Gregor Mendel Genetics Quiz
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mendelian Genetics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Gregor Mendel is responsible for the laws governing
Inheritance of traits
Was his work recognized during his lifetime?
No, it was not recognized until the turn of the 20th century
He is also known as the
¨Father of genetics¨
What type of plants did he study?
pea plants
How many plants did he test?
28,000
What did he find out?
that the plants offspring retained traits of the parents
Where was the site of Mendel’s experiment?
Czech Republic
Mendel did not know about chromosomes and DNA. What did he call them?
particles
Genotype
the genetic makeup of an organism
Phenotype
A set of observable characteristics largely determined by the genotypes.
Homozygous
organism with two alleles of the same type
Heterozygous
organism with different alleles of the same type
Dominant
expressed allele in heterozygous individuals
Punnett Square
A diagram used to predict the genotype and phenotype combinations of a genetic cross.
Why did Mendel choose pea plants?
Because they can be grown in a small area, produce lots of offspring, produce pure plants when allowed to self pollinate, and several generations can be artificially cross pollinated.
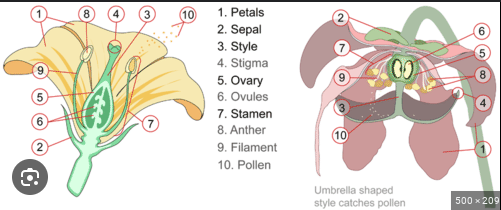
Petals
Sepal
Style
Stigma
Ovary
Ovules
Stamen
Anther
Filament
Pollen
What are the 8 characteristics of pea plants? What are the genotypes and phenotypes?
seed shape— round(R) or Wrinkled(r
seed color— yellow(Y) or green(y)
pod shape— smooth(S) or wrinkled(s)
pod color— Green(G) or Yellow(g)
seed coat color— Gray(G) or White(g)
flower position— Axial(A) or Terminal(a)
plant height— Tall(T) or Short(t)
flower color— Purple(P) or White(p)
Parent generation
The parental generation in an experiment
First generation
The first generation offspring in an experiment
Second generation
The second generation offspring in an experiment
Describe the law of dominance
In a cross of parents that are pure for contrasting traits, only one form of the trait will appear in the next generation
Describe the law of segregation
during the formation of gametes the two alleles responsible for a trait separate from each other
Describe the law of independent assortment
alleles for different traits are distributed to sex cells independently of one another
Incomplete dominance
occurs when neither allele is completely dominant and an intermediate phenotype is expressed.
codominance
occurs when both alleles are expressed equally in the phenotype of the heterozygote
what are sex linked traits
traits located on the sex chromosomes
Why are females carriers and males express the trait in X-linked traits?
Because one of their chromosomes has the mutation but the other one is normal