Bio 2040 - Exam 4
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
hermaphrodites
In animals, individuals that possess both ovaries and testes.
bilaterians
head and a tail, as well as a belly and a back.
spongocoel
A central cavity in the body of a sponge.
mesohyl
A gelatinous, protein-rich matrix in between the choanocytes and the epithelial cells of a sponge.
spicules
Needle-like structures that are made of protein, calcium carbonate, or silica and form lattice-like skeletons in sponges, possibly helping to reduce predation.
spongin
A tough protein that lends skeletal support to a sponge.
nematocyst
In a cnidarian, a powerful capsule with an inverted coiled and barbed thread that functions to immobilize small prey.
polyp
A type of cnidarian body form that is sessile and occurs mouth up.
medusa
A type of cnidarian body form that is motile and usually floats mouth down.
ocelli
Photosensitive organs found in some animal species.
cnidocyte
A characteristic feature of cnidarians; a stinging cell that functions in defense or the capture of prey.
cnidocil
On the surface of a cnidocyte, a hairlike trigger that detects stimuli.
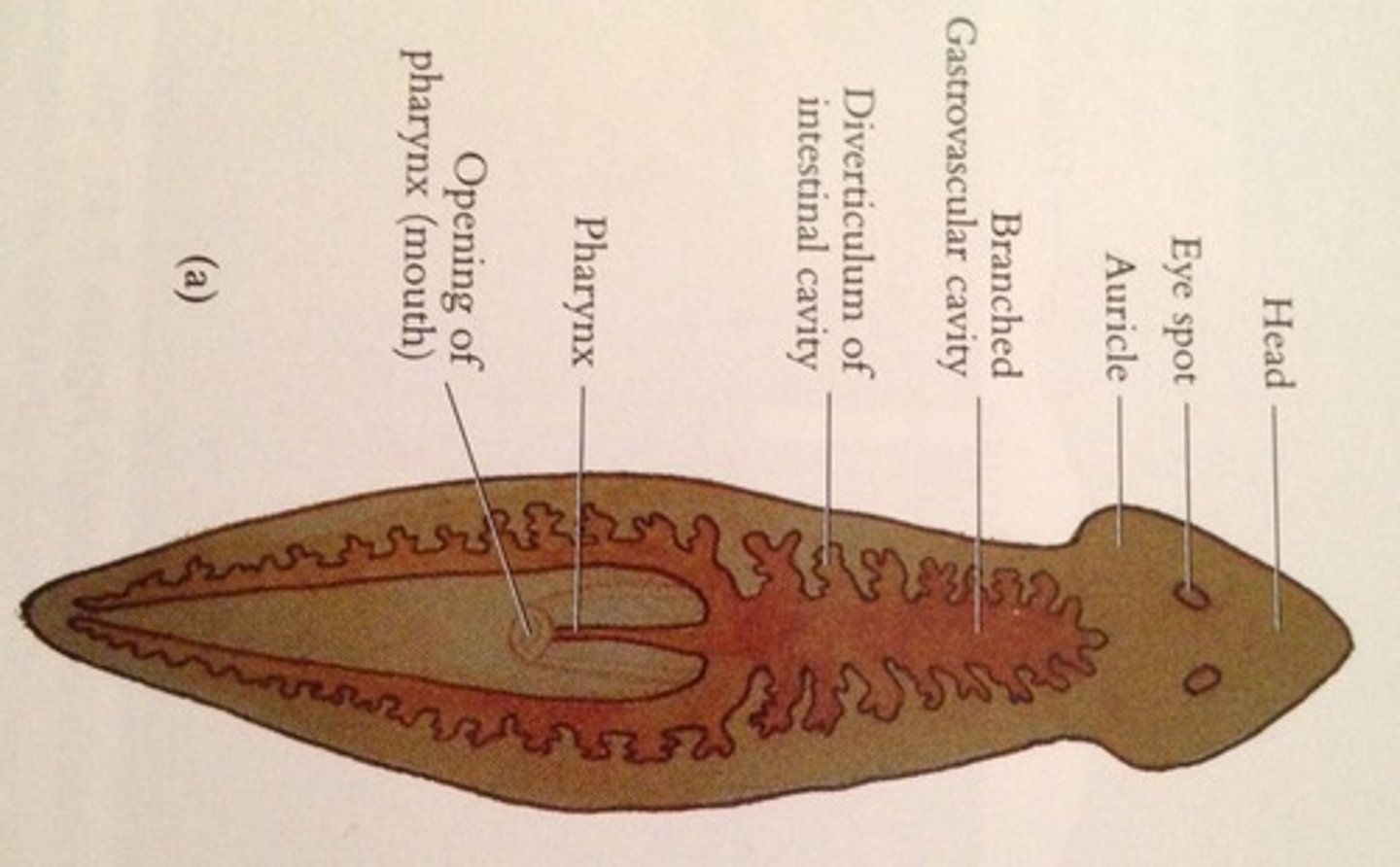
Turbellaria: planarians
Mostly marine; free-living flatworms;predatory or scavengers
Monogenea: fish flukes
Marine and freshwater; usually external parasites of fish; simple life cycle (no intermediate host)
Cestoda: tapeworms
Internal parasites of vertebrates; complex life cycle, usually with one intermediate host; no digestive system; nutrients absorbed across epidermis
Trematoda: flukes
Internal parasites of vertebrates; complex life cycle with several intermediate hosts
Rotifera
mostly freshwater and microscopic
• Digestive tract with separated mouth and anus
• Allows feeding more quickly
• Mouth opens into a muscular pharynx called a mastax
• Jointed foot with pedal glands
• Helps stick to surface
Cnidaria classes
Scyphozoa - jellyfish
Anthozoa - sea anemones, sea fans, most moral (polyp)
Hydrozoa - man o' war, hydra, some coral (polyp, colonial)
Cubozoa - box jellies, sea wasps (medusa, boxed shaped)
Cnidaria
Diploblastic - Ecto/endo
2 body forms - medusa, polyp
has mesoglea = geleninouse substance
autotomy
the ability of an organism to drop a body part and, usually, to regenerate a new one
notochord
A defining characteristic of all chordate embryos; a flexible rod that lies between the digestive tract and the nerve cord.
chordate
animal that has for at least one stage of its life: a dorsal hollow nerve cord, a notochord, a postanus tail, and pharyngeal pouches
Tunicates
animal encased in tunic
• Adult is sessile with only pharyngeal slits
• Larvae tadpole-like, with all 4 chordate traits
Closest living relatives of vertebrate:
- Rudimentary circulatory system
- Simple nervous system
- Mostly hermaphroditic
Mollusk Body Plan includes
mantle, visceral mass, foot, gills, shell
Mollusca
(snails, clams, squids, octopuses) = Radula
Economic, aesthetic, and ecological importance
open circulatory system, coelom
Trocophore larva develops into veliger with rudimentary foot, shell and mantle
pseudocoelom
A body cavity that is not completely lined by tissue derived from mesoderm
Tagmata
&
PEDICEL
fused body segments
thin structure that connects the thorax and abdomen
Cnidarian Classes
Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, Cubozoa, Anthozoa
Hydrozoa
hydra and Portuguese man of war
mostly marine; polyp stage usually dominant and colonial
Anthozoa
sea anemones, sea fans and corals
All marine; polyp stage dominant
Lophotrochozoa
Flatworms, Rotifers Mollusks, and Annelids
Flatworms
First triploblastic, muscle, preditor - mesoderm
Acoelomate
bilateral symmetry, a one-opening digestive system, and the beginnings of a brain;
• An incomplete digestive system = gastrovascular cavity
mesoderm
middle germ layer; develops into muscles, and much of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems
Acoelomate
an animal that lacks a coelom, or body cavity
Flatworms Classes
Turbellaria: planarians
Monogenea: fish flukes
Cestoda: tapeworms
Trematoda: flukes
Parthenogenesis
-Rotifers = unfertilized diploid eggs develop into females
Rotifers, nematodes, aphids, as well as other invertebrates
And vertebrates such as birds, snakes, sharks, and lizards
Bivalvia
clams, mussels, oysters, scallops
Marine or freshwater; shell with two halves or valves; primarily filter feeders with siphons
Polyplacophora
chitons
marine; eight-plated shell
Gastropoda
snails, slugs, nudibranchs - radula present
Marine, freshwater, or terrestrial; most with shell (not slugs/nudibranchs)
radula present
Cephalopoda
squid, octopus, cuttlefish, nautilus
= closed circulatory system
complex nerve system + brain
coelom
Annelida
phylum of segmented worms - Errantia, Sedentaria
Rings are segments separated by septa
• Advantages of segmentation
• Repetition provides backup
• Coelom can act as hydrostatic skeleton without distortion of body
• Permits specialization
Sedent-aria
tube worms = marine filter feeders
earthworms = decomposers
leeches = external parasites
Ecdysozoa
Nematoda and Arthropoda
cuticle = colonization of dry environments - Functions like an external skeleton & skin
ecdysis, metamorphosis, internal fertilization
Nematoda
Roundworms - collagen cuticle = can shead cuticle
Incredible wide spread - from the tropics to the poles
• Longitudinal but not circular muscles
• Pseudocoelom acts as hydrostatic skeleton and circulatory system
• Parasites, decomposers & tiny predators
Arthropoda
• Exoskeleton made of chitin and protein
2 or 3 BODY PARTD
• Provides protection, point of muscle attachment
• Relatively impermeable to water
Main Arthropod Subphyla
Chelicerata, Myriapoda, Hexapoda, Crustacea
Subphylum Chelicerata
spiders, scorpions, mites, ticks, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders
2 BODY PARTS cephalothorax and abdomen fused via PEDICEL
six pairs of appendages =
-four pairs of legs
-one pair of fangs
-one pair of pedipalps
Crustacea
crabs, lobsters, shrimp
Body of two to three parts; three or more pairs of legs; chewing mouthparts; usually marine
kinetic skull
A characteristic of lizards and snakes in which the joints between various parts of the skull are extremely mobile.
Common Characteristics of Animals
Multicellularity
Heterotrophs
No cell walls
Nervous tissue
Movement
Sexual reproduction
Subphylum Crustacea
• Crabs, lobsters, barnacles and shrimp
• Marine, fresh water, and terrestrial
• May be predators, scavengers, or filter feeders
• Nauplius larva very different from adult
• Mandibles, maxillae and maxillipeds
• First pair of walking legs may be modified into claws
• Carapace may extend over cephalothorax
Echinodermata
• Modified radial symmetry (five parts) - simple nervous system
• Endoskeleton = covered with spines
• Water vascular system with tube feet, functions in movement, gas exchange and feeding
• No excretory organs - respiration and excretion by diffusion
• Autotomy - Can intentionally detach body parts, regenerate them later
Asteroidea
sea stars
Five arms; tube feet; predatory on bivalves and otherechinoderms; eversible stomach
Ophiuroidea
brittle stars
Five long, slender arms; tube feet not used for locomotion;no pedicellariae; browse on sea bottom or filter feed
Echinoidea
sea urchins and sand dollars
Spherical (sea urchins) or disc-shaped (sand dollars); no arms; tube feet and moveable spines; pedicellariae present;many feed on seaweeds
Crinoidea
sea lilies and feather stars
Cup-shaped; often attached to substrate via stalk; arms feathery and used in filter feeding; very abundant in fossil record
Holothuroidea
Cucumber-shaped; no arms; spines absent; endo skeleton reduced; tube feet; browse on sea bottom
Phylum Chordata
Key distinguishing innovations
• Notochord
• Dorsal hollow nerve cord
• Pharyngeal slits
• Postanal tail
All chordates exhibit all four characteristics at some time during development
Tunicates (chordates phylum) (subphylum Urochordata)
Urochordata - subphylum
• Rudimentary circulatory system
• Simple nervous system
• Mostly hermaphroditic
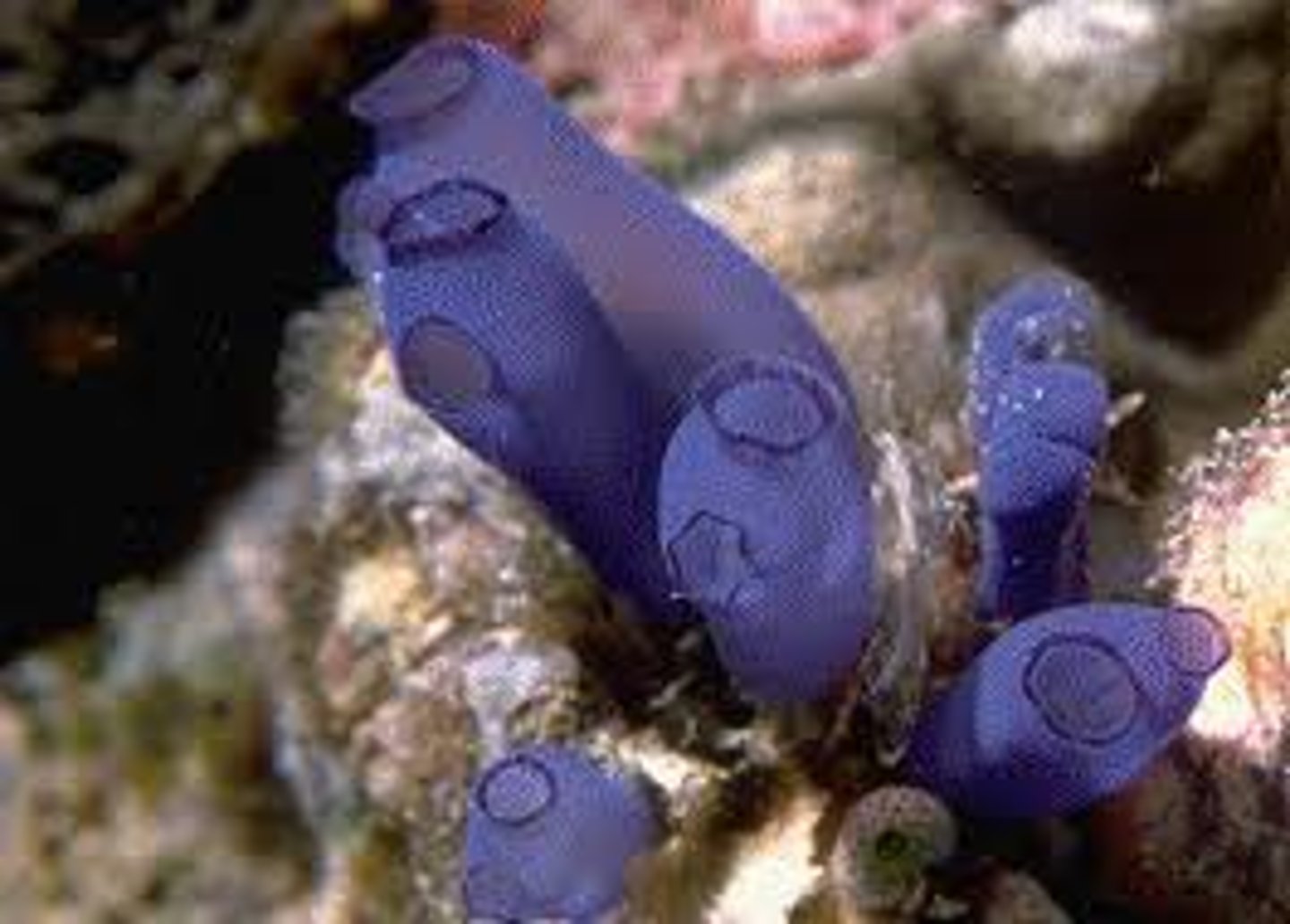

Urochordata
• Tunicates - animal encased in tunic
• Adult is sessile with only pharyngeal slits
• Larvae tadpole-like, with all 4 chordate traits
• Closest living relatives of vertebrates
• Cephalochordates more closely related to echninoderms
• May be colonial or solitary
• Filter feeders with two siphons
T/F?
The diets of insects, overall, are extremely varied, so different insects can specialize in almost any food source.
True
Cyclostomes
Clade of vertebrates that lack, eyes, vertebrae, fins and a jaw. consists of the hagfishes and lampreys
gnathostomes
vertebrates with jaws
fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals
• Earliest-diverging gnathostomes were fishes = Jaws allowed more efficient prey capture
• They also developed fins
• Hinged jaws developed from gill arches = Two pairs of gill arches were lost
oviparous
Refers to an animal whose young hatch from eggs laid outside the mother's body.
ovoviparous
Refers to an animal that retains fertilized eggs covered by a protective sheath or other structure within the body, where the young hatch.
(give live birth)
viviparous
Refers to an animal whose embryos develop within the uterus, receiving nourishment from the mother via a placenta.
(give live birth)
osteichythan
A clade that includes all vertebrates with a bony skeleton.
includes bony fish and tetrapods
operculum
A protective flap that covers the gills of a bony fish.
swim bladder
A gas-filled, balloon-like structure that helps a fish remain buoyant in the water even when it is completely stationary.
Actinopterygii
ray-finned fishes
includes all bony fishes (except coelacanths and lungfishes)
lionfish, moray eels, sea dragon
• Special joint in skull gives powerful bite
• Swim bladder filled with oil rather than air
Sarcopterygii
The lobe-finned fish - The Actinistia (coelacanths/lobe-finned) and the Dipnoi (lungfishes)
Fins supported by skeletal extensions of the pectoral and pelvic areas and moved by muscles
Dipnoi
(lungfishes) fish with primitive lungs that live in oxygen-poor freshwater swamps and ponds.
freshwater lobe fins with both lungs and gills; sister group of tetrapods
Vertebrates
Chordates with a Backbone
• Vertebral column
• Cranium
• Endoskeleton of cartilage or bone
• Diversity of internal organs
Living Vertebrates main clades
Cyclostomata - Lampreys and hagfish
Chondrichthyes - sharks skates and rays
Actinopterygii - Ray-finned fishes, most bony fish
Sarcopterygii - Lobe-finned fishes, of which coelacanths (2) and lungfishes (6) are the only living members
Amphibia - Frogs, toads, salamanders
Testudines - turtles
Squamata - lizards, snakes
Crocodilia - Crocodiles, alligators
Aves - birds
Mammalia - mammals
Chondrichthyes characteristics
Dual-chambered heart - single circulation
• Sharks among earliest fish to develop teeth
• Teeth not set into jaw, so easily replaced
• Powerful sense of smell
• Lateral line - pressure wave detection
• Internal fertilization
• Oviparous, Ovoviparous, Viviparous
Buccal pumping
found in fishes and amphibians
A form of breathing in which animals take in water or air into their mouths, then raise the floor of the mouth, creating a positive pressure that pumps water or air across the gills or into the lungs;
desiccation
drying out
two chambered heart
type of circulatory system that occurs in fish, has a single circuit flow
three chambered heart
has two atria and one ventricle; found in amphibians and reptiles (except crocodilians)
Hox genes control the development of what vertebrate structure?
limbs
Apoda
caecilians (legless)
Nearly blind tropical burrowers
• Secondarily legless
• Uterine milk nourishes young inside mother's body
Internal fert - bear live young
Urodela
salamanders and newts
Often have colorful skin patterns, advertising toxicity
• Like most amphibians, restricted to moist areas & times
Secondarily legless
evolved from legged ancestors
meaning they had legs but evolved separately to lose them
monotreme
Egg laying mammals
marsupial
A mammal, such as a koala, kangaroo, or opossum, whose young complete their embryonic development inside a maternal pouch called the marsupium.
short GESTATION period
eutherian
Long gestation
Placental mammal; mammal whose young complete their embryonic development within the uterus, joined to the mother by the placenta.
The four features that distinguish mammals are
mammary glands
hair
specialized teeth
enlarged skull
The three main types of mammals are
Metatheria (marsupials)
Prototheria (monotremes [lay eggs])
Eutheria (placental mammals)
amniotic egg
A type of egg produced by amniotes that contains the developing embryo and the four separate extraembryonic membranes that it produces: the amnion, the yolk sac, the allantois, and the chorion.
shelled egg
Amniotic egg broke tie to water
Shell is permeable to oxygen and carbon dioxide
amniotes
A group of tetrapods that produce amniotic eggs; includes turtles, lizards, snakes, crocodiles, birds, and mammals.
Cyclostomata
jawless vertebrates (hagfish and lampreys)
• All Cyclostomata are jawless, eel-like animals
• Hagfish
• Lack eyes, jaws, fins, and vertebrae
• Skeleton comprised of notochord and cartilaginous skull
• Essentially blind with a keen sense of smell
• Produce copious amounts of slime
Key innovations of amniotes
Desiccation-resistant skin
Thoractive breathing
kidneys - conserve water=concentrate waste
Internal fertilization
Advantages of reptile
concentrated urine, egg w/ amnion, Desiccation-resistant skin
4 chambered heart
birds, crocodilia and mammals
crocodilia
teeth in sockets
4 chambered heart
care for young
Deuterostomia
(phylums) Echinoderms and Chordates
Osteichthyans
Member of a vertebrate clade with jaws and mostly bony skeletons.
• Includes all vertebrates with a bony skeleton
Bony fishes are most numerous of all fishes
Two living clades:
- Actinopterygii = ray-finned fishes
- Sarcopterygii = lobe-finned fishes
• Bony skeleton and scale-covered skin
• Operculum covers gills
• Swim bladder for buoyancy (lung derivative)
• Most species reproduce via external fertilization
Tiktaalik rosae
bridge between fish and amphibians