nervous system
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
motor neurone
cns → effector
synapse
physical gap between 2 neurones
electronic impulse converted to chemical neurotransmitter
diffuses across and binds to next neurone
slows down
stimulus
a change in environment
receptor
detects stimulus and converts info to impulse
effector
muscle/gland = contract/secrete hormone
response
response to stimulus
reflex arc
REACTION = AUTOMATIC/INVOLUNTARY
protects person from damage
doesn’t go to brain
stimulus → receptor →sensory neurone → relay neurone → motor neurone → effector → response
order of nervous system
stimulus → receptor →sensory neurone → CNS→ motor neurone → effector → response
relay neurones in brain
neurone differentiation
fatty myelin sheath - insulation
long - dendrons/dendrites
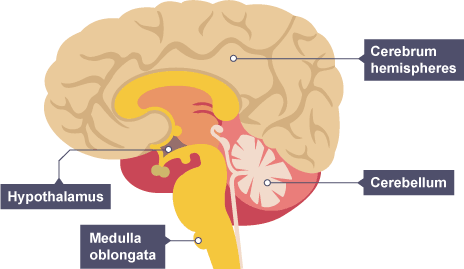
cerebellum
muscle movement/coordination
cerebral cortex
consciousness, intelligence, memory and language
medulla
unconcious activity - breathing + heartbeat
hypothalmus
temperature regulation
location of cerebral cortex, medulla and cerebellum
3 ways to study brain
mri scans (magnetic resonance imaging) - detailed picture
electrically stimulating brain - sees what part of brain controls what
studying patients with brain damage
why is studying brain risky
brain is complex and delicate
can lead to damage
eye in dim light
pupil dilates
circular muscles relax
radial muscles contract
more light enters eye
what is the eye
a sense organ containing receptors sensitive to light intensity + colour
what is accomodation
changing the shape of the lens to focus on near or distant objects
optic nerve
sensory neurones that send impulses to brain
transmits visual information from eye to brain as electrical impulses
retina
contains light sensitive cells that send neural impulses to the brain when stimulated by light.
thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye
focusing on distant objects
ciliary muscles relax = larger diameter
suspensory ligaments pulled tight
lens pulled thinner = slightly refracts/less convergent
Light focused on retina
focusing on near objects
ciliary muscles contract = smaller diameter
suspensory ligament loosen
lens = thick, strongly refracts/more convergent
light focused on retina
blind spot
unaware of this - brain fills gap
point where the optic nerve leaves the eye - no retina
eye in bright light
pupil constrics
circular muscles contract
radial muscles relax
less light enters eye
pupil
hole through which light enters the eye
controls the amount of light that enters the eye
ciliary muscles
controls the shape of the lens
contract and relax to change the shape of the lens
allows accomodation
sclera
white outer layer
tough + strong so the eyeball is not easily damaged
myopia
short sightedness
close = clear
distant = blurred
light focused in front of retina = blurry
concave lens
hyperopia
long sightedness
distant = clear
close = blurry
light focused behind retina = blurry
convex lens
cornea
transparent part of sclera at from of eyeball
lets into eye
curved surface refracts light rays, focused on retina
iris
circular + radial muscles that contract and relax to change the size of the pupil
controls size of puil
controls amount of light reaching retina
suspensory ligament
holds lens in place
attach the lens to ciliary muscles (helps accomodation)
corrective technology
spectacles/contact lenses
laser eye surgery (aters shape of cornea)
replacement lens
lens
clear disc held in place by suspensory ligament + ciliary muscles
fine tunes the focusing of light rays, changing their direction to produce a clear image on retina
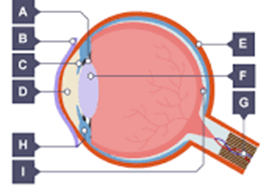
a - suspensory ligament
b - cornea
c - iris
d - pupil
e - sclera
f - lens
g - optic nerve
h - ciliary muscle
i - retina