SPORT PSYCHOLOGY
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Sport psychology
Study of how the human mind influences sports, athletic performance, exercise and physical activity
MENTAL SKILLS
SCAMS - mental skills
Self confidence
Concentration
Arousal
Motivation
Stress management
Stress management
Stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the demands of the task and the ability level of the performer to respond in a situation where failure has consequences.
Concentration
The ability to focus on a task at hand while ignoring irrelevant cues or distractions
Arousal
Degree of stimulation or alertness present in a performer about to perform a skilled task
Motivation
Direction and intensity of effort by a performer towards a given task
Self-confidence
Belief that a performer has in their own ability to successfully perform a desired skill or behaviour
MENTAL SKILL STRATEGIES
GRIPS - mental skill strategies
Goal setting
Relaxation
Imagery
Performance routines
Self talk
Goal setting
Process of deciding on something you want to achieve, planning the steps to follow that will help reach the goal, and then working towards achieving the goal.
Improves performance by;
Focusing attention on important elements of skills
Boost self—confidence through achievement of realistic targets
Positive mental attitude
Improve intrinsic motivation
Types
outcome goals → end results/times, difficult to achieve
Performance goals → compare past/present, realistic
Process goals → actions during comp, improve performance
Short-term → help achieve long-term goals
Long-term → achieved by attaining short-term goals
Mental Skills
Increase and maintain arousal
Decrease motivation (unrealistic goal) increase motivation (realistic goal)
Increase concentration → focus on goal
Reduce stress
Increase or decrease self-confidence
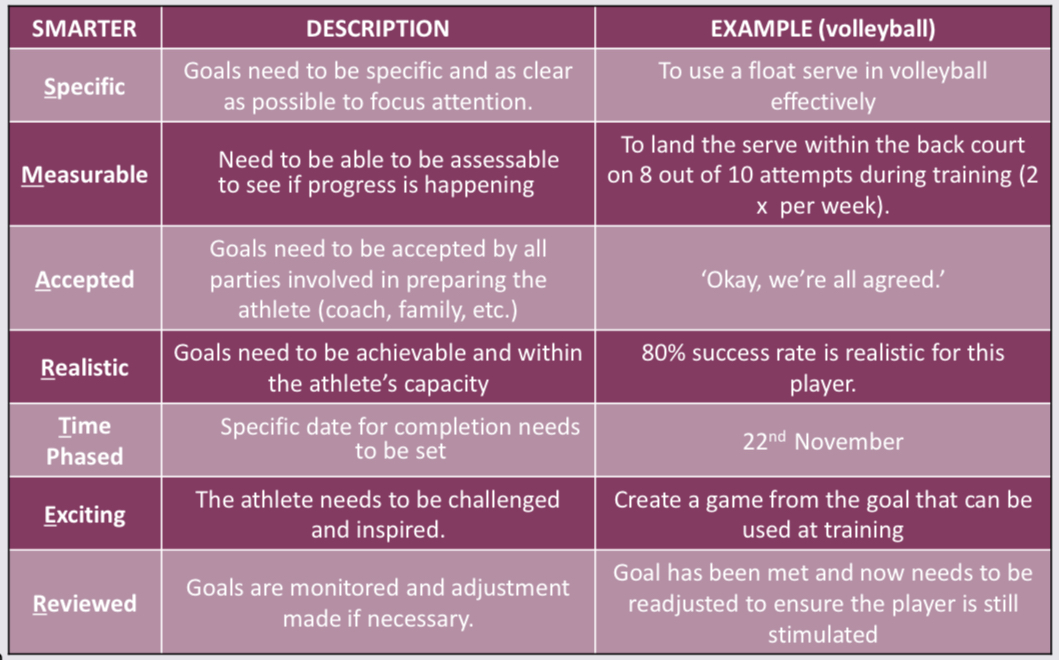
SMARTER principle
Relaxation
An activity undertaken to reduce tension and the effects of physical and mental stress. It involves employing a relaxation activity to achieve the physical or mental benefits.
physically → coordination
Mentally → decision making/cue recognition
METHODS
progressive muscle relaxation
Breathing techniques/controlled breathing/centred breathing
Music
Autogenic training
Thought stopping/self-talk
Massage
Flotation tanks
Meditation
Matching hypothesis → physical stress = physical relaxation and mental stress = mental relaxation
MENTAL SKILLS
Reduce stress
High motivation = decline in performance and over-motivated athletes use relaxation to control thoughts and focus.
High performers shift concentration quickly from broad to narrow but over-aroused have narrow focus → relaxation focus on relevant cues.
Reduce arousal
Improve self confidence
Imagery
The mental recreation, using as many senses as possible, of a successful past performance or skill
Kinaesthetic senses → feel body as it moves through different actions: nerves in muscles, joints, tendons provide feedback.
Auditory senses → monitor the way your playing environment sounds.
Tactile senses → take in how your equipment feels.
Internal imagery → imagine what you would see if you were performing the skill.
External imagery → where you watch your performance from the view of an external observer.
Reduce stress stress
Increase/maintain motivation
Focus and concentrate on particular skill
Increase or decrease arousal
Increase self-confidence
Performance routines
A ritual a performer follows to prepare for the execution of a task or skill
→ decrease chances of performer being affected by internal or external distractions.
Mental Skills
Increase/decrease arousal
Decrease stress
Increase motivation
Increase concentration
Increase self-confidence
Self-talk
Talking to/thinking to yourself positively before, during or after performance
Positive cue words and positive emotions
reinforce skill learning
Changing bad habits
Motivating performer
Focusing attention
Building self-confidence
Mental skills
Reduces stress
Increase motivation
Change concentration - key phrases
Increase or decrease arousal
GROUP COHESION
Group Cohesion
A term used to describe the extent to which a group stays together and unified in the pursuit of common goals and objectives
task cohesion
Social cohesion
Independent of each other
→ highly skilled and task motivated team can win even if they are not close friends
→ social competition = little task cohesion but high social cohesion
Task cohesion
How committed are the team members to achieving their predetermined common performance goal.
Social cohesion
The degree to which team members like each other and enjoy being together. Reflects friendship within a group.
Strategies to improve group cohesion
Use of leadership
communication
Use of leadership
Leadership groups are commonly used to give the playing group a greater sense of power whilst Leo entrusting the players with setting standards (both on and off the field)
Communication
Communicating clearly and regularly so all members understand their roles and responsibilities → clear and understood expectations/norms.
Goal setting (individual and team)
Set challenging but realistic goals for the team as a whole and for individual players - players are involved in this process
within subunits - mid, attack, defence
DEVELOPS task cohesion
Team building
Helps to develop social cohesion by encouraging social interaction away from the sport
DEVELOPS social cohesion
Roles and expectations
Every team has their own group roles and group norms, which influence the behaviour of its members as individuals and collectively.
group roles → shared expectations of how an individual should behave in a certain positions. Groups have formal and informal roles:
Formal → leadership group, coach, medical staff, fitness coordinator (task cohesion)
Informal → social organiser, end-of-season tour organiser (social cohesion)
Group norms → shared expectations of how group members should behave. Norms can be both formal and informal.
Formal → improve task cohesion - warm up together, arrive in uniform
Informal → improve social cohesion - not official rules or policies but set of expectations developed by a leadership group introducing new players into team and culture (e.g. mistake = penalty)
Benefits of cohesion
communication and motivation within group are extensive
Increased feeling of the group rather than as individuals
Players work together to achieve team goals ahead of personal goals.
Players enjoy each other’s success
High cohesiveness = high success rate in achieving goals
More satisfied and willing to stay in group longer
Barriers to cohesion
personality clashes
Conflicting roles among group members
Frequent changes to the group
Disagreement on group objectives
Lack of communication
Power struggle between players
FACTORS AFFECTING GROUP COHESION
Social loafing
Tendency of individuals to lessen their effort when they are part of a group.
other athletes working at lower intensity = excuse to put in less effort
Belief that effort wont make a difference to the team
Individual effort cannot be determined
Task is perceived as meaningless
Individual is competing against a perceived weaker opponent
TRAITS
decreased effort at training
Arrives late/leaves early to/from training
Misses training
Decreased form
Expect team mates to cover their mistakes
Social loafing has a negative impact on individual and team performance - decreasing team cohesion
MINIMISED BY:
Team contract - group expectations, individual responsibilities, consequences of breaching rules
Develop rules of conduct
Create appropriate group sizes
Evaluate all members of group individually
Rotate responsibility and positions where possible to maximise individual contributions
Provide regular feedback to each individual player
Make a roster to ensure all players assist with setting up and putting away equipment
Set challenging individual and team goals for each training session
Make individuals accountable for effort by publishing results/stats for the team
Leadership
Refers to the leadership style the coach and the captain used and how this affects the group cohesion.
authoritarian, democratic, lazed-faire (casual)
Good leaders are key to developing socially cohesive team
Team goals
Individual roles
Team rules
Standards of behaviour
Team dynamics
The collective identity/goals/aims/norms/standards of the team OR the characteristics of the team including team stability, prior successes and failures.
team stability → maintaining same playing group over time increases cohesion
Stable group becomes cohesive and cohesive group becomes stable
Prior successes and failures increase cohesion
Common goals within team increases cohesion
Shared understanding of strategies and tactics being used increases cohesion
Demands of the task also impact interaction and cohesiveness - three levels of communication/interaction;
Co-acting activities → team members work independently of each other to achieve the result
Mixed activities → combination of co-acting and interacting activities
Interacting activities → high level of interaction between team members (task cohesiveness very important)