M6 | Requirements Engineering
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Statements that describe what the software system should be, but not how it is to be constructed.
Requirements
Describe the user’s needs and desires for a software system.
Requirements
Must be clearly and fully understood by the software engineers who develop the system.
Requirements
In software engineering, this distinguishes the “what” from the “how.”
Requirements
A set of activities related to the development and agreement of the final set of requirement specifications.
Requirements Engineering (RE)
One of the top reasons for software project failures.
Incomplete requirement specifications
One of the important reasons for software project success.
Clear requirement statements
Which activities are typically involved in requirements engineering for a software project?
Elicitation, Documentation and Definition, Specification, Prototyping, Analysis, Review and Validation, Agreement and Acceptance
Are all requirements engineering activities needed to the same degree for all software projects?
No
Which emerging task is considered key in software development, regardless of the process model?
Managing requirements and user involvement
The first step of requirements engineering.
Ensure all preparations are made and plan the requirements engineering activities
Who must understand and agree to the requirements engineering process?
Both the requirements solicitors and the providers
Requirements engineering processes can follow which approaches?
Agile and flexible, or traditional and rigorous
The first step in requirements engineering.
Put together a plan for requirements engineering
What should a requirements engineering plan include?
Process to be used, resources needed, schedule for completing the requirements activities
How long can it take to develop a requirements engineering plan depending on the project size and complexity?
Several hours to several days or weeks
For large software projects, why is the preparation effort for requirements engineering important?
It satisfies the entrance criteria for RE activities and is vital to the success of the rest of the project
When does the requirements engineering (RE) process commence?
Once the preparation for requirements engineering is completed
What is true about the steps within requirements engineering?
There are many different steps
Why is it essential that the planned RE steps are clear to all participants?
To ensure everyone understands and follows the agreed-upon process
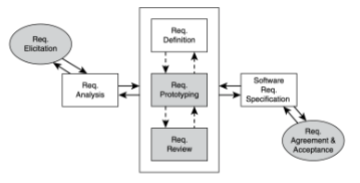
What does this diagram represent?
Requirements Engineering Process
The first step in the requirements engineering process, where requirements analysts gather information from users and customers.
Elicitation
During which step are gathered requirements checked for accuracy, conflicts, categorized, and prioritized?
Analysis
Who performs the elicitation and gathering of requirements from users and customers?
Requirements analysts
Why is there usually little opportunity to go back from requirements analysis to elicitation?
Because users who provide requirements information are scarcely available
After requirements analysis, the material is processed through which three potential sub-activities?
Requirements definition and documentation, requirements prototyping, requirements review
What do the last two steps of requirements engineering lead to?
Finalization of the Software Requirements Specification (SRS) and other technical documentation
What happens to project costs if requirements engineering is not performed?
Costs increase
Without documented requirements, what becomes difficult to base testing on?
Requirements
What problem occurs when there are no agreed-upon requirements?
Feature creep or scope creep cannot be controlled
Why is project schedule and cost hard to manage without clear requirements?
Because there are no documented requirements to guide planning
The process of finding out what the user or client actually needs for the software project.
Requirements Elicitation
Where do many software engineers typically start their careers?
Coding, designing, or testing a software system
From which background do the majority of requirements analysts typically come?
Business side, with good industry domain knowledge and communication skills
Besides business-side professionals, which other group often progresses to the role of requirements analyst?
Experienced user/customer support personnel
What two skills are important for eliciting user requirements?
Communication skills and industry domain knowledge
Why are strong communication skills essential in requirements elicitation?
Because users/customers do not always know how to state their needs
At the high level of requirements elicitation, what must the analyst do?
Probe and understand the business rationale and justification for the software/project
At the low level of requirements elicitation, what must the analyst do?
Elicit and gather the specific details of the users’ needs and desires
Requirements elicitation operates at which two levels?
High level (business rationale/justification) and low level (user needs and desires)
What do high-level requirements help establish before eliciting detailed functional requirements?
Proper customer expectations
How do high-level requirements support the software project?
They facilitate high-level scoping and direct attention to the proper business area
What do high-level requirements typically include?
A list of major functionality the customer perceives the new software will deliver
After gathering high-level requirements, what must be elicited next?
Detailed requirements
For a new software system, how many main categories of information must detailed requirements address?
Six
When a software system already exists, what do users often base their requirements discussion on?
Requirements in the currently existing system
After requirements are elicited and collected, why must they still be analyzed?
Because they are still just an unorganized set of data
What are the two main tasks of requirements analysis?
Categorizing (clustering) the requirements and prioritizing the requirements
In requirements analysis, why must each requirement be labeled?
So it is uniquely identifiable and traceable
What can be used to help identify each category of requirements?
Prefixes
In addition to priority, what may guide the natural clustering of requirements?
The six dimensions of requirements
What tool can be used during requirements analysis to describe system behavior?
Use Cases (UCs)
What are use cases (UCs)?
A sequence of actions that a system should perform within the business flow context of the user or actor
What type of use cases are used to describe system requirements in object-oriented contexts?
Object-Oriented Use Cases (OO UCs)
In use case modeling, what does the term "actors" refer to?
All external interfaces with the system
Which requirements analysis method is based on the understanding that different stakeholders view requirements differently?
Viewpoint-Oriented Requirements Definition (VORD)
In VORD, why might a financial stakeholder provide different requirements than an HR stakeholder?
Because requirements are expressed in the lingo and emphasis of each stakeholder’s domain
What is the first step of the VORD methodology?
Identify the stakeholders and the viewpoints
In VORD, which step involves eliminating duplication and grouping common viewpoints?
Structure and categorize the viewpoints
Which step of VORD focuses on refining and recording the identified viewpoints?
Document and refine the identified viewpoints
In VORD, what is the final step where viewpoints are connected to the system and its services?I
Map the viewpoints to the system and the services it is to provide
Why is prioritization of requirements necessary in software projects?
Because not all identified requirements can be developed and delivered due to constraints
Which of the following are common constraints that limit the development and delivery of all requirements?
Limited resources, limited time, limited technical capabilities
Which of the following is NOT typically a criterion for establishing requirements priority?
Developer’s personal preference
Which criteria for prioritizing requirements focus on market and competitive advantage?
Competition/current market condition and immediate sales advantage
Fixing urgent issues in the existing product is an example of which requirement prioritization criterion?
Critical problems in the existing product
What is the most significant reason to ensure requirements are traceable?
To track back after development and verify that all requirements have been developed, tested, packaged, and delivered
Why is it important to account for anything extra in a project that cannot be traced back to requirements?
To ensure that only agreed-upon requirements are included
What does backward from traceability mean?
Links the software requirement to the document source or person who created it
What does forward from traceability mean?
Links the requirement to design and implementation
What does backward to traceability mean?
Links design and implementation back to the requirements
What does forward to traceability mean?
Links documents preceding the requirements to the requirements
What two things are also important to ensure requirements are traceable?
Linking related requirements + unique identification of requirements
What are the three central activities in a requirements engineering process?
Requirements definition, prototyping, and review
What does requirements definition involve?
Formally spelling out the requirements
What is the most popular notation for representing requirements in the industry?
UML
Examples of notations used for requirements definition include:
I/O diagrams, Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs), Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERDs)
How are requirements often prototyped?
With heavy user participation
What activity is closely related to requirements definition and prototyping?
Review of requirements with users and customers
How can requirements reviews be conducted?
Informally and frequently (Agile) or formally
After requirements have been analyzed and reviewed, where should they be formally recorded?
Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document
What is the last step of requirements engineering?
Requirements Agreement or “sign-off”
Once the SRS is agreed upon, how should future changes be handled?
Controlled or monitored
What is Requirements Engineering (RE)?
A set of activities related to the development and agreement of the final set of requirement specifications
Which steps are involved in the RE process?
Elicitation, documentation and definition, specification, prototyping, analysis, review and validation, agreement and acceptance
Which notations are commonly used in documenting requirements?
Use Cases (UCs), I/O Diagrams (IODs), Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs), Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERDs)
What is the output of the RE process?
Software Requirements Specification (SRS)