cognitive theories
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Are there distinct modes of cognitive processing?
2 two modes of cognitive processing:
Dual-Processing Model
System 1 (Intuitive processor): Fast, emotional, automatic
System 2 (Conscious processor): Slow, logical, deliberate
through Cognitive Styles
Can personality be described in terms of “cognitive styles?
yeah kinda ig:
Cognitive Styles:
Field Dependence/Independence
Pessimistic Attribution Style
Self-Complexity
Need for Cognition
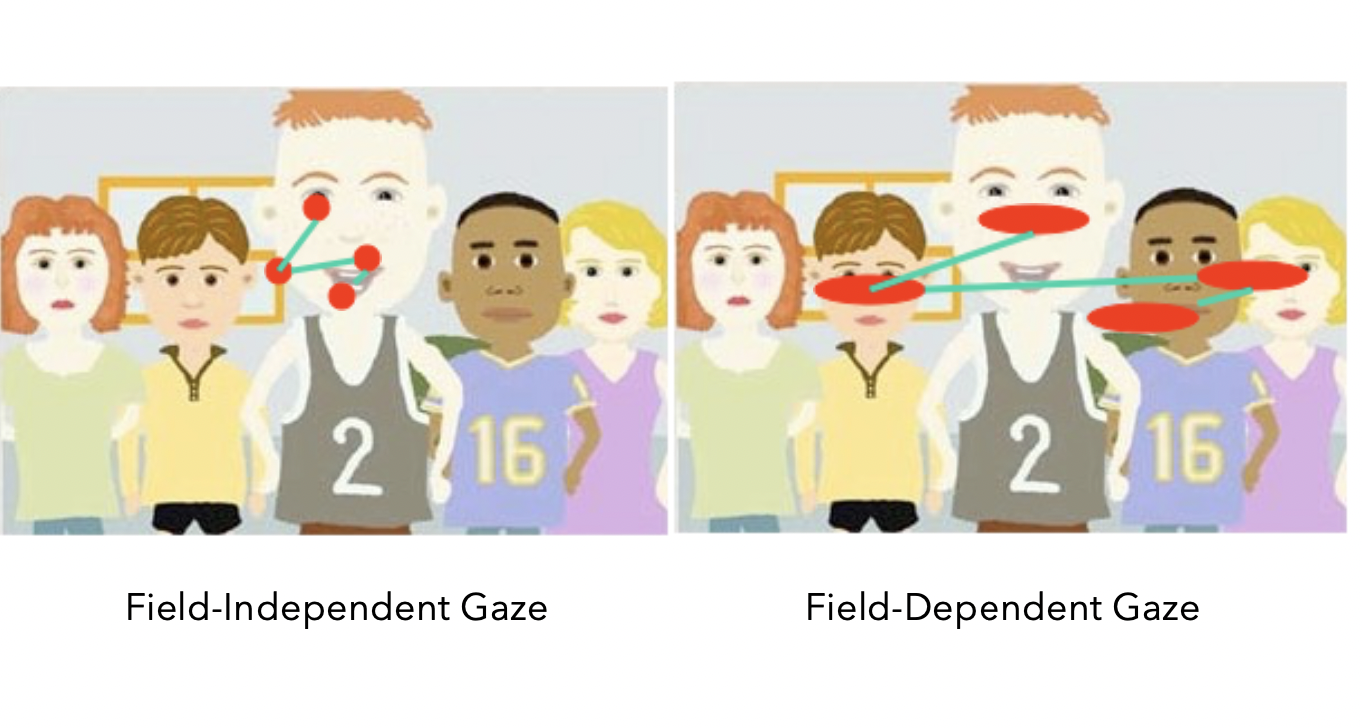
define field dependence/independence
Field dependence vs. field independence
Field dependence: tendency to focus on context around focal object + relationships among objects in environment; correlated with extraversion
Field independence: tendency to separate a focal object from its context and focus on the attributes of the focal object; correlated with introversion
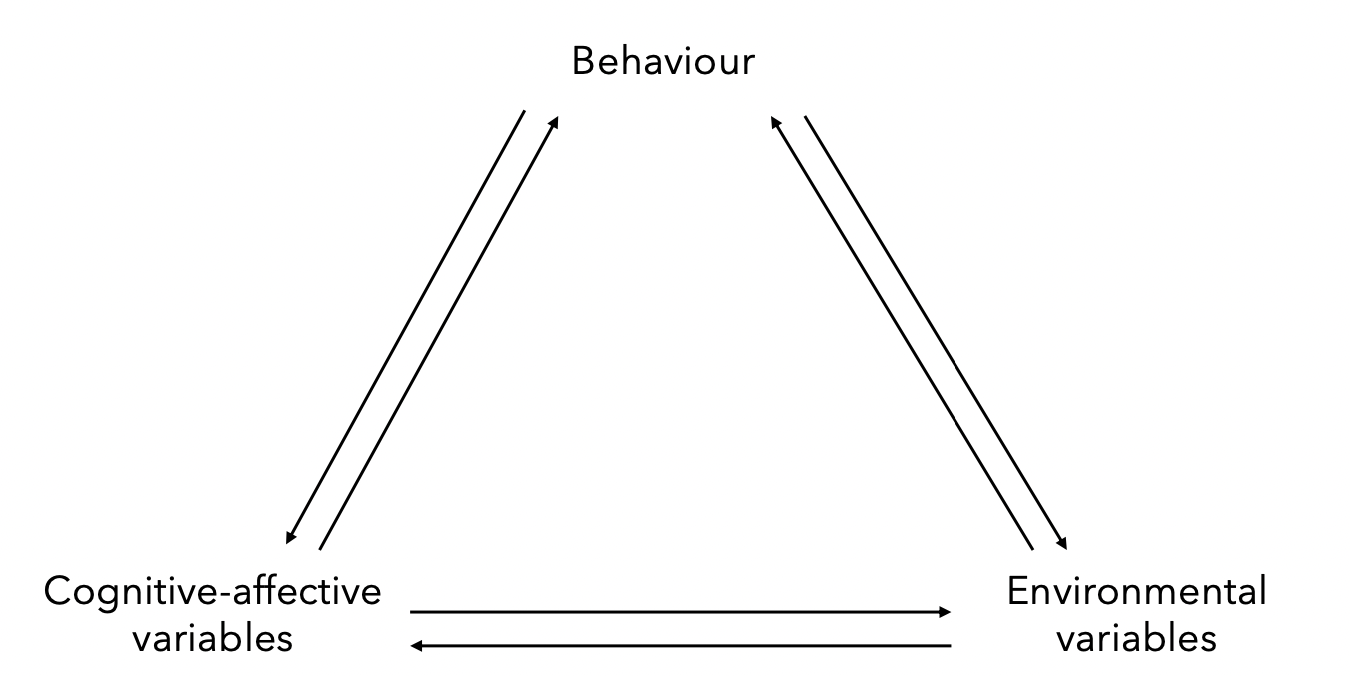
discuss reciprocal determinism
Behavior, person, and environment influence each other
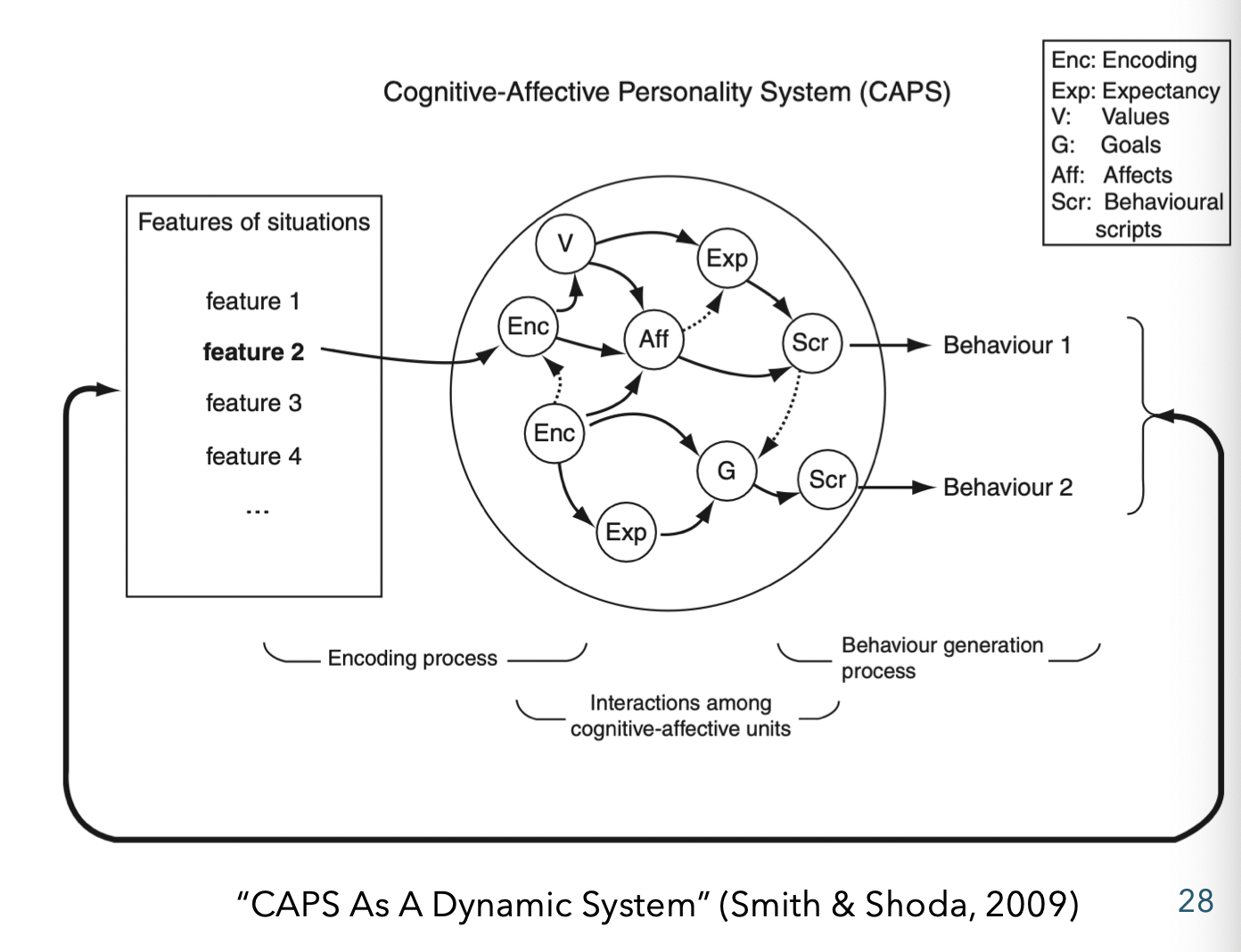
distinguish between encodings, expectancies and beliefs, affects, goals and values, and competencies and self-regulation skills
encodings (e.g. schemas)
expectancies and beliefs (e.g. stimulus-outcome expectancies, response-outcome expectancies, self-efficacy, locus of control)
affects (e.g. negative affect, positive affect)
goals and values (e.g. achievement)
competencies and self-regulation skills (e.g. self- monitoring, self-reinforcement, attentional skills, cognitive restructuring skills, ability to develop action plans, capacity for delay-of-gratification, affect-control skills)
define behavioural signatures
Stable patterns in specific situations
discuss the operation of the cognitive-affective personality system (i.e., CAPS)
cognitive-affective variables all interact to form a “dynamic” system
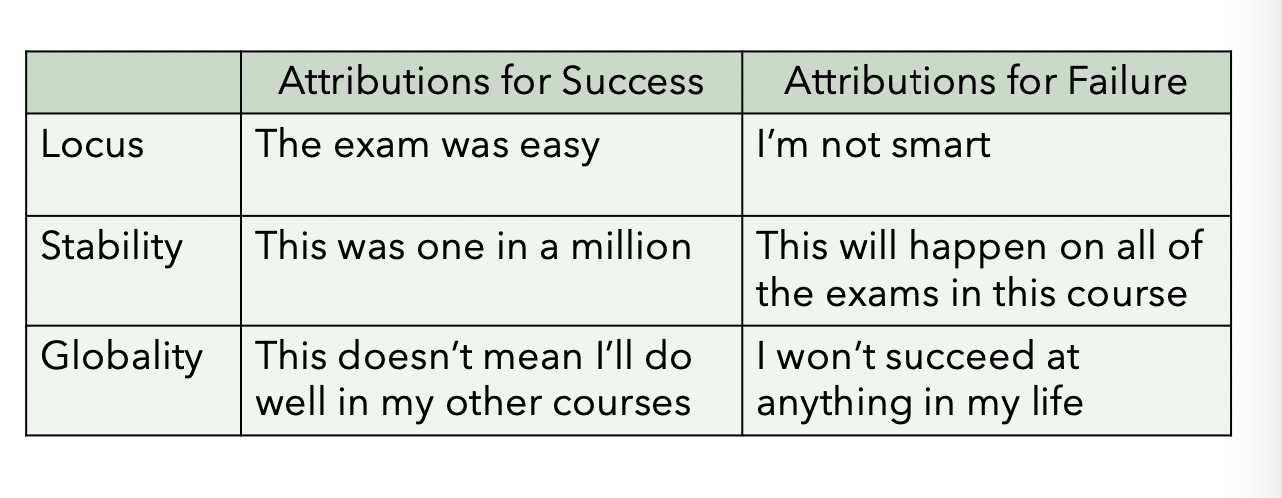
define: pessimistic attribution style (congitive style)
pessimistic attribution style
negative explanations for events
Attributions for events vary on 3 dimensions:
locus (internal or external to the individual),
stability
globality (across contexts)
ppl who show ^ are prone to depression (learned helplessness model)
Success: Due to external, unstable, and specific factors Failure: Due to internal, stable, and global factors

define: self-complexity
Refers to:
(a) the number of self-aspects that are used to represent the self in the self-schema
(b) the degree of redundancy among these self-aspectsHigh self-complexity: Many self-aspects that are not redundant
buffers against the harmful effects of stress by preventing events that occur in one self-aspect from “spilling over” and adversely affecting other self-aspect
Low self-complexity: Few self-aspects that are not redundant
define: need for cognition (cognitive states)
Refers to a tendency to engage in and enjoy thinking
Associated with:
higher levels of intelligence
greater curiosity
lower social anxiety
higher conscientiousness and openness, lower neuroticism
higher self esteem
what are the 5 cognitive-affective variables
”person” variables that interact with environmental variables (i.e., situations) to determine behaviour
Encodings
Expectancies and beliefs
Affects
Goals and values
Competencies/self-regulation