OB exam 2
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
What is a normal fontanel?
soft spot, posterior and anterior diamond shaped
Right Occipitoposterior (ROP)
baby leaning right on moms pelvis facing up
Left Occipitoposterior (LOP)
baby leaning left on moms pelvis, facing up
Right Occipitotransverse (ROT)
presentation of the fetal occiput transverse to the mothers right
Left Occipitotransverse (LOT)
presentation of fetal occiput transverse to the mothers left
Right Occipitoanterior (ROA)
baby leaning right on moms pelvis facing moms back
Left Occipitoanterior (LOA)
baby leaning left on moms pelvis facing moms back
MOST COMMON
PT teaching on fontanels
close within 18mo to yr,
Why do infants have fontanels?
help the baby get through the birth canal
Definition of true labor
cervial dilation
Signs of Labor
cervical change
backache
weight loss (1-3.5)
lightening (feeling fetus “drop” fetus descends into pelvis)
contractions
inc vaginal discharge or bloody show
energy burst
n/v and indigestion
cervix becomes soft, partially effaced, begin to dilate
rupture of membrane (cnxt start about 24hrs after)
SVE interpretation
dilated, effacement, station
Effacement
how much the cervix has thinned out
Station
how far fingers in touch baby (-5 to +5, +4 is on the floor)
1st stage of labor
onset of contractions of to full dilation
2nd stage of labor
full dilation to birth
Contractions during first stage of labor (latent)?
irregular, mild to moderate
occurs every 5-30 min
lasts 30.45 secs
First stages of labor (active)?
rapid dilation and effacement
some fetal descent
feelings of helplessness
anxiety, restlessness inc as contractions become stronger
How many cm dilated is the pt in the first stage of labor (active)?
4-7cm
3rd stage of labor
baby delivery to placenta delivery
schultze and duncan presentation
Schultze presentation
shiny fetal surface of placenta emerges first (clean)
Duncan presentation
dull maternal surface of placenta emerges second (dirty)
Contractions during the first stage of labor (active)?
more regular
every 3-5 min
lasting 40-70 sec
How many cm dilated is the pt in the first stage of labor (transition)?
8-10cm
Contractions during the first stage of labor (transition)
strong to very strong
every 2-3min
lasts 45-90sec
First stage of labor (transition)
complete dilation
tired, restless, irritable
feeling out of control, pt states “cannot continue”
n / v
urge to push
inc rectal pressure and feelings of having a bowel movement
inc blood show
most difficult part of labor
4th stage of labor
postpartum (of both baby and placenta), 2 hrs post delivery of placenta
maternal stabilization of vitals
lochia scant to moderate rubra
Which stage of labor does the spontaneous rupture of membrane happen?
transition
What happens if the ROM lasts greater than 24hrs (only water broke no baby)?
infection
5 P’s of labor
Passenger
Power
Passaway
Position
Psychologic response
Occitput Presentation
back of head
Chin presentation
mentum
Shoulder presentation
scapula
Breech presenation
sacrum or feet
Normal assessment of labor
Types of anesthesia
epidural
spinal anesthesia
local
general
pudendal nerve block
combined epidural spinal
nitrous oxide
Epidural and spinal blocks contraindications
low platelets/coagulopathies, current infection, maternal behavior
Complications of anesthesia
spinal headache from leakage of CSF
Interventions of anesthesia
bloodpatch for spinal headahce
Maternal effects of IV pain meds
Infant effects of maternal pain meds
can cause respiratory depression
What should a nurse do IMMEDIATELY after ROM happens?
assess FHS (110-160) for abrupt declaration, indicates fetal distress to rule out umbilical cord prolapse
How should the amniotic fluid look after the ROM happens?
waterly, clear, slightly yellow tinge
no foul order
700-1000 mL
How should you confirm that amniotic fluid is present and not urine?
nitrazine paper (6.5-7 pH)
Amnioinfusion
infusion of room temperature isotonic fluid into the uterine cavity to increase fluid around the cord & prevent compression during uterine contractions
Indications for an amnioinfusion
oligohydramnios
fetal cord compression
Oligohydramnios
scant amount or absence of amniotic fluid
What is oligohydramnios caused by? e
uteroplacental insufficency
PROM
postmaturity of fetus
What device is used to infuse for an amnioinfusion?
IUPC
How does an amnioinfusion help?
reduces the severity of variable decels caused by cord compression
Maternal hypotension
placenta cant perfuse oxygen
FHR variability
Early decels
onset at beginning of contraction
Late decels
happen at peak of contractions (late recovery)
Variable decels
sudden drop, rapid return
Prolonged decels
usually 7mins, low until it recovers
Assessment of fetal wellbeing during intrapartum
how does the baby react to contractions
Assessment of fetal wellbeing during antepartum
accelerations
Uteroplacental insufficiency means
baby is not getting enough oxygen
Signs of uteroplacental insufficiency
late decels
bradycardia
tachycardia
absent variability
Side effects of tocolytics
Indications for tocolytics
suppression of uterine activity
Magensium sulfate (tocolytic agent)
maternal and fetal or neonatal adverse reactions are less severe and less frequent with the beta adrenergic agonists, REDUCES NEONATAL NEUROLOGIC MORBIDITY
Indications for PTL meds
to accelerate fetal lung maturity and reduce severity of respiratory complications (tocolytic therapy)
How do we know when someone is experiencing PTL?
cervical length shortening
When to discontinue oxytocin
when decelerations occur and contractions come in too hard and too fast
Care management of prolapsed cord
immediately manually lift the presenting part off the umbilical cord with sterile gloved hand
Methods of induction/augmentation
mechanical dilation
medications
AROM
Mechanical dilation
Medications (for induction)
oxytocin - watch for tachysytole
AROM
chorioamnionitis - bacterial infection
When to use vacuum extractors/forceps?
maternal exhaustion ot fetal compromise
Indications for forcepts
maternal exhaustion
fetal distress
abnormal presentation or breech requiring delivery of head
Indications for vaccum
maternal exhaustion and ineffective pushing efforts
fetal distress in second stage
not used to assist before 34wks gestation
Complications of cesarean section?
infection
Vertex presentation
chin to chest (what we want)
Sinciput presentstion
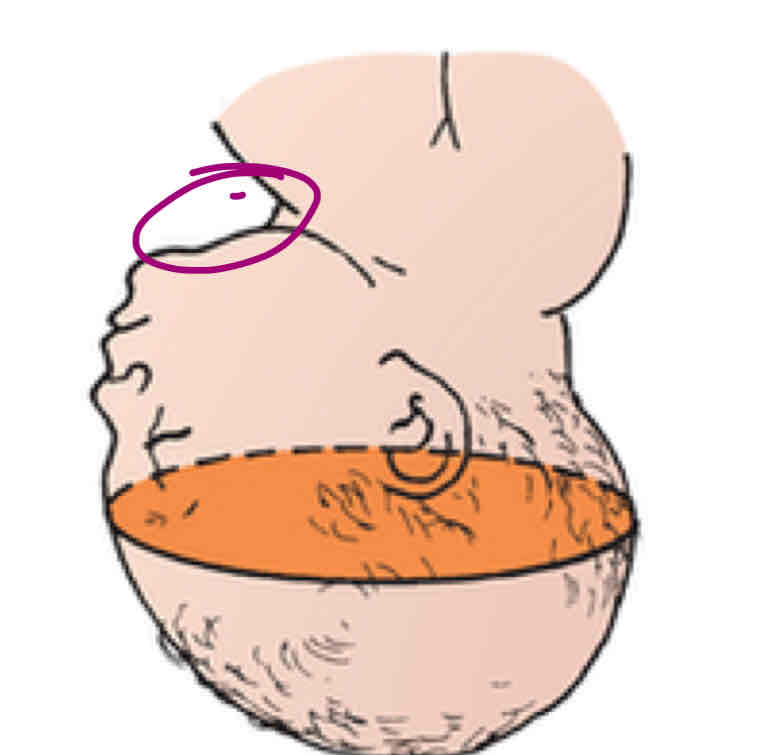
Brown presentation
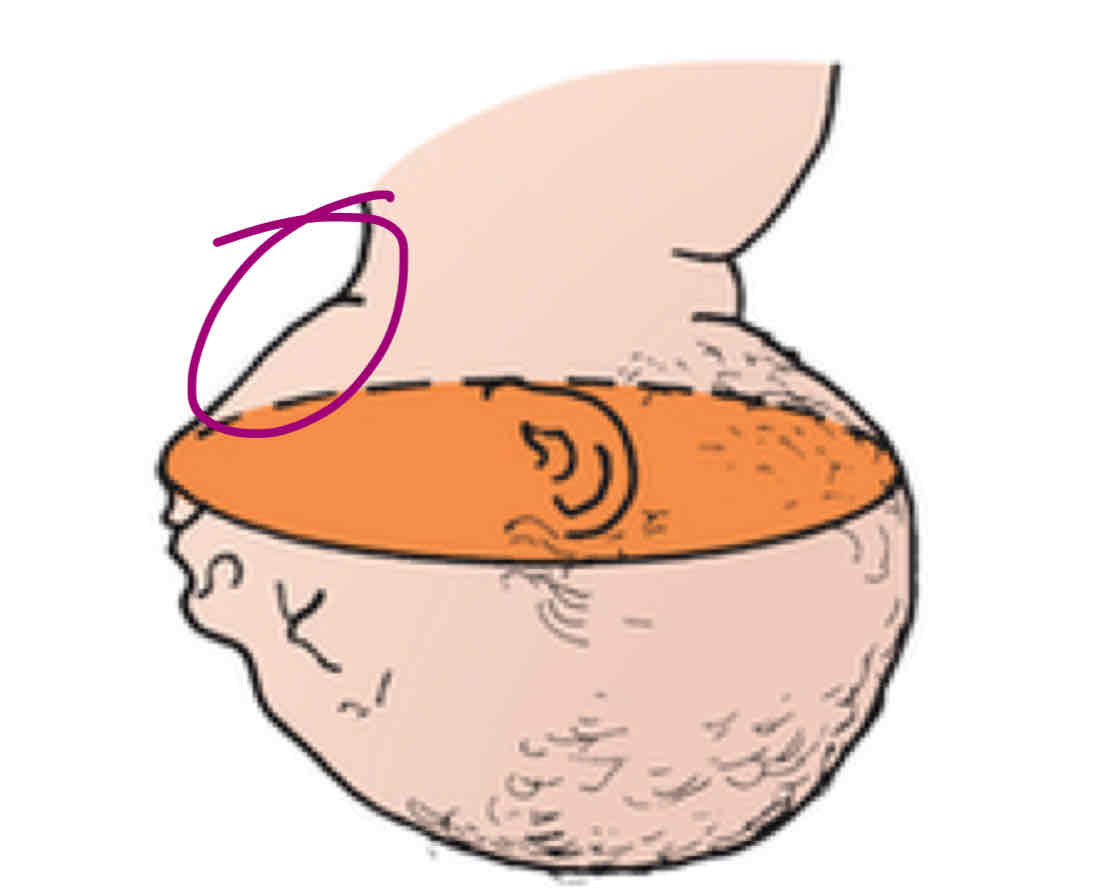
Engagement and descent
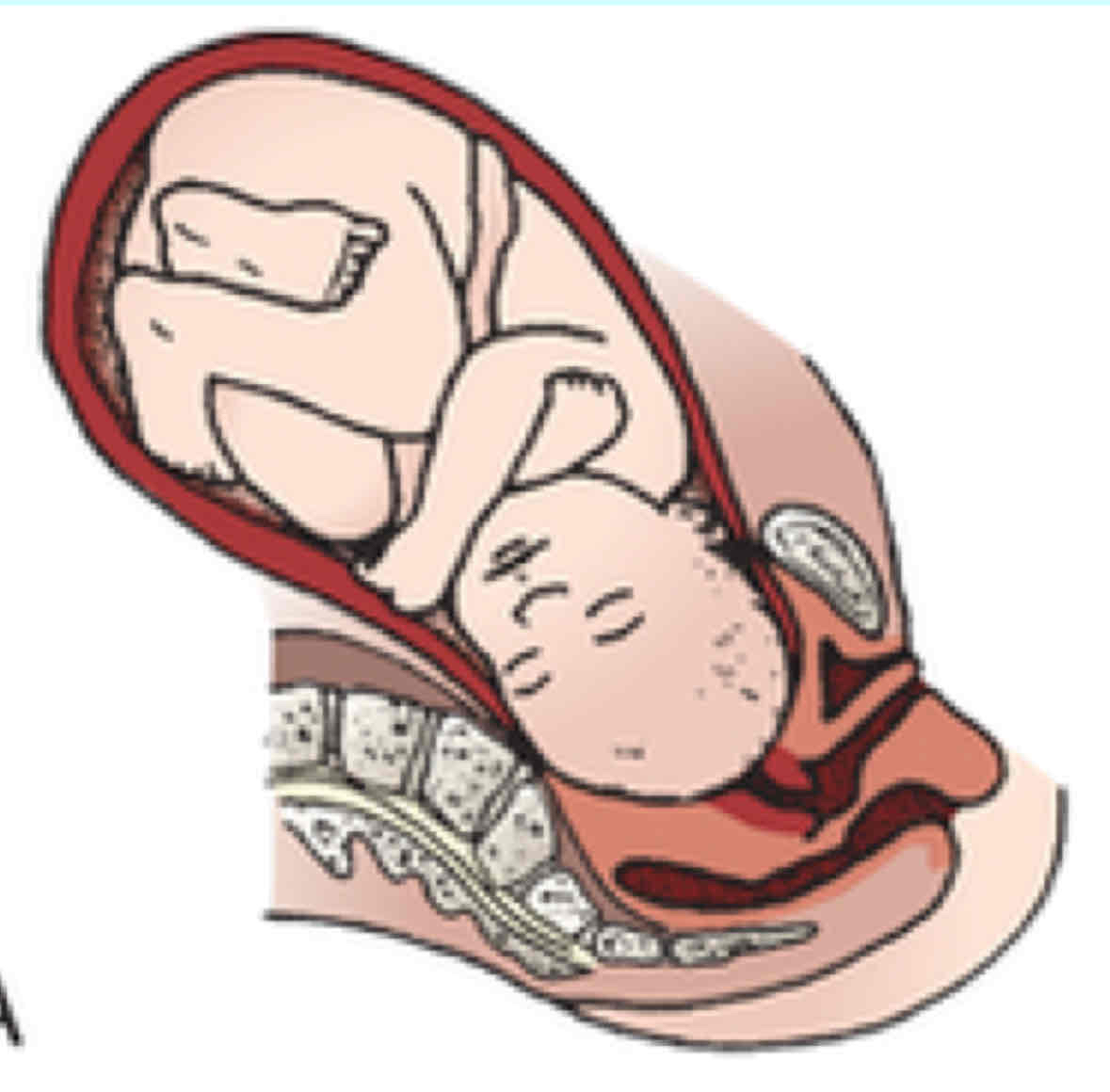
Flexion
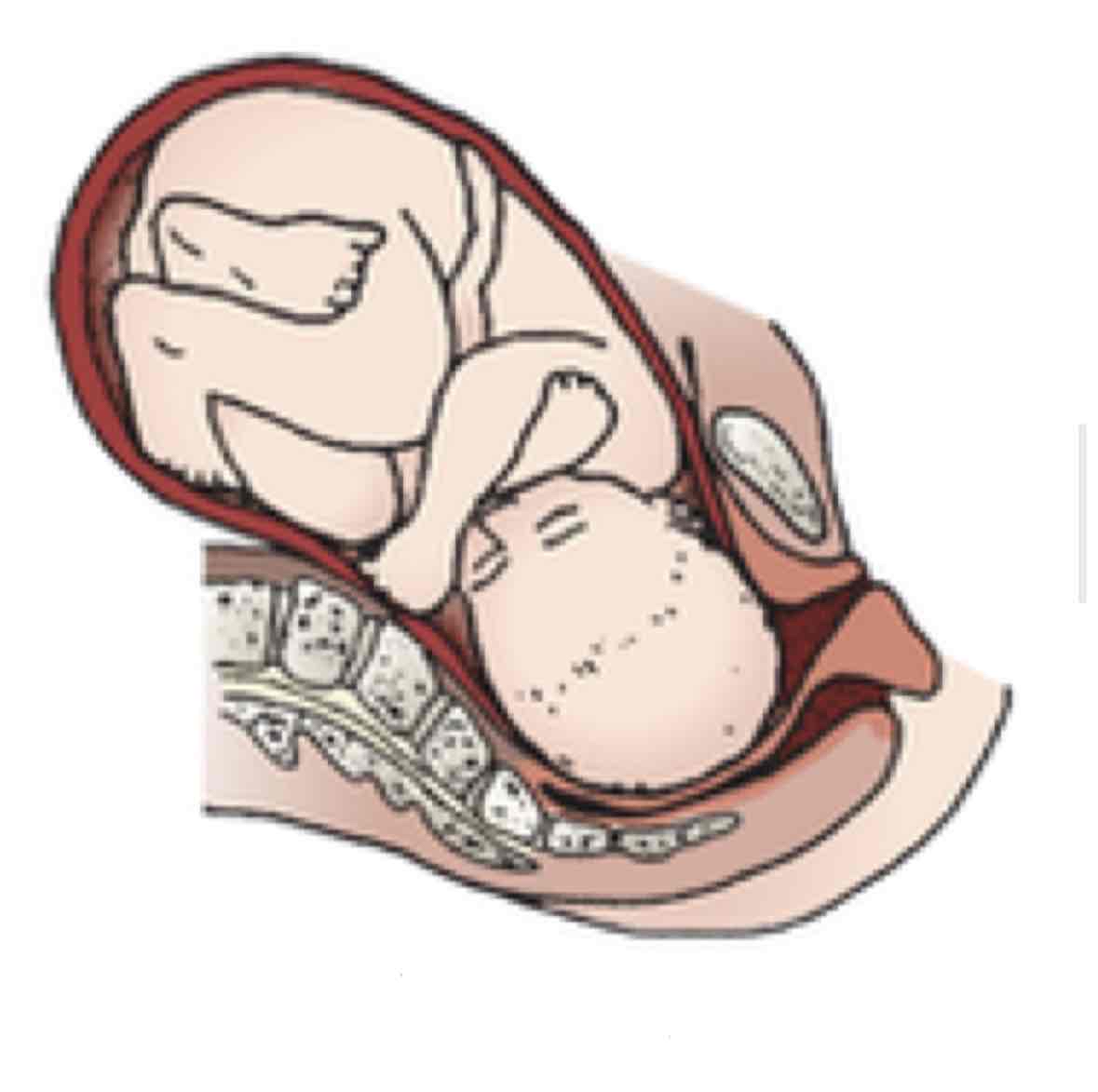
Internal rotation
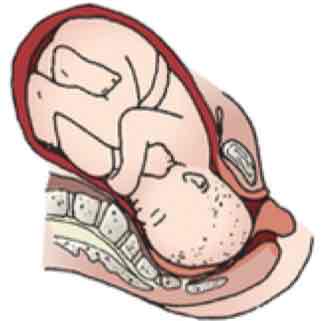
Extension
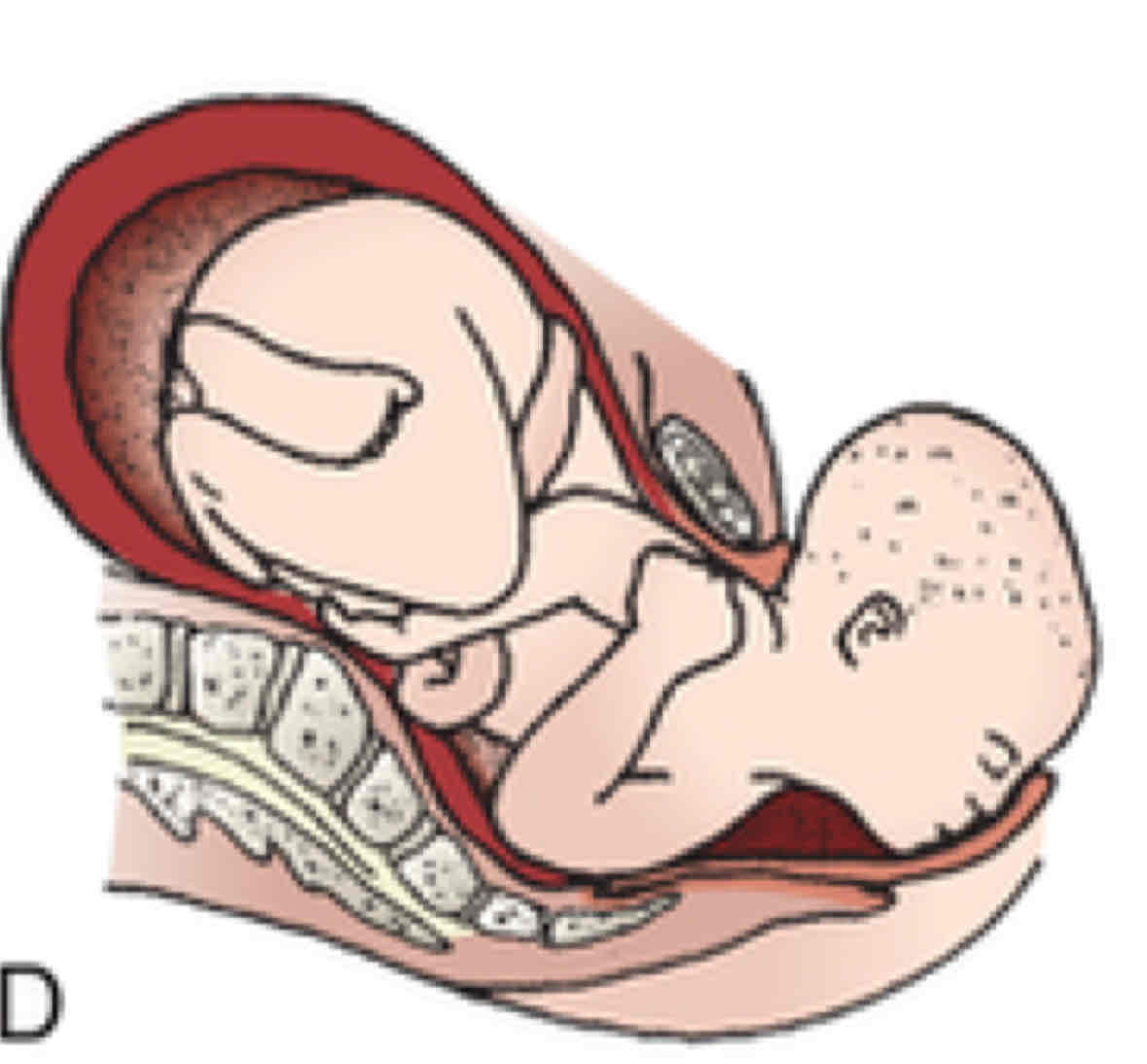
External rotation
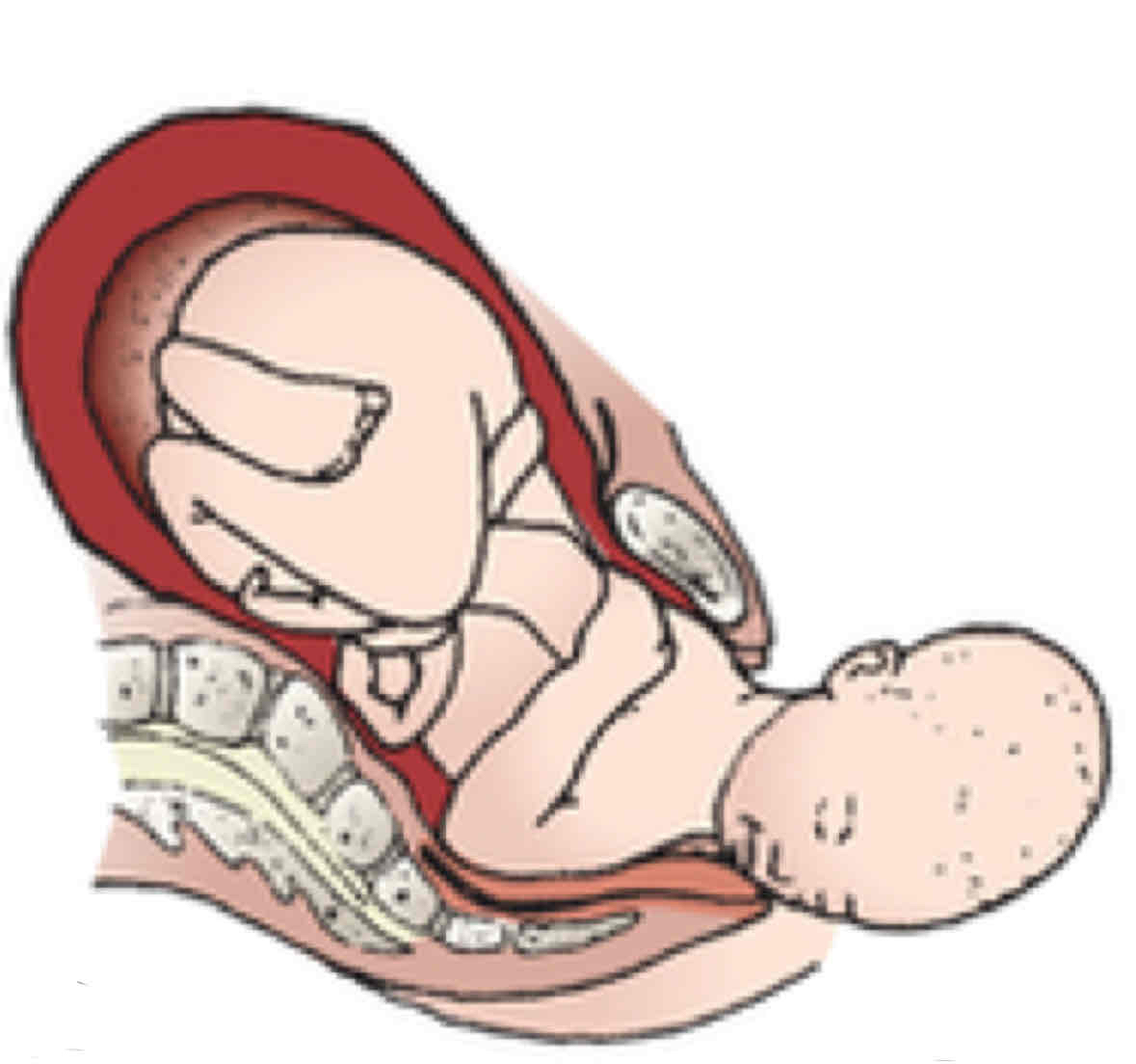
Expulsion
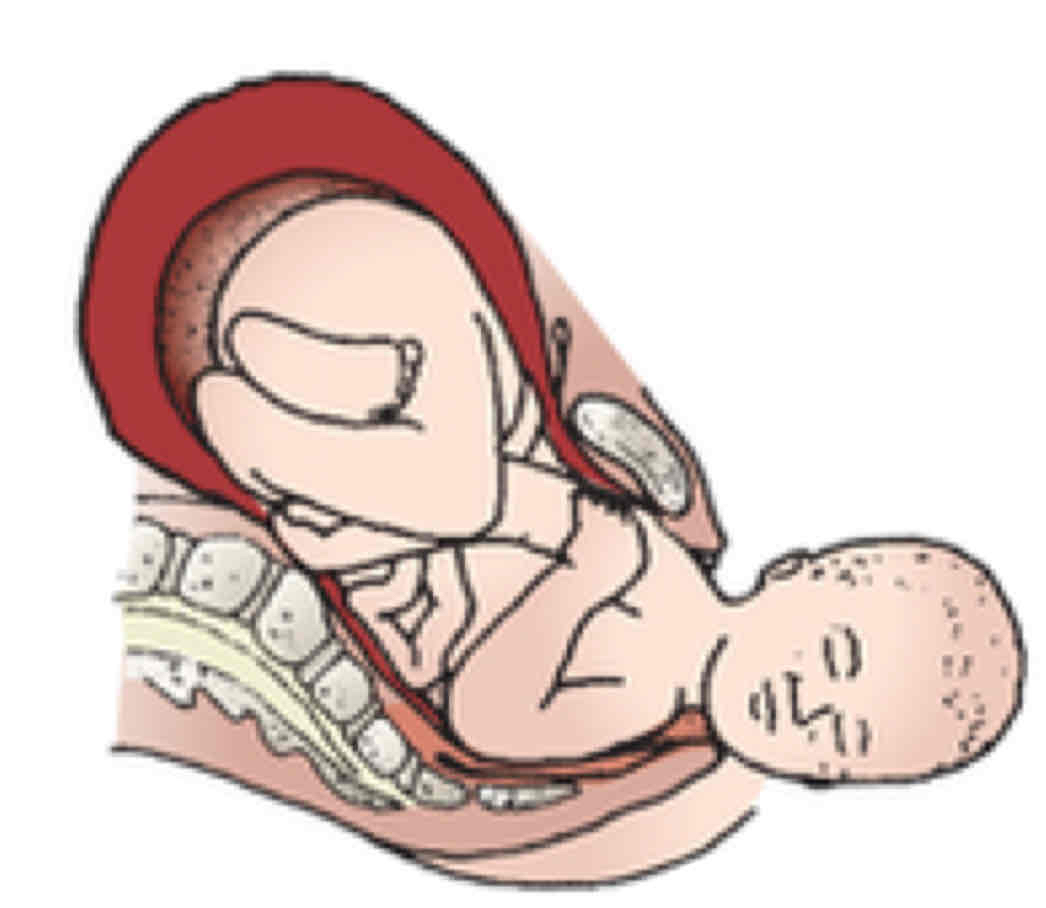
Syncliticism
fetal position we want
Asyncliticism
head tilted, what we dont want
What do steroids do for PTL?
promote lung maturity
Terbutaline
(asthma med = fast hr) slows and prevents contractions of uterus
Side effects of magnesium sulfate
muscle weakness, blurred vision, n/v , headache, iv site irritation
Side effects of steroids
flushing of face, glucose in urine
Side effects of terbutaline
inc HR,