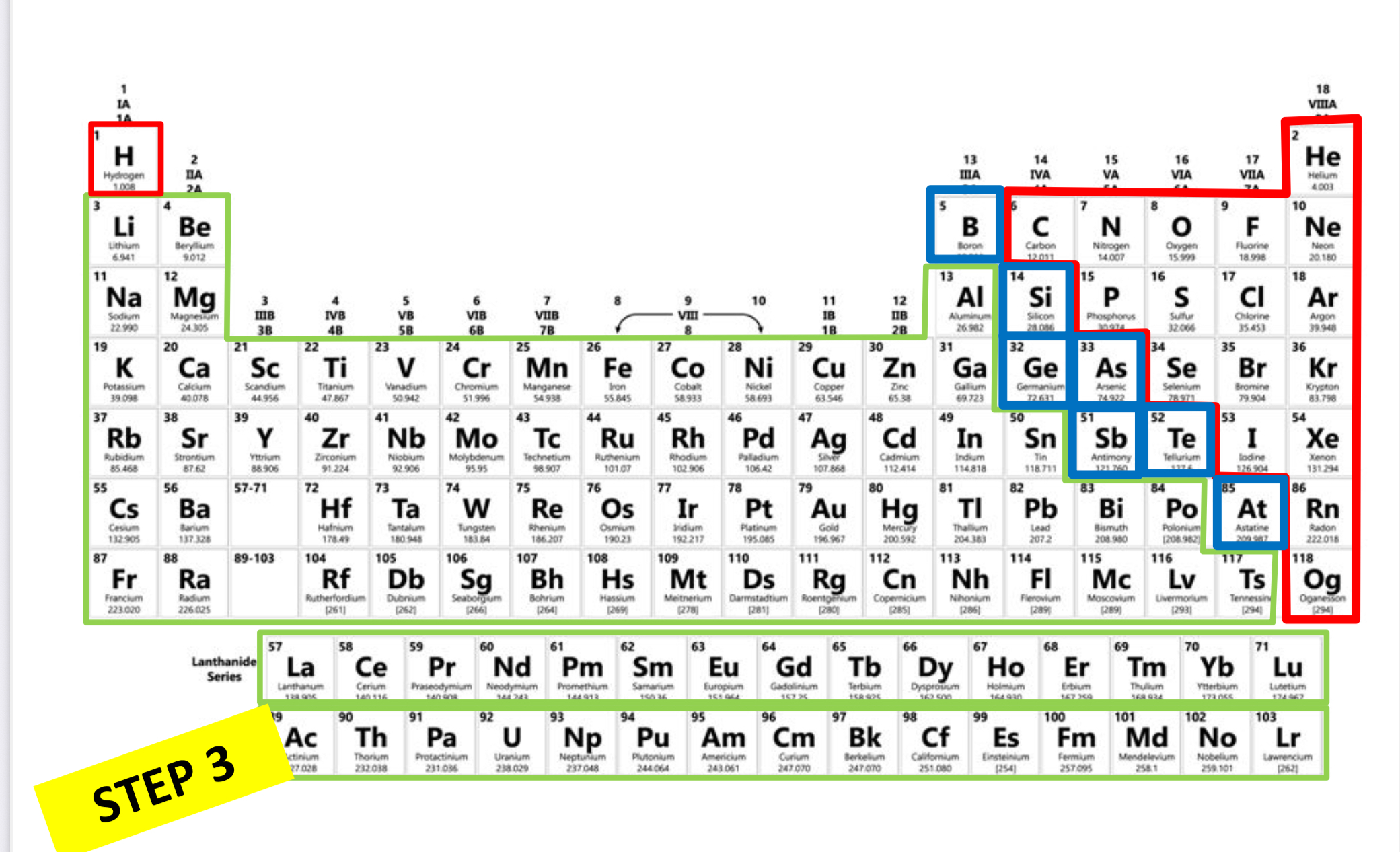
Which is metal?
Green
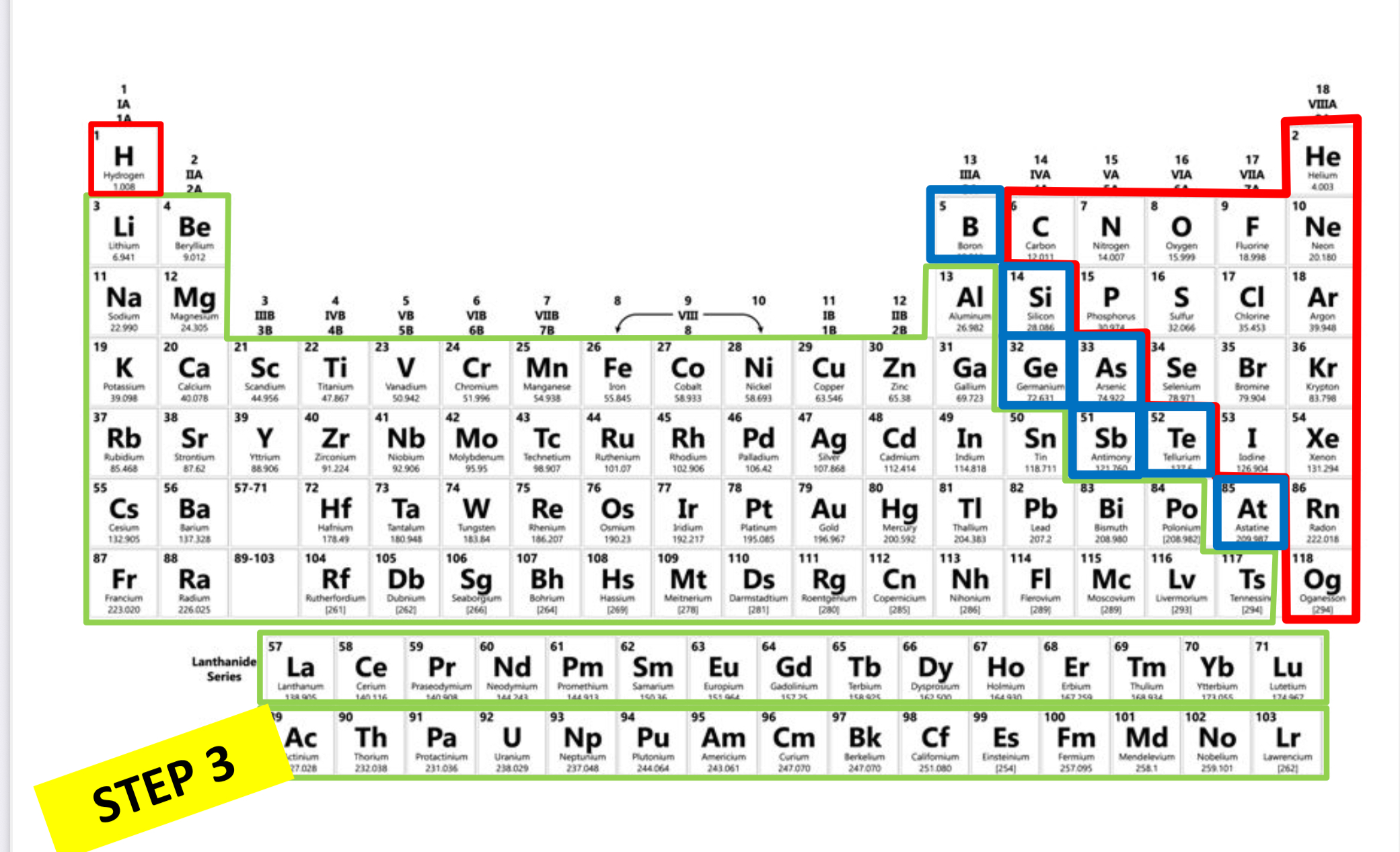
Which is nonmetal?
Red
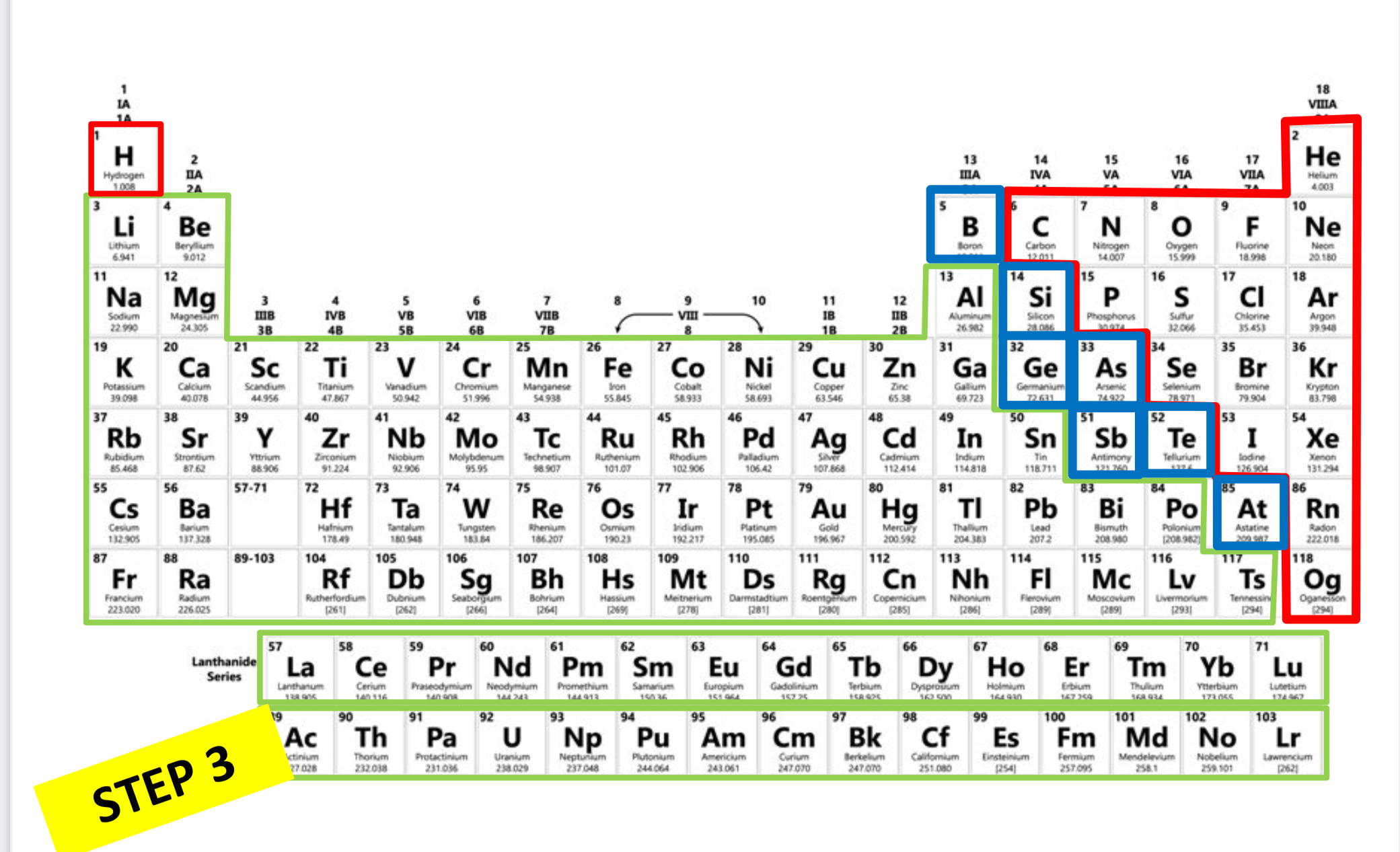
Which is metalloid?
Blue
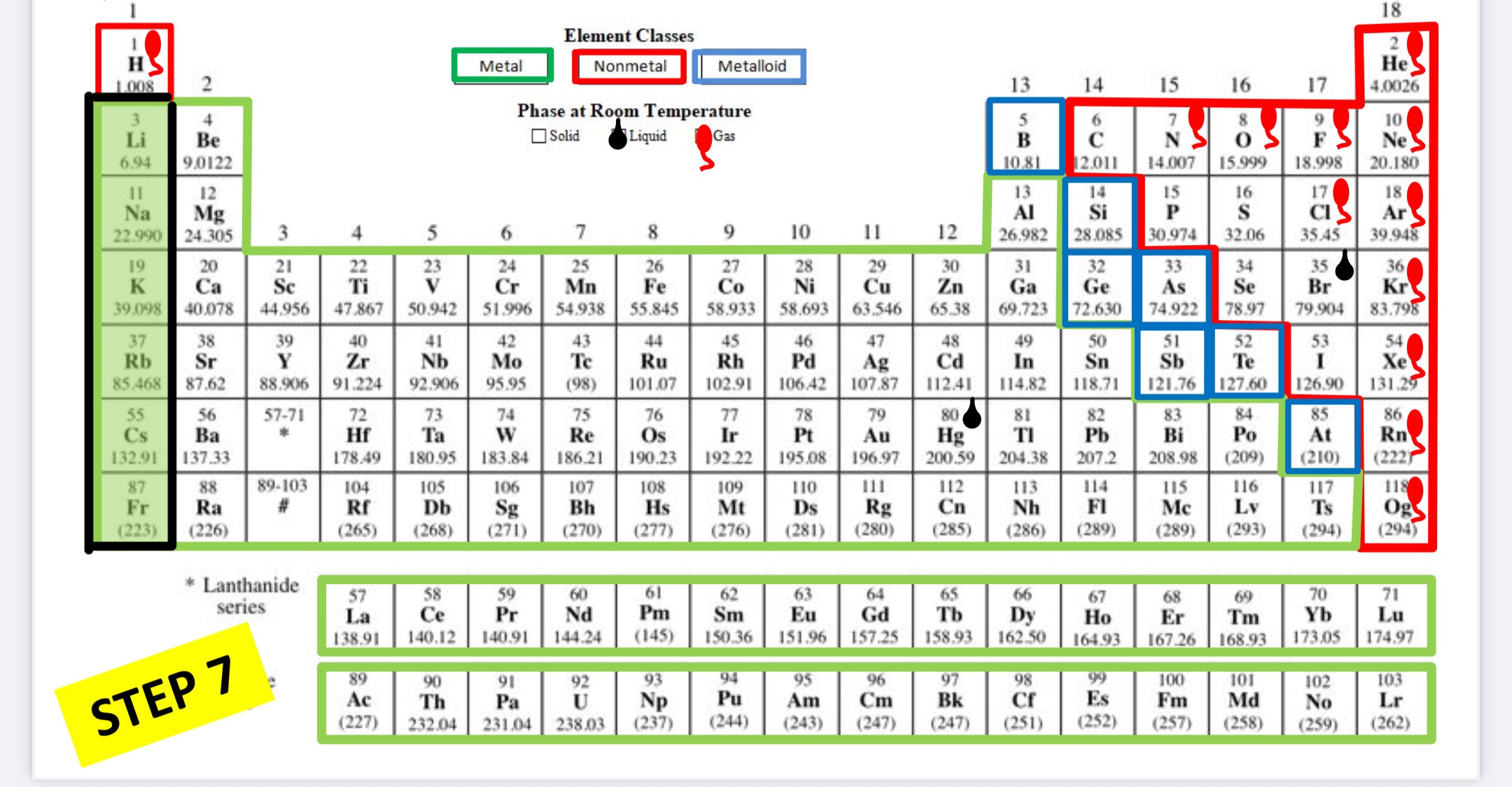
What family is this?
Alkali metals
What family is this?
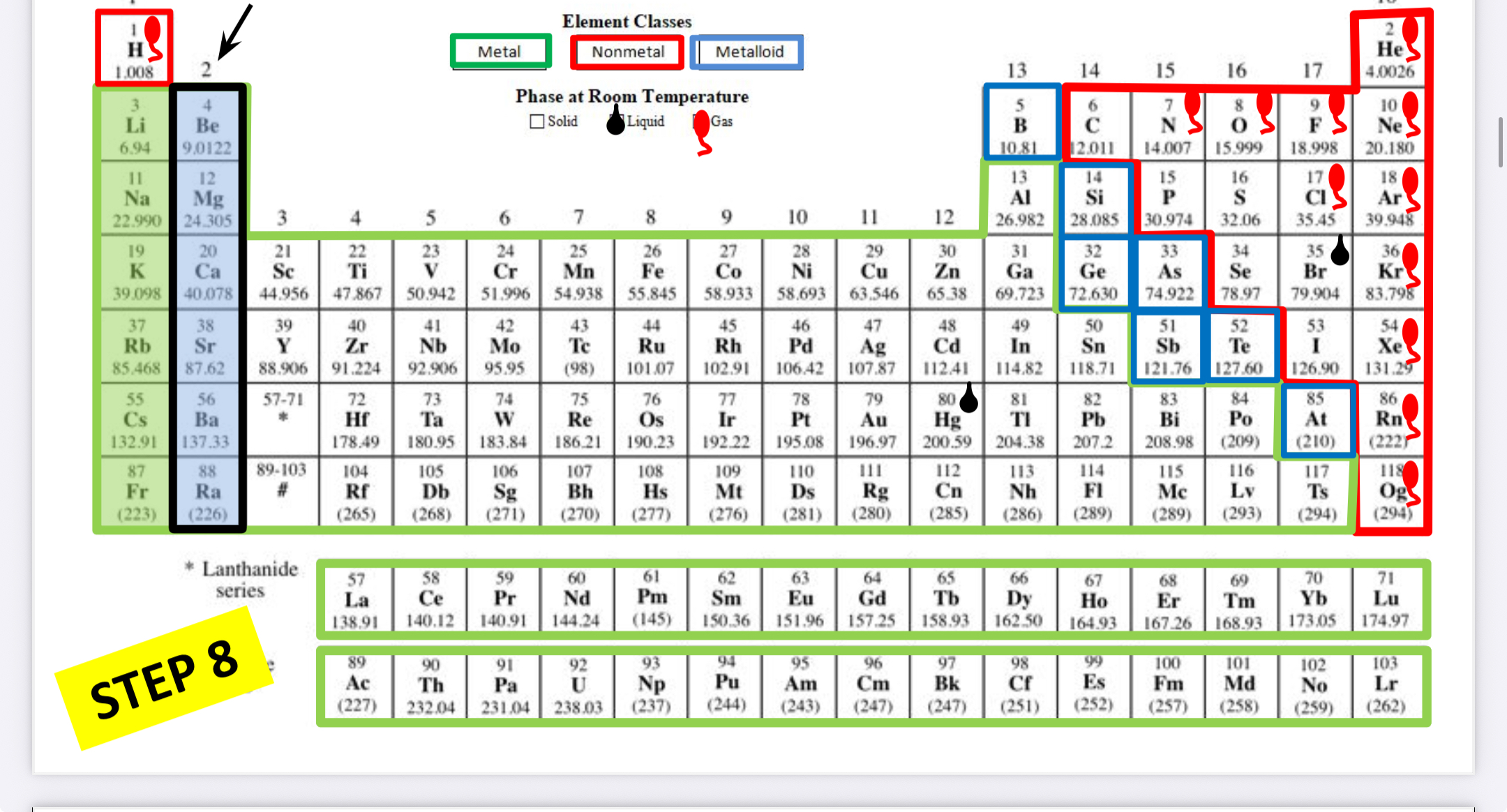
Alkaline earth metals
What family is this?
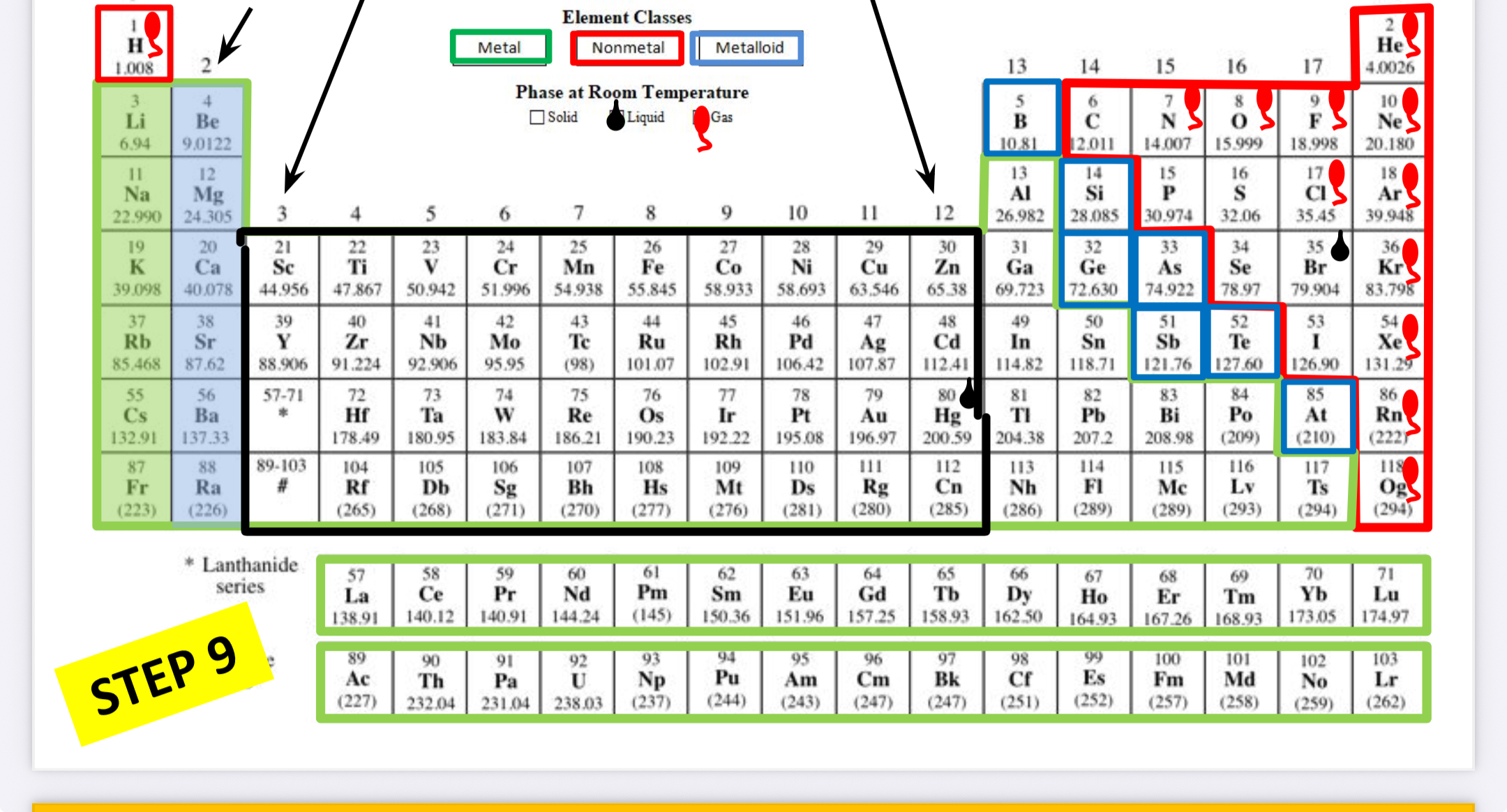
Transition metals (group 3-12)
What family is this?
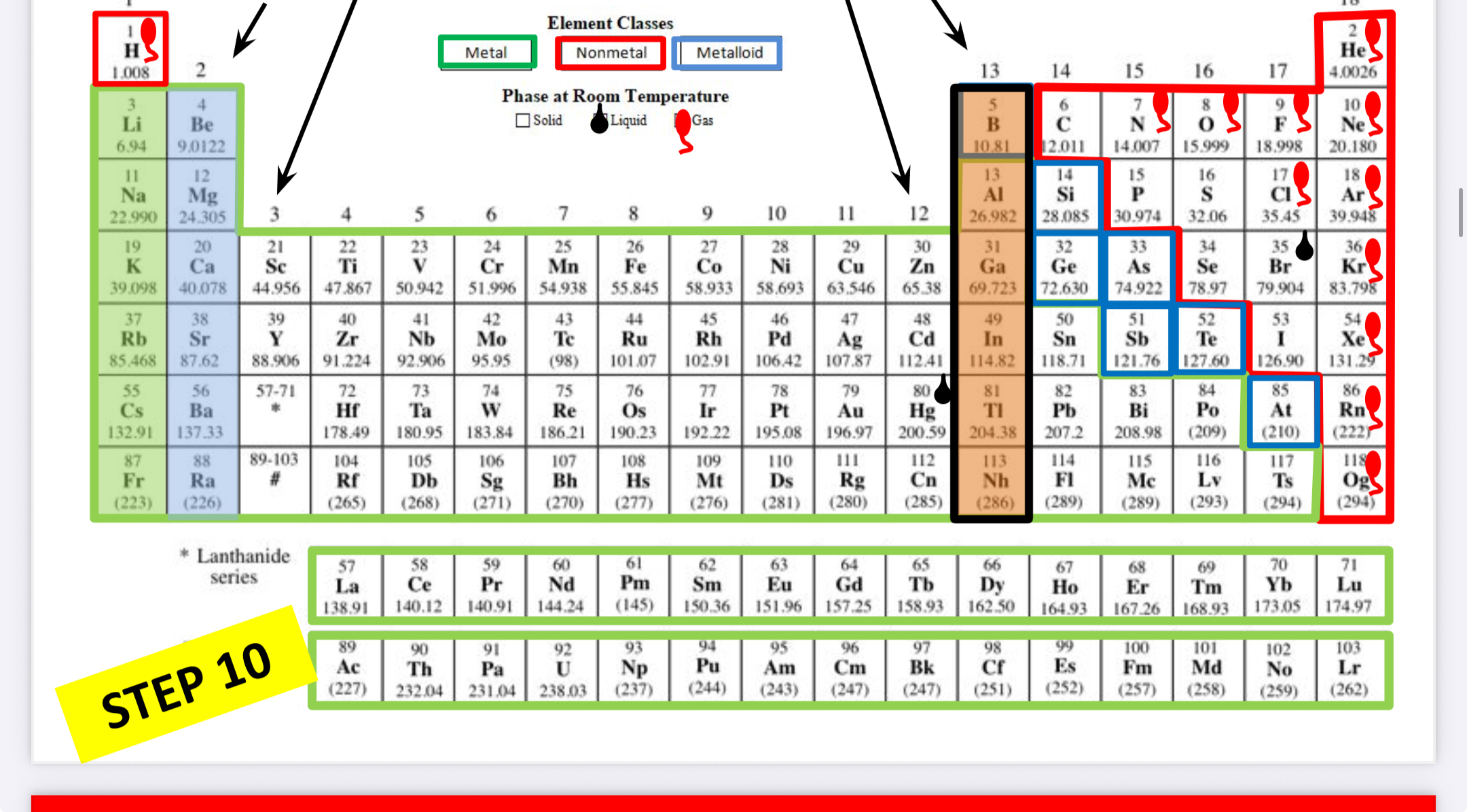
Boron family
What family is this?
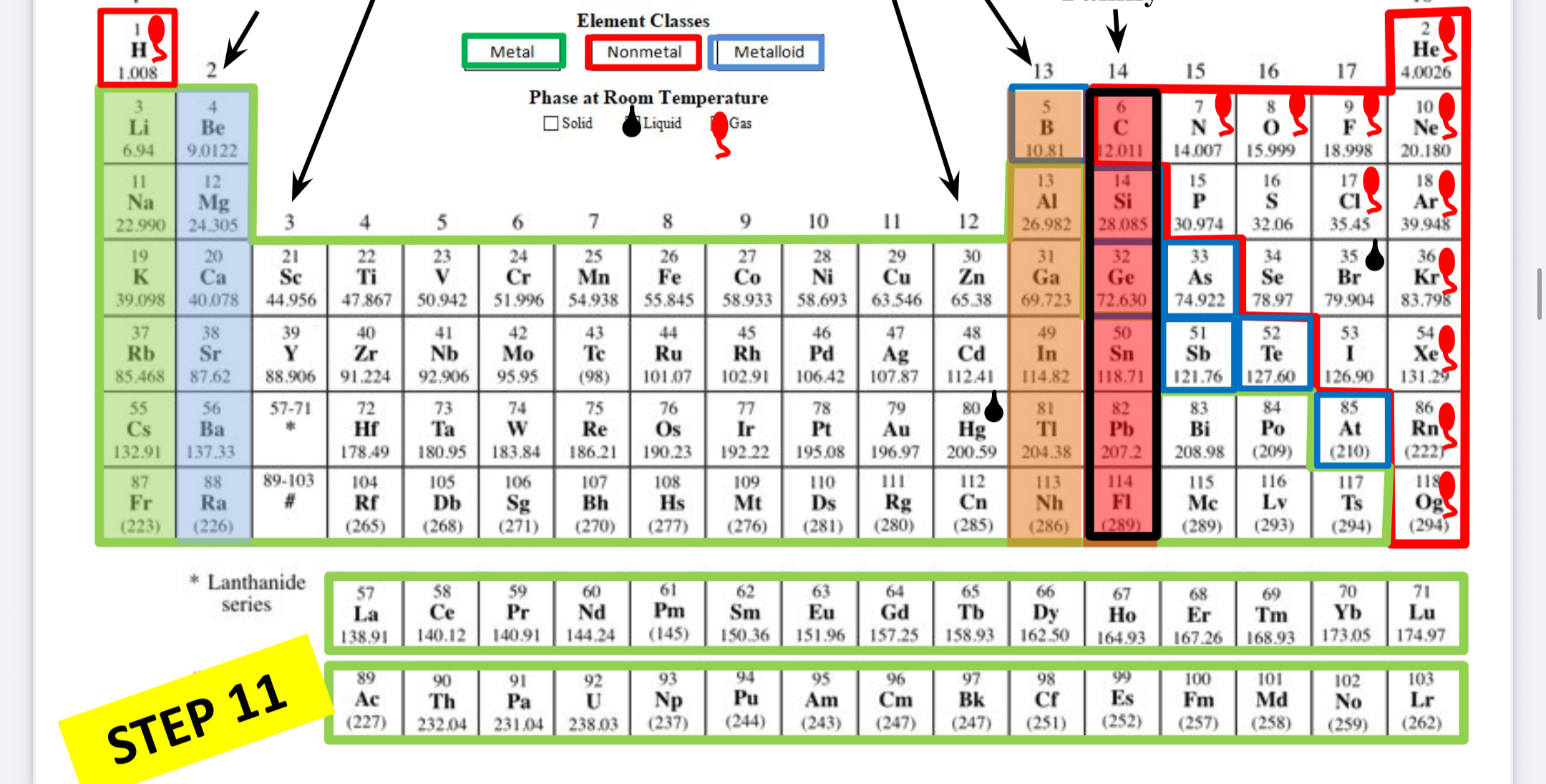
Carbon family
What family is this?
Nitrogen family
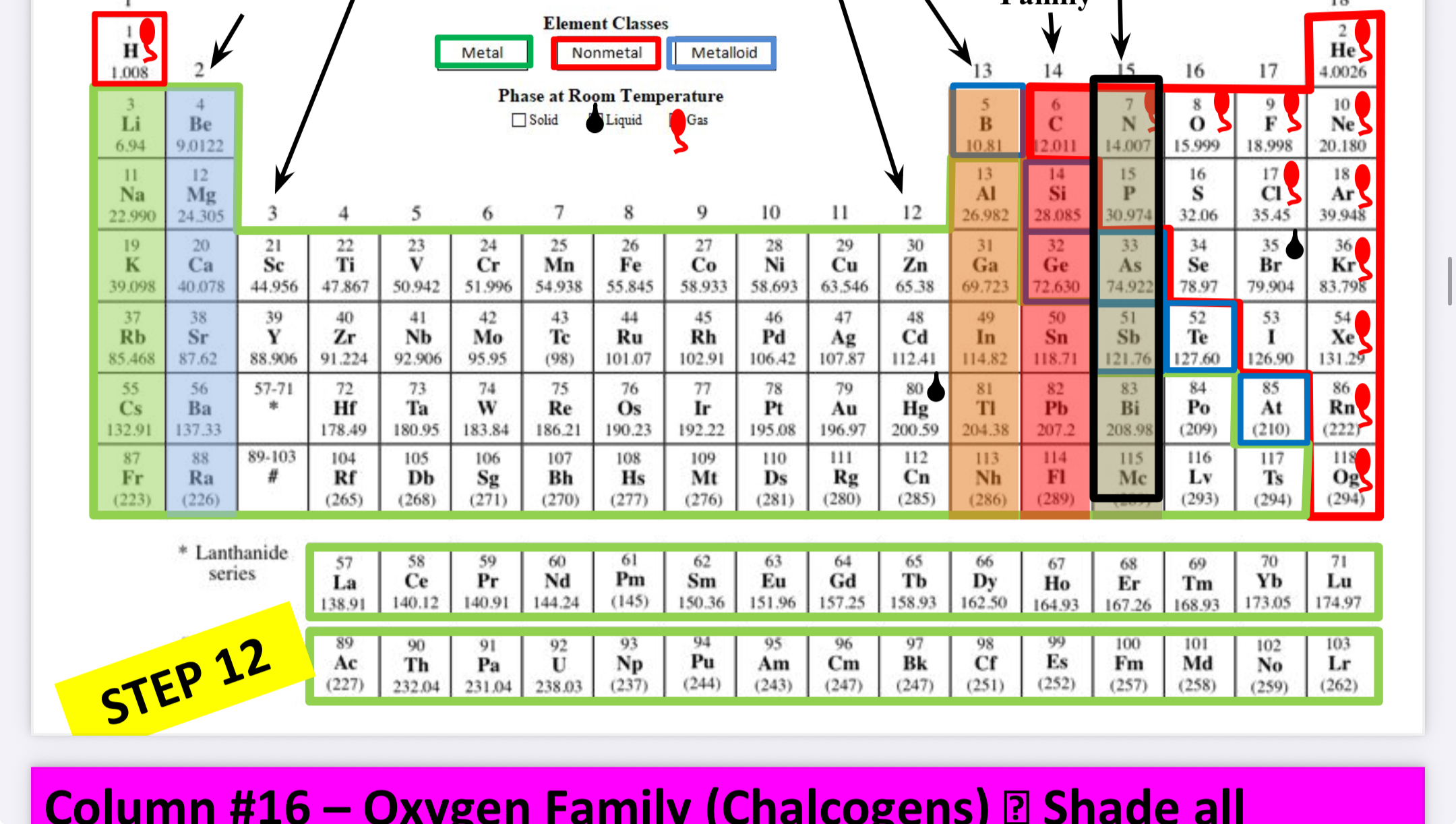
What family is this?
Oxygen family (chalogens)
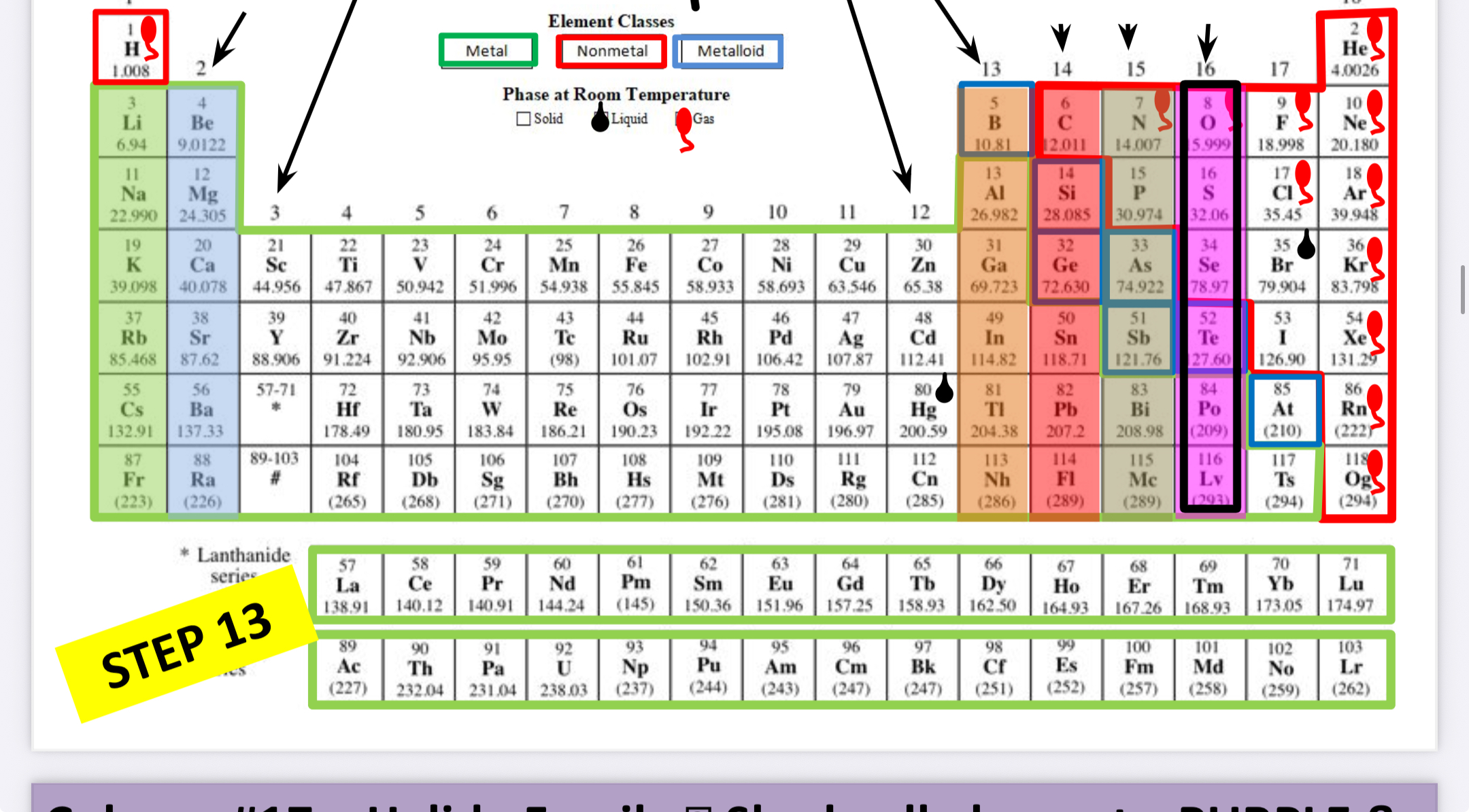
What family is this?
Halogens (Halides)
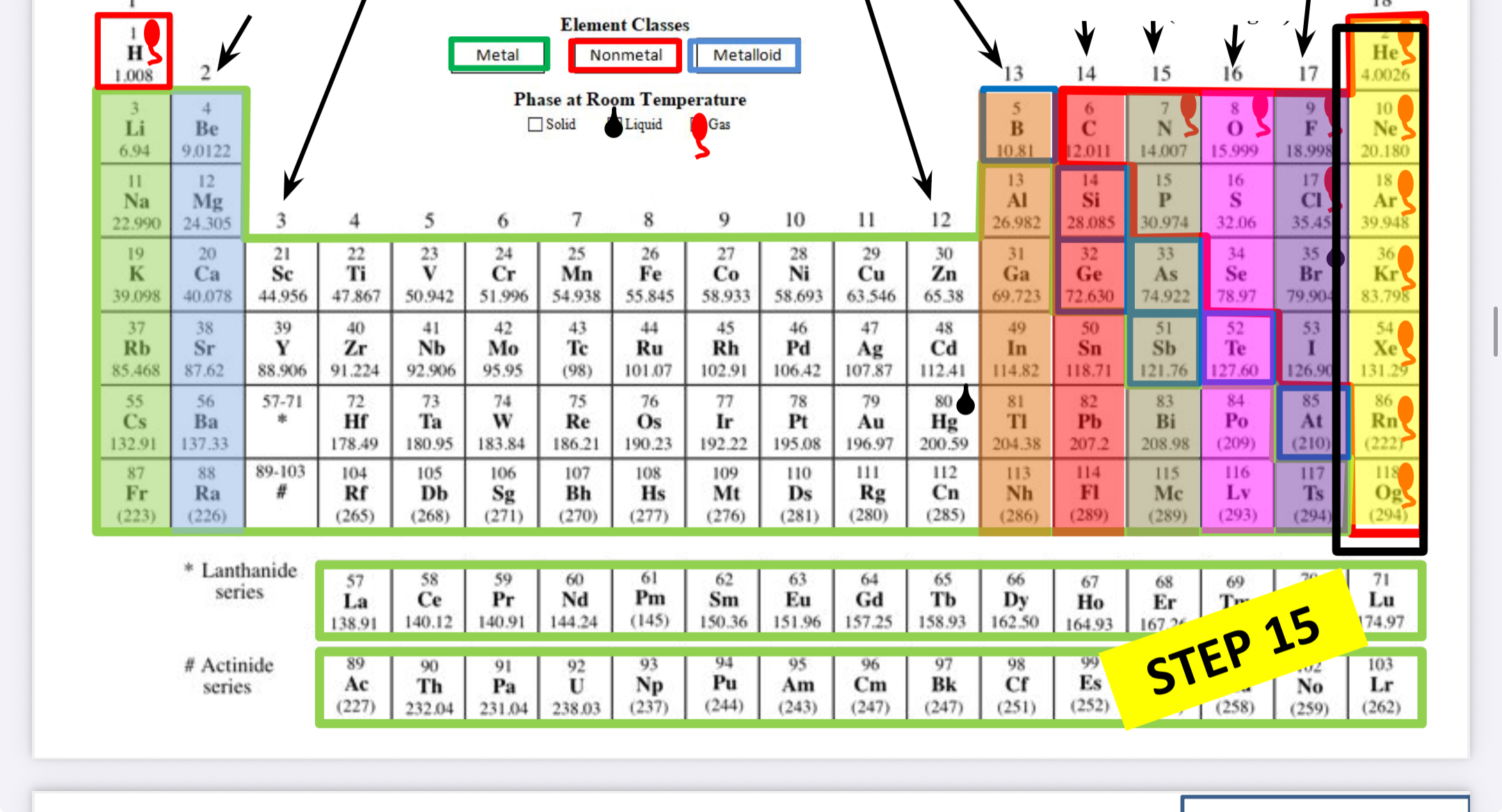
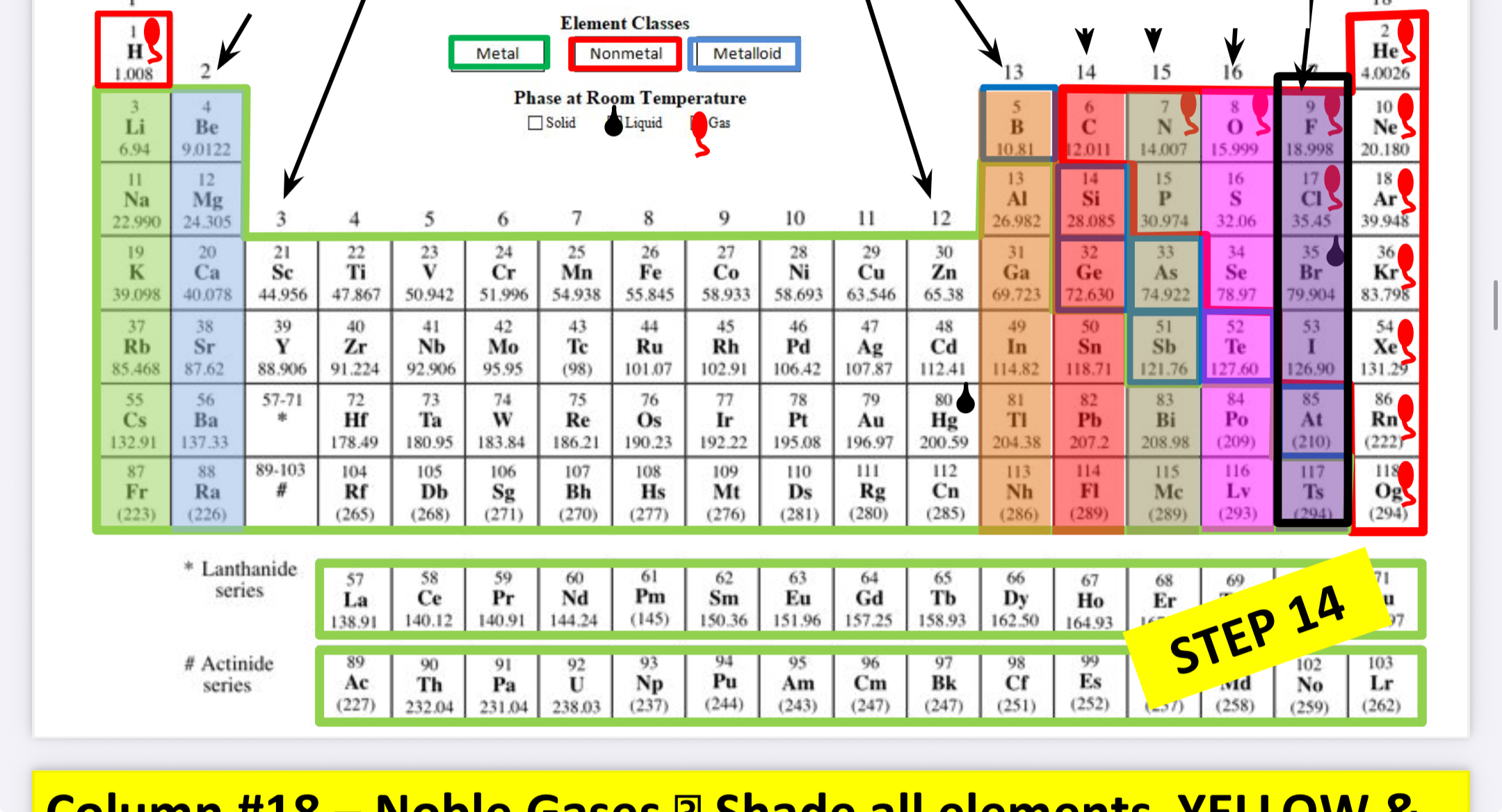
What family is this?
Noble gases
the quantity of energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or an ion
increases as you go across P.T. (left to right) (requires more energy to remove an electron)
decreases as you go down P.T. (top to bottom) (requires less energy to remove an electron from an atom)
Most reactive
metals: far left bottom (Fr)
Lowest ionization energy (easily loses electron)
nonmetals: far right top (F)
Highest ionization energy (very difficult to lose electron/ "wants" to gain one)
Ionization energy
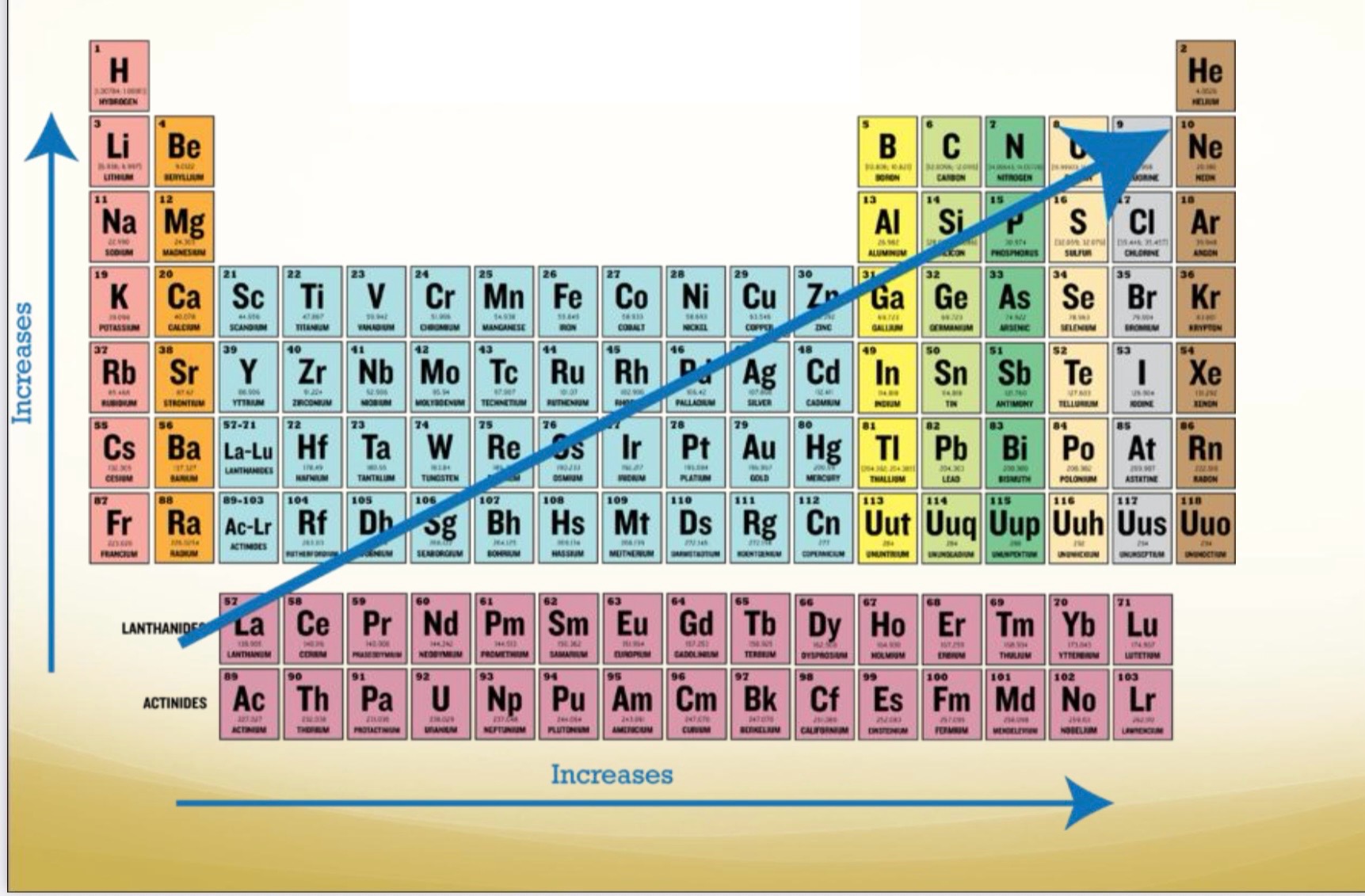
What trend is this
Ionization energy
decreases as you go across P.T. (left to right)
More protons to hang onto those electrons as you go left to right (so it gets smaller)
• increases as you go down P.T. (top to bottom)
Less protons to hold onto electrons (atom expands in size)
Ion Size (what is an ion?)
cations (paws-itive) are smaller than parent atom
anions are larger than parent atom
Atomic radii
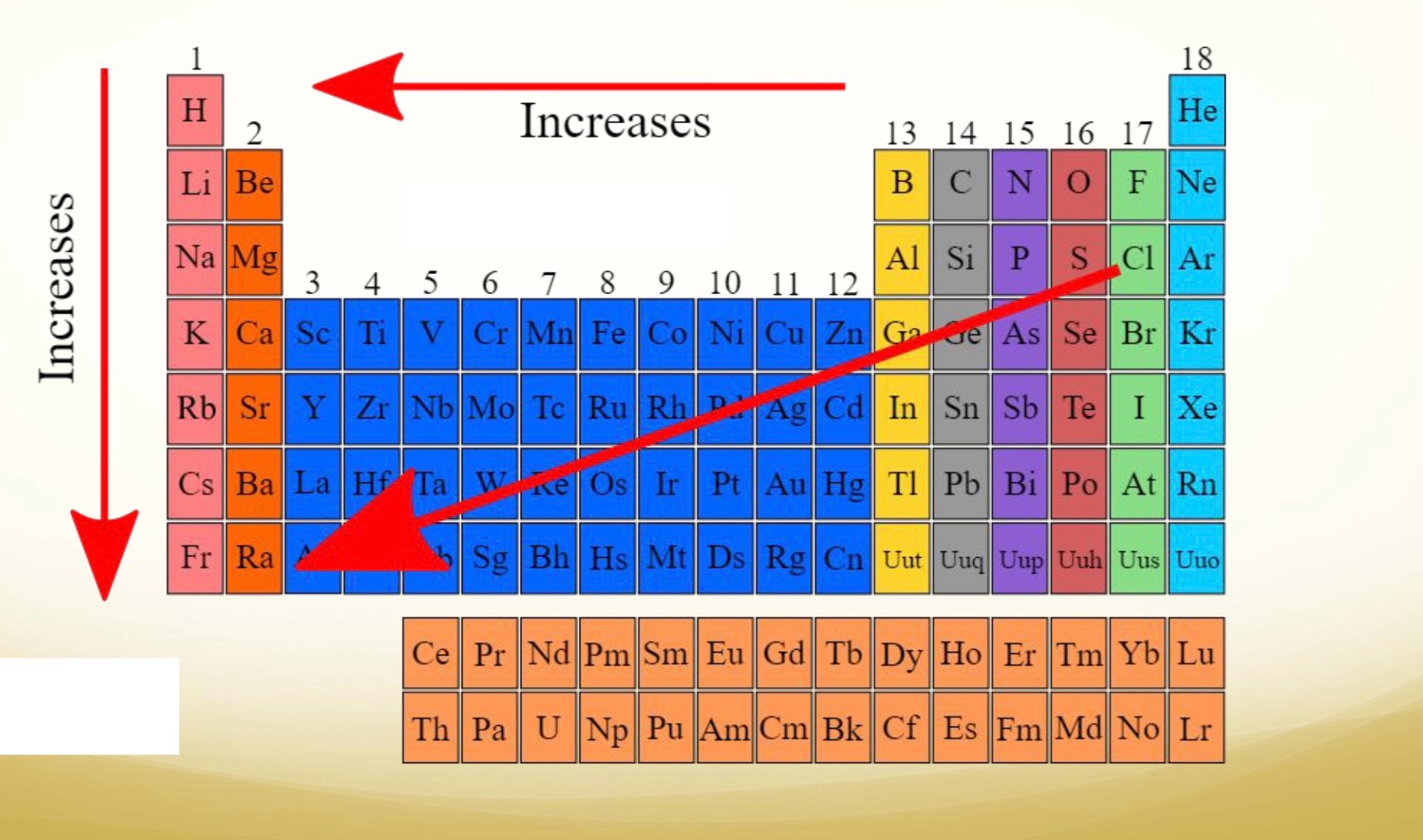
Why trend is this?
Atomic radii
the tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons to itself
increases as you go across P.T.
• Remember Fluorine? Highly electronegative, wants to gain electrons
decreases as you go down P.T.
• Remember Francium? Lowest electronegativity
electronegativity
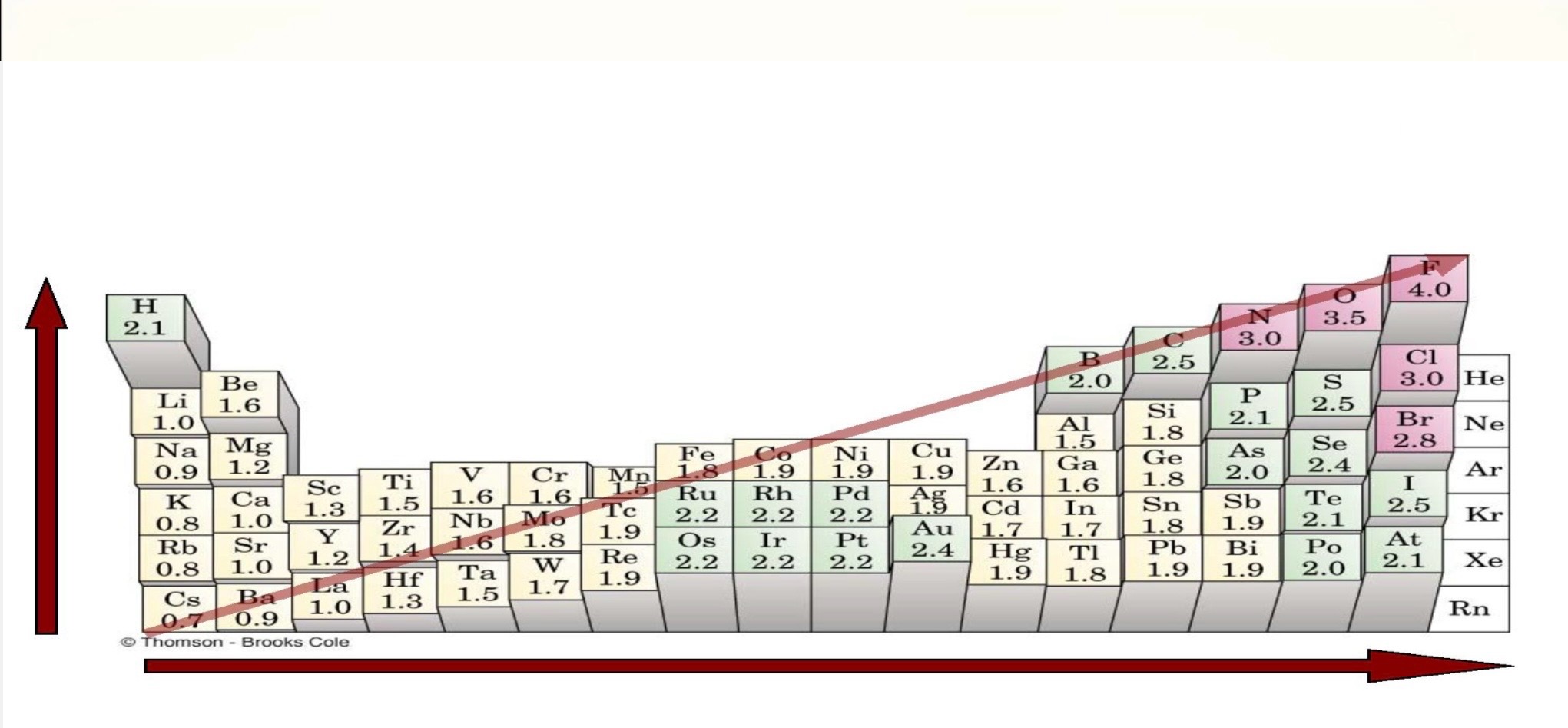
What trend is this?
Electronegativity
7 diatomics
HONClBrIF
Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Cl-Chlorine Bromine Iodine Fluorine