Ch. 21 - Lipid Metabolism
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
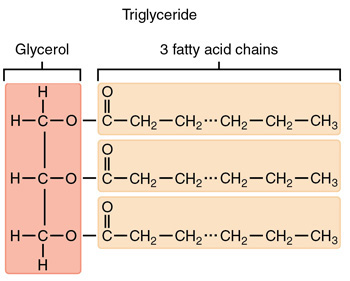
triacylglycerol (triglyceride)
main storage form of chemical energy for most organisms
phosphoacylglycerol
key component of biological membranes
lipases
enzymes that use H2O to release the fatty acids from ester bonds, releasing a free glycerol
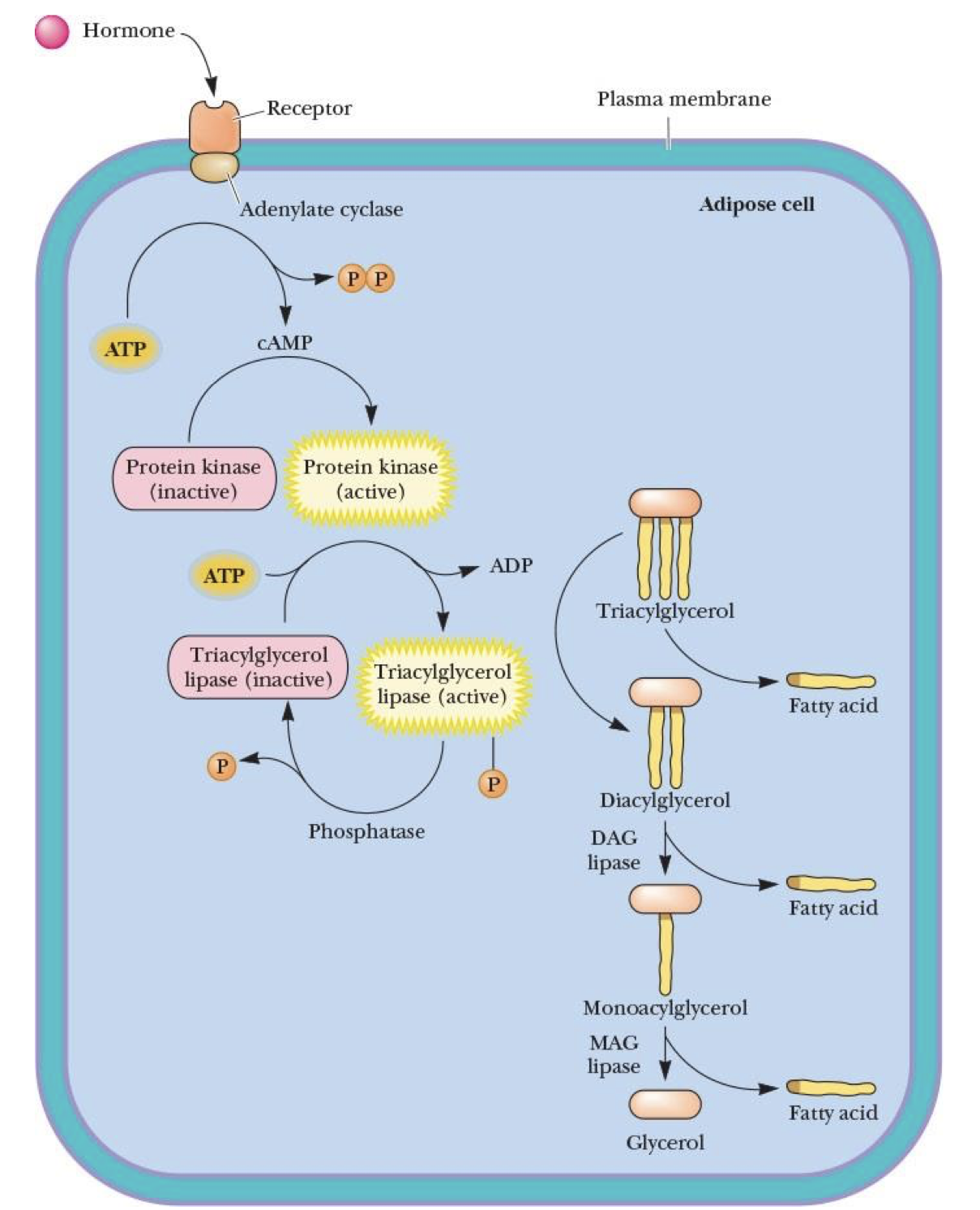
Describe the 5 steps of how liberation of fatty acids is hormone-dependent—how it’s activated
hormone binds to membrane receptor on adipose cell surface
conformational change & signal that it’s time to spend triacylglycerols
adenylate cyclase turns ATP → cAMP (messenger molecule)
cAMP then activates protein kinase
kinase activates triacylglycerol lipase by adding phosphate from ATP
triacylglycerol lipase + triacylglycerol → DAG lipase + diacylglycerol → MAG + monoacylglycerol (nów 3 free fatty acids)
activation in lipid metabolism
thioester bond formed btw carboxyl group (COOH) of fatty acid & thiol group of CoA-SH
catalyzed by Acyl-CoA synthetase—needs ATP
now becomes Acyl-CoA
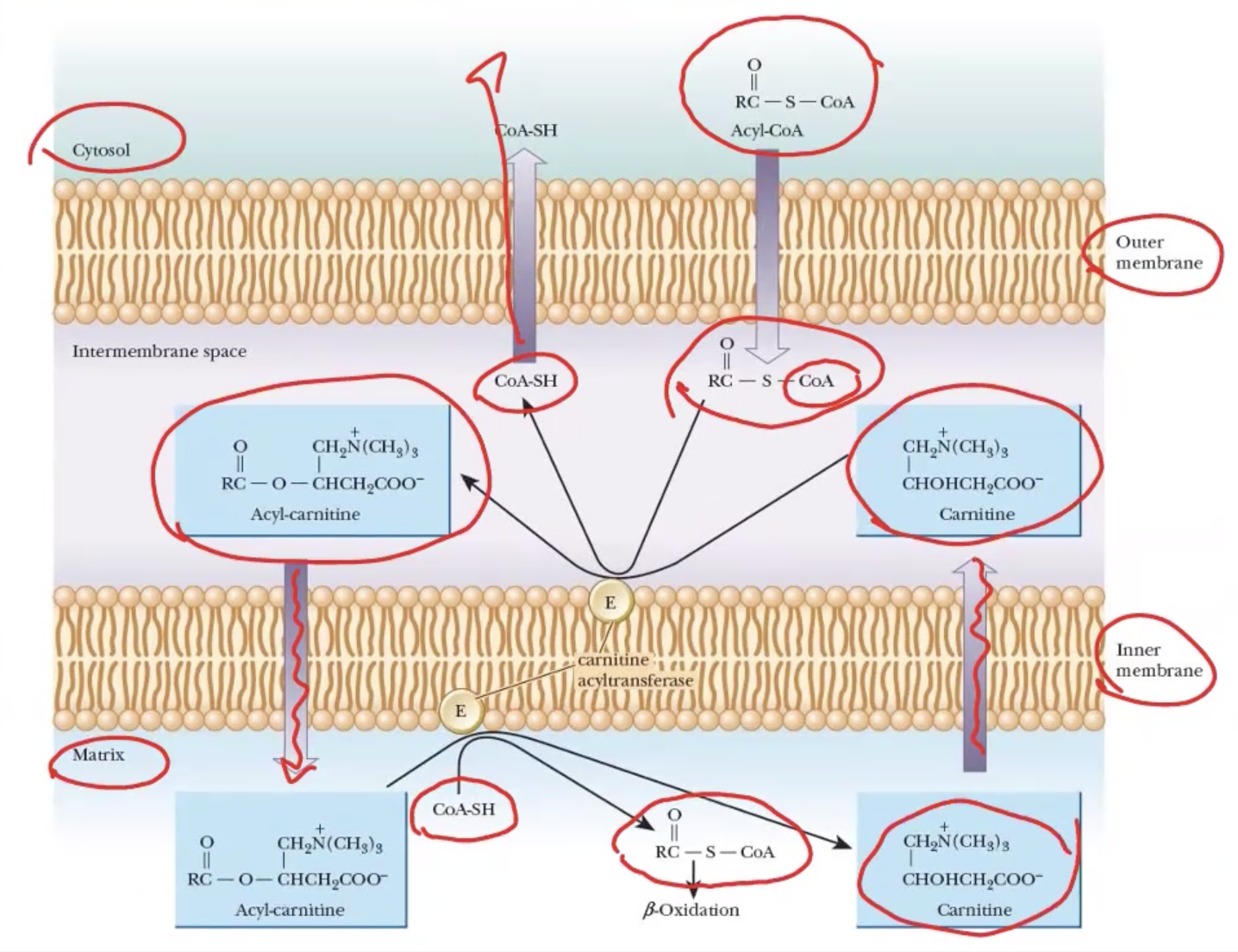
location of esterification & its ability to cross membranes
cytosol; Acyl-CoA can cross outer mitochondrial membrane but not inner
location of fatty acid oxidation after esterification
mitochondrial matrix
what is the overall rxn for the activation of fatty acid?
equivalent to using 2 ATP

Carnitine
molecule in fatty acid metabolism that shuttle acyl groups across inner mitochondrial membrane
carnitine acyltransferase—carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT-I)
found on cytosol side of inner mitochondrial membrane w/ specificity for acyl groups 14–18 carbons long
carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT-II)
found in mitochondrial matrix
How is Acyl-Coa transferred into the mitochondrial matrix if it can’t get past the inner membrane? (3 steps-ish)
Acyl-CoA passes outermembrane into intermembrane space and transfers its Acyl group to carnitine by CPT-I
carnitine exchanges w/ CoA-SH → Acyl-carnitine
free CoA-SH goes back to cytosol & is recycled
Acyl-carnitine into matrix by a transferase (CPT-II)
Acyl-carnitine recombined w/ CoA-SH → activated acyl-CoA
released carnitine goes back to intermembrane space to be recycled
*can now start oxidizing it
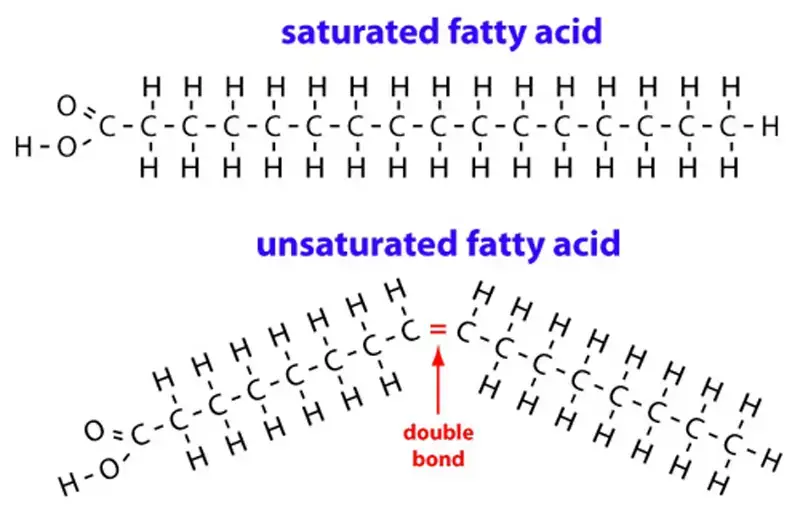
saturated fat
single bond between carbons
e.x: butter
β-Oxidation
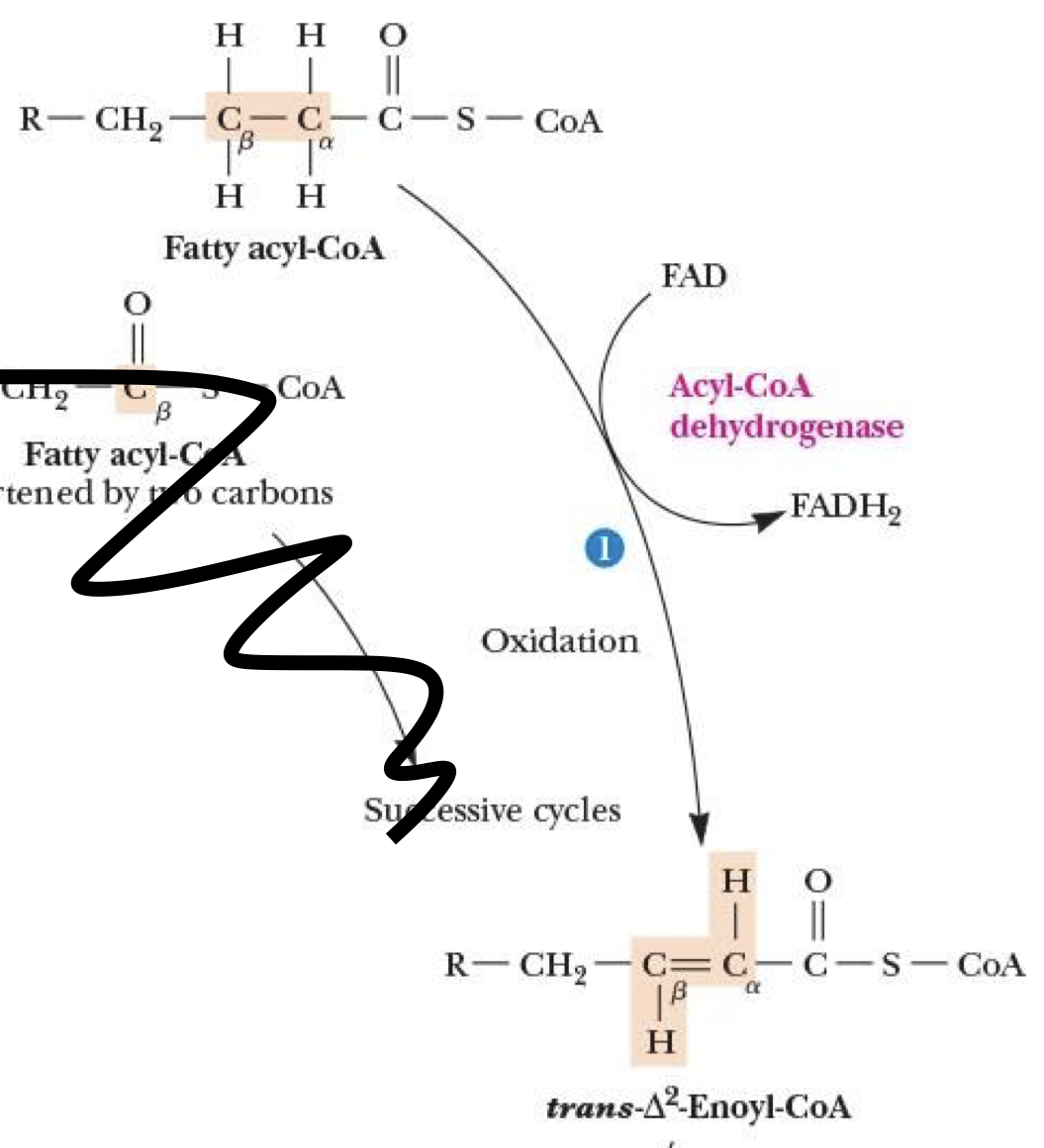
series of 4 rxns that cleaves off 2-carbon units from COOH end of fatty acid
named after Cβ in fatty acyl-CoA
*we will only focus on even numbered molecules w/ C–C (single bond)
Location of β-Oxidation
mitochondrial matrix
β-Oxidation: Step 1
activated fatty acyl-CoA + FAD → FADH2 + double-bond carbons in what was acyl-CoA
catalyzed by Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
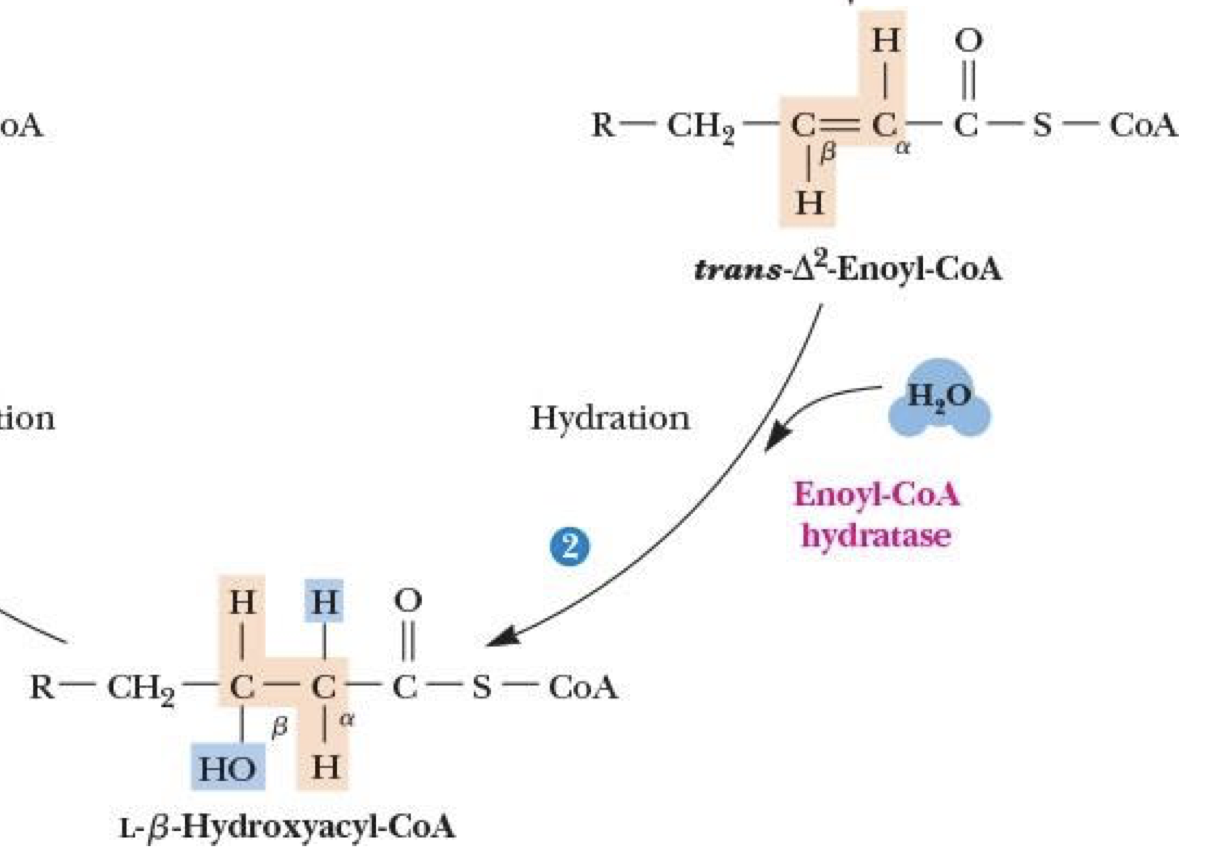
β-Oxidation: Step 2
hydration rxn—add H onto C⍺ & OH on Cβ (L-β-Hydroxyacyl-CoA)
catalyzed by Enoyl-CoA hydratase
*not redox rxn
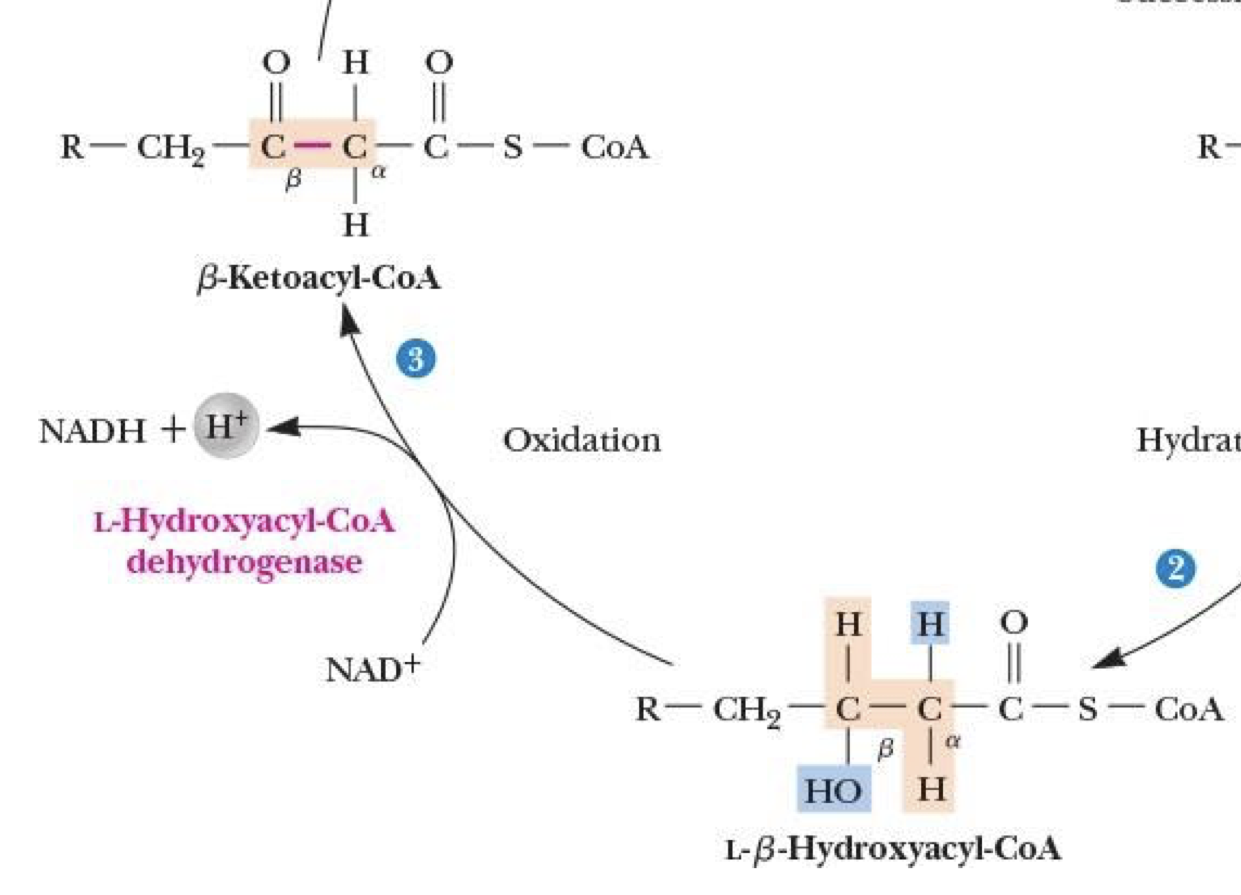
β-Oxidation: Step 3
NAD + L-β-Hydroxyacyl-CoA → NADH + H+ + β-Ketoacyl-CoA
catalyzed by L-Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase
OH from Cβ → C=O
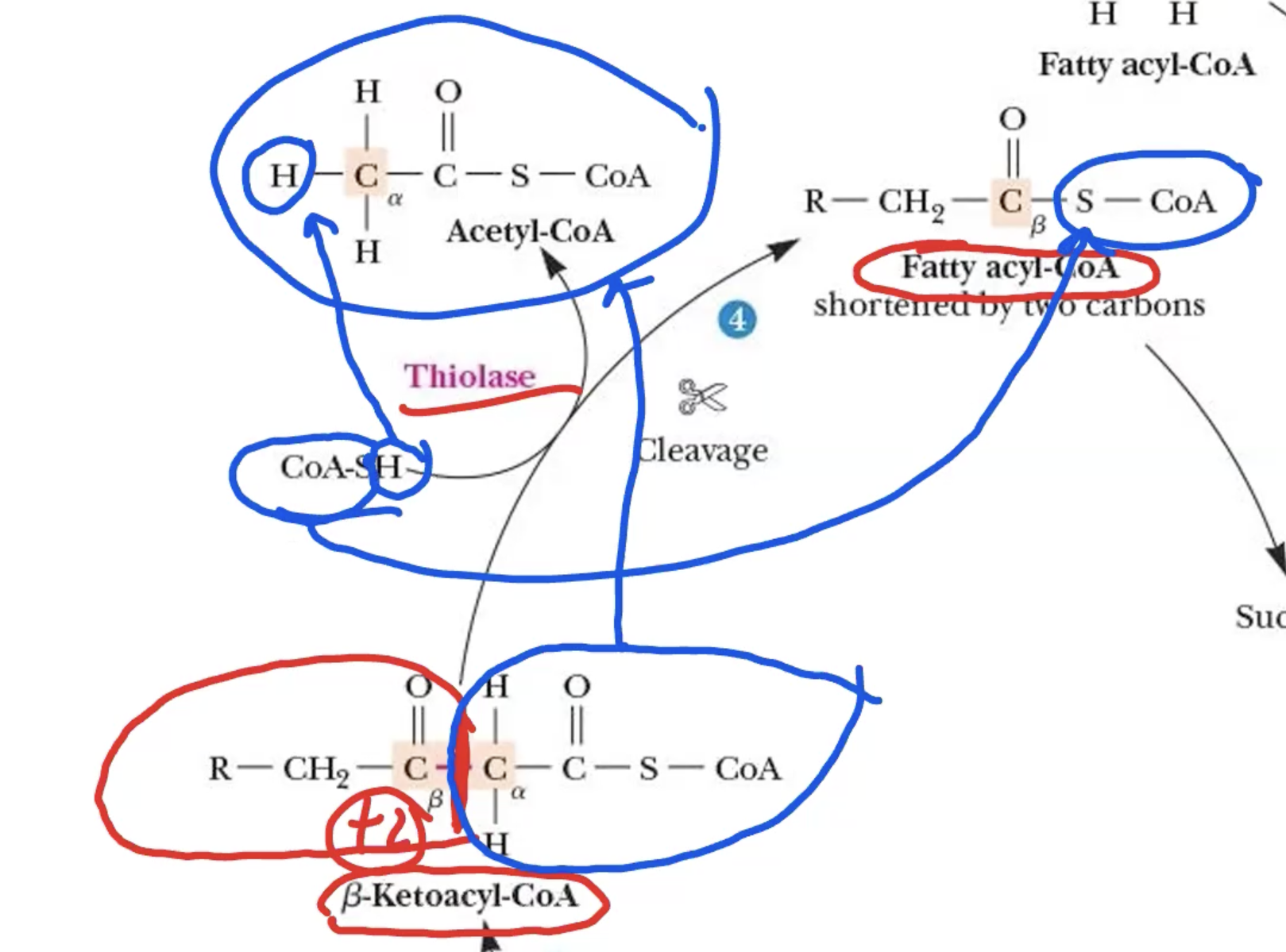
β-Oxidation: Step 4
β-Ketoacyl-CoA + CoA-SH → Acetyl-CoA + Fatty acyl-CoA
cleavage
broken btw Cβ & C⍺
C⍺ side → acetyl-CoA
Cβ side → fatty acyl-CoA (shorter by 2 carbons)
enter successive cycles until its portion becomes acetyl-CoA
catalyzed by thiolase
total products from β-oxidation (per cycle)
1 NADH = 2.5 ATP
1 FADH2 = 1.5 ATP
Acetyl-CoA which will enter Krebs → ETC → ox. phos.
all contributing to making more ATP
ratio of ATP:Carbon from glucose
5.3:1
ratio of ATP:Carbon from fats
6.6:1
why fats is better storage of energy
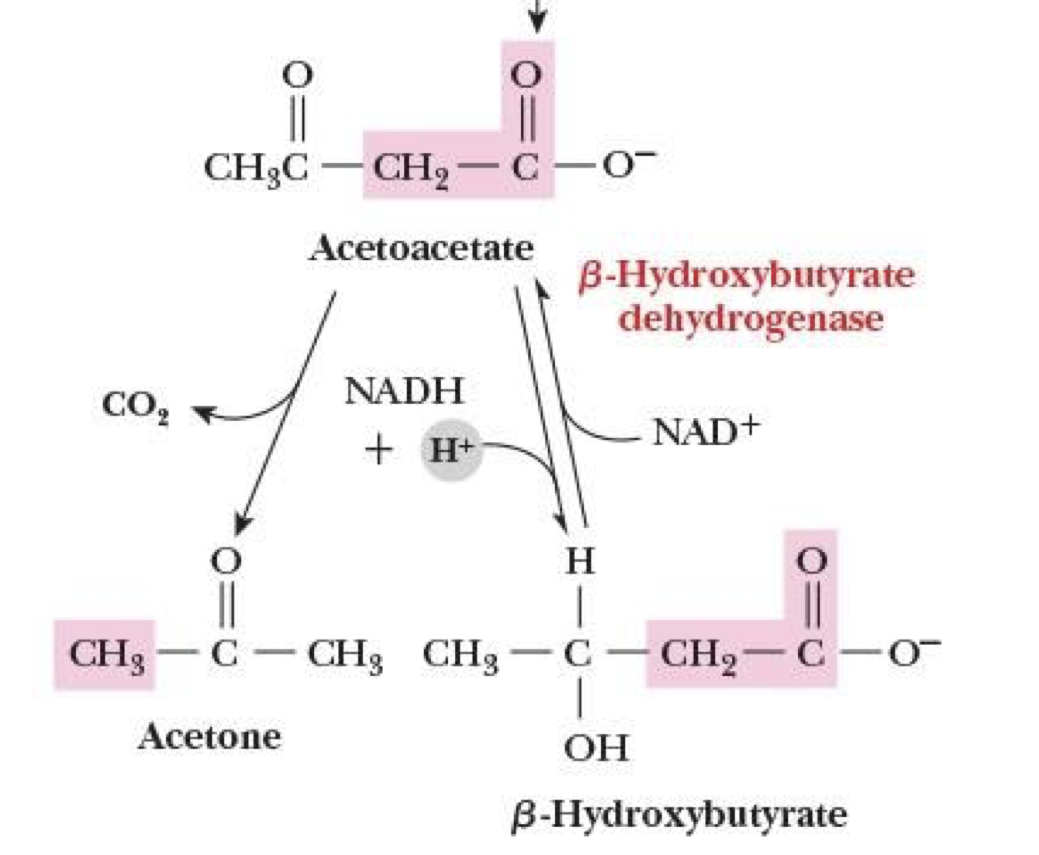
How do ketone bodies come about
when amount of acetyl-CoA is excessive compared to oxaloacetate available to react w/ it
*think of KETO diet or even starvation or diabetic patients’ inadequate intake of carbs
3 compounds that make up ketone bodies
acetone
β-hydroxybutyrate
acetoacetate
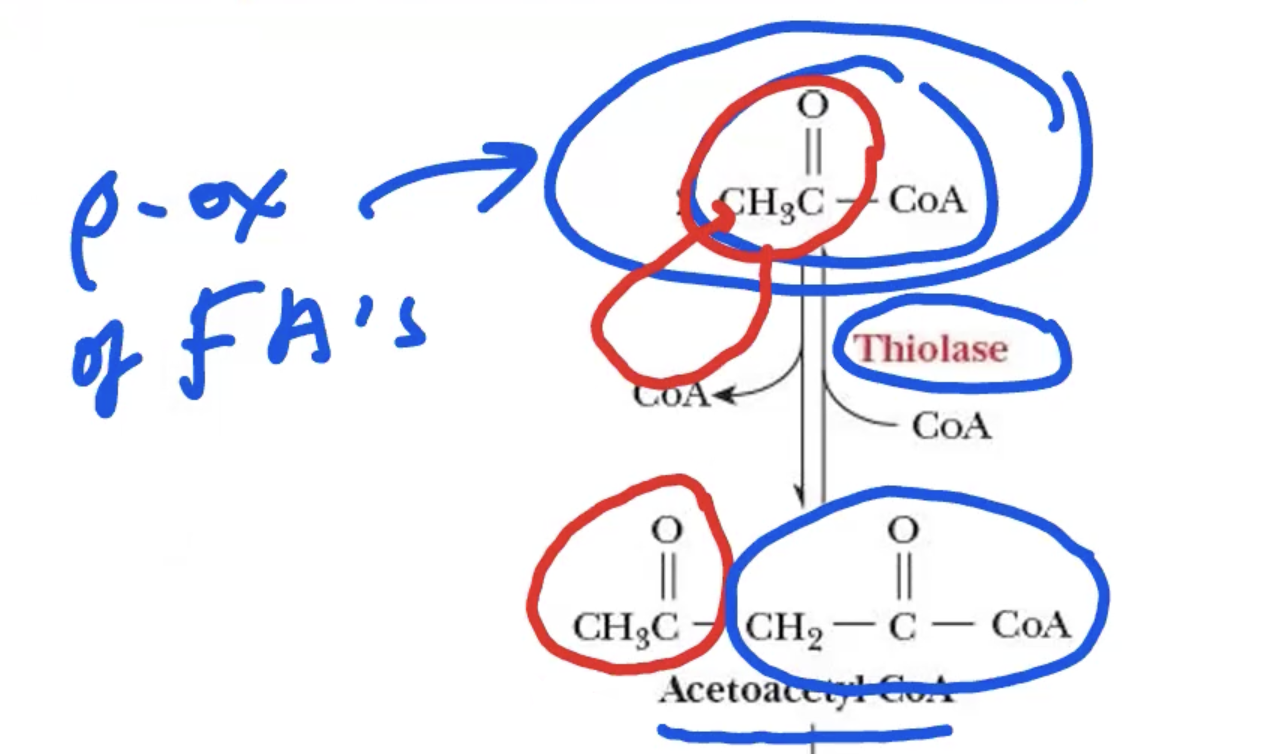
Formation of ketone bodies: Step 1 *DON’T HAVE TO MEMORIZE JUST UNDERSTAND :D
2 acetyl-CoA → acetoacetyl-CoA + 2 CoA
catalyzed by thiolase
acetyl group gets “fused” to acetyl-Coa & CoA gets KICKED TF OUT
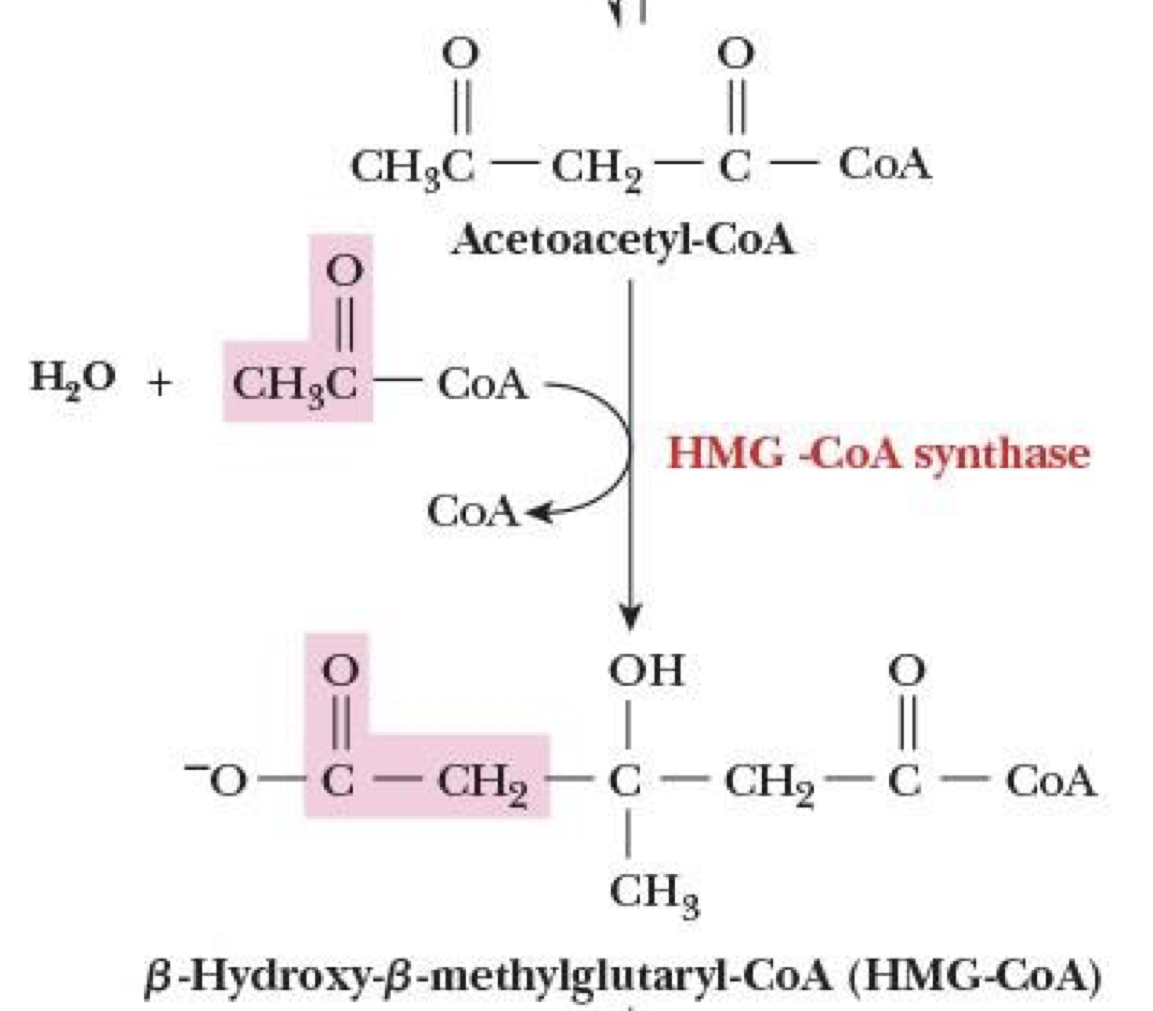
Formation of ketone bodies: Step 2
addition of H2O + acetyl-CoA onto acetoacetyl-CoA while removing a CoA
catalyzed by *long ass MF name—don’t need to memorize (HMG-CoA synthase) → product is HMG-CoA
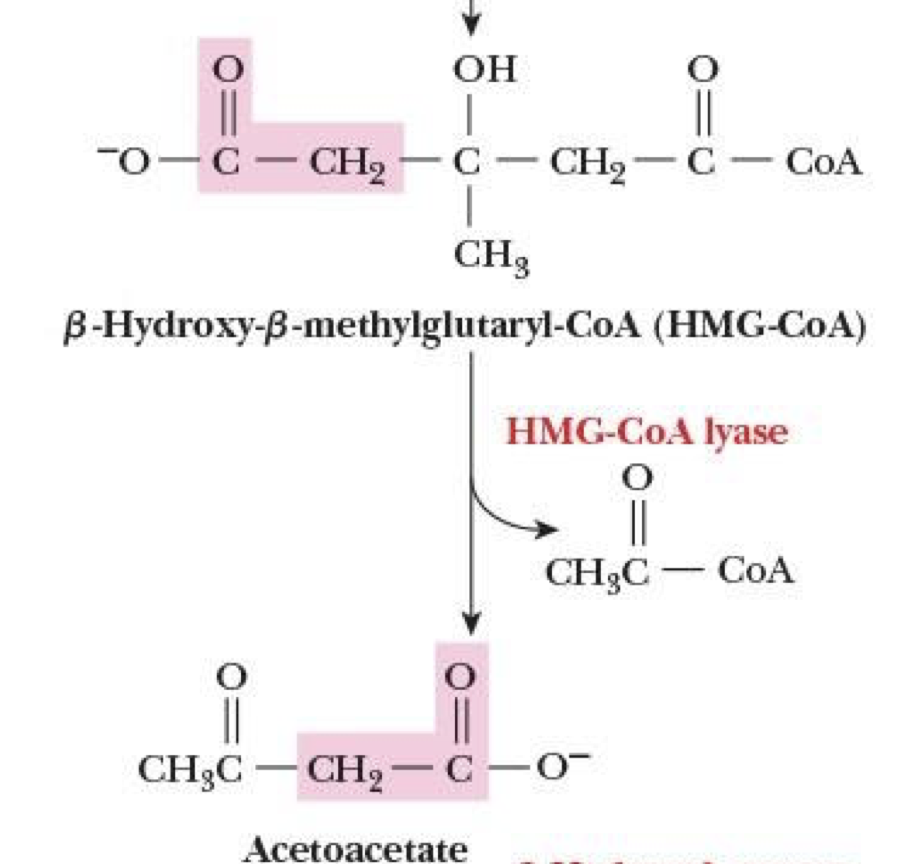
Formation of ketone bodies: Step 3
HMG-CoA → acetoacetate
cleaves (removes) an acetyl-CoA
catalyzed by HMG-CoA lyase
Formation of ketone bodies: Step 4
acetoacetate → acetone + β-Hydroxybutyrate
acetoacetate SPONT. loses CO2 → acetone
acetoacetate + NADH + H+ → β-Hydroxybutyrate + NAD+
catalyzed by β-Hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase