CC LEC LIPIDS AND LIPOPROTEINS
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
Lipids
commonly referred as fats are a rich source of energy and efficient way for storage of excess calories
Steroid hormones
Lipids are also a source of what type of hormones?
Fatty acids
building blocks of lipids
Free or unesterified
Fatty acids may exist as ____________________ form in the plasma
Albumin
Where is fatty acids mostly bound to?
Saturated fatty acids
FA w/ no double bonds
Unsaturated
FA with double bonds
Triglycerides
the main storage form of lipid in the body
composed of 3 molecules of FA and a glycerol backbone
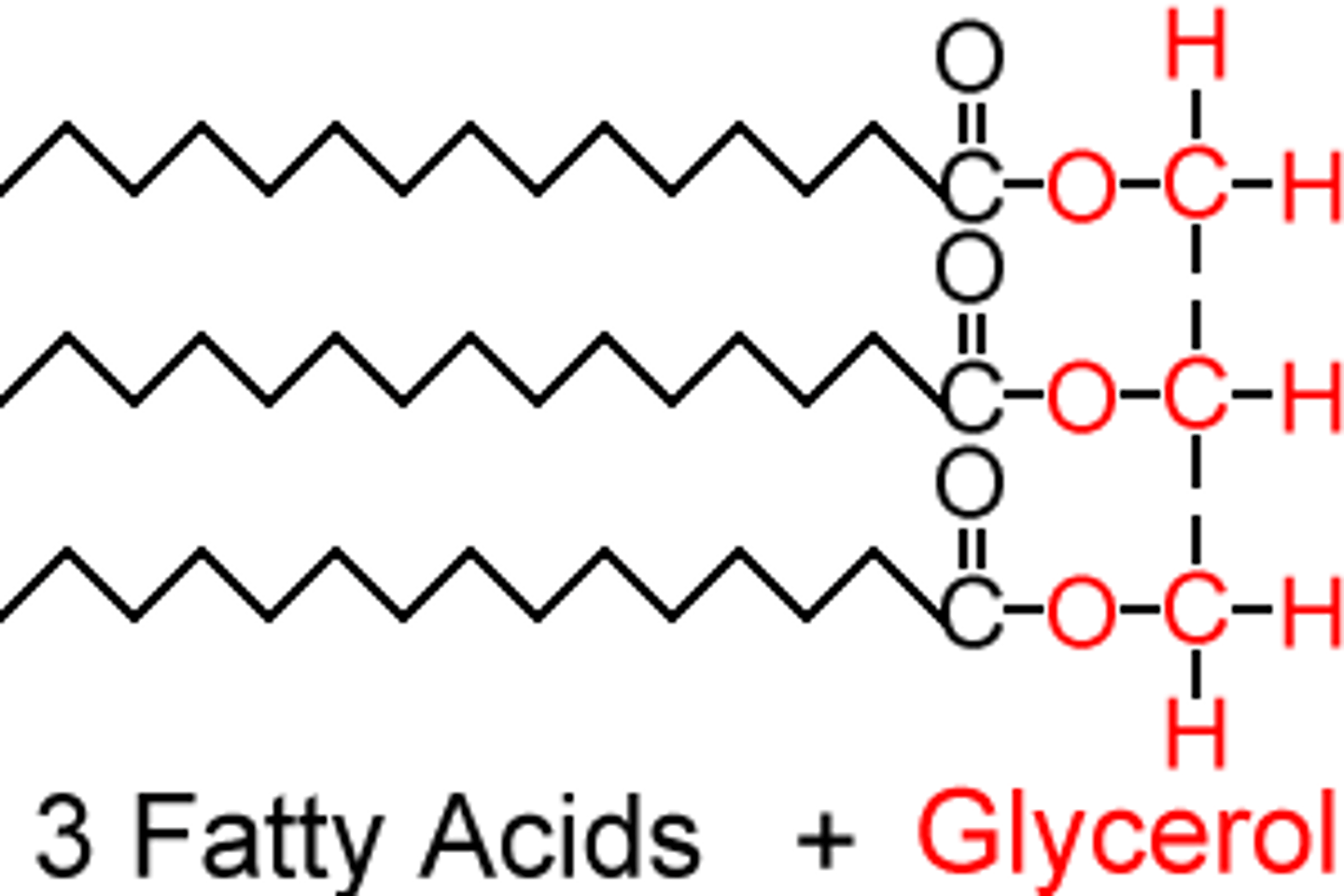
triacylglycerol
other name of triglycerides, abbreviated as TAG
Saturated triglycerides
fats coming from animal sources, solid @ room temp
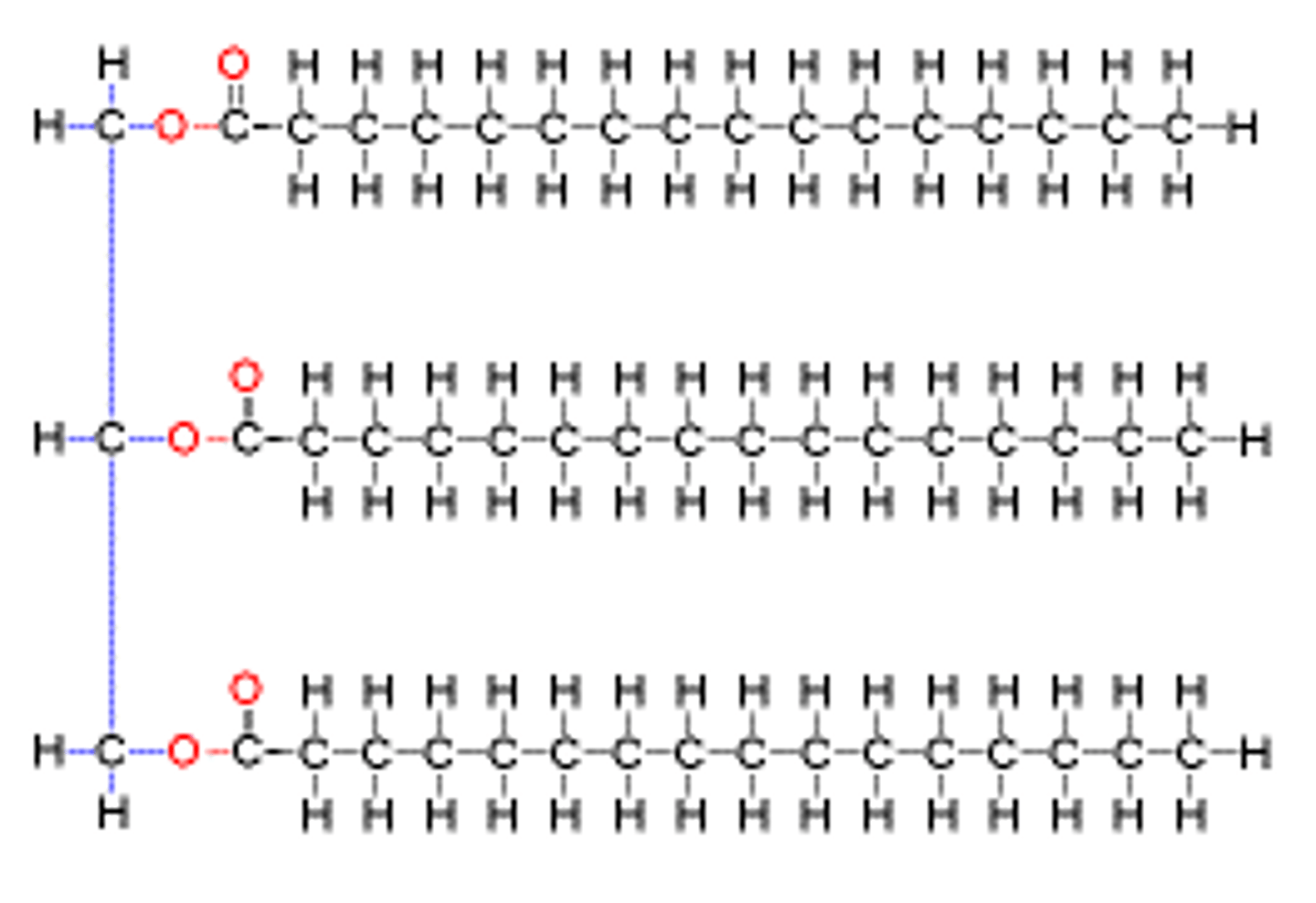
Unsaturated triglycerides
oils, coming from plant sources, liquid @ room temp
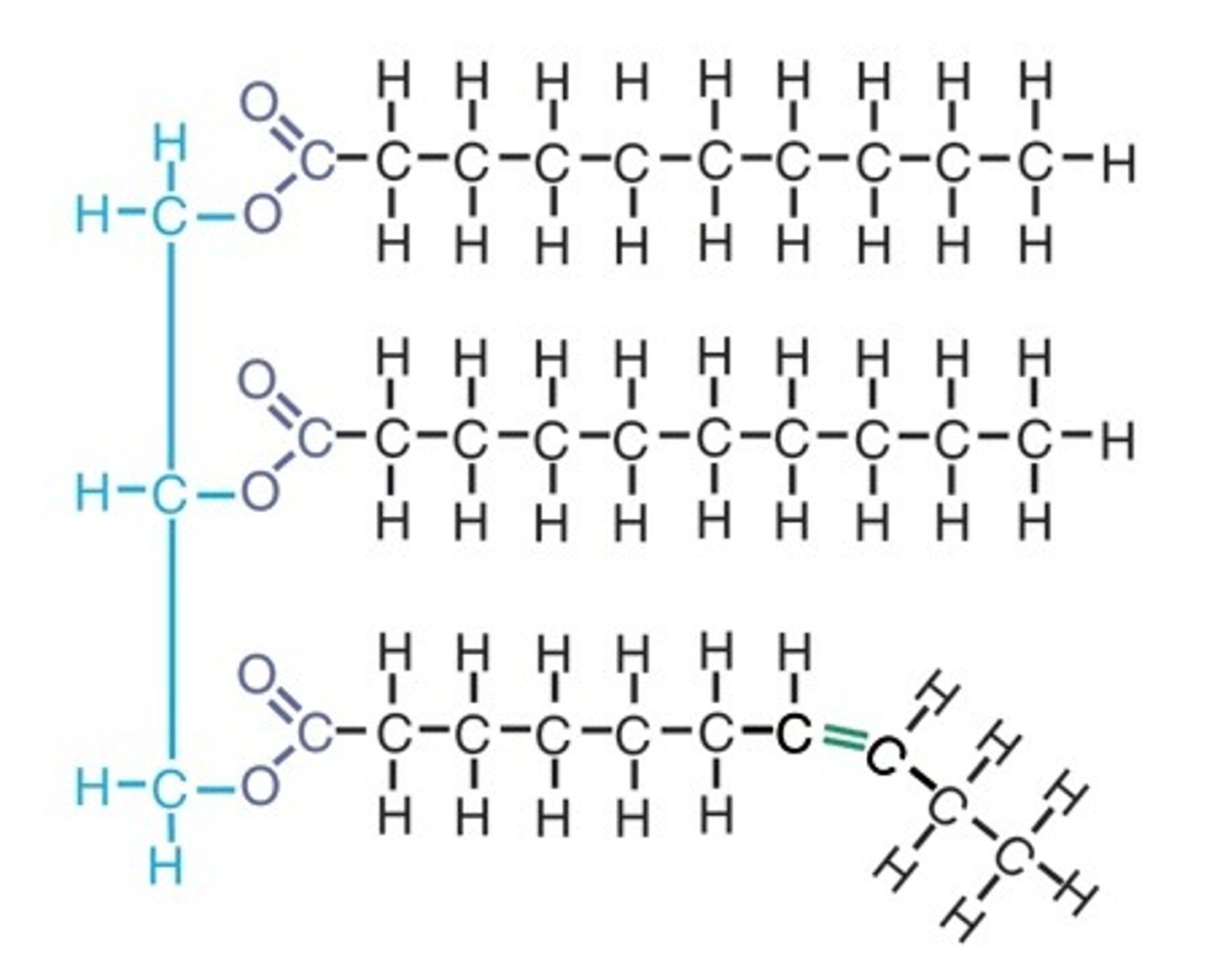
Trans fats
unsaturated fat that behaves as saturated TAG
Phospholipids
composed of fatty acids and a phospholipid head group
major membrane lipid
surfactants
Surfactants
measured to know if the lungs are matured
Hydrophilic head
phosphate head
Hydrophobic tail
fatty acid tail
Cholesterol
not readily metabolized by most cells, not a source of fuel
precursor of steroid hormones, bile acid, and vitamin D
Cholesterol esters
cholesterol + fatty acid
Free cholesterol
cholesterol not attached to FA
Lipoprotein
bonding of molecules of fat and protein
Membrane
Phospholipids and cholesterol are found on the ___________ of lipoproteins
Core
Triglycerides and cholesteryl ester are found in the ___________ of lipoproteins
Apolipoproteins
"identification marker" of lipoproteins
Chylomicrons
VLDL
LDL
HDL
What are the 4 major types of lipoproteins?
Chylomicrons
What is the largest yet least dense lipoproteins?
Exogenous triglycerides
Chylomicrons transport what type of triglycerides?
Very low-density lipoproteins
Pre-B lipoprotein
Endogenous triglycerides
VLDL transports what type of triglycerides?
Liver
This organ is also capable of producing VLDL to be transported to the peripheral tissues
Low-density lipoprotein
Beta lipoprotein
Major transport protein of cholesterol and depositing them to peripheral cells
Bad cholesterol
Atherosclerosis
Coronary heart diseases
In LDL, plasma level is directly proportional to risk of which diseases? (2)
High-density lipoprotein
smallest yet most dense
Alpha lipoprotein
Reverse cholesterol transport
Good cholesterol
Size
Triglyceride levels correlates with the lipoprotein's:
Density
Protein levels correlates with the lipoprotein's:
Apo A-1
main distribution is in the HDL
Function: Activates LCAT with esterifies cholesterol
Apo B-100
main distribution is in the VLDL and LDL
Function: Carboxy-terminal recognition signal targets LDL to the LDL receptor
Apo B-48
main distribution is in the chylomicron
Function: not recognized by LDL receptor
Apo C-II
main distribution is in the chylomicron and VLDL
Function: Lipoprotein activator
Apo C-III
Main distribution is in VLDL and HDL
Function: Lipoprotein lipase inhibitor
Apo E-4
Main distribution CM, VLDL, IDL, Remnants, and HDL
Is associated with high LDL-C, higher risk of atherosclerosis and Alzheimer's disease
Apo E-2
Associated with type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia
Intermediate density lipoprotein
Lipoprotein A
2 minor lipoproteins
Intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL)
intermediate between VLDL and LDL
increased in patients with type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia
VLDL remnant
other name for IDL
Lipoprotein A
interferes with normal thrombosis
LDL density range
In ultracentrifugation, Lp(a) is found in the:
VLDL in electrophoresis
In electrophoresis, Lp(a) migrates with:
Sinking pre-Beta lipoprotein
Other name for Lp(a)
Lipoprotein X
Beta-VLDL
Abnormal lipoproteins (2)
Lipoprotein X
found in patients with obstructive biliary disease
abnormal lipoprotein rich in unesterified cholesterol and phospholipids
Lipoprotein X
Cathodal lipoprotein (migrates to cathode in electrophoresis)
Beta-VLDL
more cholesterol than TAG
VLDL density range
In ultracentrifugation, B-VLDL is found in what density range?
LDL in electrophoresis
B-VLDL migrates with _______ in electrophoresis
Floating Beta-lipoprotein
Other name for Beta VLDL
Lipoprotein lipase
responsible for hydrolysis of TAG in lipoproteins
ATP-binding cassette protein
responsible for efflux of cholesterol from peripheral cells into HDL
Lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase
catalyzes the esterification of cholesterol (HDL) by promoting transfer of fatty acids from lecithin to cholesterol
Cholesterol ester transport protein
transfer cholesterol ester from HDL to Apo B-100 - containing lipoproteins (VLDL and LDL) in exchange for TAG
Phospholipid transport protein
transfer of phospholipid to and from HDL, important for HDL growth and remodeling
LDL-receptor
binds ApoE and ApoB100 and mediates endocytosis of lipoproteins
Lipid absorption pathway
Exogenous pathway
Endogenous pathway
Reverse cholesterol transport pathway
4 major pathways of lipids (LEER)
Lipid absorption pathway
- Lipids from diet converted into simple forms to be absorbed
- Those lipids that are absorbed are packaged into chylomicrons
What pathway?
Exogenous pathway
Chylomicrons packaged from lipids absorbed during lipid absorption pathway, will first shrink into CM remnants first before being accepted by the liver
What pathway?
Endogenous pathway
- Lipids produced by the liver are packaged into VLDL
- VLDL will tend to go to the peripheral tissues
- On the way to the peripheral tissues, it is attacked by LPL and becomes IDL
-IDL eventually becomes LDL
-LDL will now be transported to the peripheral tissues
What pathway?
Reverse cholesterol transport pathway
- Once HDL is formed it goes back to the liver
What pathway?
Chromatographic methods
Immunochemical methods
Electrophoresis
Ultracentrifugation
4 methods of lipoprotein assay (CIEU)
Chromatographic methods
using gel chromatograph affinity
Immunochemical methods
utilize antibodies directed towards specific apoproteins
Electrophoresis
separates lipoproteins based on their electric charge followed by staining using fat stains
Ultracentrifugation
THE reference method for lipoprotein assay
separates lipoproteins based on their densities
Amido black B
fat stain
1. HDL
2. LDL
3. VLDL
4. Chylomicrons
In ultracentrifugation, order the 4 lipoproteins from densest to least dense
Chemical and enzymatic
2 methods of cholesterol determination
Extraction
Saponification
Purification
Colorimetry
4 chemical methods for cholesterol determination
Extraction
removal of cholesterol from proteins using organic solvents
Saponification
hydrolysis of cholesterol esters to FA and free cholesterol using alcohol KOH
Purification
precipitation of free cholesterol using digitonin
Colorimetry
formation of colored product
Colorimetry only. Protein, chromogen, and color differences are interferences.
1 step approach, what is done and what are its interferences?
Extraction and colorimetry. Chromogen and color differences are the only interferences.
2 step approach, what is done and what are its interferences?
Extraction, saponification, and colorimetry. Partially removed chromogen interferences.
3 step approach, what is done and what are its interferences?
Extraction, Saponification, Purification, Colorimetry done. All interferences removed.
4 step approach, what is done and what are its interferences?
Liebermann-Burchardt reaction
Salkowski reaction
2 colorimetry methods
Liebermann-Burchardt method
acetic anhydride + sulfuric acid = cholestadienyl monosulfonic acid (GREEN)
simple method of cholesterol determination
Salkowski method
Ferric iron + sulfuric acid = cholestadienyl disulfonic acid
(RED)
Green
Liebermann-Burchardt end product color
Red
Salkowski method end product color
Cholesterol esterase
Cholesterol ester + H2O = Cholesterol + fatty acid
What enzyme catalyzes this reaction?
The first enzyme of the enzymatic method of cholesterol determination
Cholesterol oxidase and Cholest-4-en-3-one
Cholesterol + O2 = Cholest-4-en-3-one + H2O2
What enzyme catalyzes this reaction and what can already be measured here?
Peroxidase and Quinoneimine dye
H2O2 + Phenol + 4-aminoantipyrine = Quinoneimine dye + H2O
What is the enzyme and what is being measured here?
500nm
Quinoneimine dye absorbance
240nm
Cholest-4-en-3-one absorbance
Polarographic method
measures amount of oxygen produced when H2O2 is reacted with peroxidase
Extraction
Saponification
Oxidation
Colorimetry
4 chemical methods for TAG determination
Extraction
removal of lipids from proteins using organic solvents
Saponification
TAG cleaved to FA and glycerol using alcoholic KOH
Oxidation
Glycerol converted to a measurable compound (formaldehyde) using sodium periodate
Formaldehyde
In colorimetry method for TAG determination, what is being measured?
Hantzch method
Acetyl acetone and ammonia (TAG determination)