MicroBiology
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
pathology
study of disease
etiology
study of the cause of a disease
endemic
disease that is always present in a population
sporadic
occurs occasionally
pandemic
occurs worldwide
epidemic
many people in a given area get a certain disease in a short time
infection
invasion of the body by a pathogenic organism
disease
any change other than an injury that interferes with the normal functions of the body
pathogen
disease causing microorganism
zoonotic
virus travels by animals
vaccine
weakened or inactive viruses to produce immunity from a disease
pili
transfers dna
Conjugation
Sexual reproduction in bacteria
flagella
used for movement
binary fission
asexual reproduction in bacteria
disinfectant
reduces population
sterilization
complete elimination, from extreme heat or radiation
pasteurization
use of mild heating to kill organisms that spoil (milk, eggs)
radiation
destroys DNA so that it can not reproduce
What are the characteristics of viruses?
no cells, does not use energy, cannot make its own proteins, reproduces with a living host, has genetic material, and grows
What do they have in common with living things?
they have genetic material and change/mutate
How are they different from living things?
Not made of cells, cannot make its own protein, cannot use energy, cannot reproduce w/o living host
What are 2 parts all viruses must have?
capsid and nucleic acid
What are the extra parts?
the envelope
What are the functions of each part?
Capsid- protection
Nucleic Acid- tells virus what host and how to effect it
Envelope- spikes to attach to host
Be able to label a bacteriophage
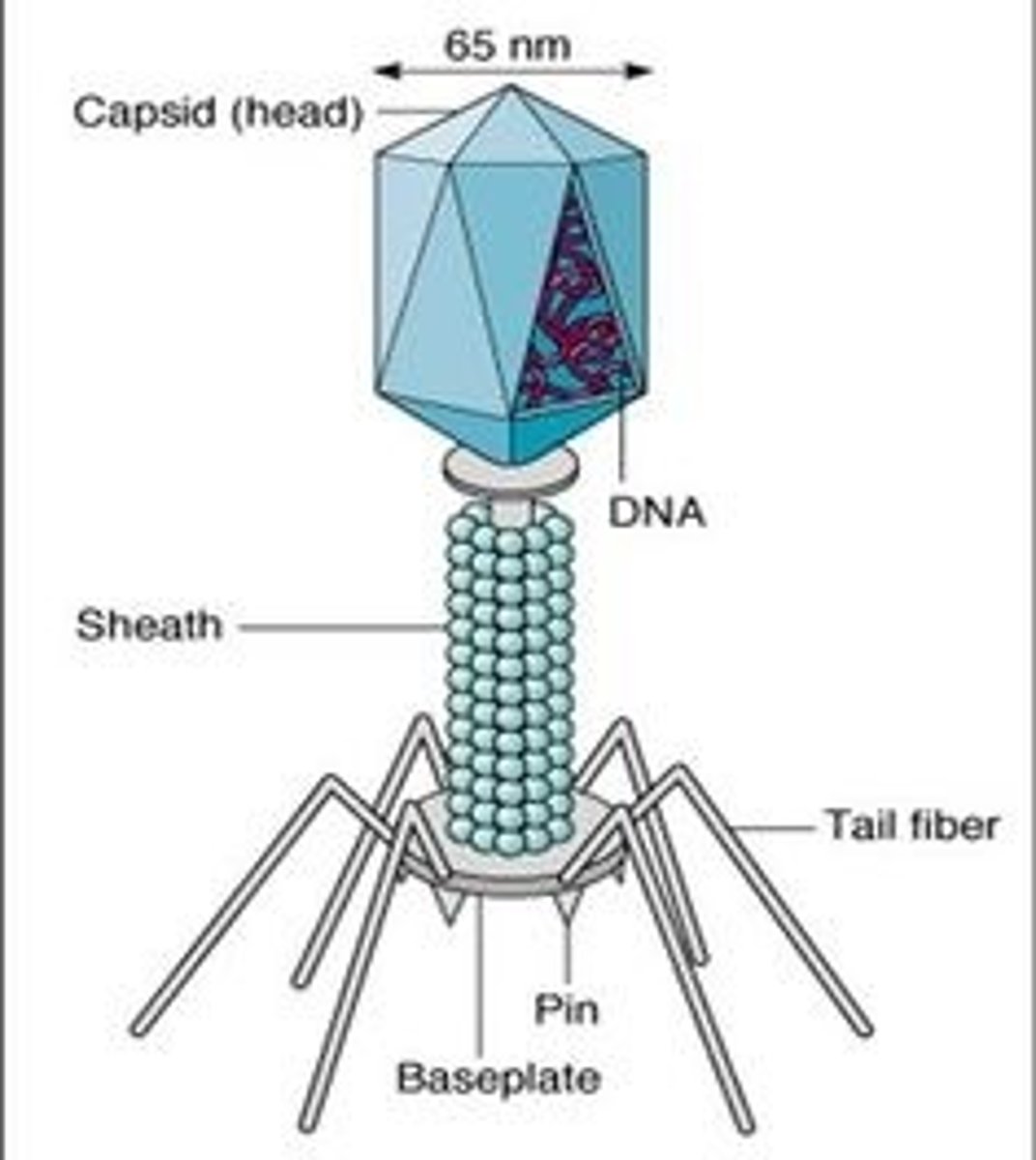
Be able to label corona virus
What are the steps of the lytic cycle and what happens during each?
Attachment- virus attaches to host cell
Entry- inserts viral RNA/DNA; destroys cell's DNA and takes over; polymerase replicates viral DNA/RNA
Replication- viral DNA makes more copies of itself
Assembly- new viruses assemble their dna and protein capsids
Lysis- enzymes cause cell to burst
How is the lysogenic cycle different?
it takes longer and doesn't replicate right away; the DNA is inactive and is copied during cell division
What are different ways to transmit a disease?
Direct (person to person) contact,
indirect contact,
droplets (sneeze),
waterborne, foodborne, airborne, zoonotic
What type of virus is corona
RNA
How is corona transmitted?
inhalation, sneezing, talking
What is the effect on the body for corona?
the alveoli become inflammed
How to treat corona?
Vaccine
How is ebola transmitted?
contact with infected body fluids
How did Ebola end?
How did the workers protect themselves form Ebola?
How did the girl become infected with the flu?
A man sneezed in the elevator and she breathed it in.
What cells does the flu infect?
Throat cells
What are the symptoms from the infection?
A raw, swollen, and sore throat
her nerves are hypersensitive
What happened in the body of the girl who got the flu?
At first her immune system sprays a poison to kill the virus cells (the natural killer cells). Then the T cells activate and take out the infected cells in the blood stream. The B cells manufacture antibodies and paralyze the virus.
What are the 3 types of vaccines?
Live (weakened)- virus in a weakened form
Inactive- virus is killed by heat or formaldehyde
mRNA- gives mRNA to make antigens....eventually wears down
How are RNA viruses different than DNA viruses?
RNA are always mutating
How did Salk and Jenner contribute to medical advancement?
They made the polio and smallpox vaccine.
How did they make each vaccine?
Salk killed polio with formaldehyde
Jenner used cowpox for smallpox vaccine
Explain how gene therapy works.
viruses are engineered to carry a beneficial genes and inset them into a cell, they either inject the virus into the patient or take a sample tissue and do it in labs
what type of bacteria live in extreme, harsh environments?
archaebacteria
How does bacteria reproduce?
Asexual- binary fission parent divides into 2 identical daughter cells
Sexual- conjugation DNA is passed through the pili, plasmids are exchanged, creates diversity
How is viral reproduction different than bacterial reproduction?
viruses need a living host
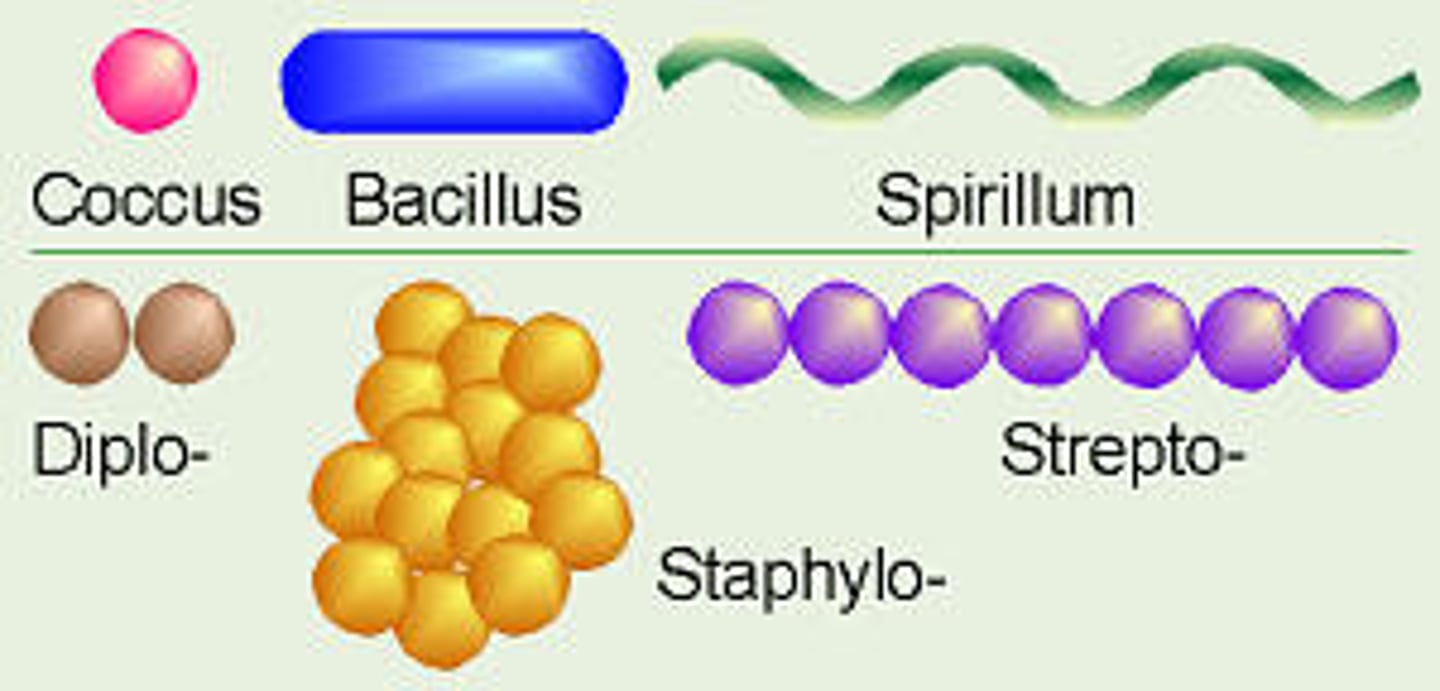
Know the shapes of bacteria and arrangements
and a S shaped one named vibrio
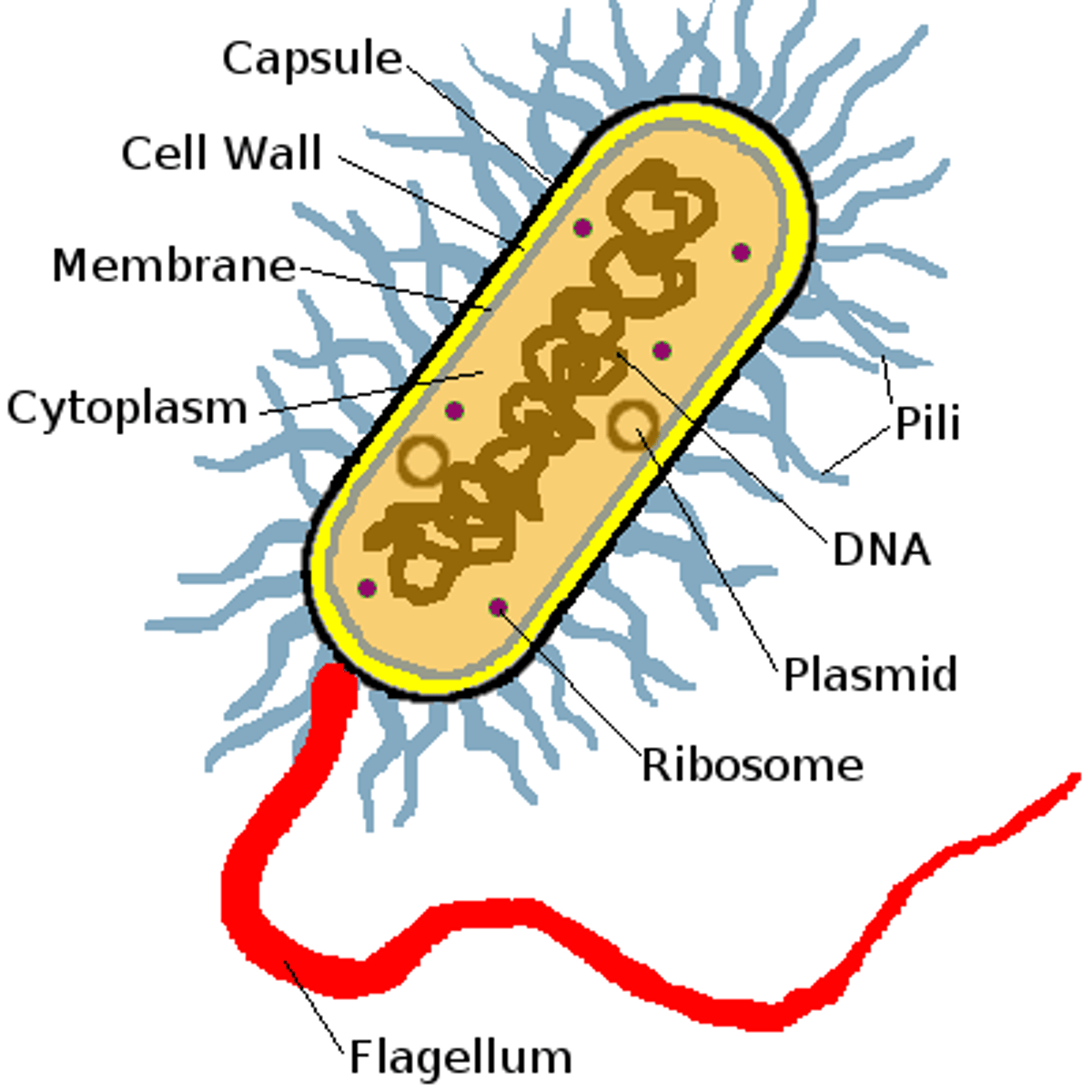
Know the parts of a bacterium
Capsule- outermost
Cell wall
Cell membrane- innermost
nuclear area
ribosomes
pili
flagella
where are bacteria found?
everywhere
what is the difference of how viruses and bacteria cause diseases?
Viruses burst cell
Bacteria releases toxins
What are the different ways to control bacteria?
disinfectant, sterilization, refrigeration, radiation, heat, alcohol
why are bacteria considered prokaryotes?
They have no nucleus, are single-cellular, and have no complex organelles.
what are several beneficial uses for bacteria
They decompose, purify sewage, make drugs, break down oil spills, make food, and digest food.
what are antibiotics? why are they useless for viral infections?
They are medicine that fights against life (bacteria)
They wouldn't work because viruses are not alive
Explain the role of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle.