Variations in Drug Responses
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What are three patient-specific factors that cause individual variation in drug responses?
Body weight and composition, age, and pathophysiology.
What are three examples of pathophysiology that can alter drug responses?
Kidney disease, liver disease, and altered acid-base or electrolyte status.
What is tolerance?
A decreased responsiveness to a drug as a result of repeated drug administration.
What are three types of tolerance?
Pharmacodynamic tolerance (the result of long-term administration)
Metabolic tolerance (the result of increased drug metabolism)
Tachyphylaxis (a rapid decrease in drug responsiveness)
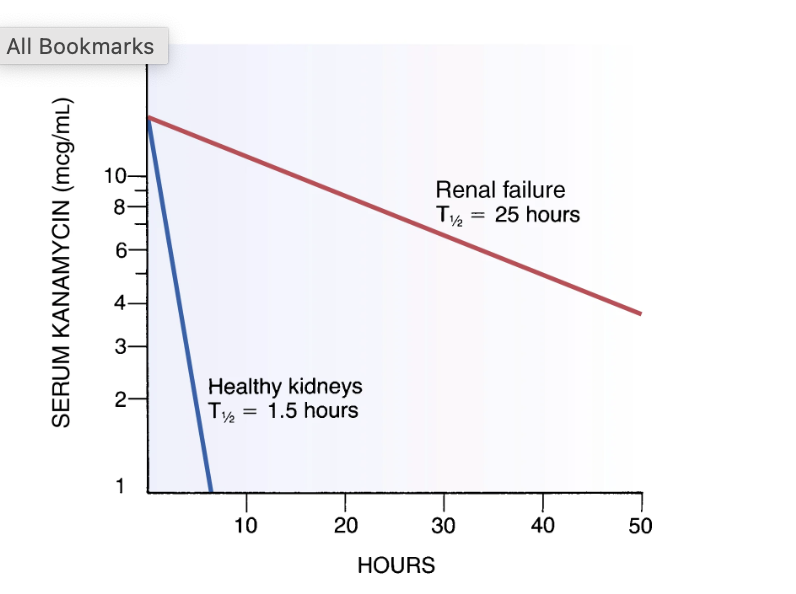
Graph
The final graph shows how long a drug stays in the body. The half-life (T1/2) is the time it takes for the drug concentration in the blood to decrease by half.
In a person with healthy kidneys, the half-life of Kanamycin is 1.5 hours, so the drug is cleared from the body quickly.
In someone with renal failure, the half-life is 25 hours. This means the drug stays in the body much longer, so the dose would need to be adjusted to prevent toxicity.
What is the placebo effect?
A drug's psychological response due to the patient's belief that they are receiving an effective treatment.
What does bioavailability mean, and how does it relate to drug response?
Bioavailability refers to the amount of drug that reaches the bloodstream from a dose. Variability in a drug's absorption and bioavailability can cause differences in how patients respond.
What are five factors that contribute to individual variation in drug responses?
Genetics, sex, comorbidities, diet, and ancestry.
more effective in women than men
white euros more likely to get blood clots
starvation can lead to a lot of protein binding
What are two other potential causes of individual variation in drug responses?
Failure to take medications as prescribed and drug interactions.
What are two common causes of unexpected drug responses?
Failure to take medications as prescribed (not taking them correctly) and drug interactions (when one drug affects another).
What are two categories of congenital anomalies caused by teratogens?
Gross malformations (like cleft palate or clubfoot) and neurobehavioral/metabolic anomalies.
What is the most important way to minimize the risk of teratogenesis?
Pregnant patients should avoid all unnecessary drug use (e.g., alcohol and cocaine).
What is a key step in responding to potential teratogen exposure?
Identifying the details of the exposure and using diagnostic tools like ultrasound scans.
What system does the FDA use to categorize the risk of a drug during pregnancy?
The FDA Risk Categories (A, B, C, D, X), which classify drugs based on their potential to cause harm to a fetus.
A is safest
X is for a fact it causes fetal harm
How do drugs affect an infant through breastfeeding?
Drugs can be excreted in breast milk, and the infant can experience effects from the drug.
What are two ways to reduce the risk of drug exposure to an infant during breastfeeding?
Take drugs immediately after breastfeeding.
Avoid drugs with long half-lives.
What kind of drugs are safest to take while breastfeeding?
Drugs that are less likely to enter the breast milk and those that have the least effect on the infant.
What kinds of drugs should be avoided entirely during breastfeeding?
Drugs that are known to be hazardous to infants.
How does oral drug absorption differ in neonates and infants?
Gastric emptying is prolonged and irregular, and gastric acidity is very low until around age 2.
How do intramuscular (IM) and percutaneous (skin) drug absorption differ in infants?
IM absorption is slow and erratic, while percutaneous absorption is much faster due to the infant's thin skin.
How does protein binding affect drug distribution in infants?
Protein binding is limited, so free drug concentrations are higher. This means that a lower dose may be needed to achieve the desired effect.
low albumin and low distribution
How does the blood-brain barrier differ in neonates and infants?
The blood-brain barrier is not fully developed, so drugs can more easily enter the central nervous system. This makes infants more sensitive to drugs that act on the brain.
How do hepatic metabolism and renal excretion affect drug action in infants?
Both liver metabolism and kidney excretion are not fully developed at birth, making infants highly sensitive to drugs. Drug dosages must be reduced to avoid toxicity.
slow both
How do the pharmacokinetic parameters of children aged 1 and older compare to those of adults?
Most pharmacokinetic parameters are similar to those of adults.
What is one important difference in drug metabolism for children aged 1 and older?
They metabolize drugs faster than adults, especially until age 2. This metabolism then gradually declines, with a sharp decline at puberty.
What is the clinical implication of children's faster drug metabolism?
You may need to increase the dosage or decrease the interval between doses to achieve a therapeutic effect.
What is the best way to provide patient education to promote adherence?
Provide patient education in writing, and include demonstrations when appropriate.
What are the three key points about dosage and administration that should be included in patient education?
Dosage size and timing
Route and technique of administration
Duration of treatment
What practical instruction is essential for patient education?
How to properly store the drug.
What should patients be taught about the expected effects of their medication?
The nature and time course of both desired responses and adverse responses.
How do altered pharmacokinetics affect older adults?
Older adults are more sensitive to drugs than younger adults, and they have greater variation in how their bodies process drugs.
How do multiple or severe illnesses affect drug therapy in older adults?
They can complicate drug therapy due to the severity of the illness and the presence of multiple pathologies (comorbidities).
Why is multiple-drug therapy a concern for older adults?
It increases the risk of excessive prescribing and adverse drug interactions.
What is a common problem with medication in older adults?
Poor adherence to medication schedules.
What four factors alter drug absorption in older adults?
Increased gastric pH, and decreased surface area, splanchnic blood flow, GI motility, and gastric emptying.
How is drug distribution altered in older adults?
They have an increased percentage of body fat, and decreased lean body mass, total body water, serum albumin, and cardiac output.
less proteins to bind to
How is drug metabolism altered in older adults?
Metabolism is decreased due to reduced hepatic blood flow, liver mass, and enzyme activity.
How is drug excretion altered in older adults?
Excretion is decreased due to reduced renal blood flow, glomerular filtration rate (GFR), tubular secretion, and the number of nephrons.
What underlies altered drug sensitivity in older adults?
Alterations in receptor properties, such as a change in the number of receptors or their affinity for drugs.
Name two classes of drugs that have more intense effects in older adults.
Warfarin and certain central nervous system (CNS) depressants.
Are beta blockers more or less effective in older adults, and why?
They are less effective, even at the same concentration, because older adults have a reduction in the number of beta receptors and a reduction in the receptors' affinity for beta blockers.
How much more likely are ADRs in the elderly compared to younger adults?
They are seven times more likely.
What percentage of hospital admissions are due to ADRs?
They account for 16% of hospital admissions.
What percentage of all medication-related deaths are accounted for by ADRs?
They account for 50% of all medication-related deaths.
Are most ADRs dose-related or idiosyncratic?
The majority are dose-related rather than idiosyncratic (a unique reaction to a drug).
What is a common characteristic of ADR symptoms in older adults?
The symptoms are often nonspecific (e.g., dizziness, confusion).
What is the main reason for drug accumulation leading to ADRs in older adults?
Reduced renal function is a primary cause of drug accumulation.
What are two common patient-specific factors that predispose older adults to ADRs?
Polypharmacy (using multiple drugs) and a greater severity of illness with multiple comorbidities.
How do drugs with a low therapeutic index increase the risk of ADRs?
They have a narrow safety margin, meaning the dose needed for a therapeutic effect is close to the dose that can cause toxicity.
What are three other factors that can predispose a patient to an ADR?
Increased individual variations due to altered pharmacokinetics, inadequate supervision of long-term therapy, and poor patient adherence.
What are two key strategies for helping patients with unintentional nonadherence?
Simplify the drug regimen.
Provide clear and concise verbal and written instructions.
What are two practical ways to make taking medication easier for patients?
Use an appropriate dosage form (e.g., liquid instead of a large pill).
Provide clearly labeled and easy-to-open containers.
What are three ways to support a patient with unintentional nonadherence?
Set up daily reminders.
Involve a support system (family/friends).
Conduct frequent monitoring.
What is transcultural nursing?
It means being sensitive to cultural differences while focusing on individual patients, their needs, and their preferences.
What are two advantages of self-care and complementary medicine?
Rapid treatment for minor injuries
Increased patient control and comfort
What is a financial advantage of complementary medicine?
It can lead to decreased costs if the therapy is effective.
What are two major disadvantages of using complementary medicine?
Delayed care for serious injuries or problems
Potential adverse interactions with prescribed medications
What is a key regulatory drawback of many complementary therapies?
Their positive effects are often not proven, and they are not regulated by the FDA.
When should you inquire about a patient's self-care practices?
During history taking.
How should a nurse provide education on self-care practices?
Like they would with a prescription drug.
Besides the practices themselves, what should a nurse know and understand about the patient?
What the patient believes about the therapy.
What are three reasons a patient might not report their self-care practices?
They may not consider the practices drug therapy.
They may lack knowledge about the practice or what it does.
They may fear being misunderstood.
How are herbals classified under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994?
They are classified as "Dietary Supplements."
What is a key regulatory difference for herbals compared to drugs?
They do not require FDA approval before being marketed.
What claims can be made on herbal products, and what claims are prohibited?
Physiologic effects can be noted, but no claims can be made about preventing or curing a disease.
What disclaimer must be included on herbal products?
That the product is not FDA-approved and no premarketing testing is required.
Supplements?
What is St. John's Wort widely used to treat?
Depression.
For what severity of depression has St. John's Wort been shown to be effective in clinical studies?
Mild to moderate depression, but not severe depression.
How does St. John's Wort interact with other drugs?
t interacts adversely with many drugs by inducing (increasing the activity of) cytochrome P450 enzymes and P-glycoprotein.
What other common drug effect can St. John's Wort intensify?
It can intensify the effects of serotonin.
A patient with cancer is receiving morphine for pain control. The patient calls
the nurse to report that the morphine is no longer controlling his pain. What
is the most appropriate response by the nurse?
A. “Increasing the dose of morphine will make you so sleepy that you will
not be able to function.”
B. “This means that you have developed a psychologic addiction to
morphine.”
C. “You have developed a tolerance to morphine and will need a higher
dose.”
D. “It is recommended that we wait to increase the morphine until the pain
is more severe.”
33
C
A patient was discharged from the hospital with instructions to take an
antibiotic for 7 days to treat a bladder infection. Twelve days later, a
home care nurse visits the patient and finds that the symptoms have
not resolved. What is the most important question for the nurse to ask?
A. “Do you think you have another bladder infection?”
B. “Have you taken all of the antibiotics as directed?”
C. “How much water have you been drinking each day?”
D. “What antibiotic do you usually take to treat an infection?”
35
B
A patient is taking a Category A drug during pregnancy.
Which statement by the nurse is accurate?
A. “The risk of harm to the fetus is remote.”
B. “The drug is safe to take during pregnancy.”
C. “This drug has caused congenital birth defects.”
D. “No controlled studies of this drug have been done in
humans.”
A
A patient who is breastfeeding her newborn infant is prescribed an
antibiotic to take after discharge. Which statement should the nurse
include when providing discharge instructions?
A. “Drink plenty of fluids to dilute the drug in your breast milk.”
B. “Take the drug at night with a full glass of water.”
C. “Pump your breasts and then discard all of the milk.”
D. “Take the antibiotic immediately after breastfeeding.”
39
D
A toddler has been prescribed a medication that does not have an
established pediatric dose. To calculate the appropriate dose for the
child, what information should the nurse consider?
A. The child’s weight is 26 pounds.
B. The child’s height is 32 inches.
C. The child’s body surface area is 0.52 kg/m 2.
D. The child’s age is 24 months.
41
C
The nurse is assessing an 82-year-old patient before the administration
of medications. Which laboratory result would provide the best index
of this patient’s renal function?
A. Serum creatinine
B. Blood urea nitrogen
C. Urinalysis
D. Creatinine clearance
43
D
Which statement about St. John’s wort does the nurse identify as true?
A. St. John’s wort is often used in combination with other
antidepressants for a more rapid response to treatment.
B. Use of St. John’s wort in patients taking digoxin results in increased
digoxin levels.
C. St. John’s wort has been found to be effective in the treatment of
severe depression.
D. Serotonin syndrome is a potential adverse effect of therapy with St.
John’s wort.
45
D
An older adult patient frequently forgets to take an oral medication
that has been prescribed to be taken 3 times a day. Which action by
the nurse is best?
A. Assess the patient’s ability to swallow the medication.
B. Arrange for a neighbor to call the patient 3 times a day.
C. Call the prescriber for a sustained-release form of the drug.
D. Give the patient verbal and written instructions about the drug.
47
C