Atoms AND History of Atoms.
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Democritus
Greek Philosopher who said they were small, hard particles that were all made of the same material but were different shapes and sizes. this piece is' ‘indivisible’. He also said the atom was a solid sphere with nothing new inside.

Dalton
He deduced that all elements are composed of atoms. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike. Atoms of different elements are different. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements.

Thompson
Atoms were made from positively charged substances with negatively charged electrons scattered about, like raisins in a pudding. This model is known as the "plum pudding model."
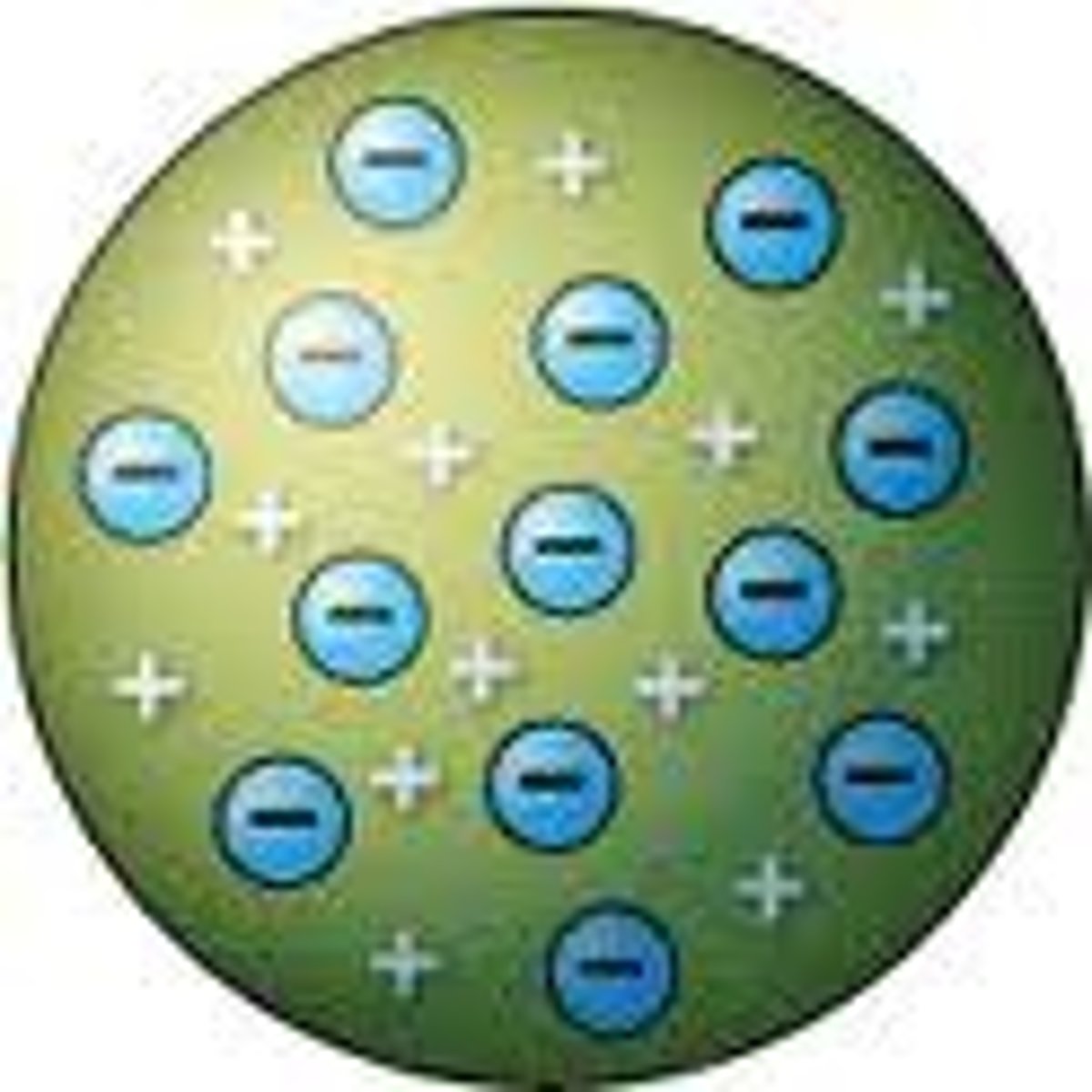
Rutherford
An English physicists reasoned that all atoms are positively charged particles contained in the nucleus. He also said that negatively charged particles were scattered outside the nucleus around the atom’s edge.
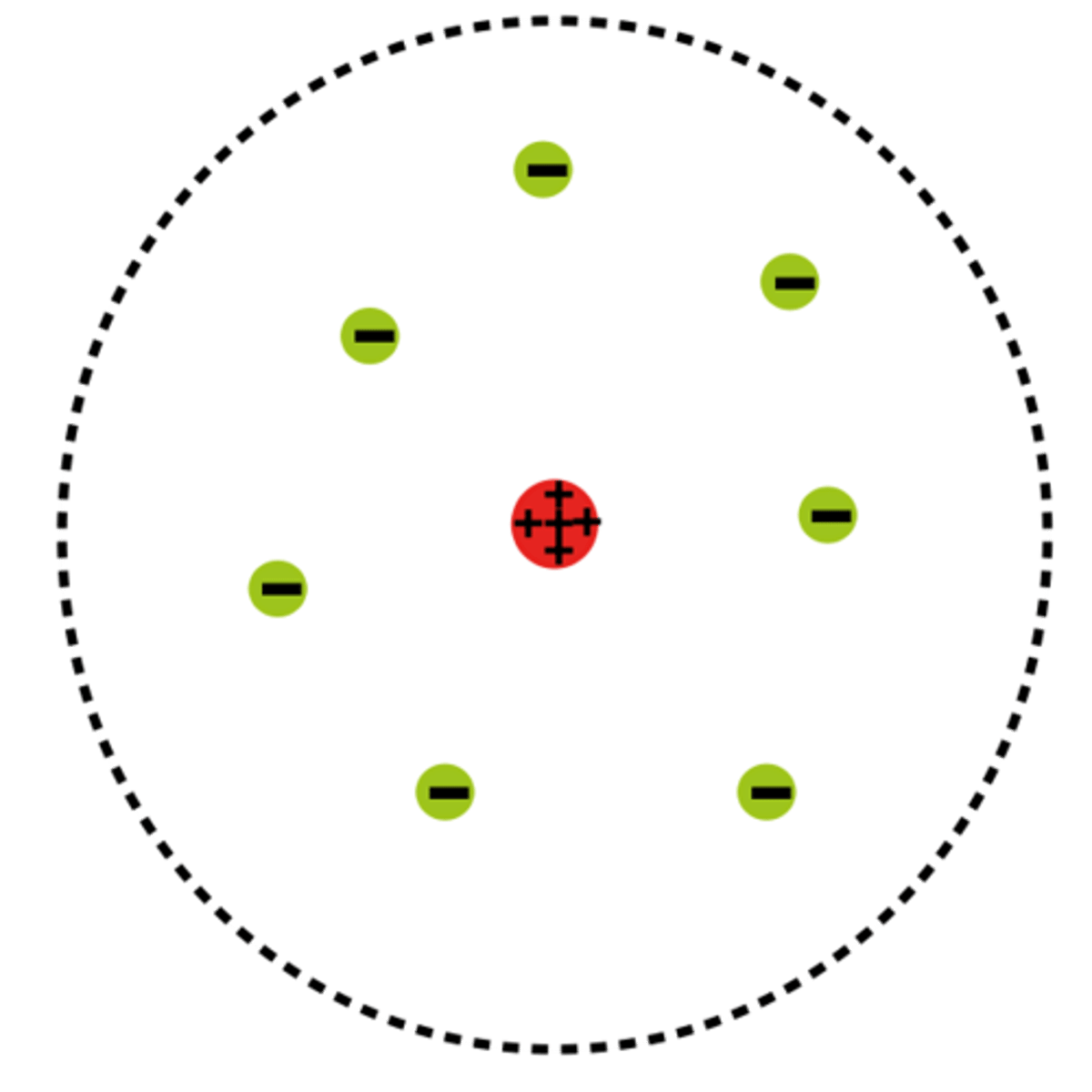
Bohr
Believed that the small positively charged nucleus was orbited by electrons like planets around the sun. It was a two-dimensional model. The fixed energies the electrons have are called energy levels.
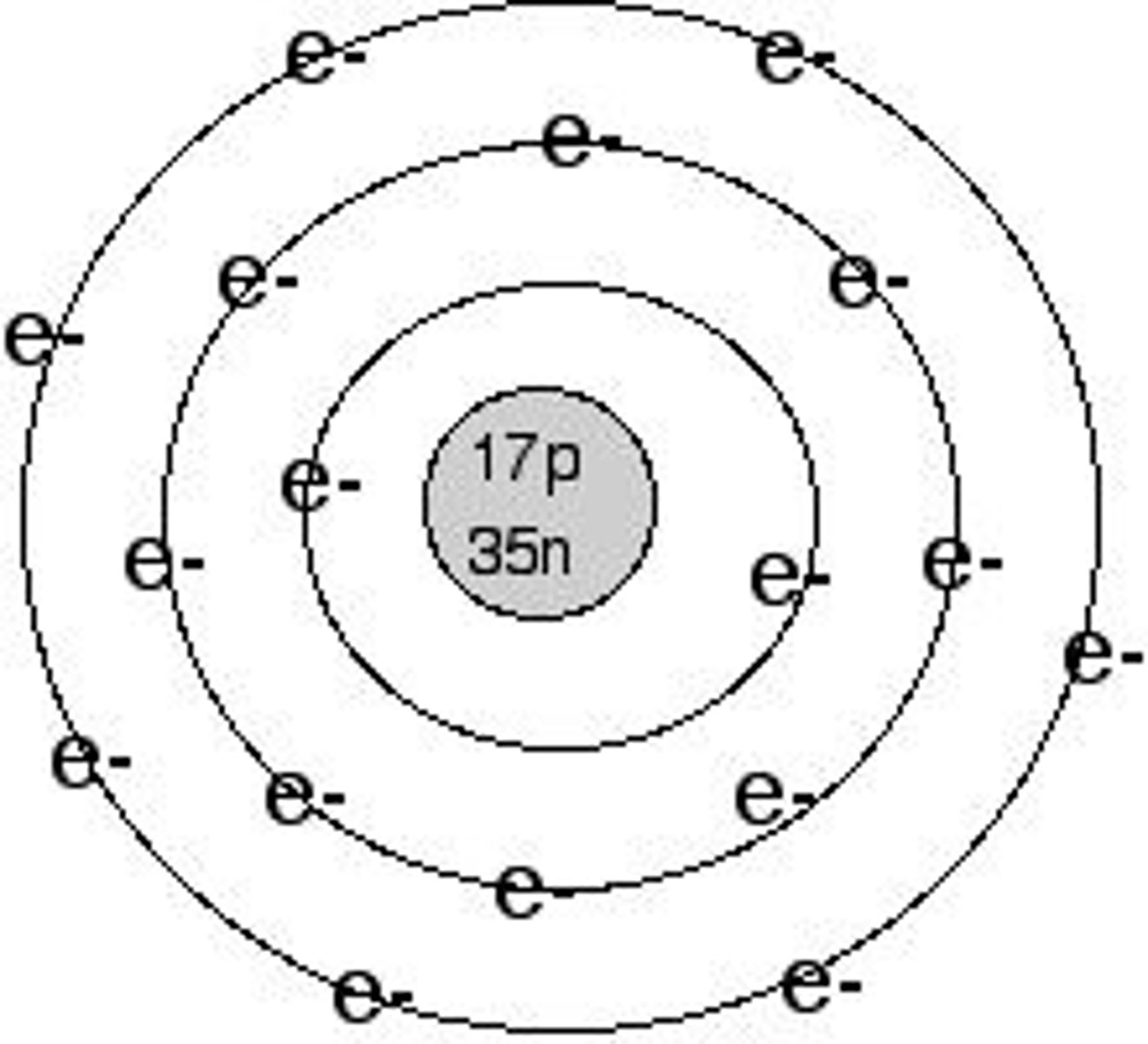
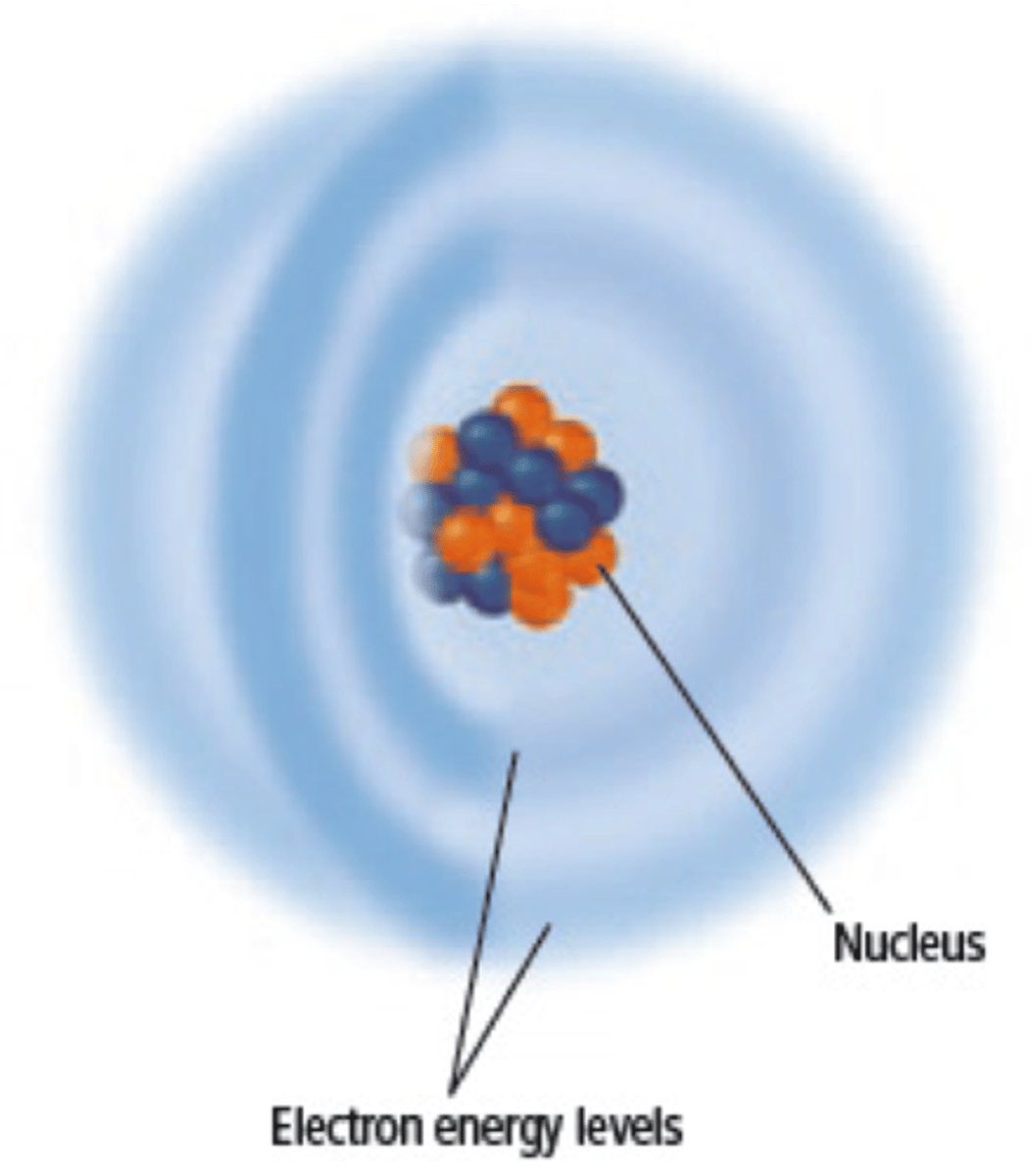
Modern Model
Small Positively charged nucleus is orbited by electrons that are travelling in 3 dimensional orbits.
Order of Atomic Philosophers
Democritus, Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford, Bohr, Modern Model
Nucleus
Small, Holds Protons and Neutrons
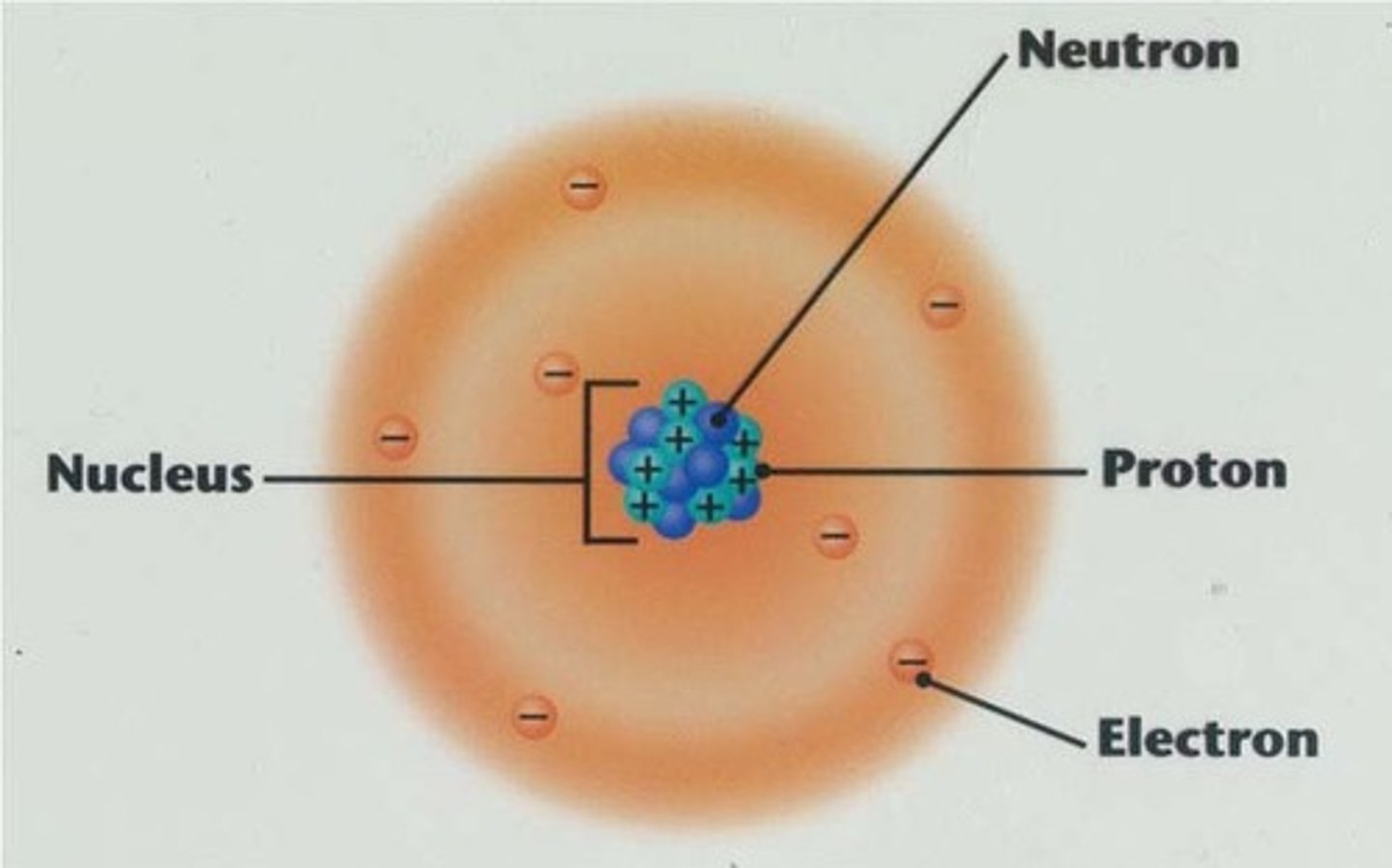
Electron Cloud
Big, Holds Electrons

Mass of a proton
1 amu

Mass of a Neutron
1 amu

Mass of an Electron
.00001 amu

Where is most of the mass in the atom?
Nucleus
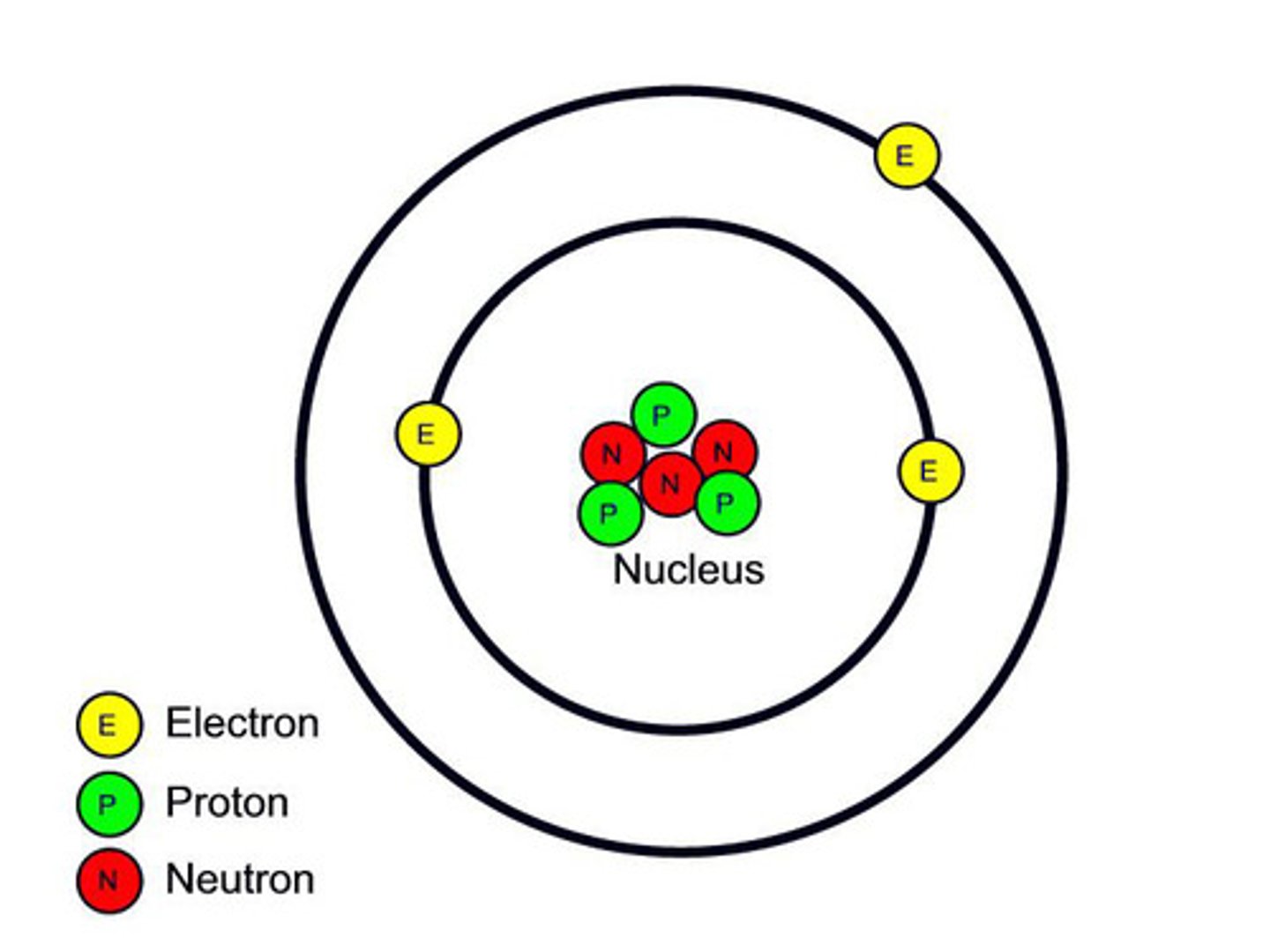
What two subatomic particles are the same size?
Protons and Neutrons
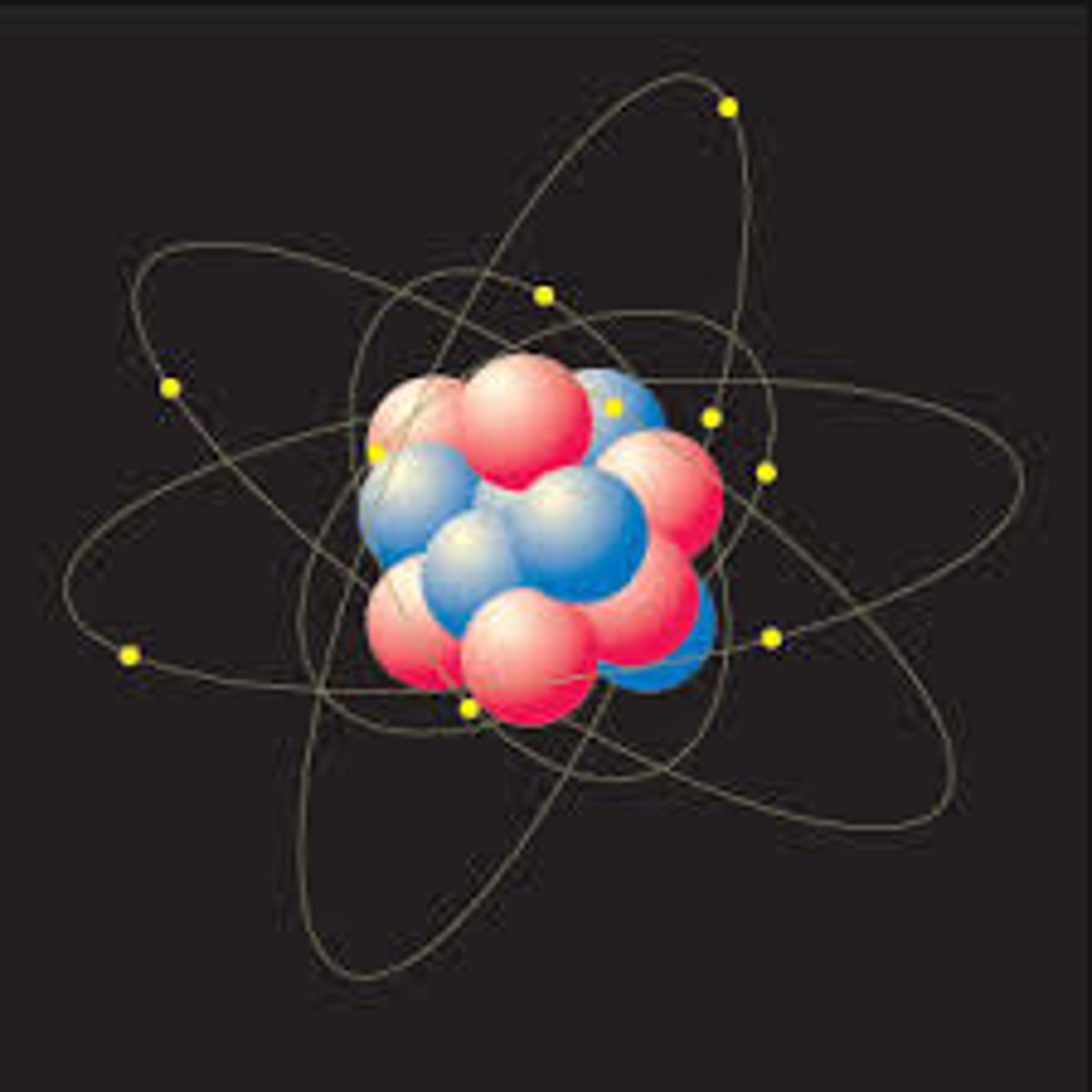
Charge of a Proton
Positive
Democritus
He named the smallest piece of matter: ATOMOS meaning ‘‘not to be cut’’.
Arnold Sommerfield
German Physicist, modified Bohr’s atomic theory to include ‘elliptical orbits’. Electrons are moving around the nucleus. Assumed that orbits doesn’t have to be spherical but can also be elliptical.
Erwin Schrodinger
Physicist and a Biologist, was considered the "‘Father of Quantom Mechanics”. His atomic model is based on the' ‘principle of wave mechanics’
-A space in which electrons are likely to be found.
-Electrons whirl about the nucleus billions of times in one second
-They are not moving around in random patterns.
-Location of electrons depends on how much energy the electron has.
Louis de Broglie, Erwin Schrodinger and Werner Heisenberg
The physicists that led the development of a better model of the atom.
Eugen Goldstein
He discovered the idea about the positively charged particle called ‘proton’.
A cloud of negative charge
An electron is imagined to be ____________________ having a certain geometrical shape.
Electron configuration
The way in which electrons are distributed in the different orbitals around the nucleus of an atom is called ________. Filling of electrons start from lower energy level to highest level.
Atom
-The smallest particle of an element.
-The smallest amount of an substance that can take part in any chemical reaction.
S- Spherical
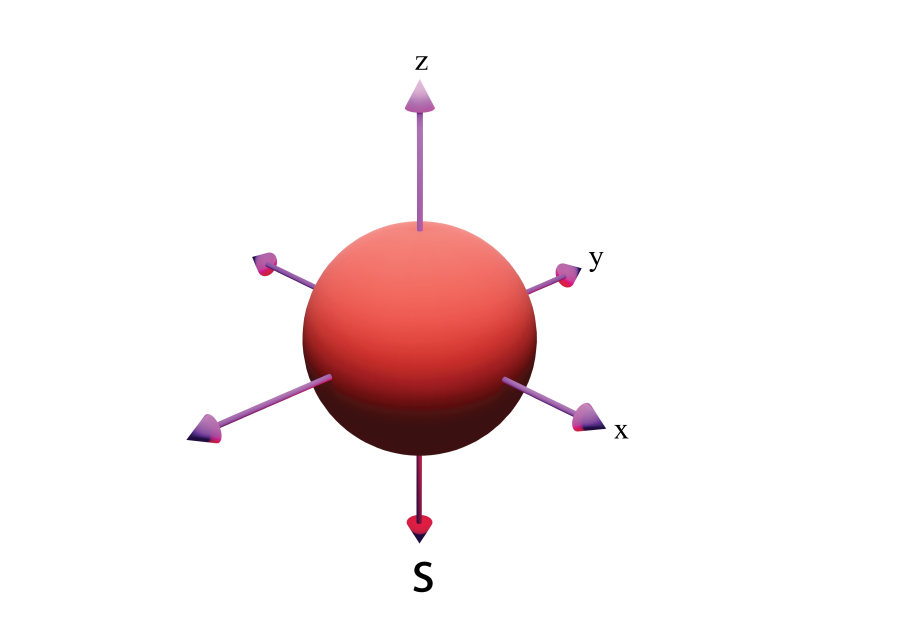
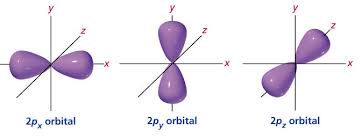
P -Dumbell
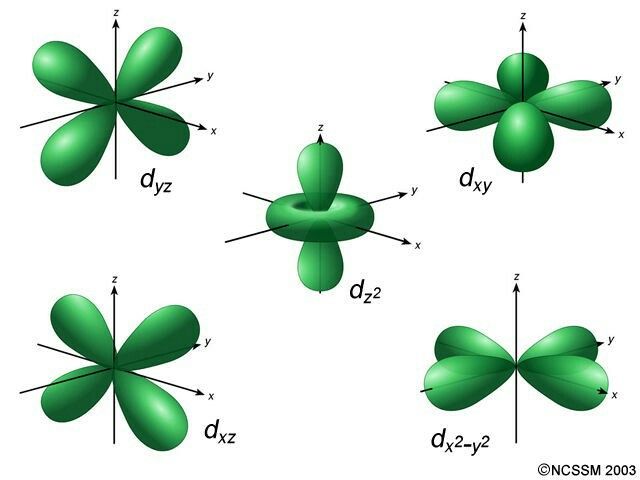
D- Cloverleaf
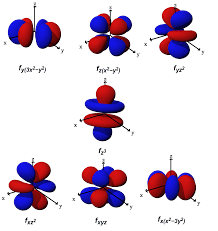
F- Complex
1 orbital
s (Spherical)
3 orbitals
P (Dumbell)
5 orbitals
d (Cloverleaf)
7 orbitals
f (complex)
s,p,d,f
These sublevels define the orbital shape