Neuropathology of Toxic and Metabolic Syndromes 2
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is Hepatic Encephalopathy?
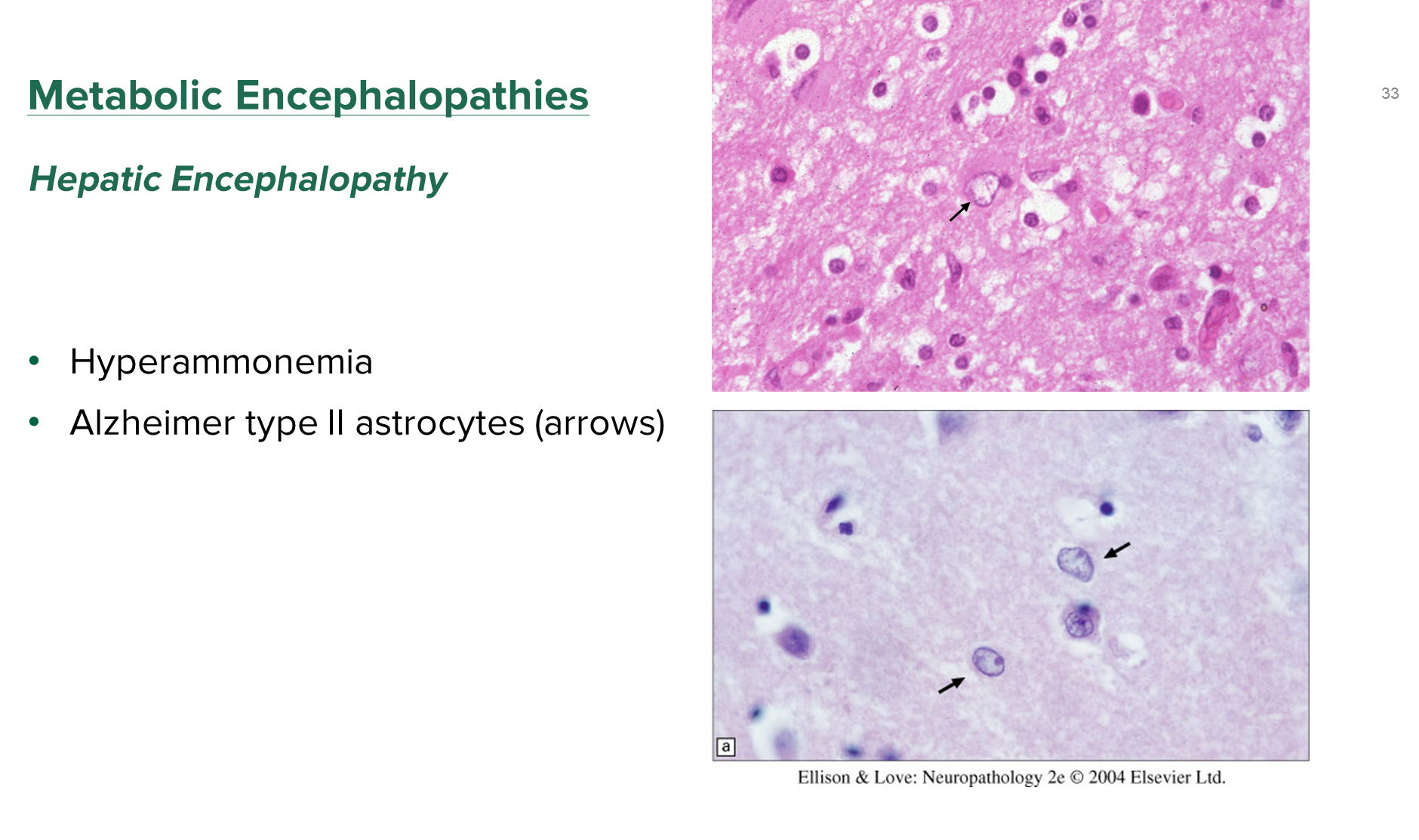
Hepatic Encephalopathy is a reversible neurological dysfunction caused by liver dysfunction. Resulting in a accumulating of ammonia
1) Patients liver is unable to detoxify ammonia leading to toxins crossing the blood brain barrier and leading to astrocyte swelling
→ Alzheimer type II astrocytes are the swollen astrocytes
What is Wilson’s Disease
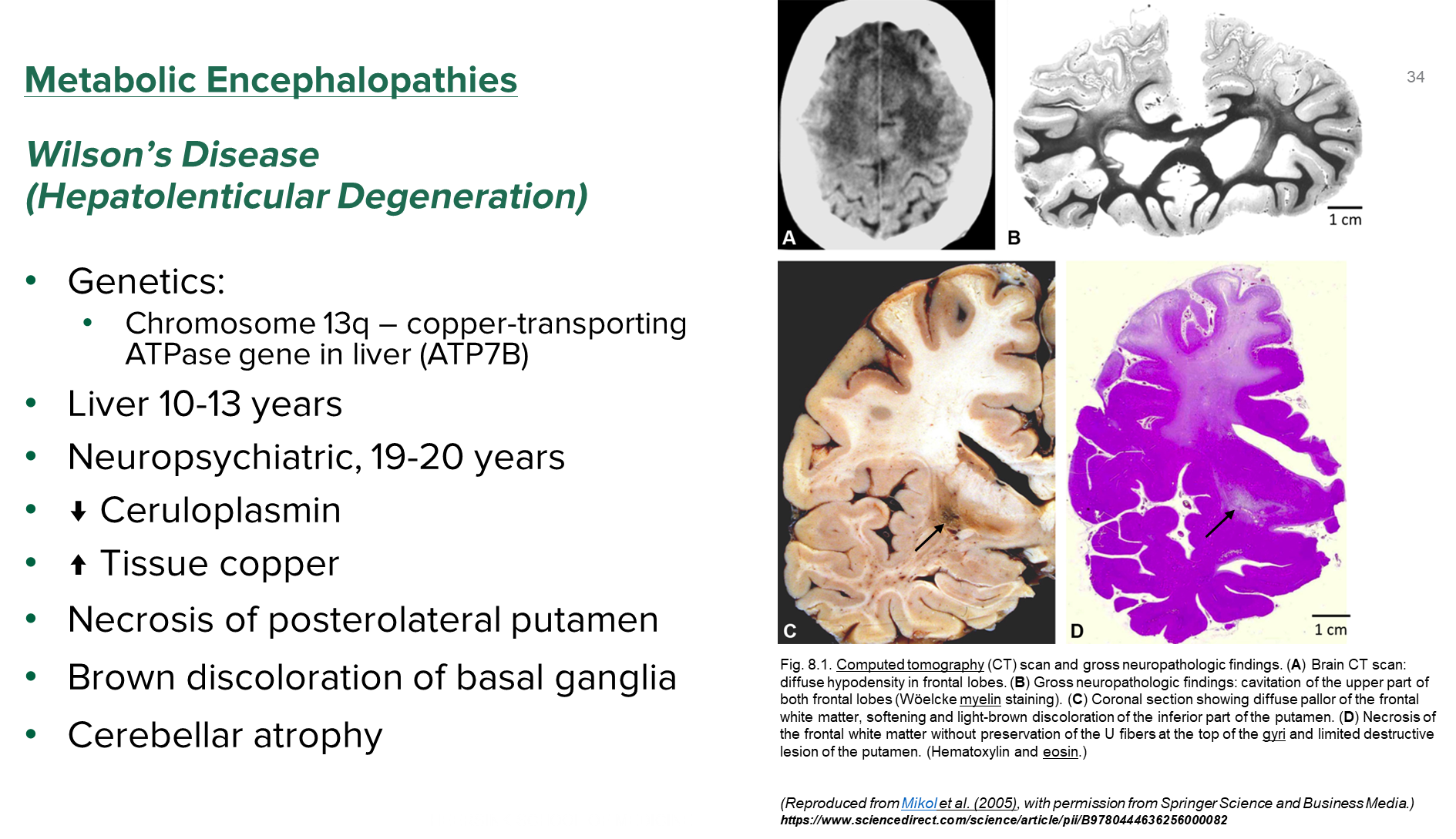
Hepatolenticular Degeneration or Wilson’s Disease is a autosomal recessive disorder of copper metabolism caused by a mutation on ATP7B on chromosome 13
1) Patients will have liver symptoms appear as early as 10-13, with neuropsychiatric symptoms presenting around the age of 20
→ patients have decreased ceruloplasmin and increased tissue copper
2) causes necrosis of the posterolateral putamen with a brown discoloration of the basal ganglia
→ may also have cerebellar atrophy
What is Reye’s Syndrome?
Reye Syndrome is acute encephalopathy in children recovering from a acute viral infection who were treated with aspirin
→ Aspirin will impair mitochondrial function in the virally affected mitochondria, impairing beta oxidation of fatty acids
1) patients develop microvesicular steatosis (fatty liver) along with coagulative necrosis of the liver
2) Patients develop cerebral edema with watershed infarcts
What is GM2 Sphingolipidosis?
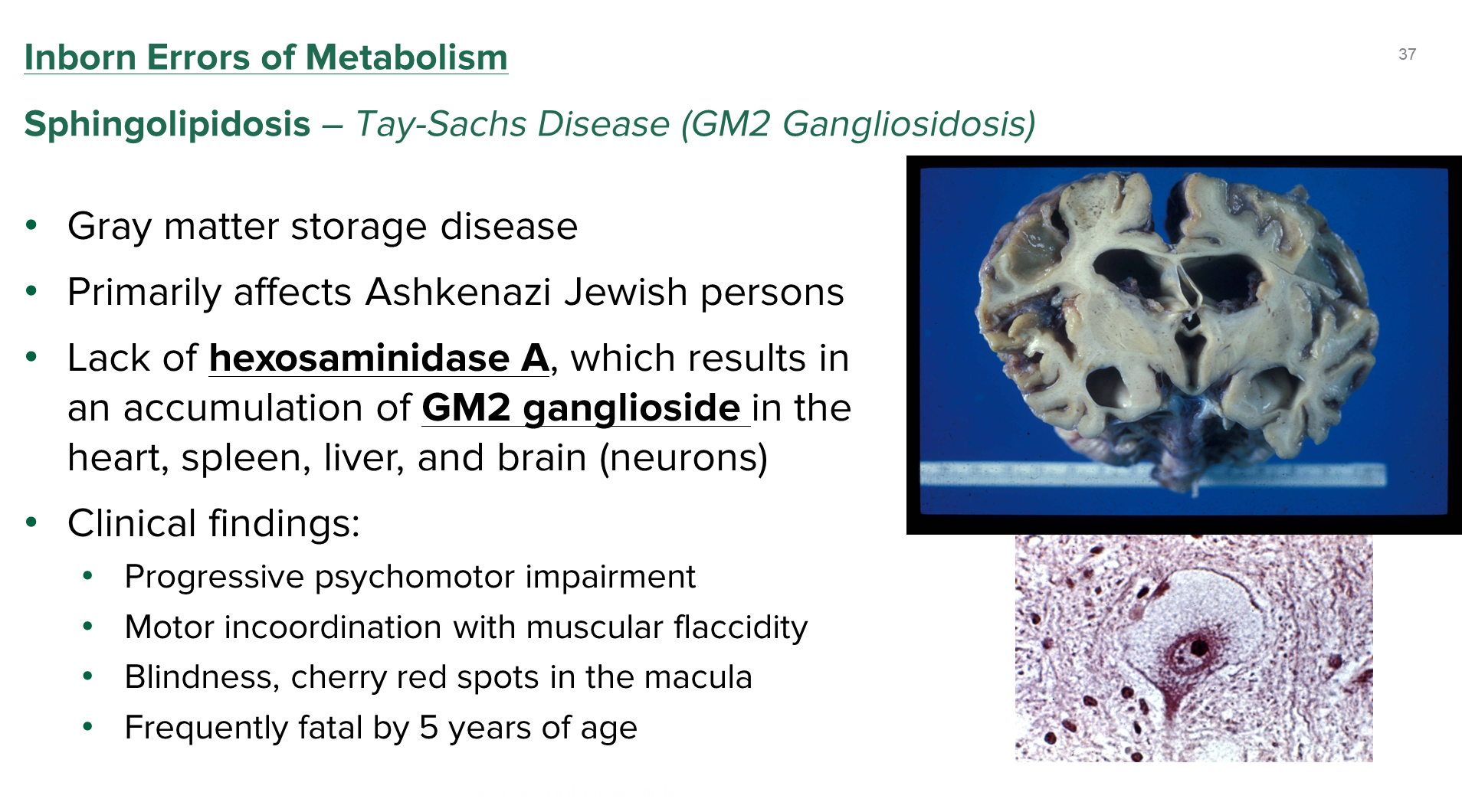
GM2 Sphingolipidosis or Tay Sachs is a gray matter storage disease seen in Ashkenazi Jews
1) patients have a lack of hexosaminidase A resulting in an accumulation of GM2 ganglioside in various organs
→ patients will have progressive impairment of physical and mental activity
→ patients have flaccid muscles with cherry red spots in the macula resulting in blindness
What are the three types of Gaucher’s Disease?
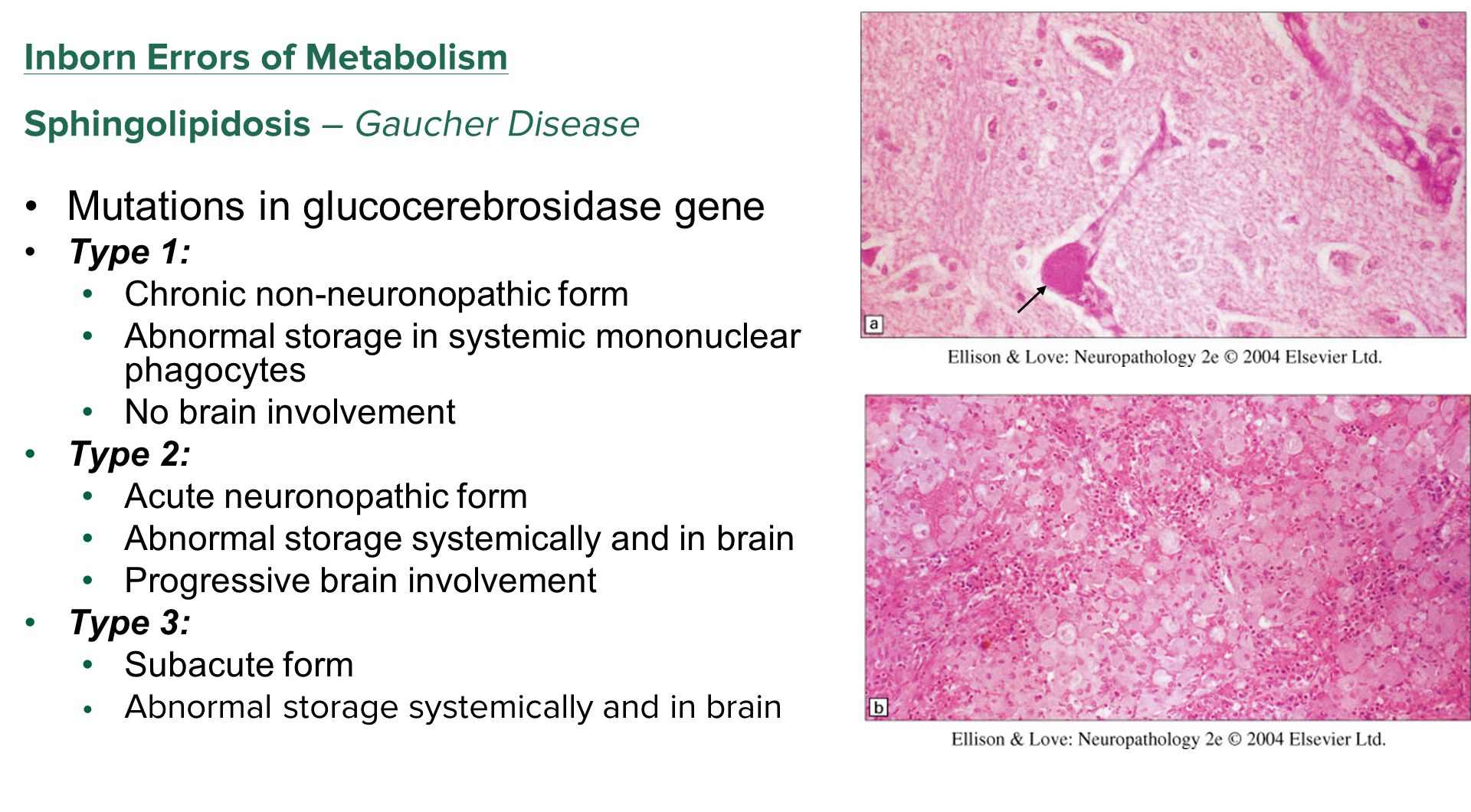
Sphingolipidosis or Gaucher’s Disease is caused by mutations in glucocerebrosidase gene. Subdivided into three types
1) Type 1
→ Chronic non-neuronopathic form - does not affect the brain as much
→ Abnormal storage in macrophages (mononuclear phagocytes)
2) Type 2
→ Acute form that affects the brain
→ Abnormal storage systemically with progressive brain involvement
3) Type 3
→ Subacute form
→ Abnormal storage systemically and in the brain
What is Metachromatic Leukodystrophy

Metachromatic Leukodystrophy is a form of sphingolipidosis and a lysosomal storage disorder
1) An autosomal recessive disorder of arylsulfatase A in lysosomes leading to an accumulation of sulfatides, a type of lipid, within the lysosomes
→ leads to myelin loss and gliosis (proliferation of glial cells)
→ causes both CNS and PNS damage in the white matter
What is Mucopolysaccharidoses?
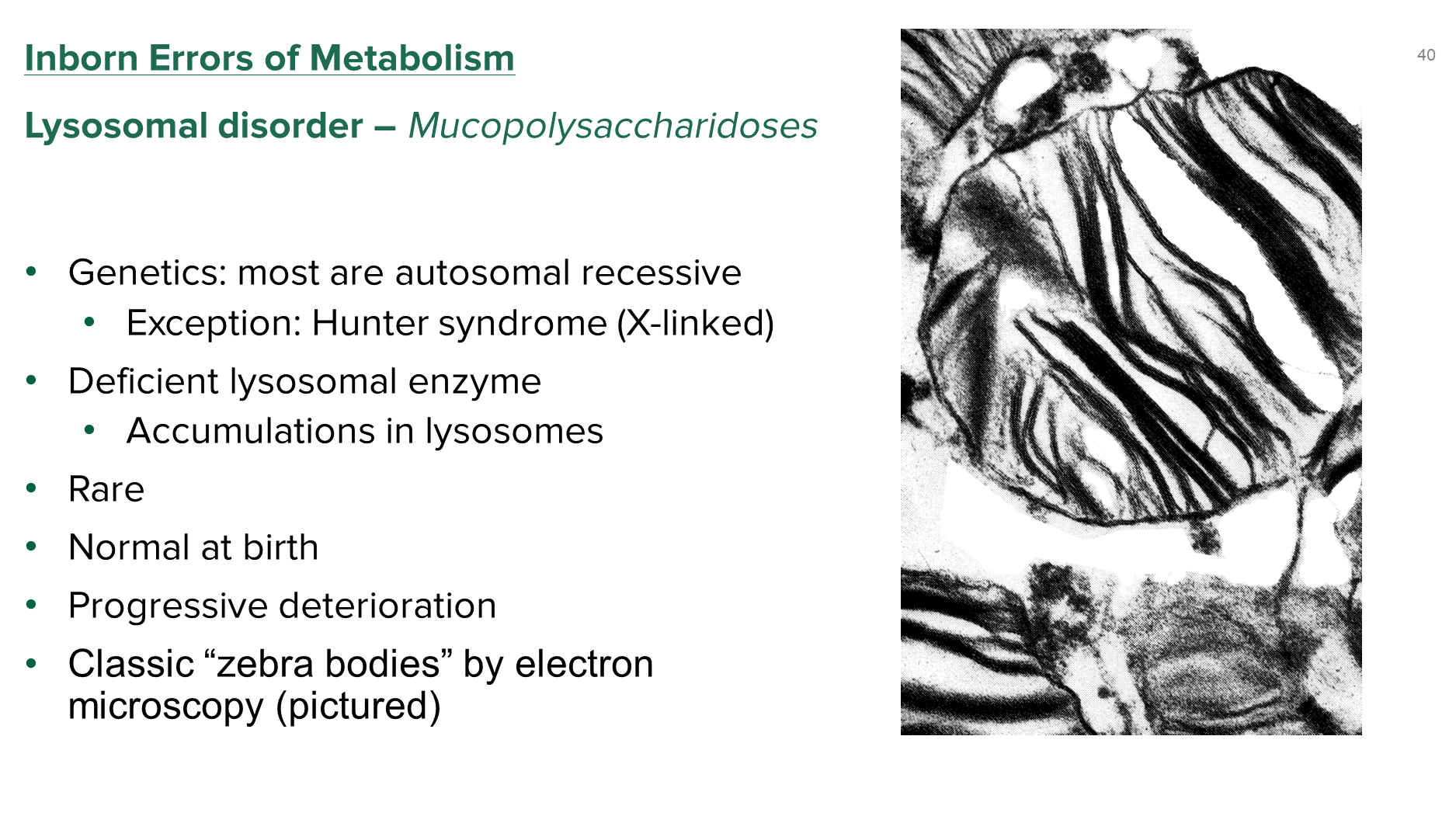
Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of lysosomal disorders resulting in abnormal accumulation in the lysosomes
1) The majority are autosomal recessive with the major exception being Hunter syndrome
→ patients will often be normal at birth with progressive deterioration
→ electron microscopy will have a classic zebra bodies appearance within lysosomes
What is Adrenoleukodystrophy?
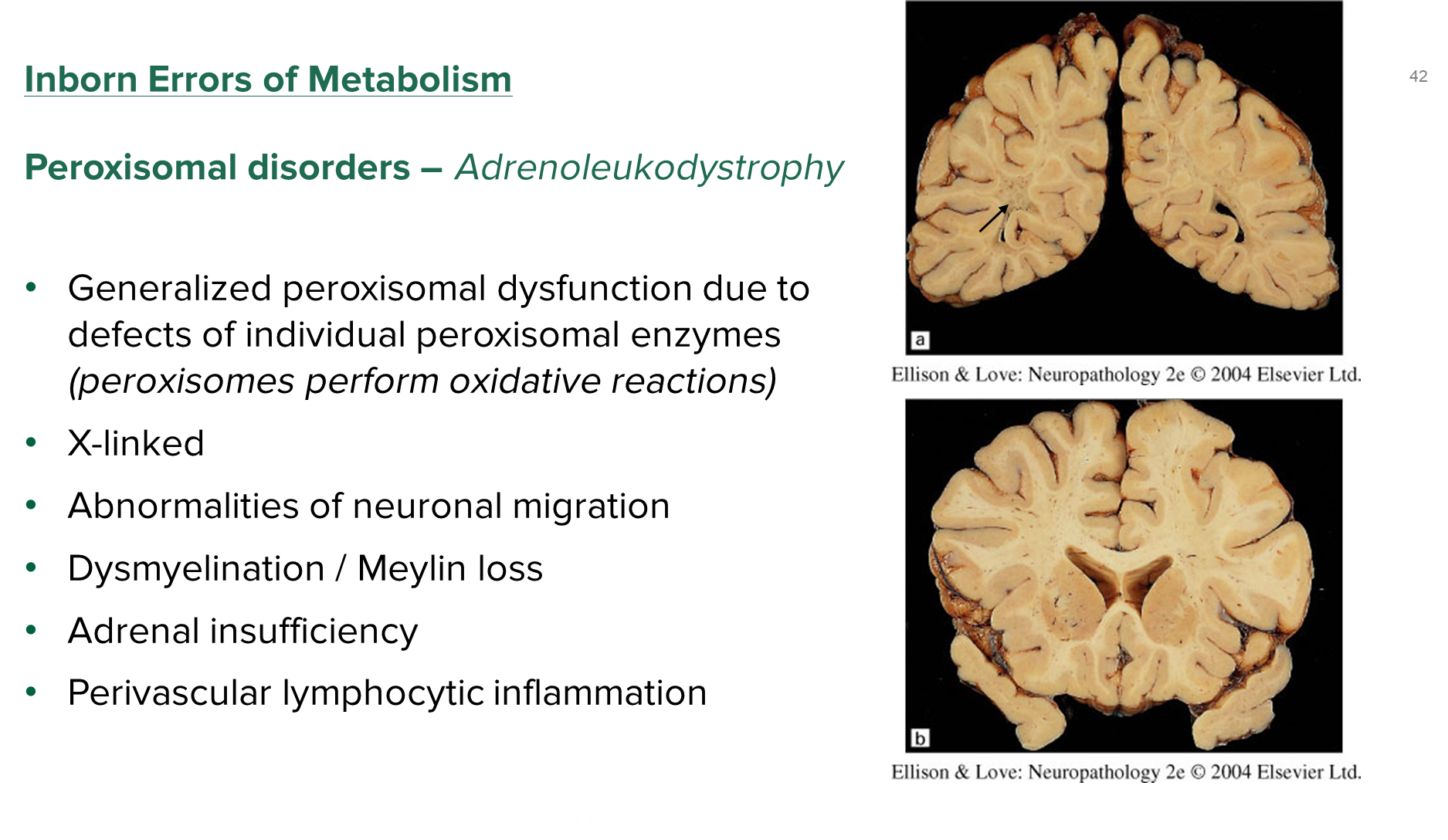
Adrenoleukodystrophy is a peroxisomal disorder caused by a defect in individual peroxisomal enzymes
1) These disorders are X-linked and appear more often in men, resulting in abnormalities of neuronal migration
→ patients will be born with dysmyelination or myelin loss
→ patients often present with adrenal insufficiency
2) Importantly, these patients will also have perivascular lymphocytic inflammation
→ white matter is darker and speckled
What is Phenyloketonuria?

Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a autosomal recessive amino acid metabolism disorder caused by mutations in the structural gene for phenylalanine (12q)
1) Patients will present with elevated levels of phenylalanine greater than 0.12
→ these kids are musty and hypopigmented
→ patients also can have microcephaly and developmental delay
2) Limit phenylalanine or proteins in their diet
What is Leigh’s Disease?
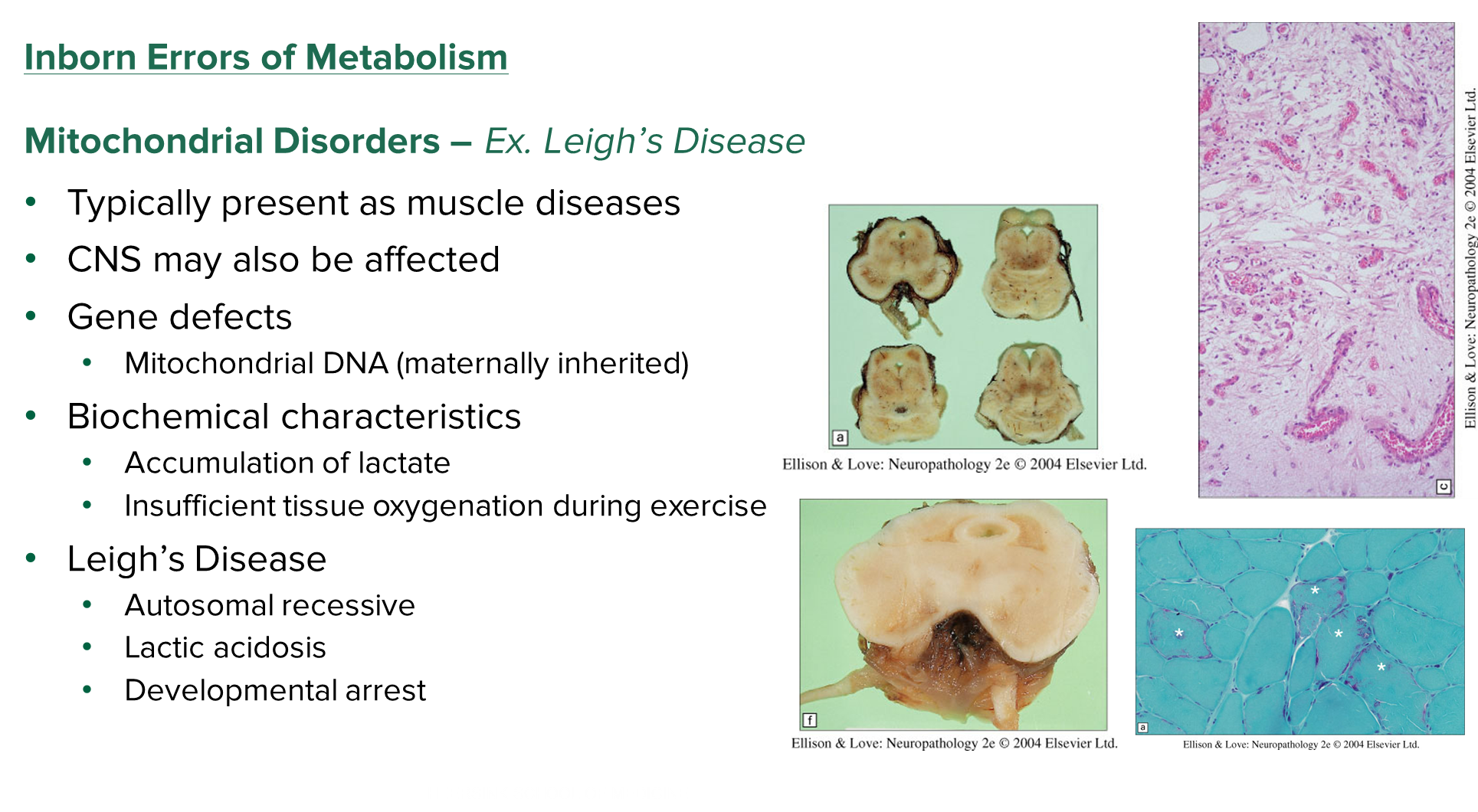
Leigh’s Disease is a mitochondrial disorder that causes muscle and CNS issues
1) this disease is maternally inherited due to being passed down through mitochondrial DNA
→ patients will have high lactate levels (lactic acidosis) and low tissue oxygen during exercise
→ developmental arrest